Early Warning Signs Of Kidney Cancer
Before symptoms of kidney cancer are noticeable, a laboratory test or an imaging study may reveal a possible diagnosis.
For example, a routine urine test may find traces of blood that the naked eye cant see. Signs of kidney cancer also may be detected during a computed tomography scan, which consists of X-rays taken at different angles and processed by a computer into 3D images. This imaging test may show a growth in the kidneyand may even be able to tell a noncancerous cyst from a solid cancer tumor if dye is injected into a vein beforehand.
Magnetic resonance imaging produces detailed images of the kidneys using a computer and magnetic fields in place of X-rays. During an MRI, a dye called gadolinium may be used to increase tumor visibility.
Finally, an ultrasound uses sound waves to look for signs of a kidney tumor, and determine whether a mass in the kidney is a fluid-filled cyst or a solid tumor.
Why Have A Kidney Biopsy
Your doctor may need to do a kidney biopsy to find out why your kidneys are not working well or why there is blood or protein in your urine. While a blood test and a urine test are the most common ways to test for kidney disease, a kidney biopsy can tell your doctor if you have other rare conditions that are damaging your kidneys, such as focal segmental glomerular sclerosis .
Doctors also use kidney biopsies to:
- Monitor how quickly kidney damage is getting worse
- Check how well your transplanted kidney is working
- Find out why your transplanted kidney is not working properly
- Create treatment plans based on the condition of your kidneys
- Find out how well treatments are working
- Diagnose cancer
Technical Details And Complications
When performing a renal mass biopsy, consideration should be given to several technical factors that may affect the diagnostic and complication rates. The guidance modality that best depicts the lesion, adjacent structures and the needle-tip should be used to guide the biopsy. Each modality has its advantages and disadvantages. US provides real-time imaging without ionizing radiation but may not visualize the lesion. CT is more expensive, however, usually allows better depiction of the mass and surrounding structures. MR imaging is seldom used but may be helpful to biopsy a mass that is not seen by US or CT. Operator preference, and equipment availability will also play a part in deciding which imaging modality is chosen.
Given the lack of conclusive evidence that large needles confer a greater diagnostic effectiveness, the authors obtain fine-needle specimens initially and obtain a preliminary impression by a cytology technologist during the biopsy procedure. If the specimens are not adequate, large needle biopsies are obtained.
Needle track seeding is a potential complication of renal mass biopsy. The true incidence is difficult to ascertain. The scarcity of published reports implies that it is a rare event, and probably not more common than other percutaneous biopsy sites. To the best of our knowledge, there is no evidence to suggest that use of large needles increases the risk of needle track seeding relative to fine needles.
Don’t Miss: Is Watermelon Bad For Your Kidneys
What Happens During A Kidney Biopsy
During a kidney biopsy, a doctor collects a sample of tissue from your kidney. Most biopsies are done through your back, although people with a transplanted kidney have the biopsy through their lower abdomen .
Your doctor will use one of these methods to take the sample:
- Percutaneous biopsy: In this more common type of kidney biopsy, a doctor numbs the skin located over the kidney and inserts a needle to take a small tissue sample from the kidney. Your doctor may use ultrasound imaging to guide the needle to the best location in the kidney.
- Open biopsy: In an open biopsy, a doctor makes an incision , removes tissue from the kidney, and closes the incision with stitches. Your doctor will give you anesthesia so you do not feel pain during the procedure. This type of biopsy is rare except at the time of kidney transplant.
