How Is Chronic Kidney Disease Diagnosed
The doctor will take your complete medical history along with your family history, such as if anyone in your family has or had diabetes, whether you are on any medications , and so on. They will perform a thorough physical examination to see if you have any signs or symptoms of CKD.
A few tests will help your doctor confirm the diagnosis of CKD. These are:
- Kidney function tests: This test will look at your creatinine levels to check if you have trouble with your kidney.
- Blood tests: Low hemoglobin levels are found in CKD.
- Urine test: This will be done particularly to check for the presence of protein or persistent protein in the urine, which is a sign of kidney damage. Other things that the doctor will look for include red blood cells and white blood cells .
- Ultrasonography: To check for any cysts or scarring or size of the kidney.
How Our Doctors Determine Your Gfr
GFR is a blood test our nephrologists use to measure the amount of creatinine in the blood. Creatinine is a normal waste product from the muscles that is filtered out through the kidneys. The higher the amount of creatinine found in the blood, the lower the amount of creatinine being filtered out by the kidneys, which tells us how well the kidneys are functioning.
Early detection of kidney disease is important to slow the progression of CKD and a nephorologist should be consulted. While you cannot reverse damage, in stages 1 and 2, it is possible to prevent further damage and maintain kidney function. Changes in lifestyle and diet, along with regular checkups, can help keep the kidneys from further deterioration. Stages 3, 4 or 5 CKD are when your kidney function is moderately to severly reduced. During these stages is most likely when you will experience physical changes. If you have not been seen by and evaluated by a nephrologist, it is extremely important that you make an appointment with a nephrologist, like the experienced, reputable physicians at Dallas Nephrology Associates.
Glomerular filtration rate is calculated using the creatinine level in the blood, your age, ethnicity and gender. Creatinine is a normal waste product found in your body that can build up while your kidney function declines. Therefore, the higher level of creatinine, the lower your kidney function.
Chronic Kidney Disease: Detection And Evaluation
TODD GEHR, MD, Virginia Commonwealth University School of Medicine, Richmond, Virginia
Am Fam Physician. 2011 Nov 15 84:1138-1148.
Chronic kidney disease affects an estimated 27 million adults in the United States, and is associated with significantly increased risk of cardiovascular disease and stroke. Patients should be assessed annually to determine whether they are at increased risk of developing chronic kidney disease based on clinical and sociodemographic factors. Diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and older age are the primary risk factors that warrant screening. Other risk factors include cardiovascular disease, family history of chronic kidney disease, and ethnic and racial minority status. Serum creatinine levels can be used to estimate the glomerular filtration rate, and spot urine testing can detect proteinuria. After the diagnosis of chronic kidney disease is made, staging based on estimated glomerular filtration rate determines prognosis, evaluation, and management. Further evaluation should focus on the specific type of kidney disease and on identifying complications related to the disease stage. Patients should be assessed for risk factors leading to the further loss of kidney function and cardiovascular disease. Patients with estimated glomerular filtration rates less than 30 mL per minute per 1.73 m2, significant proteinuria, or rapid loss of kidney function should be referred to a nephrologist for further evaluation and management.
Read Also: Blood In Kidney Causes
Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate Test
Please note: eGFR is an estimate of how well your kidneys are working. The way eGFR is calculated will be changing. Currently the test considers your age, sex and race, among other things. A task force led by the National Kidney Foundation and the American Society of Nephrology is working on recommendations that may remove Black race as a factor in the eGFR calculation. The task force has been seeking the input of kidney disease experts to come up with the best way to make the eGFR test as accurate as possible. American Kidney Fund advised the task force to remove race from the eGFR so there is no bias in testing kidney function. This would help to make sure that every person will receive health care that is fair and of the highest quality. When the NKF-ASN task force makes its recommendations, AKF will promptly review them and then update our educational materials.
What Are The Causes Of Stage 5 Ckd
Chronic kidney disease occurs when the kidneys lose more than 80% of their function. This leads to disrupted kidney function over a few years.
Diabetes and hypertension are the leading causes of chronic kidney disease. Both are known to cause damage to the blood vessels over a time period which impacts the blood flow and result in impaired kidney function.
