The Tubule Returns Needed Substances To Your Blood And Removes Wastes
A blood vessel runs alongside the tubule. As the filtered fluid moves along the tubule, the blood vessel reabsorbs almost all of the water, along with minerals and nutrients your body needs. The tubule helps remove excess acid from the blood. The remaining fluid and wastes in the tubule become urine.
What Are The Functional Units Of The Kidney
nephronnephrons
Then, what is the name of the functional unit of the kidney?
nephron
Secondly, why are nephrons considered functional units of the kidney? A nephron is the basic structural and functional unit of the kidneys that regulates water and soluble substances in the blood by filtering the blood, reabsorbing what is needed, and excreting the rest as urine. Its function is vital for homeostasis of blood volume, blood pressure, and plasma osmolarity.
Also asked, what is the functional unit of the kidney quizlet?
The functional unit of the kidney is the nephron and it is called the functional unit because its the smallest structure in the kidney that can carry out its functions. There are about more than 1 million nephrons in each kidney.
What is the functional unit of the urinary system?
The basic structural and functional unit of the kidney is the nephron. Its chief function is to regulate the concentration of water and soluble substances like sodium by filtering the blood, reabsorbing what is needed and excreting the rest as urine.
What Are Some Of The Causes Of Chronic Kidney Disease
Chronic kidney disease is defined as having some type of kidney abnormality, or “marker”, such as protein in the urine and having decreased kidney function for three months or longer.
There are many causes of chronic kidney disease. The kidneys may be affected by diseases such as diabetes and high blood pressure. Some kidney conditions are inherited .
Others are congenital; that is, individuals may be born with an abnormality that can affect their kidneys. The following are some of the most common types and causes of kidney damage.
Diabetes is a disease in which your body does not make enough insulin or cannot use normal amounts of insulin properly. This results in a high blood sugar level, which can cause problems in many parts of your body. Diabetes is the leading cause of kidney disease.
High blood pressure is another common cause of kidney disease and other complications such as heart attacks and strokes. High blood pressure occurs when the force of blood against your artery walls increases. When high blood pressure is controlled, the risk of complications such as chronic kidney disease is decreased.
Glomerulonephritis is a disease that causes inflammation of the kidney’s tiny filtering units called the glomeruli. Glomerulonephritis may happen suddenly, for example, after a strep throat, and the individual may get well again.However, the disease may develop slowly over several years and it may cause progressive loss of kidney function.
Also Check: Does Kidney Stone Pain Get Worse At Night
Now Its Your Turn To Think Which Part You Like Most Of Article
What is your opinion or what do you think about this article ?
So Anything else important, may i missed to write in this?
So Kindly let me know by leaving a comment below.
I want to hear from you.
Stay tuned for more article like these & also keep visiting.
But also Dont forgot to subscribe our newsletters.
Stay Healthy And Fit , Enjoy Your Life More. Chill karo And Learn More.
Sending Lots Of Love And Positive Energy From chrosta To You.
THANKS A LOT
How Is Chronic Kidney Disease Detected
Early detection and treatment of chronic kidney disease are the keys to keeping kidney disease from progressing to kidney failure. Some simple tests can be done to detect early kidney disease. They are:
It is especially important that people who have an increased risk for chronic kidney disease have these tests. You may have an increased risk for kidney disease if you:
- are older
Also Check: Can Kidney Stones Affect Your Psa Count
Components Of Kidney Function Test
The components of the Kidney function test could be broadly divided into two categories.
The tests that are part of the Kidney Function test panel are:
- Urine examination
- Dilution Test
Urine Examination
This examination consists of a physical examination where the color, odor, quantity, specific gravity etc of the urine is noted. Microscopic examination of urine is done to weed out any pus cells, red blood cells casts, Crystals etc.
Serum Urea
Urea is the end product of the protein catabolism. The urea is produced from the amino group of the amino acids and is produced in the liver by means of the Urea cycle. Urea undergoes filtrations at the glomerulus as well as secretion and reabsorption at the tubular level. The rise in the level of serum urea is generally seen as a marker of renal dysfunction especially glomerular dysfunction. Urea level only rises when the glomerular function is reduced below 50%. The normal serum urea level is between 20-45 mg/dl. But the level might also be affected by diet as well as certain non-kidney related disorders. A high protein diet might increase the blood urea level. Similarly, a low protein diet might decrease blood urea level.