What Is A Kidney Biopsy
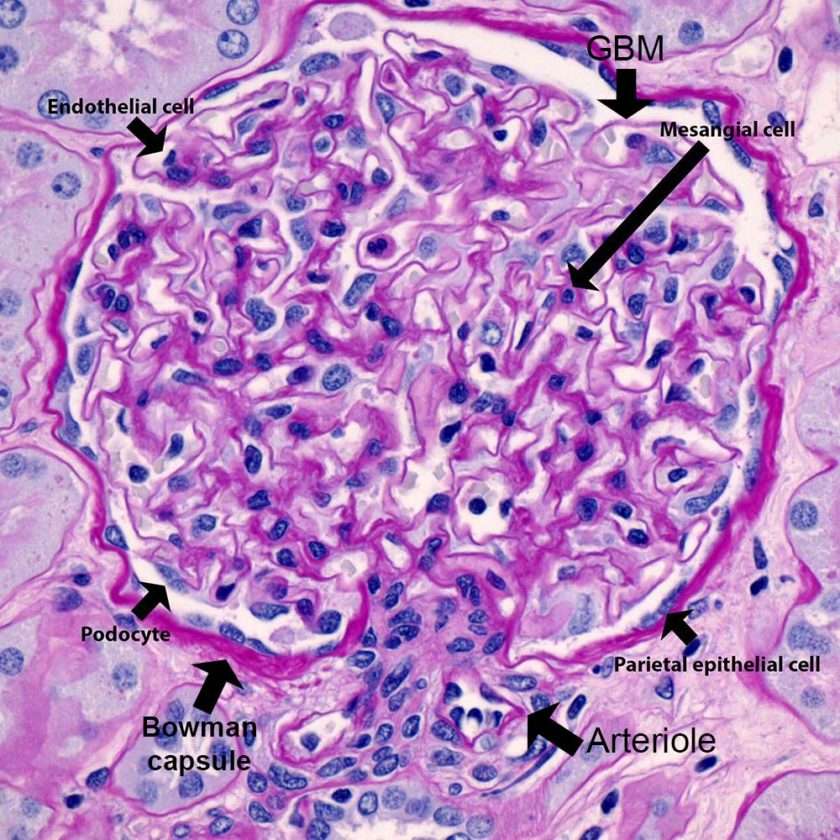
A kidney biopsy is a procedure that involves taking a small piece of kidney tissue for examination with a microscope. A pathologista doctor who specializes in diagnosing diseasesexamines the kidney tissue sample in a lab. The pathologist looks for signs of kidney disease or infection. If the kidney has been transplanted and is not working, a kidney biopsy may help identify the cause.
One of the following specialists will perform the kidney biopsy at a hospital or an outpatient center:
- a nephrologista doctor who specializes in treating kidney disease
- a urologista doctor who specializes in treating urologic and sexual problems
- a transplant surgeona doctor who specializes in performing organ transplants
- an interventional radiologista doctor who performs procedures using imaging equipment
Recommended Reading: Can Kidney Stones Cause High Blood Sugar
How Are Renal Cysts Treated
Renal cysts generally do not require treatment unless they are causing symptoms or harming kidney function. Treatment options include:
- Sclerotherapy: Also known as percutaneous alcohol ablation, sclerotherapy involves the insertion of a long needle through the skin and into the cyst under ultrasound guidance. The doctor will drain the cyst and fill it with an alcohol-based solution that causes the tissue to harden and shrink, reducing the chance of recurrence. The procedure is usually performed on an outpatient basis with a local anesthetic.
- Surgery: For larger cysts, a surgeon will make a small incision and access the cyst with a laparoscope. The surgeon will then drain the cyst and burn or cut away its outer layer. Laparoscopic surgery requires general anesthesia.
Staging For Kidney Cancer
Clinical staging is performed with Physical Examination, Abdominal CT scan, and Chest X-Ray. In cases of advanced or high-risk disease, additional testing such as MRI and Bone Scan may be necessary.
The prognosis of kidney cancer is directly linked to the stage of disease. Staging is a process that demonstrates how far the cancer has spread. Both the treatment and prognosis for kidney cancer depend significantly on the stage of disease.