The other conditions that trigger the risk of chronic kidney disease include
- Inflammation of the kidneys structural units
- Glomerulonephritis
- Interstitial nephritis
- Prolonged obstruction of the urinary tract by conditions such as stones or pyelonephritis, enlarged prostate, and tumors of the kidneys
- OTC consumption for a long time
- Some autoimmune disorders also elevate the risk of chronic kidney disease
Read Also: Is Honey Good For Kidney
S To Take At Stage 3 Kidney Disease
- Make healthy lifestyle choicesEating a kidney-friendly diet, quitting smoking, exercising, and maintaining a healthy weight can help you slow progression at stage 3 kidney disease.
- Monitor your healthManaging underlying conditions and risk factors such as high blood pressure, diabetes, and/or infection can also help slow the progression of CKD. Talk to your doctor about whether or not you need to modify any of the vitamins, supplements, or medications you may be taking for other health conditions , or if you start taking any new medications.
- Talk to your doctor about a referral to see a kidney doctorSeeing a kidney doctor can help you manage your kidney health. Your doctor can help you determine when it’s time to see a nephrologist and give you a referral. Once you start seeing a nephrologist, you’ll still see your regular doctor to monitor you overall health.
- Meet with a renal dietitianFollowing a kidney-friendly diet is key to slowing the progression of CKD, and you dont have to do it alone. A renal dietitian can help you address any nutrition concerns and learn about eating well.