Blood Urea Nitrogen
Calcium
Normal Results: 8.5 to 10.2 mg/dlC
Serum Creatinine Level
Dilution Test
Stay tuned with BYJUS to know more in detail about the kidney, kidney function test and importance of excretory system.
Nephrotoxicity Or Renal Toxicity
The nephron, comprised of glomerulus and renal tubule, is the functional unit of the kidney. The three main functions of the kidneys include plasma filtration and maintenance of whole-body electrolyte homeostasis, elimination, and concentration of waste products from both endogenous metabolism and exogenous metabolism, and synthesis and secretion of hormones . Renal blood flow is approximately 25% of resting cardiac output. The glomerular, tubular, and renal interstitial cells frequently encounter significant concentrations of endogenous and exogenous metabolites that can induce changes in kidney function and structure. As such, the kidney is at risk due to exposure to high volumes of blood-borne endogenous and exogenous metabolites including toxicants and toxic metabolites . Nephrotoxicity or renal toxicity can be a result of hemodynamic changes, direct injury to cells and tissue, inflammatory tissue injury, and/or obstruction of renal excretion. Nephrotoxicity is frequently induced by a wide spectrum of therapeutic drugs and environmental pollutants .
Don’t Miss: Can Stress Cause A Uti Or Kidney Infection
Kidneys: The Main Osmoregulatory Organ
The kidneys, illustrated in Figure 22.4, are a pair of bean-shaped structures that are located just below and posterior to the liver in the peritoneal cavity. The adrenal glands sit on top of each kidney and are also called the suprarenal glands. Kidneys filter blood and purify it. All the blood in the human body is filtered many times a day by the kidneys; these organs use up almost 25 percent of the oxygen absorbed through the lungs to perform this function. Oxygen allows the kidney cells to efficiently manufacture chemical energy in the form of ATP through aerobic respiration. The filtrate coming out of the kidneys is called urine.
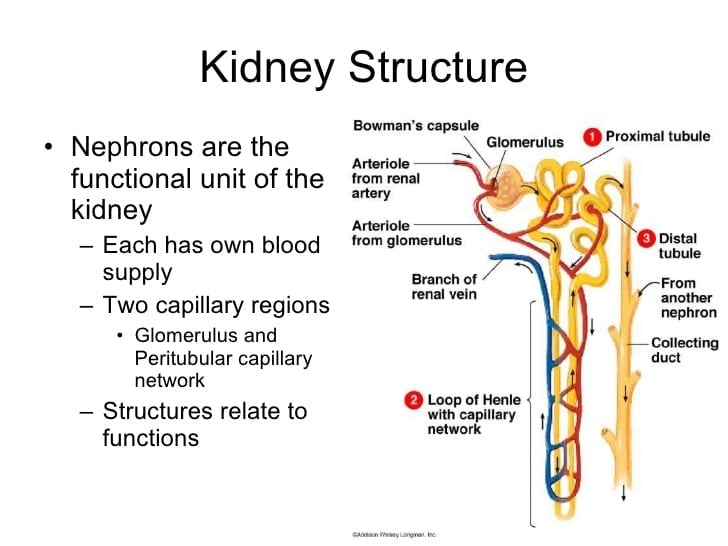
The Nephron Is The Functional Unit Of The Kidney
The Nephron Is the Functional Unit of the Kidney
Each kidney in the human contains about 1 million;nephrons,;each capable of forming urine. The kidneycannot regenerate new nephrons.Therefore, with renal injury, disease, or normal aging, there is a gradual decrease in nephron number. After age 40, the number of functioning nephrons usually decreases about 10 per cent every 10 years; thus, at age 80, many people have 40 per cent fewer functioning nephrons than they did at age 40. This loss is not life threatening because adaptive changes in the remaining nephrons allow them to excrete the proper amounts of water, electrolytes, and waste products.
Each nephron contains a tuft of glomerular cap-illaries called the;glomerulus,;through which large amounts of fluid are filtered from the blood, and a long;tubule;in which the filtered fluid is converted into urine on its way to the pelvis of the kidney .