TNM System
You May Like: Where Are My Kidneys In My Body
Also Check: Can Apple Cider Vinegar Hurt Your Kidneys
Need For A Renal Biopsy
Your doctor might order a kidney biopsy if you have one or more of the following:
- A kidney problem that cant otherwise be identified
- An unexplained drop in kidney function
- The constant presence of blood in the urine
- Presence of protein found in the urine
- Monitor a transplanted kidney
The decision of undergoing biopsy is based on patients signs, symptoms, test results, and overall health. It will not be needed for every patient suffering from the above.
What Happens After A Bone Marrow Biopsy
You may feel slight pain for about a week after the procedure but most people will not. To help manage the pain, your doctor may recommend over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen. You will also need to care for the incision wound, which involves keeping it dry for 24 hours after the biopsy.
Avoid strenuous activities for about one or two days to avoid opening your wound. And contact your doctor immediately if you experience:
- excess bleeding
- drainage
- fever
The lab will test your bone marrow during this time. Waiting for the results can take one to three weeks. Once your results come in, your doctor may call or schedule a follow-up appointment to discuss the findings.
Also Check: Constipation Kidney Stones
Considerations For A Renal Biopsy
Although renal biopsies are effective tools for diagnosing the presence or extent of kidney disease, there are problems associated with their use. One problem is that they produce false-negative results. Another is that they cannot be performed if kidney cancer is suspected, because the biopsies themselves can cause the spread of malignant cells. In the case of a known malignancy, removal of the tumor, or removal of the kidney , is recommended.
What Causes Cysts On The Liver And Kidneys
A cyst is a sac like structure that resembles like a membranous tissue containing fluid like substances inside which can grow anywhere in the body or skin. A cyst is a bump on the skin or a lump under the skin, but in some cases like kidneys and liver, it is located internally. Polycystic kidney disease causes the cyst to form in the kidneys that can adversely affect kidney functions. On the other side, a cyst in the liver leads to the fluid-filled sacs throughout the organ. What Causes Cysts on the Liver and Kidneys?
There are many causes that can cause a cyst in the liver and kidneys. In the liver, most of the people inherit the condition but it can also occur without any genetic link. Women are more prone to this condition than man. Polycystic liver disease is most common in polycystic kidney disease. There are mainly three types of PKD:
- Autosomal dominant PKD is common in adults and mainly happens to patients whose parents with PKD condition. What Causes Cysts on the Liver and Kidneys?
- Autosomal recessive PKD is less common and mainly occur when both the parents have a gene for the disease.
- Acquired cystic kidney disease is not inherited and occurs in middle or old age. It is common in people who already have one or the other kidney problem especially the one that has kidney failure or is on dialysis. What Causes Cysts on the Liver and Kidneys?
The symptoms of this condition are only visible in advanced stages. Some of the common visible signs are:
Latest Posts
You May Like: Is Watermelon Good For Ckd Patients
What Can I Expect After A Transplant Kidney Biopsy
During a standard biopsy, you will be observed for 1-2 hours in the recovery area to ensure you are well, can drink fluids, and pass urine comfortably. When released from the biopsy area, you should go directly home and stay indoors overnight. The next day you can walk or drive a car as needed. It will be important to avoid strenuous activity or heavy lifting for up to another two days after the procedure. If an open biopsy is required, you will receive further instructions.
Why Do I Need A Kidney Biopsy
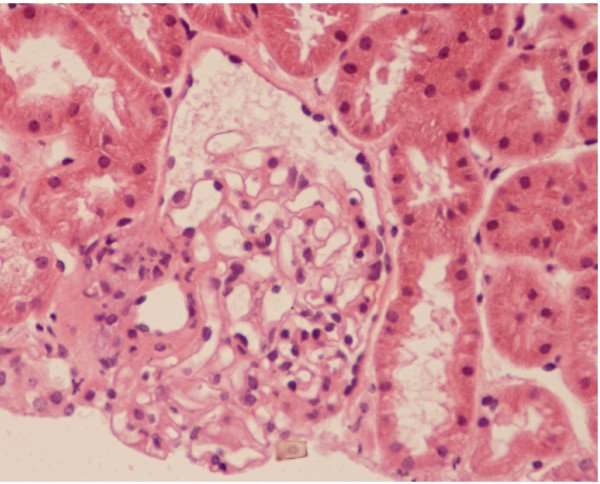
You should tell your kidney doctor before the day of the biopsy if you are taking medication to thin your blood or make your blood less likely to clot.