- Learn everything you can about CKDTaking a KidneyCare:365 class can help you learn more about how to manage and slow the progression of CKD.
What Medications Are Prescribed For People With Chronic Kidney Disease
Depending on the cause of your kidney disease, you may be prescribed one or more medications. Medications your nephrologist may prescribe include:
- An angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor or an angiotensin receptor blocker to lower your blood pressure.
- A diuretic to help your body eliminate extra fluid.
- Medications to lower cholesterol levels.
- Erythropoetin, to build red blood cells if you are anemic.
- Vitamin D and calcitrol to prevent bone loss.
- Phosphate binder if your kidneys cant eliminate phosphate.
Also Check: Carbonation And Kidney Stones
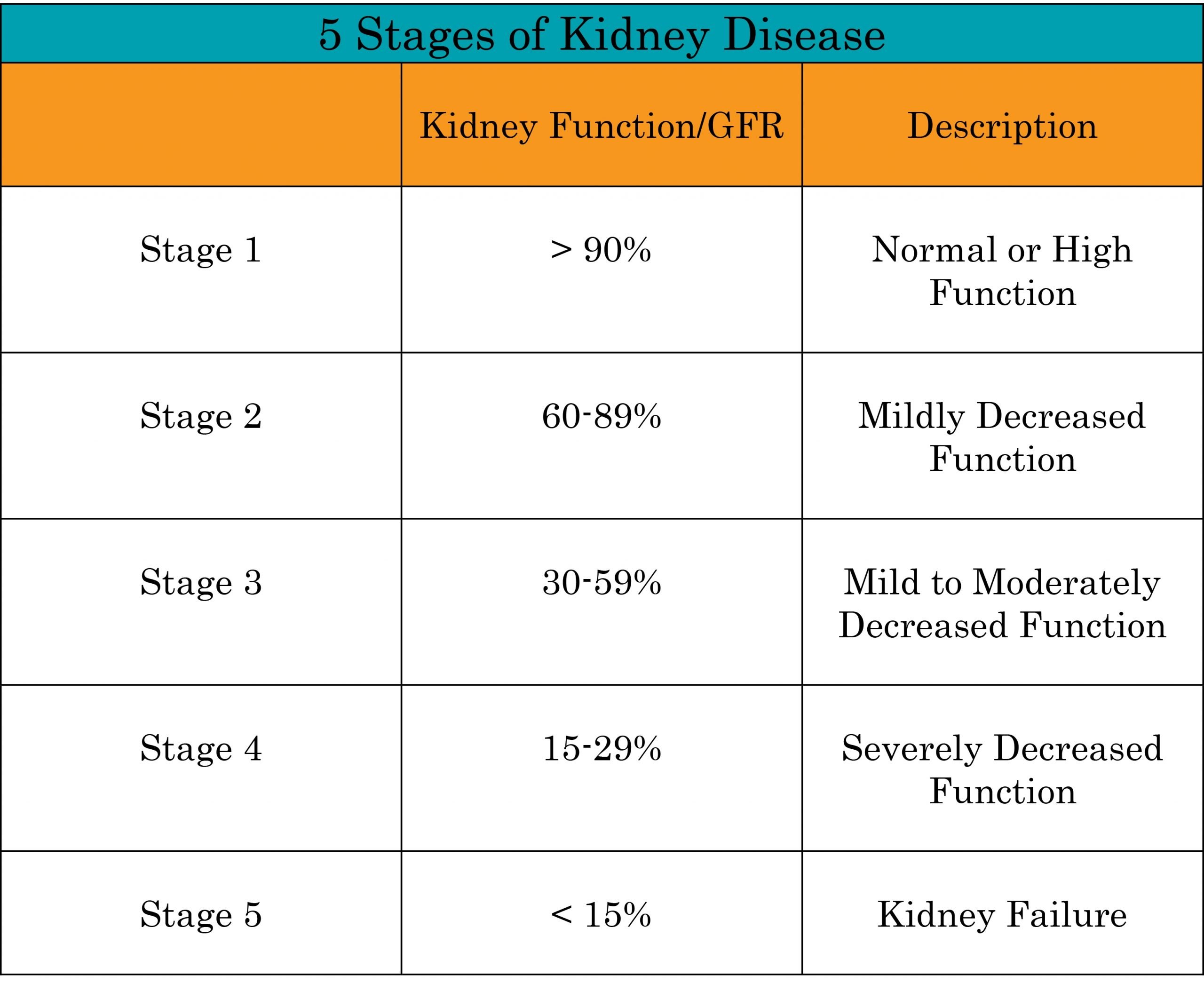
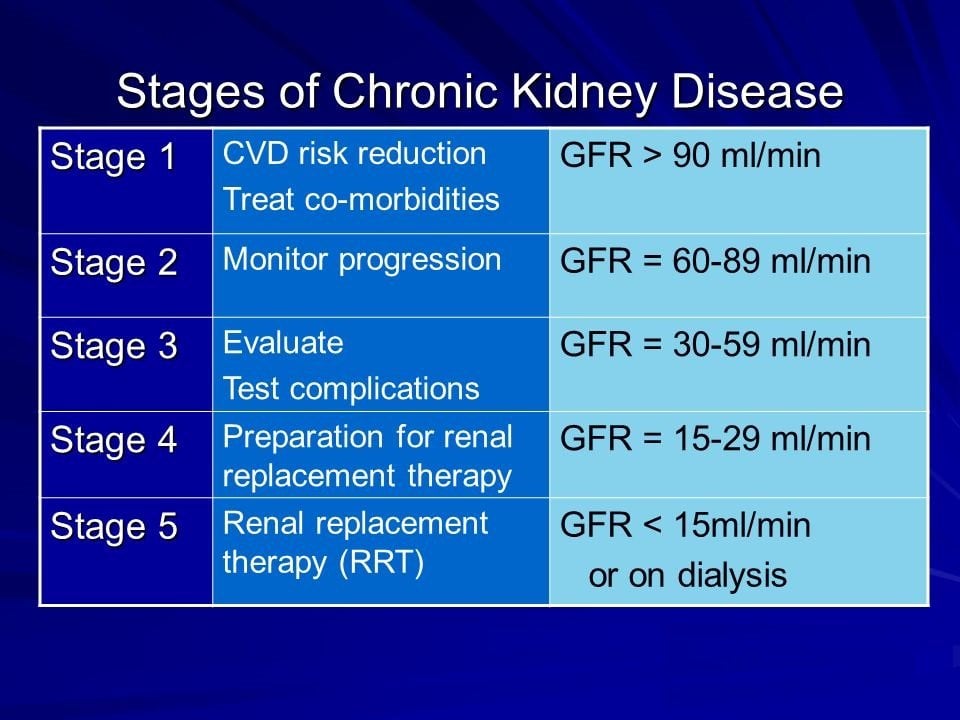
Kidney Gfr Chart By Age And Ckd Stages Table
Synopsis: Chart of Kidney Glomerular Filtration Rate number according to your age, includes table showing chronic kidney disease stages. Your GFR number tells you how much kidney function you have, as kidney disease gets worse, the GFR number goes down. “Normal” GFR is approximately 100 but you will often see it reported as > 90 or > 60 . The normal range of Kidney Glomerular Filtration Rate is 100 to 130 mL/min/1.73m2 in men and 90 to 120mL/min/1.73m2 in women below the age of 40.