The glomerulus contains a network of branching and anastomosing glomerular capillaries that, com-pared with other capillaries, have high hydrostatic pressure . The glomerular capillar-ies are covered by epithelial cells, and the total glomerulus is encased in;Bowmans capsule.;Fluid filtered from the glomerular capillaries flows into Bowmans capsule and then into the;proximal tubule,;which lies in the cortex of the kidney .
About 20 to 30 per cent of the nephrons have glomeruli that lie deep in the renal cortex near the medulla and are calledjuxtamedullary nephrons.
Recommended Reading: Can Kidney Disease Cause Osteoporosis
Where Are The Kidneys And How Do They Function
There are two kidneys, each about the size of a fist, located on either side of the spine at the lowest level of the rib cage. Each kidney contains up to a million functioning units called nephrons. A nephron consists of a filtering unit of tiny blood vessels called a glomerulus attached to a tubule. When blood enters the glomerulus, it is filtered and the remaining fluid then passes along the tubule. In the tubule, chemicals and water are either added to or removed from this filtered fluid according to the body’s needs, the final product being the urine we excrete.
The kidneys perform their life-sustaining job of filtering and returning to the bloodstream about 200 quarts of fluid every 24 hours. About two quarts are removed from the body in the form of urine, and about 198 quarts are recovered. The urine we excrete has been stored in the bladder for anywhere from 1 to 8 hours.
What Clinical Trials Are Open
Clinical trials that are currently open and are recruiting can be viewed at www.ClinicalTrials.gov.
This content is provided as a service of the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, part of the National Institutes of Health. The NIDDK translates and disseminates research findings to increase knowledge and understanding about health and disease among patients, health professionals, and the public. Content produced by the NIDDK is carefully reviewed by NIDDK scientists and other experts.
Read Also: What Herbs Help The Kidneys
What Is Peritoneal Dialysis And How Does It Work
In this type of dialysis, your blood is cleaned inside your body. The doctor will do surgery to place a plastic tube called a catheter into your abdomen to make an access. During the treatment, your abdominal area is slowly filled with dialysate through the catheter. The blood stays in the arteries and veins that line your peritoneal cavity. Extra fluid and waste products are drawn out of your blood and into the dialysate. There are two major kinds of peritoneal dialysis.
What Is The Structural Organisation Of Cell Class 9
Protects cell contents, controls exit and entry of materials from the cell. Nucleus: Nucleus is covered by double membrane; called nuclear membrane. The fluid which is inside the nucleus is called nucleoplasm.NCERT CBSE 9 Biology.
| Plant cell | |
|---|---|
| It cannot change its shape. | Cell can often change its shape. |
Read Also: How Do Doctors Break Up A Kidney Stone
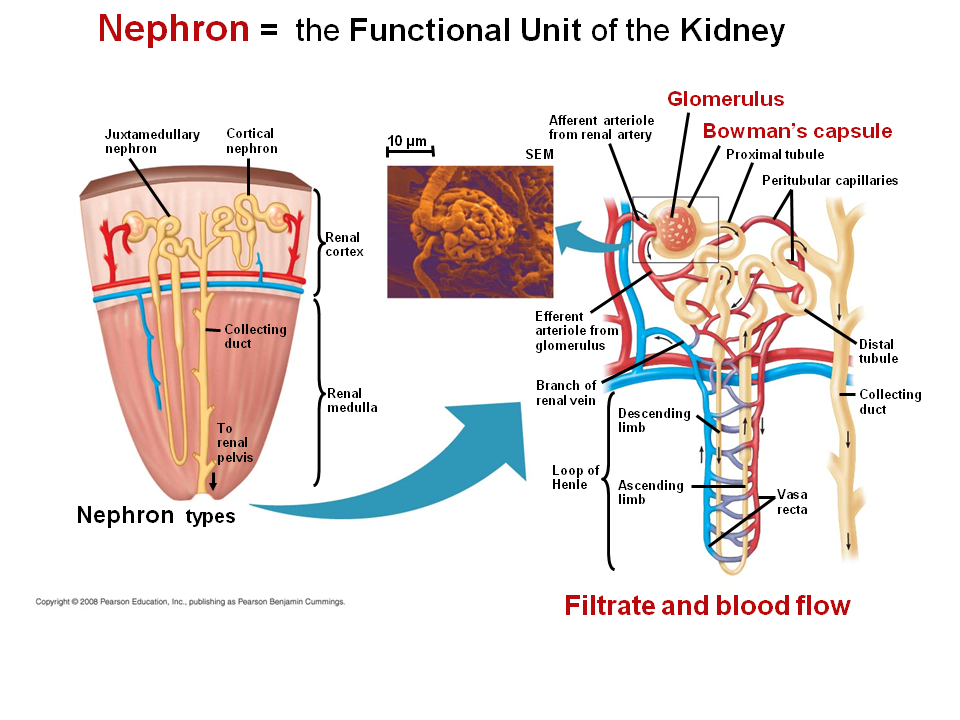
Kidney Function And Physiology