There are lots of medications that do this, but common ones are aspirin, clopidogrel, warfarin, dabigatran, apixaban and rivaroxaban. These will need to be stopped before the day of your biopsy .
You should not stop taking these medications without consulting your kidney doctor. They will tell you if and when you need to stop taking them and when you should start taking them again.
You will usually go to the hospital on the morning of your biopsy. The kidney team will tell you where to go and at what time – this may involve attending the kidney ward. You can eat, drink and take your medication as normal . You should plan to have a light breakfast as your biopsy will involve you lying flat on your stomach or your back if you have a transplant.
You may need to have blood tests to check your blood levels and how well your blood clots, or these may have been done before the day of your biopsy.
Before you have your biopsy, a small plastic tube will be inserted into the back of your hand. Your cannula may be used to give you a medication called Desmopressin . Desmopressin reduces the risk of bleeding after your biopsy, and is given slowly over 30-60 minutes. It may not be needed in every patient but you may still need the cannula in case you need to have any treatment after the biopsy.
Also Check: Osteocleanse
Risks Associated With Renal Biopsy
Seek immediate medical attention if you find one or more of the symptoms.
- Presence of blood or blood clots in urine found longer than a day after your biopsy
- Unable to urinate
- Frequent or urgent need to urinate
- Burning sensation when urinating
- Have chills or a fever
- Worsening pain at the biopsy site
- Blood or pus oozing out of the biopsy site that saturates the bandage
- Feel faint, dizzy or weak
Renal biopsy can sometimes come with a risk of causing an internal damage to the targeted organ or nearby areas.
Results Of A Renal Biopsy
The tissue sample that was retrieved during your renal biopsy is sent to a laboratory for examination. A pathologist, a doctor who specializes in disease diagnosis, examines the tissue.
Your sample is analyzed under microscopes and with reactive dyes. The pathologist identifies and assesses any deposits or scars that appear. Infections and other abnormal conditions will also be detected.
The pathologist will compile the results and make a report to your doctor. Results are usually ready in about a week.
If the kidney tissue shows a normal structure that is free of deposits and other defects, the results are considered normal.
The results of a renal biopsy are considered abnormal if there are changes in the kidney tissue. There are numerous causes for this result. Sometimes, diseases that begin in other parts of your body can cause damage to the kidneys.
If results are abnormal, it could indicate:
- restrictions or weaknesses in the flow of blood to the kidneys
- connective tissue diseases
Recommended Reading: Can Aleve Cause Kidney Damage
How Do I Prepare For A Kidney Biopsy
Some medications can decrease blood clotting and increase the risk of bleeding during the procedure. You should stop taking these medications, including aspirin, warfarin, apixaban, ibuprofen, and other blood thinners and anti-inflammatory drugs at least one week before a kidney biopsy. Your doctor will ask about any other medicines or supplements you take and recommend any needed changes to your medication regimen.
Your doctor will take urine and blood samples before the biopsy to make sure you do not have any infections or other conditions that could cause complications. In most cases, doctors tell people not to drink or eat anything after midnight prior to the biopsy.
Itâs important to take other medication as usual on the day of biopsy. Blood pressure medication should be taken to avoid high blood pressure at the time of biopsy, and medicine may be taken with sips of water.
How Is Acquired Cystic Kidney Disease Treated
If acquired cystic kidney disease is not causing complications, a person does not need treatment. A health care provider will treat infections with antibioticsmedications that kill bacteria. If large cysts are causing pain, a health care provider may drain the cyst using a long needle inserted into the cyst through the skin.