Stage 5 Kidney Failure Life Expectancy With Dialysis
You will need dialysis if youre in stage 5 or end stage kidney failure. This is generally when you have a GFR of < 15 or have lost about 85-90 percent of the kidney function. Dialysis can help your body remain functioning and balanced while your kidneys fail. Then how long is the life expectancy with dialysis?
Recommended Reading: Does Red Wine Cause Kidney Stones
Dialysis And Peritoneal Access Dialysis
In end-stage kidney disease, kidney functions can be replaced only by dialysis or by kidney transplantation. The planning for dialysis and transplantation is usually started in stage 4 of chronic kidney disease. Most patients are candidates for both hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis . There are few differences in outcomes between the two procedures. The physician or an educator will discuss the appropriate options with the patient and help them make a decision that will match their personal and medical needs. It is best to choose a modality of dialysis after understanding both procedures and matching them to one’s lifestyle, daily activities, schedule, distance from the dialysis unit, support system, and personal preference.
The doctor will consider multiple factors when recommending the appropriate point to start dialysis, including the patient’s laboratory work and actual or estimated glomerular filtration rate, nutritional status, fluid volume status, the presence of symptoms compatible with advanced kidney failure, and risk of future complications. Dialysis is usually started before individuals are very symptomatic or at risk for life-threatening complications.
Dialysis
There are two types of dialysis 1) hemodialysis and 2) peritoneal dialysis. Before dialysis can be initiated, a dialysis access has to be created.
Dialysis access
Peritoneal access
Brief Descriptions Of The 5 Stages Of Ckd Based On Gfr
- Stage 1 – Normal kidney function
- Stage 2 – Mild loss of kidney function
- Stage 3 – Moderate loss of kidney function
- Stage 4 – Severe loss of kidney function
- Stage 5 – End-stage renal disease
The first stage of chronic kidney disease is the “normal” state. In this category, there are no symptoms and your GFR remains at a healthy level. There are no risks associated with being in this stage for an extended period of time.
Chronic kidney disease can also exist as a mild decline in renal function . Most people are typically without symptoms at this stage as well. The GFR is between 60 up to 90.
Chronic kidney disease can also exist as a moderate decline in renal function . Again, most people are without signs or symptoms at this stage. The GFR is between 30 up to 60.
The final stages of these diseases are classified as stage four and stage five. In these cases, people will typically be experiencing severe health problems caused by their kidneys. While stage four is characterized by a GFR between 15-30, ESRD means that your GFR has dipped below 15 – generally less than five years after diagnosis.
Read Also: Does Pop Cause Kidney Stones
What Does My Egfr Mean
A normal eGFR is 60 or more. If your eGFR is less than 60 for three months or more, your kidneys may not be working well. Use this chart to see what your eGFR may mean.
| Stage 1 | Stage 4 | Stage 5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
eGFR in normal range with other signs of kidney damage, like protein in urine or physical damage to the kidneys |
eGFR in normal range with other signs of kidney damage, like protein in urine or physical damage to the kidneys |
eGFR 30-59, moderate kidney damage |
eGFR 15-29, severe kidney damage |
eGFR less than 15, the kidneys are close to failure or have already failed |
No matter what your eGFR is, take these steps to keep your kidneys as healthy as possible:
- Keep a healthy blood pressure .
- Control your blood sugar if you have diabetes.
- Do something active for at least 30 minutes most days of the week, such as walking or biking.
- Keep a weight your doctor says is healthy for you.
- Do not smoke or use tobacco.
- Ask your doctor about medicines that may help protect your kidneys.
No matter what your eGFR is, ask your doctor when you should be tested again and what other tests you should have. Your doctor may want to do other tests to look for signs of kidney problems, such as:
Medicare Spending For Ckd
- Medicare spending for patients with CKD ages 65 and older exceeded $50 billion in 2013 and represented 20 percent of all Medicare spending in this age group.
- More than 70 percent of Medicare spending for CKD patients ages 65 and older was incurred by those who also had diabetes, congestive heart failure, or both.
- Although spending was 12.7 percent higher for African Americans than Caucasians in 2013, this represented a reduction from the 19.6 percent gap that occurred in 2010.
- Spending was more than twice as high for patients with all three chronic conditions of CKD, diabetes, and congestive heart failure than in patients with only CKD .