Kidneys filter blood in a three-step process. First, the nephrons filter blood that runs through the capillary network in the glomerulus. Almost all solutes, except for proteins, are filtered out into the glomerulus by a process called glomerular filtration. Second, the filtrate is collected in the renal tubules. Most of the solutes get reabsorbed in the PCT by a process called tubular reabsorption. In the loop of Henle, the filtrate continues to exchange solutes and water with the renal medulla and the peritubular capillary network. Water is also reabsorbed during this step. Then, additional solutes and wastes are secreted into the kidney tubules during tubular secretion, which is, in essence, the opposite process to tubular reabsorption. The collecting ducts collect filtrate coming from the nephrons and fuse in the medullary papillae. From here, the papillae deliver the filtrate, now called urine, into the minor calyces that eventually connect to the ureters through the renal pelvis. This entire process is illustrated in Figure 22.7.
Kidney Structures And Functions Explained
Your kidneys are paired organs found on each side of the back portion of the abdominal cavity. The larger left kidney is located a bit higher than the right kidney. Unlike other organs found in the abdomen, the kidneys are located behind the lining of the abdominal cavity, thus they are considered retroperitoneal organs. These bean-shaped organs are protected by the back muscles and the ribs, as well as the fat that surrounds them like a protective padding. Learn more about the kidney structures and functions from this short article.
You May Like: Is Mulberry Good For Kidneys
Nephron Number And Blood Pressure
Adults with essential hypertension have been found to have a lower number of rental units compared to subjects with normal blood pressure.
Although birth weight in these studies is unknown, the association supports the role of lower renal unit counts in the development of hypertension.
In the same group of subjects who had blood pressure and birth weight, significant correlations were found between birth weight and renal unit count, blood pressure and renal unit count, and blood pressure and birth weight in Caucasian subjects.
These relationships did exist did not reach significance in African American subjects; however, the prevalence of hypertension was twice as high in African Americans with a lower than the average number of rental units.
This suggests that developmental procedures may contribute to the risk of hypertension in this population. The observation that salt sensitivity is more prevalent in subjects with lower birth weight is consistent with a possible role of kidney unit count.
What Is Involved In The First Phase Of Treatment
In the first phase, high doses of intravenous fluids are given to flush out the kidneys and bloodstream. This flushing process is called diuresis and helps mildly damaged kidney cells to function again by removing the toxic metabolites and creating a healthier environment for healing.
If enough functional kidney cells remain, they may be able to adequately meet the bodys needs for filtration and waste removal. Fluid therapy includes replacement of various electrolytes, especially potassium. Other important aspects of initial treatment include proper nutrition and drugs to control vomiting and diarrhea. Your dog will often begin to feel better soon after this stage of treatment is begun.
My Dog Is In Kidney Failure What Should I Expect
The kidneys are an amazing organ. Made up of millions of tiny units, they will remain functional until up to 2/3 of the tissue is destroyed. This is why a person can donate a kidney without harm to their own body. If your dog has been diagnosed with chronic renal failure it means this damage has occurred over a long period of time. We will do all that we can to detect kidney failure early. This allows more options and it will certainly give us a better chance to keep your dog healthy as long as possible. The following information will help you to understand what happens in this disease, how we diagnose it and most importantly, how it is treated.
