Urine Formation Per Day
Glomerular filtration rate is termed as the volume of filtrate formed by both kidneys per minute. On average, 125 mL/min filtrate is produced in men and 105 mL/min filtrate is produced in women. However, 99% of produced filtrate is returned to circulation by the process of reabsorption. Therefore, only about 12 litres of urine are produced per day in a healthy human body. Lets see the table below for more information on the quantity of urine formed per day for men and women.
In the table below, we have mentioned the quantity of urine that is formed daily in men and women.
| Gender |
Blood Flows In And Out Of The Kidneys Through Renal Arteries And Veins
Blood enters the kidneys through renal arteries. These arteries branch into tiny capillaries that interact with urinary structures inside the kidneys . Here the blood is filtered. Waste is removed and vital substances are reabsorbed back into the bloodstream. The filtered blood leaves through the renal veins. All the blood in the body moves in and out of the kidneys hundreds of times each daythats about 200 quarts of liquid to be filtered every 24 hours.
How Do Uric Acid Stones Form
If you have high levels of uric acid, then crystals start to form. These uric acid crystals combine with other substances in your body and create a solid mass. The mass keeps growing. It may stay in the kidney or move down the urinary tract and settle in the ureter.
If the stones are very small, they may pass out of your body in your urine without too much pain. But if they dont pass, they cause urine to back up in the kidney, ureter, bladder or urethra. Thats when you get pain and other symptoms.
Also Check: Is Robinsons Barley Water Good For Kidneys
The Kidneys Are Retroperitoneal Organs In The Abdomen
The kidneys are located behind the peritoneum, and so are called retroperitoneal organs. They sit in the back of the abdomen between the levels of the T12 and L03 vertebrae. The right kidney is slightly lower than the left kidney to accommodate the liver. Both kidneys are bean-shaped and about the size of an adult fist.
Waste Ions And Hydrogen Ions Secreted From The Blood Complete The Formation Of Urine
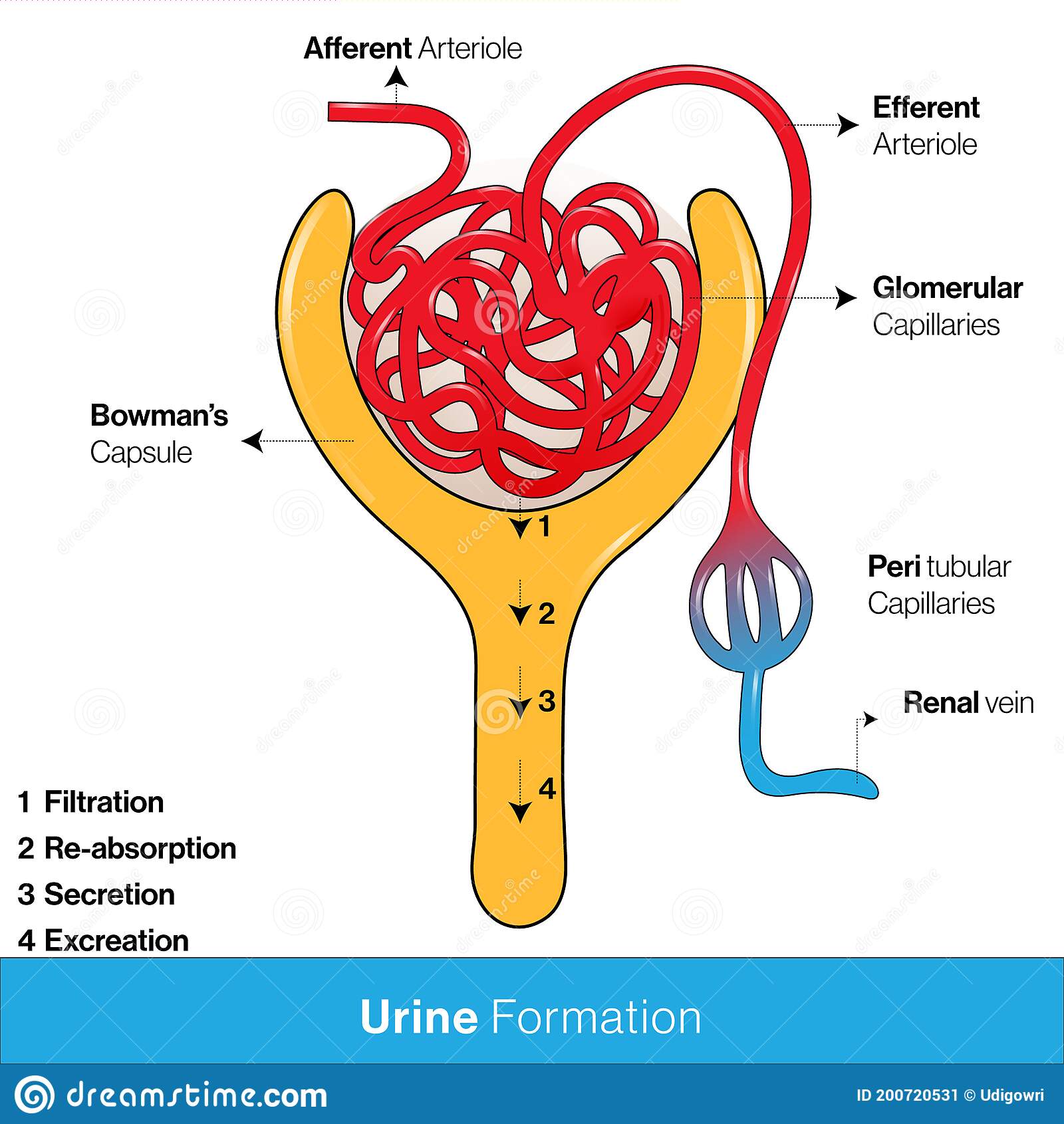
The filtrate absorbed in the glomerulus flows through the renal tubule, where nutrients and water are reabsorbed into capillaries. At the same time, waste ions and hydrogen ions pass from the capillaries into the renal tubule. This process is called secretion. The secreted ions combine with the remaining filtrate and become urine. The urine flows out of the nephron tubule into a collecting duct. It passes out of the kidney through the renal pelvis, into the ureter, and down to the bladder.
