What Are Laboratory Tests Useful In Aki
Laboratory workup for AKI includes:
- Urine analysis with microscopy: This is possible, the most useful test in determining the cause of AKI. The tests performance increases when a seasoned nephrologist examines the urine sample under the microscope. The finding of muddy brown casts with or without tubular cells is practically diagnostic acute tubular necrosis. In contrast, the presence of dysmorphic red blood cells or red blood cell casts indicates glomerular disease. White blood cells or white blood cell casts suggest interstitial nephritis or pyelonephritis. Hyaline casts point towards prerenal AKI.
- Kidney function tests: Increased blood urea nitrogen and creatinine are the hallmarks of AKI diagnosis. However, BUN can also be elevated in patients with gastrointestinal bleeding, steroid treatment, and protein loading. A BUN- creatinine ratio that exceeds 20:1 is suggestive of prerenal AKI.
- Urine electrolytes: The fractional excretion of sodium FENa is a useful and common indicator. However, it is only valuable in the context of oliguria . In oliguric patients with FENa equal to or less than 1%, the cause is probably prerenal. A FENa value of more than 1% is a sign the renal tubules have lost their capacity to reabsorb sodium. However, acute tubular secondary to rhabdomyolysis, severe burns, radiocontrast nephropathy, and acute glomerulonephritis can have FENa values of less than 1%.
How Does Infection Cause Aki
Many types of infection can cause acute kidney injury. The same infection can cause AKI by different individuals mechanisms.
Infections can cause kidney injury by direct invasion or by inducing autoimmune mechanisms. Viruses, bacteria, parasites, and fungi can cause AKI.
Examples of an infection that cause acute kidney injury due to direct damage to kidney tissue include:
- Leptospirosis: Mainly by interstitial nephritis.
- Tuberculosis
- Acute pyelonephritis: E. coli is the most frequent microorganism. However, other microorganisms like Klebsiella spp., Enterobacter spp., Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus, and Enterococci can also cause acute pyelonephritis.
- Nematode infections
- Fungal infections: Fungal infections are particularly frequent in hospitalized patients, infections from microorganisms like Candida, Aspergillus, and Mucor can present as fungal balls, micro-abscesses in the renal vasculature that causes microinfarctions.
- Leishmaniasis
Examples of infections that cause immune-mediated kidney injury include:
- Streptococcal pharyngitis and erysipelas: Weeks after the primary infection resolves, immune complexes deposits in the kidneys basal membrane cause glomerulonephritis.
- Hepatitis B infection: Hepatitis B infections can produce glomerulonephritis by similar mechanisms as streptococcus.
- Human immunodeficiency virus
- Hanta Virus
. The setting of acute kidney injury during sepsis is one of the most important predictors of death or mortality.
Less Iron Than Normal
Iron is a mineral found in many foods, such as meats and leafy greens. Your body uses iron to make red blood cells. A common cause of anemia in people with CKD is iron deficiency. Iron deficiency means you do not have enough iron in your body. It can be caused by not getting enough iron in your diet or by losing blood, either through blood tests or during dialysis. If you dont take in enough iron through your diet, you can get anemia. Around half of people with CKD stages 2 to 5 have some kind of iron deficiency.
Also Check: Renal Diet Orange Juice
Chronic Kidney Disease As A Risk Factor
Chronic kidney disease at baseline was associated with acute kidney injury in several of these series.,â,,,
Warth et al studied 1,038 patients and found an incidence of acute kidney injury of 11% in the 135 with chronic kidney disease and who received acetaminophen or narcotics for pain control, compared with 4.8% in the remaining 903 patients without chronic kidney disease, who received ketorolac or celecoxib.
Perregaard et al studied 3,410 patients who underwent total hip arthroplasty and found an incidence of acute kidney injury of 2.2% overall, but 7% in the 134 patients with chronic kidney disease based on KDIGO creatinine criteria.
Nowicka et al found an incidence of acute kidney injury of 16.7% in the 48 patients with chronic kidney disease , compared with 4.5% in the remaining 289.
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Postrenal Aki
Postrenal AKI presents itself with symptoms of urine retention or prostatic disease. Including post urinary drip, increased urine frequency, or a dilated bladder.
In the case of kidney stones, symptoms may include severe low back pain, tenderness in a point between the ribs and the spinal column, and fever. Also, patients with an obstructive tumor may have a history of unexplained weight loss in the last months.
Don’t Miss: Are Grapes Good For Kidney Stones
What Causes Acute Kidney Injury
Acute kidney injury can have many different causes. AKI can be caused by the following:
Some diseases and conditions can slow blood flow to your kidneys and cause AKI.