What Are The Clinical Signs Of Chronic Kidney Failure
When disease or advanced age causes the filtration process to become inefficient and ineffective, blood flow to the kidneys is increased in an attempt to increase filtration. The body must increase the amount of blood flowing through the kidneys since less and less of the metabolic toxins are being removed each time. This results in the production of more urine. To keep the dog from becoming dehydrated due to increased fluid loss in the urine, thirst and water consumption is increased.
Thus, one of the earliest clinical signs of kidney failure is increased water consumption and urination, and is called compensated renal failure. After approximately 2/3 of the kidney tissue is destroyed, there is a rapid rise in waste products in the bloodstream and an apparent sudden onset of severe disease. The clinical signs of more advanced kidney failure include loss of appetite, depression, vomiting, diarrhea, and very bad breath. Occasionally, ulcers will be found in the mouth.
Is Kidney Failure Permanent
Usually, but not always. Some kinds of acute kidney failure, also known as acute renal failure, get better after treatment. In some cases of acute kidney failure, dialysis may only be needed for a short time until the kidneys get better.
In chronic or end stage kidney failure, your kidneys do not get better and you will need dialysis for the rest of your life. If your doctor says you are a candidate, you may choose to be placed on a waiting list for a new kidney.
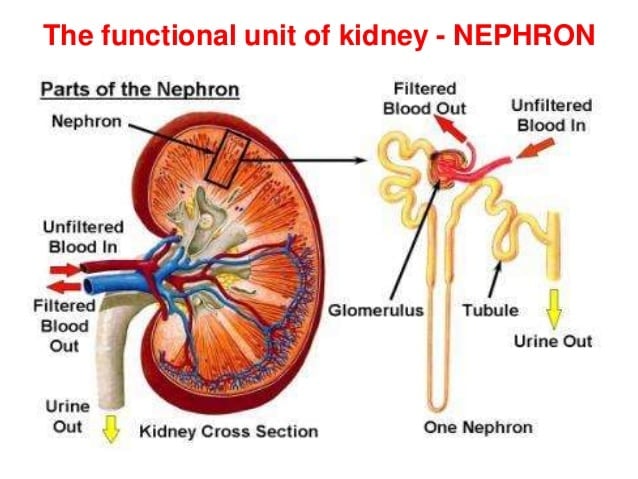
What Is The Functional Unit Of The Kidney
The functional units of the kidney refer to the glomeruli, which are the filtering units that filter the blood. The term functional pertains to how well the kidney maintains and functions. When a person has kidney disease, the function of the kidney may be impaired and it may not be able to filter the blood properly. The functional units will determine the health or death of a human kidney
The kidneys filter blood from the blood in the body and they also store other chemicals as well as waste products from the body. The filtering units in the kidney to form a barrier to block the blood from flowing into the urinary system. When these filters become damaged, there is an increased risk of the blood being exposed to toxins, which can result in damage to the kidneys themselves. When the kidneys are damaged, they cannot filter the blood properly and that can lead to problems.
To understand what is the functional unit of the kidney, one must understand the structure of the kidney. This organ is found in the lower portion of the urinary tract and it has two branches, the tubule and the ureter. The tubule has the job of storing the stones that form in the kidneys, along with bacteria and other substances. The ureter carries urine away from the body and allows it to pass through the kidney. Without these organs, the kidney cannot function properly.
Tubular Reabsorption And Secretion
Tubular reabsorption occurs in the PCT part of the renal tubule. Almost all nutrients are reabsorbed, and this occurs either by passive or active transport. Reabsorption of water and some key electrolytes are regulated and can be influenced by hormones. Sodium is the most abundant ion and most of it is reabsorbed by active transport and then transported to the peritubular capillaries. Because Na+ is actively transported out of the tubule, water follows it to even out the osmotic pressure. Water is also independently reabsorbed into the peritubular capillaries due to the presence of aquaporins, or water channels, in the PCT. This occurs due to the low blood pressure and high osmotic pressure in the peritubular capillaries. However, every solute has a transport maximum and the excess is not reabsorbed.