Don’t Miss: Does Kidney Failure Cause Pain In Dogs
Which Section Of The Kidney Is Urine Formed
The renal medulla contains the renal pyramids, where urine formation takes place. Urine passes from the renal pyramids into the renal pelvis. This funnel-shaped structure occupies the central cavity of each kidney and then narrows as it extends out to join the ureter.The renal medullarenal medullaThe renal medulla is the innermost part of the kidney. The renal medulla is split up into a number of sections, known as the renal pyramids. The renal medulla contains the structures of the nephrons responsible for maintaining the salt and water balance of the blood. https://en.wikipedia.org wiki Renal_medulla
Which Is The Correct Order Of Blood Flow Through The Kidneys
What is the correct order of blood flow through the kidney? Blood enters the kidney through the renal artery and then enters the glomerulus via the afferent arteriole. Filtrate containing waste remains behind for excretion. Filtered blood exits the kidney through the renal vein, returning to the heart.
Also Check: What Is The Job Of The Kidneys
How Are Kidney Stones Diagnosed
Your healthcare provider will discuss your medical history and possibly order some tests. These tests include:
- Imaging tests: An X-ray, CT scan and ultrasound will help your healthcare provider see the size, shape, location and number of your kidney stones. These tests help your provider decide what treatment you need.
- Blood test: A blood test will reveal how well your kidneys are functioning, check for infection and look for biochemical problems that may lead to kidney stones.
- Urine test: This test also looks for signs of infection and examines the levels of the substances that form kidney stones.
Read Also: Can You Have A Child With One Kidney
Kidneys: The Main Osmoregulatory Organ
The kidneys, illustrated in Figure 22.4, are a pair of bean-shaped structures that are located just below and posterior to the liver in the peritoneal cavity. The adrenal glands sit on top of each kidney and are also called the suprarenal glands. Kidneys filter blood and purify it. All the blood in the human body is filtered many times a day by the kidneys these organs use up almost 25 percent of the oxygen absorbed through the lungs to perform this function. Oxygen allows the kidney cells to efficiently manufacture chemical energy in the form of ATP through aerobic respiration. The filtrate coming out of the kidneys is called urine.