These diseases and conditions include:
- Low blood pressure or shock
- Blood or fluid loss
- Heart attack, heart failure, and other conditions leading to decreased heart function
- Organ failure
- Overuse of pain medicines called NSAIDs, which are used to reduce swelling or relieve pain from headaches, colds, flu, and other ailments. Examples include ibuprofen, ketoprofen, and naproxen.
- Severe allergic reactions
Direct Damage to the Kidneys
Some disease and conditions can damage your kidneys and lead to AKI. Some examples include:
- A type of severe, life-threatening infection called sepsis
- A type of cancer called multiple myeloma
- A rare condition that causes inflammation and scarring to your blood vessels, making them stiff, weak, and narrow
- An allergic reaction to certain types of drugs
- A group of diseases that affect the connective tissue that supports your internal organs
- Conditions that cause inflammation or damage to the kidney tubules, to the small blood vessels in the kidneys, or to the filtering units in the kidneys .
Blockage of the urinary tract
In some people, conditions or diseases can block the passage of urine out of the body and can lead to AKI.
Blockage can be caused by:
- Bladder, prostate, or cervical cancer
- Enlarged prostate
- Blood clots in the urinary tract
The following tests may be done:
The Connection Between Anemia And Ckd
When your kidneys are working properly, they produce a hormone known as erythropoietin . This hormone signals your body to produce red blood cells.
If you have CKD, your kidneys may not make enough EPO. As a result, your red blood cell count may drop enough to cause anemia.
If youre undergoing hemodialysis to treat CKD, that may also contribute to anemia. Thats because hemodialysis can cause blood loss.
Read Also: Is Watermelon Good For Your Kidneys
Assessment Of Acute Kidney Injury
The bedside Schwartz equation was used to estimate kidney function where the estimated glomerular filtration rate =/Cr, where k=0.413). Acute kidney injury was defined using the Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes guidelines using on admission creatinine levels and predicted baseline creatinine from the CC. A 1.5-fold increase in creatinine from baseline was defined as AKI. AKI was further staged as follows: stage 1, 1.51.9x increase from baseline stage 2, 2.02.9 increase in creatinine from baseline stage 3, 3.0x increase in creatinine from baseline or an eGFR < 35mL/min/1.73m2. Data on urine output or proteinuria are not available.
What Is The Kidney And What Does It Do
The kidneys are two coffee bean-shaped organs found in the posterior part of the abdominal cavity which name is retroperitoneum. They connect with the bladder through two thin muscle tubes called the ureters.
The kidneys primary function is to filter blood, remove excess fluid, electrolytes, and waste material to make urine. Urine flows from the kidneys to the bladder. Then, it goes from the bladder to the urethra and finally, from the urethra to the toilet.
The kidneys are vital in maintaining a healthy balance of electrolytes, fluids, acids, and bases in the body. They are also crucial in arterial tension regulation and are the target of important antihypertensive medications . Kidneys also produce essential hormones that control red blood cell production.
Each kidney is made up of millions of nephrons. Each nephron has two main parts the glomerulus and the tubule. The glomerulus is the filter, it works more or less in the same way as a coffee filter does. The tubule removes and adds different elements to the original filtrate according to the bodys needs.
For example, in the dehydrated person, the tubule will absorb a lot of the fluid from the original glomerular filtrate. If a person has excess acid in the body, the tubules will excrete that acid and reabsorb bicarbonate in turn. The substances and fluid the tubules do not reabsorb become urine that flows into the bladder.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Functional Unit Of The Kidneys
What Is Intrinsic Aki
In intrinsic acute kidney injury, there is structural kidney damage that can be the consequence of primary kidney disease, a complication of another disease in a distant organ, drug toxicity, or prolonged hypo-perfusion.
The approach to intrinsic renal injury varies according to the affected part of the kidney. Intrinsic kidney diseases are broadly categorized as glomerular, tubular, or interstitial.
Glomerular causes involve the inflammation of the glomeruli and the blood vessels surrounding them. Glomerulonephritis is usually the result of an autoimmune process like Systemic Lupus Erythematosus or Goodpasture Syndrome and streptococcic glomerulonephritis.
The term interstitial nephritis refers to the inflammation of kidney tissue that is not part of the nephron. Allergic interstitial nephritis is the most common form of acute interstitial nephritis.
Most of the time, AIN is the result of medication drugs. The most common culprits are NSAIDs and antibiotics like cephalosporins, penicillins, sulfonamides, rifampin, and ciprofloxacin.