When a surgeon transplants a new kidney into a patients body to treat kidney failure, acquired cystic kidney disease in the damaged kidneys, which usually remain in place after a transplant, often disappears.
A surgeon may perform an operation to remove tumors or suspected tumors. In rare cases, a surgeon performs an operation to stop cysts from bleeding.
Also Check: Tea Good For Kidneys
What Are Some Of The Risks Of A Transplant Kidney Biopsy
While the risks of a biopsy are small, complications could occur. Bleeding may occur. About a third of patients have some light red color in the urine for a day or so of little consequence. About 1-3% of patients have bleeding with clots that required a bladder irrigation with a catheter to clear them. If the bleeding is severe enough, a transfusion may be needed. However, this is a very rare occurrence in less than 1% of patients. Very rarely a urine infection may occur, especially in patients with a history of frequent urine infections. Other problems to watch for include fever, pain at the site of the biopsy, dizziness, or not being able to urinate.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 11/04/2019.
References
What Is A Transplant Kidney Biopsy
While a kidney biopsy is a procedure where small samples of the kidney are removed in order to be examined by a pathologist under a microscope. A transplant kidney biopsy is done either as a screening test or to see what is happening with a kidney that is not working properly. It provides more information than can be obtained from a noninvasive procedure . Biopsy is considered the best option to diagnose problems with transplanted kidneys.
Read Also: Red Wine And Kidney Stones
How Will I Recover From A Kidney Biopsy
Youâll lie flat for several hours after the procedure while your doctor and nurses monitor you. After a native kidney biopsy, most patients spend one night in the hospital.
After a transplant kidney biopsy, most people go home the same day. Youâll need someone to give you a ride home, because you may feel drowsy from the medications.
You should expect to remain quiet and rest for about a day after the procedure.
Monoclonal Gammopathies And Paraprotein Diseases
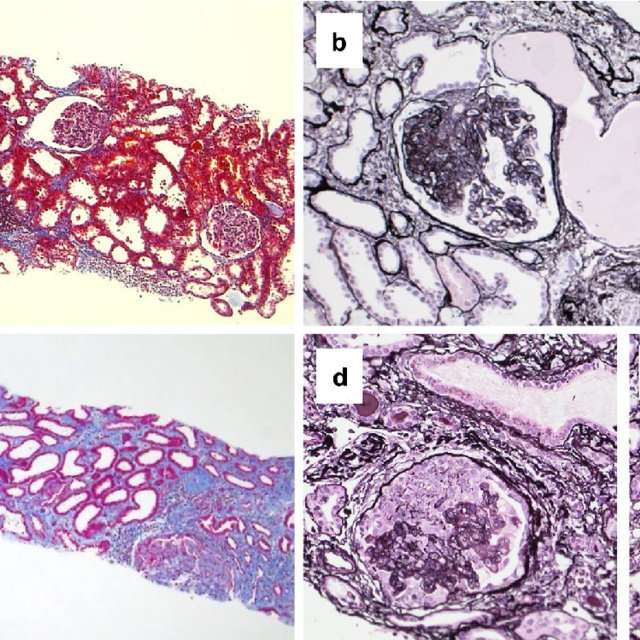
Patients with monoclonal gammopathies may require a kidney biopsy to document end organ damage from the offending paraprotein. Although it has been suggested that patients with monoclonal gammopathies and amyloidosis have a higher risk of complications from bleeding diathesis , there is no evidence that this translates to a higher clinical risk with PRBs. One series found a statistically increased risk of bleeding in patients who had renal amyloidosis , but the definition of bleeding was a hemoglobin decrease > 1 g/dl and did not include need for transfusion or intervention. A second series found no difference in overall or major bleeding complications after PRB in patients with systemic amyloidosis versus controls . Another series found no increased risk of PRB complications for patients with monoclonal gammopathies versus controls .
You May Like: Pomegranate Juice Kidney Stones