Dont Miss: Can Soda Pop Cause Kidney Stones
Read Also: Which Region Of The Kidney Is The Most Superficial
How Does Urination Occur
To urinate, your brain signals the sphincters to relax. Then it signals the muscular bladder wall to tighten, squeezing urine through the urethra and out of your bladder.
How often you need to urinate depends on how quickly your kidneys produce the urine that fills the bladder and how much urine your bladder can comfortably hold. The muscles of your bladder wall remain relaxed while the bladder fills with urine, and the sphincter muscles remain contracted to keep urine in the bladder. As your bladder fills up, signals sent to your brain tell you to find a toilet soon.
Read Also: Can You Have 4 Kidneys
What Color Is Urine When Kidneys Are Failing
Kidney failure is a condition in which one or both kidneys can no longer work on their own. It may be due to an acute injury to the kidneys or a chronic disease that gradually causes them to stop functioning. When kidneys are healthy, they clean the blood by removing excess fluid, minerals and wastes. But when they are failing, harmful wastes build up in the body and excess fluid is retained, changing the appearance, amount and number of times urine is passed.
Read Also: Is Watermelon Good For Kidneys
Components Of The Urinary System
The urinary system consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra. The kidneys form the urine and account for the other functions attributed to the urinary system. The ureters carry the urine away from kidneys to the urinary bladder, which is a temporary reservoir for the urine. The urethra is a tubular structure that carries the urine from the urinary bladder to the outside.
Read Also: Can Soda Pop Cause Kidney Stones
Faqs On Urine Formation
Find some of the frequently asked questions on the process of urine formation below:
Q.1: Where and how is urine produced?Ans: Urine is produced in the nephrons of the kidneys. Urine formation involves the following processes:- a. Glomerular Filtrationc. Tubular Secretion
Q.2: Why do the kidneys form urine?Ans: Urine is a yellow fluid formed by the nephrons of the kidneys. Urine is formed to excrete excess water, salt and nitrogenous wastes like urea. Other toxic substances are also excreted through urine.
Q.3: What are the \ steps of urine formation?Ans: Following are the steps of urine formation:a. Glomerular Filtrationc. Tubular Secretion
Q.4: What is the composition of urine, and write the steps of urine formation?Ans: Urine is a yellow colour fluid consisting of excess water, salt, and nitrogenous wastes like urea. Urine is produced in the nephrons of the kidneys. Urine formation involves the following processes:- a. Glomerular Filtration
Don’t Miss: Does Soda Affect Your Kidneys
What Affects The Amount Of Urine You Produce
The amount of urine you produce depends on many factors, such as the amount of liquid and food you consume and the amount of fluid you lose through sweating and breathing. Certain medicines, medical conditions, and types of food can also affect the amount of urine you produce. Children produce less urine than adults.
What Are The Kidneys And Urinary Tract
The urinary tract is one of the systems that our bodies use to get rid of waste products. The kidneys are the part of the urinary tract that makes urine . Urine has salts, toxins, and water that need to be filtered out of the blood. After the kidneys make urine, it leaves the body using the rest of the urinary tract as a pathway.
Recommended Reading: What Can Help Kidney Pain
The Passive Mechanism Hypothesis For The Inner Medulla
In contrast to the outer medulla, with active NaCl transport from thick ascending limbs generating the single effect, isolated perfused tubule experiments in rabbit thin ascending limbs demonstrated no significant active NaCl transport . Instead, the thin ascending limb had relatively high permeabilities to sodium and urea while being impermeable to water . In contrast, the inner medullary thin descending limb is highly water-permeable but has low urea and sodium permeabilities . Moreover, it had long been known that urea administration enhances maximum urine concentration in protein-deprived rats and humans , and evidence from some species showed that urea tended to accumulate in the inner medulla, with concentrations similar to those of NaCl . Several inner medullary concentrating mechanism models were published that failed to gain general acceptance .
In recent years, mathematical simulations of the urine concentrating mechanism have become increasingly comprehensive and sophisticated in the representation of medullary architecture and tubular transport . This evolution is a consequence of faster computers with increased computational capacity, the increasing body of experimental knowledge, and the sustained failure of simulations to exhibit a significant inner medullary concentration gradient.