In the loop of Henle, the permeability of the membrane changes. The descending limb is permeable to water, not solutes; the opposite is true for the ascending limb. Additionally, the loop of Henle invades the renal medulla, which is naturally high in salt concentration and tends to absorb water from the renal tubule and concentrate the filtrate. The osmotic gradient increases as it moves deeper into the medulla. Because two sides of the loop of Henle perform opposing functions, as illustrated in Figure 22.8, it acts as a countercurrent multiplier. The vasa recta around it acts as the countercurrent exchanger.
What Are The Functional Units Of Kidney
functional unitkidneykidneykidney’s
. Simply so, what is the functional unit of the kidney quizlet?
The functional unit of the kidney is the nephron and it is called the functional unit because its the smallest structure in the kidney that can carry out its functions. There are about more than 1 million nephrons in each kidney.
Likewise, why are nephrons considered functional units of the kidney? A nephron is the basic structural and functional unit of the kidneys that regulates water and soluble substances in the blood by filtering the blood, reabsorbing what is needed, and excreting the rest as urine. Its function is vital for homeostasis of blood volume, blood pressure, and plasma osmolarity.
what is the functional unit of the urinary system?
The basic structural and functional unit of the kidney is the nephron. Its chief function is to regulate the concentration of water and soluble substances like sodium by filtering the blood, reabsorbing what is needed and excreting the rest as urine.
What is the basic functional unit of the kidney What are its primary functions?
A nephron is the basic structural and functional unit of the kidney. The name nephron comes from the Greek word meaning kidney. Its chief function is to regulate water and soluble substances by filtering the blood, reabsorbing what is needed and excreting the rest as urine.
Why Are The Kidneys So Important
Most people know that a major function of the kidneys is to remove waste products and excess fluid from the body. These waste products and excess fluid are removed through the urine. The production of urine involves highly complex steps of excretion and re-absorption. This process is necessary to maintain a stable balance of body chemicals.
The critical regulation of the body’s salt, potassium and acid content is performed by the kidneys. The kidneys also produce hormones that affect the function of other organs. For example, a hormone produced by the kidneys stimulates red blood cell production. Other hormones produced by the kidneys help regulate blood pressure and control calcium metabolism.
The kidneys are powerful chemical factories that perform the following functions:
- remove waste products from the body
- remove drugs from the body
- balance the body’s fluids
- release hormones that regulate blood pressure
- produce an active form of vitamin D that promotes strong, healthy bones
- control the production of red blood cells
Below you will find more information about the kidneys and the vital role they play in keeping your body functioning.
How Long Do Hemodialysis Treatments Last
The time needed for your dialysis depends on:
- how well your kidneys work
- how much fluid weight you gain between treatments
- how much waste you have in your body
- how big you are
- the type of artificial kidney used
Usually, each hemodialysis treatment lasts about four hours and is done three times per week.
A type of hemodialysis called high-flux dialysis may take less time. You can speak to your doctor to see if this is an appropriate treatment for you.
What Can I Expect From This First Phase Of Treatment
There are three possible outcomes from the first phase of treatment:
Unfortunately, there are no reliable tests that will predict the outcome. Each case should be treated aggressively and monitored closely. Even dogs that have severe kidney failure may respond favorably to treatment and resume a normal quality of life after treatment.
How Is Chronic Kidney Failure Diagnosed
There are two basic tests for kidney function:
A urinalysis is needed to evaluate kidney function. A low urine specific gravity is the earliest indication of kidney failure. An increase in protein in the urine also indicates decreased kidney function.
A blood biochemistry analysis assesses the function of various internal organs. Measuring the level of two waste products in the blood, namely blood urea nitrogen and blood creatinine , indicates decreased kidney function. Tests to measure the blood levels of other substances such as albumin, globulin, potassium, sodium, phosphorus and calcium, as well as the red and white blood cell counts are important in order to determine the extent of failure and the best course of treatment.
A dog in compensated chronic kidney failure with marginal kidney function may have normal levels of BUN and creatinine but will have a low urine specific gravity. If a major stress such as illness or surgery occurs, the kidneys may fail, sending the blood test values up quickly.
A dog diagnosed with low urine specific gravity as well as elevated BUN and CREA is said to be azotemic.
In general terms, the degree of kidney failure may be estimated as follows: