How Does One Make The Diagnosis Of Primary Aldosteronism
An adrenal adenoma or bilateral adrenal hyperplasia cause increased production of aldosterone. Increased mineralocorticoid activity is a main mechanism for initiating and maintaining metabolic alkalosis. Increased Na reabsorption and H+/K+-ATPase activity with resultant increased reclamation of HCO3 and volume expansion cause hypertension, hypokalemia and metabolic alkalosis found in primary aldosteronism.
In some families, glucocorticoid remediable aldosteronism occurs due to a genetic defect in the aldosterone synthase gene. There is a family history of difficult to control hypertension that is amenable to steroid therapy. It can be diagnosed by the presence of elevated 18-OH-cortisol and 18-oxocortisol in urine. One can differentiate primary aldosteronism from other chloride-resistant metabolic alkaloses based on renin and aldosterone levels .
Differential diagnosis of the patient with hypertension, hypokalemia and metabolic alkalosis
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
The management of hyperchloremic acidosis is with an interprofessional team that consists of a nephrologist, internist, endocrinologist, cardiologist, and a pulmonologist. The acidosis can result in many symptoms and even lead to cardiac arrest and respiratory failure. The key is to manage the primary condition causing the hyperchloremic acidosis. Patients with respiratory and cardiac symptoms may need close monitoring, and the acidosis may have to be reversed with bicarbonate. It is vital to rule out any medication causing the acidosis. For most patients, the prognosis is okay as long as the primary condition is managed. Failure to manage the primary condition can lead to high morbidity and mortality.
What Are The Actions Of The Renin
To understand the physiology of renin and aldosterone in maintaining metabolic alkalosis, one first needs to review renal HCO3 excretion. Assuming ECF HCO3 = 24 mEq/L and GFR = 180 L/day, 4320 mEq of HCO3 is filtered by the kidneys. Eighty-five percent is absorbed in the proximal tubules, 10% in thick ascending loop of Henle, and > 5% in the distal nephron resulting in 1 mEq/day of bicarbonate excretion under normal conditions. Carbonic anhydrase is an important zinc metalloenzyme involved in the reabsorption of HCO3 in kidney. It catalyzes the following reaction:
CO2 + OH HCO3
In the proximal tubule, cytosolic CA Type II catalyzes the reaction to extrude H+from apical membrane and HCO3 leaves the cell across the basolateral membrane . The extruded proton combines with luminal HCO3 to form H2O + CO2.
Figure 2.
Proximal tubule HCO3- reabsorption.
Proton and HCO3 formation in the cell is catalyzed by cytosolic CA. CA inhibition markedly reduces trans-epithelial HCO3reabsorption. HCO3is reabsorbed with secretion of H+ into the lumen. Na+/H+ exchanger is the major mode of proximal HCO3and Na+absorption . The remaining 1/3 of HCO3reabsorption is carried out by H+-ATPase.
Potassium depletion increases expression of NHE-3 and NBC transporters resulting in increased proximal HCO3reabsorption. Similarly, angiotensin II increases NHE-3 and NBC transporters via cAMP/protein kinase C-tyrosine kinase pathways.
Figure 4.
Intercalated cell H+ and HCO3- transport.
Read Also: Is Orange Juice Good For Kidney Disease
Treatment Dependent On Cause
Treatment for metabolic acidosis depends on the cause. Some causes are temporary and the acidosis will go away without treatment.
This condition can also be a complication of other chronic health problems. Treating the underlying condition may help prevent or treat the metabolic acidosis.
Metabolic acidosis is acidosis due to changes that affect the blood circulation, kidneys, or digestion. This may be caused by:
- Diabetic ketoacidosis. The body burns fats instead of sugars, causing ketones or acids to build up.
- Diarrhea. Severe diarrhea or vomiting can lead to hyperchloremic acidosis. This causes low levels of base called bicarbonate, which help to balance acids in the blood.
- Poor kidney function. Kidney disease and kidney failure can lead to renal tubular acidosis. This happens when your kidneys cant get filter out acids through the urine properly.
- Lactic acidosis. This occurs when the body overproduces or underutilizes lactic acid. Causes include heart failure, cardiac arrest, and severe .
- Diet. Eating excess animal products may make more acids in the body.
- Exercise. The body makes more lactic acid if youre not getting enough oxygen for a long time during intense exercise.
Other causes of acidosis include:
- alcohol or drug abuse
- drugs that slow breathing like benzodiazepines, sleep medications, pain medications, and certain narcotics
Treatment for metabolic acidosis works in three main ways:
Other kinds of treatment for metabolic acidosis include:
What Should You Expect To Find On History And Physical Examination Of Patients With Metabolic Alkalosis

You should take a careful history and physical exam in order to provide clues into initiating and maintenance factors for metabolic alkalosis. .
The history in the patient with metabolic alkalosis
History should include:
-
Medication use especially diuretics, laxative use and alkali intake, as well as ingestion of licorice.
-
Family history should be sought regarding hypertension and electrolyte abnormalities to suggest inherited disorders such as Bartter and Liddle syndromes.
-
GI symptoms of vomiting or diarrhea can explain metabolic alkalosis. Certain villous adenomas may be chloride secreting.
-
Other diseases: obstructive sleep apnea, cirrhosis, COPD, cystic fibrosis also can be associated with mixed acid-base disturbances. One must also be cognizant of blood transfusions.
On physical examination it is very important to assess hypertension, signs of Cushing syndrome, volume status and other co-morbid conditions as mentioned in Table I. An orthostatic decrease in blood pressure and increase in heart rate, sunken eye balls, decreased skin turgor and thirst are signs of ECF volume depletion. Cushing syndrome would be suggested by signs of hypercortisolism such as moon facies, buffalo hump, striae and hypertension. After taking a detailed history and performing a physical examination, one should next order laboratory studies.
Read Also: Is Pomegranate Juice Good For Your Kidneys
Who Is More Likely To Have Rta
You are more likely to have type 1 RTA if you inherit specific genes from your parents or if you have certain autoimmune diseases such as Sjögrens syndrome or lupus.2
If you have Fanconi syndrome or are taking medicines to treat HIV or viral hepatitis, you are more likely to have type 2 RTA.1 People who inherit genes for type 2 RTA from their parents may also have it. In adults, type 2 RTA can be a complication or side effect of multiple myeloma,3 exposure to toxins, or certain medications. In rare cases, type 2 RTA occurs in people who experience chronic rejection of a transplanted kidney.4
If you have low levels of the hormone aldosterone, cannot urinate freely because of an obstruction, or had a kidney transplant, you are more likely to develop type 4 RTA.1 One in five people develop type 4 RTA if they experience rejection of a transplanted kidney or are taking immunosuppressive medications.1
Metabolic Acidosis In Kidney Failure: Causes Symptoms And Treatment
Many kidney failure patients can suffer from metabolic acidosis when their glomerular filtration rate decreases below 20ml/min. Clinical research shows that metabolic acidosis is a main cause of kidney failure patients death. In order to help the patients prevent metabolic acidosis, it is necessary for them to know it more.
Next, we will list the causes, symptoms and treatment for metabolic acidosis in kidney failure, please see the following. Any other questions, please send an email to , and we will reply you as soon as possible.
Why the kidney failure patients can suffer from metabolic acidosis?
In normal conditions, the kidneys have the function of regulating acid-base balance. While, for the patients with severe kidney failure, due to the declined GFR, the organic acid cannot be discharged enough from body. As time goes on, the acid level in body will increase quickly, and the patients can suffer from serious acid-base imbalance.
What will happen if the kidney failure patients experience metabolic acidosis?
If the patients suffer from metabolic acidosis, a series of discomforts, such as nausea and vomiting, loss of appetite, chest pain, headaches, palpitations, muscle and bone pain, muscle weakness, abdominal pain, low blood pressure etc. For the patients with Diabetes, they also can suffer from elevated blood sugar level and dehydration. In extreme conditions, it also can cause severe complications, such as coma, stupor and seizures.
Don’t Miss: Is Pomegranate Juice Good For Your Kidneys
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Rta
The major signs of type 1 RTA and type 2 RTA are low levels of potassium and bicarbonatea waste product produced by your bodyin the blood. The potassium level drops if your kidneys send too much potassium into your urine instead of returning it to the blood.
Because potassium helps regulate your nerve and muscle health and heart rate, low potassium levels can cause
- extreme weakness
- paralysis
- death
The major signs of type 4 RTA are high potassium and low bicarbonate levels in the blood. Symptoms of type 4 RTA include9
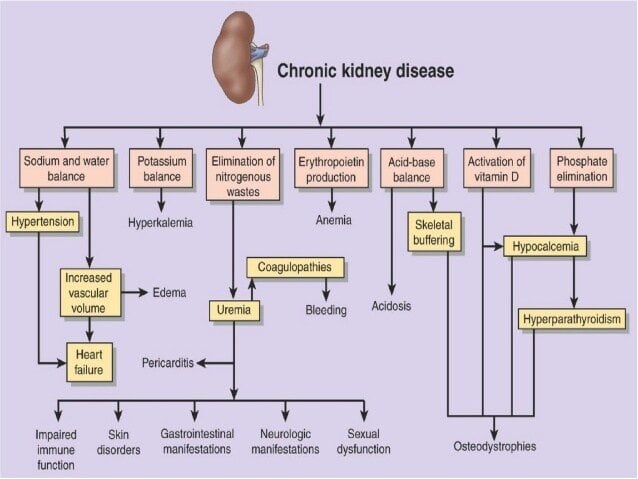
Pathogenesis Consequences And Treatment Of Metabolic Acidosis In Chronic Kidney Disease
The content on the UpToDate website is not intended nor recommended as a substitute for medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your own physician or other qualified health care professional regarding any medical questions or conditions. The use of this website is governed by the UpToDate Terms of Use ©2018 UpToDate, Inc. All topics are updated as new evidence becomes available and our peer review process is complete. INTRODUCTION Most individuals produce approximately 15,000 mmol of carbon dioxide and 50 to 100 meq of nonvolatile acid each day. Acid-base balance is maintained by normal elimination of carbon dioxide by the lungs and normal excretion of nonvolatile acid by the kidneys . The hydrogen ion concentration of the blood is determined by the ratio of the PCO2 and plasma bicarbonate concentration. Acidosis associated with chronic kidney disease will be discussed in this topic. An overview of simple acid-base disorders and renal tubular acidosis, as well as the approach to patients with metabolic acidosis, are presented elsewhere. ACID-BASE BALANCE IN CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE Acid-base balance is normally maintained by the renal excretion of the daily acid load (about 1 meq/kg per day, derived mostly from the generation of sulfuric acid during the metabolism of sulfContinue reading > >
Also Check: Watermelon Kidney Disease
Metabolic And Musculoskeletal Effects Of Acidosis
Nonspecific symptoms such as malaise and fatigue may attend metabolic acidosis. The strongest evidence that alkali therapy can ameliorate these derives from a study of patients receiving acetazolamide for glaucoma. Blinded administration of sodium acetate with the carbonic anhydrase inhibitor reduced this complex of symptoms. Whether the treatment of the acidosis of CKD would mitigate such complaints is unknown.
What Are Clinical Trials For Rta
Clinical trialsand other types of clinical studiesare part of medical research and involve people like you. When you volunteer to take part in a clinical study, you help doctors and researchers learn more about disease and improve health care for people in the future.
Researchers are studying many aspects of RTA, such as
- new drug treatments
Recommended Reading: Bleeding Kidney Treatment
When Can We Encounter Metabolic Alkalosis In Hemodialysis Patients
Patients on dialysis experience metabolic alkalosis following events that increase serum bicarbonate concentration. These patients do not experience secondary increase in serum bicarbonate concentration due to respiratory acidosis. In addition, dialysis patients encounter sustained metabolic alkalosis independent of chloride stores due to lack of kidney function. A hemodialysis patient can experience severe metabolic alkalosis with low serum chloride concentration and high calculated serum bicarbonate concentration from a few days of profuse vomiting and can clinically manifest as lethargy and confusion . Serum bicarbonate concentration can reach beyond the laboratory standard range that is seen in patients with intact kidney function. As a result, laboratory measurements may be difficult and direct electrode measurements of arterial pH and PaCO2 should be performed. Subsequently, serum bicarbonate concentration can be calculated from the following equation: Change in PaCO2 = 0.7 times change in serum bicarbonate concentration .
The primary management of such a patient will be dialysis with low bicarbonate bath . Severe metabolic alkalosis in dialysis patients have been reported with crack cocaine use, therapeutic plasma exchange, massive blood transfusions that provide massive citrate load and pica ingestion.
Does This Patient Have Metabolic Alkalosis
How does one make the diagnosis of metabolic alkalosis and differentiate simple from mixed disturbances?
Metabolic alkalosis is due either to a gain in bicarbonate or a bicarbonate precursor , loss of hydrogen ion or the loss of fluid that contains Cl in higher concentration and bicarbonate in lower concentration than serum. The brainstem is sensitive to interstitial and cellular H+changes and the decline in H+with metabolic alkalosis inhibits ventilation . In simple metabolic alkalosis the resultant compensatory alveolar hypoventilation leads to an increase in arterial carbon dioxide content . For each 1 mEq/L rise in HCO3, PaCO2 rises about 0.7 mmHg .
Based on the history, one can assess whether an increase in HCO3is due to oral or intravenous alkali administration vs. H+ loss that results in addition of HCO3 to the body. The kidney plays a crucial role in maintaining HCO3. Most often, the kidneys can excrete excess HCO3 and bicarbonaturia occurs. Factors that facilitate bicarbonaturia are adequate extracellular fluid volume, dietary salt intake, potassium balance and appropriate mineralocorticoid activity.
Step 2: Assess whether compensation is appropriate. Remember that for each 1 mEq/L rise in HCO3, PaCO2 rises about 0.7 mmHg . If compensation is not appropriate then a superimposed respiratory acidosis or alkalosis is present.
What is the cause of acid loss or alkali gain?
Extrinsic and intrinsic alkali gain
H+ loss
Intrinsic H+loss
K+ depletion
Cldepletion
You May Like: Constipation And Kidney Stones
Why Does Metabolic Acidosis Develop With Bilateral Kidney Disease
kidneys doMetabolic acidosisbuildkidneys are
Metabolic acidosis is commonly found in patients with chronic kidney disease , and its causes are: impaired ammonia excretion, reduced tubular bicarbonate reabsorption and insufficient renal bicarbonate production in relation to the amount of acids synthesised by the body and ingested with food.
One may also ask, why does uremia cause metabolic acidosis? Failure to secrete hydrogen ions and impaired excretion of ammonium may initially contribute to metabolic acidosis. In uremia, metabolic acidemia may contribute to other clinical abnormalities, such as hyperventilation, anorexia, stupor, decreased cardiac response , and muscle weakness.
Similarly one may ask, why does acute kidney injury cause metabolic acidosis?
Metabolic acidosis is the most common acid-base disturbance associated with acute kidney injury, developing as the result of impaired excretion of the daily load of metabolic fixed acid.
Can kidney cause acidosis?
It leads to an anion gap metabolic acidosis but may also cause a NG acidosis and hypokalemia due to rapid renal excretion of the anion. Chronic kidney disease with decreased renal function is a common cause of metabolic acidosis.
Effects On Accumulation Of 2
It is known that accumulation of 2-microglobulin and the development of amyloid contribute to carpal tunnel syndrome, cysts in bone, and cardiomyopathy in ESRD. Metabolic acidosis may enhance cellular 2-microglobulin generation and release in patients with ESRD, as one study found an inverse correlation between plasma bicarbonate and 2-microglobulin levels.
Recommended Reading: What Are The Three Main Regions Of The Kidney
What Happens To Patients With Metabolic Alkalosis
How does H+ loss lead to addition of HCO3- to the ECF? How does chloride depletion have an added effect?
Gastrointestinal losses from vomiting and nasogastric suction lead to proton loss that triggers metabolic alkalosis. Secretion of a proton into the lumen of the stomach results in addition of HCO3 to the ECF. Chloride is actively transported from the parietal cell into the lumen and sodium ions are absorbed. This generates a negative potential of -40 to -70 millivolts in the canaliculus.
The diffusion potential causes potassium to move into the canalicular lumen. The canalicular membrane exchanges potassium with protons mediated by an H+/K+ exchanger. Protons required for this reaction are generated from water breakdown. The hydroxyl group generated combines with CO2 and forms HCO3 which exits the parietal cell across the basolateral membrane. This mechanism is illustrated in Figure 1.
GI losses increase gastric pH which triggers more proton secretion by gastric parietal cells resulting in further proton loss and ECF HCO3 addition. Induction of Cl depletion contributes to chloride depletion metabolic alkalosis . This may be the reason why certain lower GI losses present with metabolic alkalosis .
Acidosis Due To Acute Renal Failure
Retention of metabolic acids occurs with acute renal failure.
The clinical details in these patients are often complex and the actual severity of acidosis is variable. Some other complicating factors are catabolism , vomiting, diarrhoea, lactic acidosis due to poor perfusion, bicarbonate therapy and dialysis.
Hyperkalaemia is often present and is often the factor determining the need for acute dialysis.
Don’t Miss: Can Kidney Transplant Patients Get Tattoos
Chronic Treatment Of Metabolic Acidosis
There are no FDA approved therapies for the chronic treatment of metabolic acidosis. However, the National Kidney Foundations Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative, or KDOQI, guidelines and the Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes, or KDIGO, guidelines recommend maintaining serum bicarbonate at levels above 22 mEq/L .
Unapproved methods to increase serum bicarbonate include oral alkali supplements, such as sodium bicarbonate, which introduce significant amounts of sodium to patients. Yet approximately 90% of later-stage patients with CKD suffer from sodium-sensitive comorbid conditions, such as hypertension, cardiovascular disease, heart failure or edema and require a sodium-restricted diet. As such, the use of sodium-based supplements can lead to worsening serum pressure control and volume overload in this population. Given the significant limitations on the use of sodium-based supplements, there exists a significant unmet medical need for a chronic therapy for patients with CKD and metabolic acidosis. To chronically treat the broad population of patients with CKD and metabolic acidosis, physicians need an FDA-approved treatment that is proven to be safe, effective and easy to comply with.
Metabolic Acidosis In Ckd
As renal function declines, the kidneys progressively lose the capacity to synthesize ammonia and excrete hydrogen ions. Consequently, low bicarbonate levels are more common in patients with lower eGFR approximately 19% of patients with CKD stages 45 have a serum bicarbonate < 22 mmol/L. In the presence of additional defects in tubular acid excretion, such as in hyporeninemic hypoaldosteronism, metabolic acidosis can appear early in the course of CKD. Furthermore, there is an inverse correlation with age: Serum bicarbonate decreases steadily after age 60 years. Therefore, the exact prevalence of metabolic acidosis caused solely by CKD remains to be determined.
The extrarenal generation of acid by metabolism, known as net acid production, is another player in the acid base balance. Western diets are notorious for being high in acid and are prevalent in the United States, both in people with normal or impaired kidney function and significantly above the recommended dosage of 0.8 g/kg per day in patients with advanced CKD. Maintenance of acid base balance requires the kidney to reclaim most of the filtered bicarbonate and to excrete additional H+ ions equivalent in amount to net acid production and any excreted bicarbonate. A high net endogenous acid production was shown to be associated with a faster decline in GFR in patients with CKD.
Don’t Miss: Are Grapes Good For Kidney Stones