Stage 3 Of Urine Formation: Water Conservation
The third and final stage of urine formation is water conservation. The kidneys are not only responsible for eliminating metabolic wastes from the body but they also prevent excessive water loss, in doing so. This is very important in maintaining the body’s fluid balance. Urine is made up mostly of water. It plays a significant role in the entire process of waste elimination. If, however, too much water is removed from the body, it results in dehydration, which could lead to other serious medical conditions.
When tubular fluid leaves the renal tubule it goes to the collecting tubule . At this stage the tubular fluid becomes urine. The renal tubule of several nephrons drain into the collecting tubule. This results in a significant amount of water being drained into the collecting tubule. If all this water was eliminated, it would amount to about 36 liters of urine per day. One can only imagine the devastating effects this would have on the body as this far exceeds the average volume of urine excreted by an adult, of 1 to 2 liters per day.
The collecting tubule receives tubular fluid from numerous nephrons. As it moves along the collecting tubule it become more and more concentrated. This causes water to be reabsorbed into the bloodstream, by the process of osmosis.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Treatment For Kidney Stones
How Does The Urinary System Work
The urinary system’s function is to filter blood and create urine as a waste by-product. The organs of the urinary system include the kidneys, renal pelvis, ureters, bladder and urethra.
The body takes nutrients from food and converts them to energy. After the body has taken the food components that it needs, waste products are left behind in the bowel and in the blood.
The kidney and urinary systems help the body to eliminate liquid waste called urea, and to keep chemicals, such as potassium and sodium, and water in balance. Urea is produced when foods containing protein, such as meat, poultry, and certain vegetables, are broken down in the body. Urea is carried in the bloodstream to the kidneys, where it is removed along with water and other wastes in the form of urine.
Other important functions of the kidneys include blood pressure regulation and the production of erythropoietin, which controls red blood cell production in the bone marrow. Kidneys also regulate the acid-base balance and conserve fluids.
Small Amounts Of Urine
If you have a large stone it can create a blockage that makes urine hard to pass, resulting in the flow of urine slowing or stopping altogether. If your urine stops, you need medical attention immediately.
With severe cases of kidney stones, you can also experience chills, fever, nausea, and vomiting, which may also be signs of an infection.
Kidney stones may pass without pain, or they can be excruciating. However you may be dealing with this condition, were here to help. If you find yourself dealing with one or many of these symptoms, make an appointment with Drs. Herman, Kester and the Urology Center of Florida today.
You Might Also Enjoy
You May Like: Do Kidney Stones Feel Like A Uti
Also Check: Can Drinking Cause Kidney Pain
What Causes Kidney Stones
Waste products in the blood can occasionally form crystals that collect inside the kidneys.
Over time, the crystals may build up to form a hard stone-like lump.
This is more likely to happen if you:
- do not drink enough fluids
- are taking some types of medication
- have a medical condition that raises the levels of certain substances in your urine
After a kidney stone has formed, your body will try to pass it out when you pee.
Summary On Urine Formation
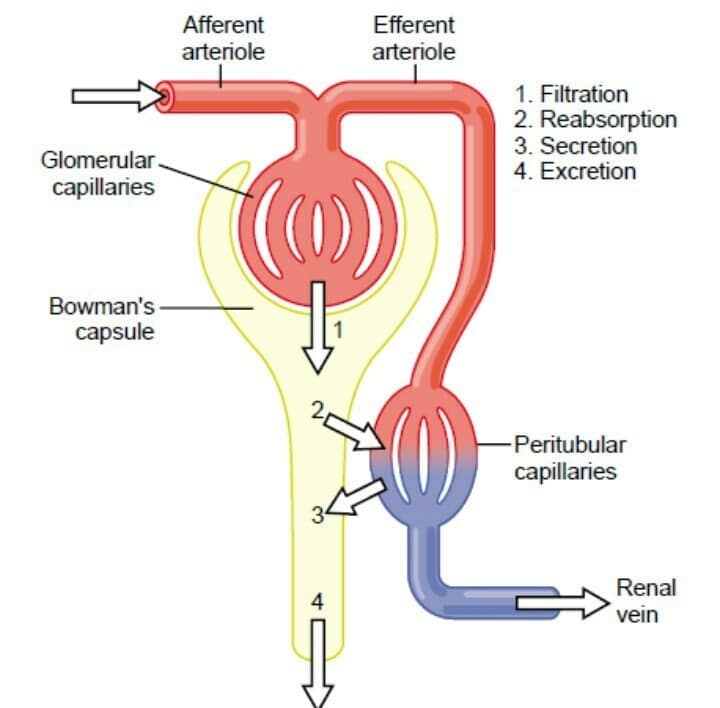
Urine formation involves a few processes like glomerular filtration, selective reabsorption, and tubular secretion. The nephron is the unit of the kidney. Each nephron undergoes all three processes of urine formation and forms concentrated urine which is transported to the urinary bladder through ureters and then is excreted out of the body.