Interstitial nephritis is often a severe condition that frequently leads to CKD.
In acute tubular necrosis, an important part of the tubular system is destroyed. It causes the kidney to lose its ability to reabsorb and secrete elements to maintain body homeostasis.
What Is Creatinine And Why Is It So Important
Creatinine is a waste product that comes from our normal metabolic processes. What makes creatinine so special is that it is one of the few substances that is completely filtrated in the glomerulus as it is neither reabsorbed nor secreted in the renal tubules.
These characteristics make creatinine levels a great indicator of how well is the kidney filtrating the blood. If creatinine rises above normal levels, that means that for some reason, the kidney is unable to excrete it in the urine, which causes it to accumulate in the blood.
Creatinine levels measurement is one of the most important diagnostic tools in renal injury. Creatinine helps calculate the glomerular filtration rate, which is the amount of blood the kidney filtrates per minute.
Normal creatinine levels range between 0.9 to 1.3 mg/dl in men and 0.6 to 1.1 in women. Any creatinine value above that is indicative of some form of kidney damage.
You May Like: Is Cranberry Juice Good For Liver
Diagnosis Of Anemia Of Renal Disease
-
Complete blood count and peripheral smear
Diagnosis of anemia of renal disease is based on demonstration of renal insufficiency, normocytic anemia, and peripheral reticulocytopenia.
The bone marrow may show erythroid hypoplasia. RBC fragmentation identified on the peripheral smear, particularly if there is thrombocytopenia, suggests simultaneous traumatic hemolysis.
What Is The Treatment For Acute Kidney Failure
Your treatment will depend on the cause of your acute kidney failure. The goal is to restore normal kidney function. Preventing fluids and wastes from building up in your body while your kidneys recover is important. In the majority of cases, a kidney specialist called a nephrologist makes an evaluation.
Read Also: Constipation Kidney Stones
Vancomycin May Also Increase Risk
Courtney et al assessed the risk of adding vancomycin to cefazolin for routine prophylaxis in a retrospective series of 1,828 total hip or knee arthroplasties and found a significantly higher rate of acute kidney injury, using AKIN criteria .
Other agents shown to be effective in treating periprosthetic joint infections or complicated skin and soft-tissue infections with resistant organisms include daptomycin and linezolid. These nonnephrotoxic alternatives to vancomycin may be a consideration if prophylaxis for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus is deemed necessary in patients at risk for acute kidney injury.
What Medications Can Cause Acute Renal Failure Or Acute Kidney Injury
Side Effects of Some Medications Cause Acute Renal Failure or Acute Kidney Injury-
NSAIDs:
Also Check: Wine For Kidney Stones
How Can You Prevent Acute Kidney Injury
There are many ways to develop acute kidney injury. Most of them are unpredictable and, therefore, not preventable .
Some cases of AKI are just a consequence of another disease like heart disease, which is complicated with heart failure or liver diseases. Each of these diseases is preventable in their own way .
AKI secondary to drug toxicity is probably the most preventable form of acute kidney injury. Patients with normal kidney function who take certain medications are at greater risk of developing acute kidney injury, including hypovolemia and hypotension. The mnemonic DAMN is quite helpful to remember these medications:
- D for diuretics
- A for ACE inhibitors and ARBs
- M for metformin
- N for NSAIDS
In Northern Ireland, the Health and Social Health System recommends patients that take these drugs to suspend them when they have severe diarrhea and vomiting for longer than 12 hours and are unable to drink any fluid.
Acute kidney injury secondary to iodine contrast media is also preventable in most cases. Before performing a contrast imaging study in a non-emergency setting, the patients creatinine levels and glomerular filtration rate should be obtained to discard undiagnosed chronic kidney disease that could turn acute iodine-based contrast.
Extensive oral hydration in the hours before the procedure has been shown to reduce the risk of acute kidney injury. Patients with risk factors for AKI should receive intravenous hydration with 0.9 sodium chloride before the procedure.
In Chronic Kidney Disease
Also Check: Can Seltzer Water Cause Kidney Stones
What Tests Are Done To Find Out If You Have Acute Kidney Injury
Acute kidney injury diagnosis in made whenever a patient meets one of the diagnostic criteria outlined in AKI definition. The most basic testing includes creatinine level determination, determining the glomerular filtration rate, and monitoring urine output.
However, once a diagnosis is made, your physician may require other tests to determine the cause of AKI, monitor its progress, and prevent complications.
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Intrinsic Aki
Intrinsic renal failure presents with different symptoms depending on the location of the injury. Glomerular pathologies usually present with macroscopic or microscopic blood in the urine , swelling , and hypertension.