- Medicare fee-for-service spending for ESRD beneficiaries rose by 1.6 percent, from $30.4 billion in 2012 to $30.9 billion in 2013, accounting for 7.1 percent of the overall Medicare paid claims costs.
You May Like: Celery Juice For Kidneys
Can My Egfr Change
Your eGFR can change over time and can change based on some other problems, like if you have not been drinking enough water.
As chronic kidney disease gets worse, your eGFR number will go down. If caught early, healthy life changes like following a kidney-friendly eating plan and getting enough exercise may help slow down the progression of CKD and how fast your eGFR changes.
What Is The Life Expectancy With Stage 4 Kidney Disease Symptoms Treatment And Diet
Written byMohan GarikiparithiPublished onNovember 23, 2017
Stage 4 kidney disease is considered an advanced from of chronic kidney disease that is characterized by a severe decrease in its ability to perform its function. At this point, the condition has reached a life-threatening territory and will require significant treatment to increase survival.
Our kidneys are two of the most important organs in the body and are responsible for removing waste and excess fluid. Most of these discarded substances are considered toxic and would lead to several abnormalities if not promptly removed.
Suffering from a damaged kidney is a major problem in the United States, with more than 30 million Americans having chronic kidney disease. Kidney function is measured based on its glomerular filtration rate , which is the process by which the kidneys filter blood and is calculated by using a mathematical formula that compares a persons size, age, sex, and race to serum creatinine levels.
The following are stages of kidney disease and their corresponding GFR:
- Stage 1 with normal or high GFR
- Stage 2 Mild CKD
- Stage 3A Moderate CKD
- Stage 3B Moderate CKD
- Stage 4 Severe CKD
- Stage 5 End Stage CKD (GFR
Also read: End stage renal disease or stage 5 kidney disease: Causes, symptoms, and treatment
You May Like: Yerba Mate Kidney Stones
What Can I Expect If I Have Kidney Disease
If you have kidney disease you can still live a productive home and work life and enjoy time with your family and friends. To have the best outcome possible, its important for you to become an active member of your treatment team.
Early detection and appropriate treatment are important in slowing the disease process, with the goal of preventing or delaying kidney failure. You will need to keep your medical appointments, take your medications as prescribed, stick to a healthy diet and monitor your blood pressure and blood sugar.
What Is The Treatment And Management Of Chronic Kidney Disease
There is no cure for chronic kidney disease. The four goals of therapy are to:
Strategies for slowing progression and treating conditions underlying chronic kidney disease include the following:
- Control of blood glucose: Maintaining good control of diabetes is critical. People with diabetes who do not control their blood glucose have a much higher risk of all complications of diabetes, including chronic kidney disease.
- Control of high blood pressure: This also slows progression of chronic kidney disease. It is recommended to keep blood pressure below 130/80 mm Hg if one has kidney disease. It is often useful to monitor blood pressure at home. Blood pressure medications known as angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers have special benefit in protecting the kidneys.
- Diet: Diet control is essential to slowing progression of chronic kidney disease and should be done in close consultation with a health care practitioner and a dietitian. For some general guidelines, see the Chronic Kidney Disease Self-Care at Home section of this article.
The complications of chronic kidney disease may require medical treatment.
- Lightheadedness
- Allergic reactions
Diuretics also may cause a decline in kidney function especially if fluid is removed rapidly from the body.
You May Like: Red Wine And Kidney Stones
How Is Kidney Disease Diagnosed
First your healthcare provider will take your medical history, conduct a physical exam, ask about any medication you are currently taking, ask about any symptoms you have noticed, and inquire if any of your family members have kidney disease.
Your healthcare provider will order blood tests, a urine test and will also check your blood pressure.
The blood tests will check:
- Your glomerulofiltration rate . This describes how efficiently your kidneys are filtering blood how many milliliters per minute your kidneys are filtering. Your GFR is used to determine the stage of your kidney disease.
- Your serum creatinine level, which tells how well your kidneys are removing this waste product. Creatinine is a waste product from muscle metabolism and is normally excreted in your urine. A high creatinine level in your blood means that your kidneys are not functioning well enough to get rid it in your urine.
A urine protein test will look for the presence of protein and blood in your urine. Well-functioning kidneys should not have blood or proteins in your urine. If you do, this means your kidneys are damaged.