Also Check: Is Resveratrol Good For Kidneys
Kidney Function And Physiology
Kidneys filter blood in a three-step process. First, the nephrons filter blood that runs through the capillary network in the glomerulus. Almost all solutes, except for proteins, are filtered out into the glomerulus by a process called glomerular filtration. Second, the filtrate is collected in the renal tubules. Most of the solutes get reabsorbed in the PCT by a process called tubular reabsorption. In the loop of Henle, the filtrate continues to exchange solutes and water with the renal medulla and the peritubular capillary network. Water is also reabsorbed during this step. Then, additional solutes and wastes are secreted into the kidney tubules during tubular secretion, which is, in essence, the opposite process to tubular reabsorption. The collecting ducts collect filtrate coming from the nephrons and fuse in the medullary papillae. From here, the papillae deliver the filtrate, now called urine, into the minor calyces that eventually connect to the ureters through the renal pelvis. This entire process is illustrated in Figure 22.7.
Physiology Of Urine Formation In The Nephrons
Nephrons take a simple filtrate of the blood and modify it into urine. Many changes take place in the different parts of the nephron before urine is created for disposal. The term forming urine will be used hereafter to describe the filtrate as it is modified into true urine. The principle task of the nephron population is to balance the plasma to homeostatic set points and excrete potential toxins in the urine. They do this by accomplishing three principle functionsfiltration, reabsorption, and secretion. They also have additional secondary functions that exert control in three areas: blood pressure , red blood cell production , and calcium absorption .
Urine is a waste byproduct formed from excess water and metabolic waste molecules during the process of renal system filtration. The primary function of the renal system is to regulate blood volume and plasma osmolarity, and waste removal via urine is essentially a convenient way that the body performs many functions using one process.
Steps involved in urine formation are Glomerular filtration, Tubular reabsorption and Tubular secretion
Figure 1:Steps involved in urine formation.
Also Check: Can You Have Multiple Kidney Stones At One Time
Tubulrn Resorpce A Sekrece
Jak jsme ji uvedli výe, tak z celkového filtrátu se zhruba 99 % zptn vrací tubulární resorpcí do extracelulární tekutiny . Hlavním úkolem tubul je tedy izoosmotická resorpce primární moi. Krom vody se vstebávají napíklad ionty , moovina, glukóza i aminokyseliny. To ve probíhá nezávisle na mnoství extracelulární tekutiny v organismu hovoíme o tzv. obligátní resorpci. Její primární význam spoívá tedy v udrení volumu tekutin v organismu za jakýchkoli podmínek.
Transport se uskuteuje bu pasivn difúzí ve smru koncentraního nebo elektrického gradientu, primárn aktivním transportem proti gradientu , nebo sekundárn aktivním transportem . Látky mohou být transportovány transcelulárn nebo paracelulárn. Voda je transportovaná vdy pasivn. Základem sekundárn aktivního transportu je Na+/K+-ATPáza umístná na bazolaterální membrán. Tou se vytvoí koncentraní gradient pro sodík, jen pestupuje dle svého elektrochemického gradientu z tubulární tekutiny do epitelových bunk pes apikální membránu. Transportní proteiny pak psobí jako symportéry , nebo antiportéry . Pro pochopení dj v tubulárním systému si tedy nejprve musíme pedstavit buky tubulárního epitelu, které jsou svojí apikální membránou obráceny k tubulární tekutin , na druhé stran k tekutin peritubulární .
Proximální tubulus
Renální práh
Henleova klika
Klinická korelace:
Látka, která blokuje tento symport , se vyuívá jako velmi úinné diuretikum hovoíme o tzv. klikových diureticích.