The triad of hematuria, hypertension, and edema is the hallmark of nephritic syndrome. Acute tubular necrosis occurs in the context of sepsis, hypotension, or exposure to nephrotoxic agents. Clinical findings are unremarkable, and diagnosis is made based on laboratory findings.
In tubular necrosis, there is polyuria instead of oliguria. That is to say, that instead of urinating too little, these patients will be urinating a lot.
With no tubular function, the kidneys lose their ability to reabsorb water from the urine. Allergic interstitial nephritis has a history of antibiotic therapy, and patients usually present with fever, rash, and eosinophilia .
You May Like: Is Celery Juice Good For Kidneys
The Need To Monitor Kidney Function With Certain Drugs
Experts have suggested that after the initial assessment of kidney function, physicians should consider regular monitoring after starting or increasing the dosage of drugs associated with nephrotoxicity, especially those used chronically in patients with multiple risk factors for impaired kidney function, Dr. Naughton noted. If there is any sign of kidney harm, the provider should review the medications you are taking in order to identify which one is causing the problem.
If multiple medications are present and the patient is clinically stable, physicians should start by discontinuing the drug most recently added to the patients medication regimen. Once that has been taken care of, further harm to the kidneys may be minimized by keeping blood pressure stable, staying hydrated, and temporarily avoiding the use of other medications that may cause nephrotoxicity.
These safety tips can ensure you get the care you need while keeping your kidneys safe. That way, they can tend to essential functions like keeping things flowing .Originally published May 11, 2017
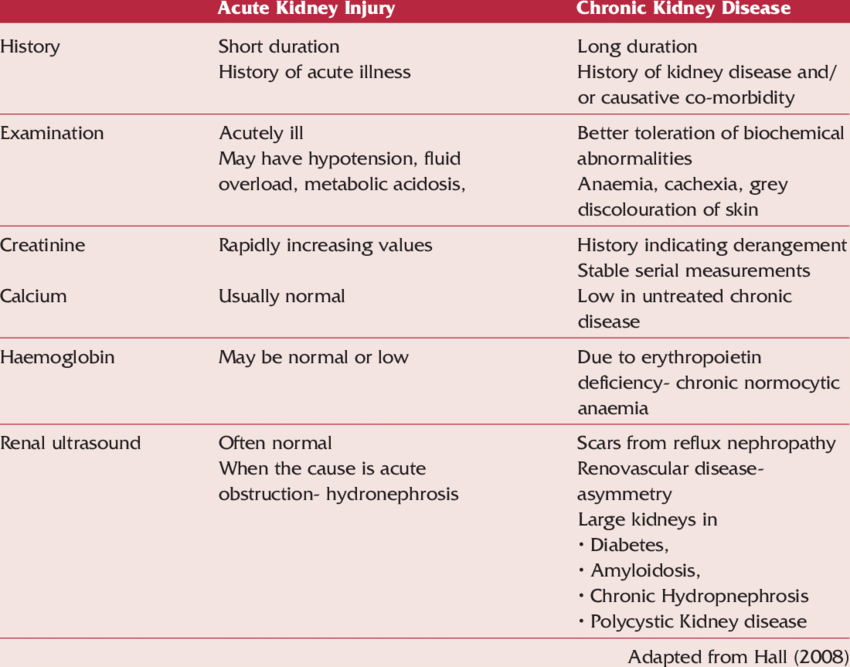
How Is Acute Renal Failure Different From Chronic Kidney Disease
It is very important to know the difference between Acute Renal Failure and Chronic Kidney Disease. In Acute Renal Failure, the kidney ceases to function abruptly. In order to treat Renal Failure, it is important to find out whether it has developed suddenly or as a result of some prolonged illness .
The Major Difference Between Acute Renal Failure and Chronic Kidney Disease is:
Also Check: What Laxative Is Safe For Kidneys
How Will I Know If I Have Anemia
Talk to your doctor if you think you may have anemia. The only way to know if you have anemia is to have a blood test. When you have kidney disease, your doctor will want you to have blood tests often. These tests are used to check not only your kidney function, but also for signs of any other problems, such as the number of red blood cells and how much iron you have in your body.
The test for anemia is a simple blood test to check for the amount of hemoglobin in your blood. Hemoglobin is a part of your red blood cells. Figuring out the amount of hemoglobin you have in your blood can tell your doctor how many red blood cells you have.
Your doctor may also ask you if youve noticed any symptoms, such as changes in skin color or feeling unusually tired.