Can Kidney Disease Be Prevented
Seeing your healthcare provider on a regular basis throughout your life is a good start for preventing kidney disease. About one in every three people in the United States is at risk for kidney disease. Identify and manage any risk factors for developing kidney disease.
- Control your high blood pressure. Normal blood pressure is 120/80.
- Control your blood sugar if you have diabetes.
- Eat a healthy diet. Follow a low-fat, low-salt diet.
- Dont smoke.
- Be active for 30 minutes at least five days a week.
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Take nonprescription pain relievers only as directed. Taking more than directed can damage your kidneys.
Preventing Or Slowing Down The Progression Of Chronic Kidney Disease
There are ways to stop chronic kidney disease becoming any worse or to slow down any progression. You should have checks every now and then by your GP or practice nurse to monitor your kidney function – the eGFR test. They will also give you treatment and advice on how to prevent or slow down the progression of CKD. This usually includes:
- Blood pressure control. The most important treatment to prevent or delay the progression of chronic kidney disease, whatever the underlying cause, is to keep your blood pressure well controlled. Most people with CKD will require medication to control their blood pressure. Depending on the amount of albumin in your urine, your doctor may recommend a target blood pressure level to aim for of below 140/90 mm Hg or 130/80 mm Hg, and even lower in some circumstances. For children and young people with CKD and high levels of albumin in the urine, blood pressure should be kept less than average for their height.
- Review of your medication. Certain medicines can affect the kidneys as a side-effect which can make CKD worse. For example, if you have CKD you should not take anti-inflammatory medicines unless advised to by a doctor. You may also need to adjust the dose of certain medicines that you may take if your CKD gets worse.
- Diet. if you have more advanced CKD then you will need to follow a special diet. See the separate leaflet called Diet in Chronic Kidney Disease.
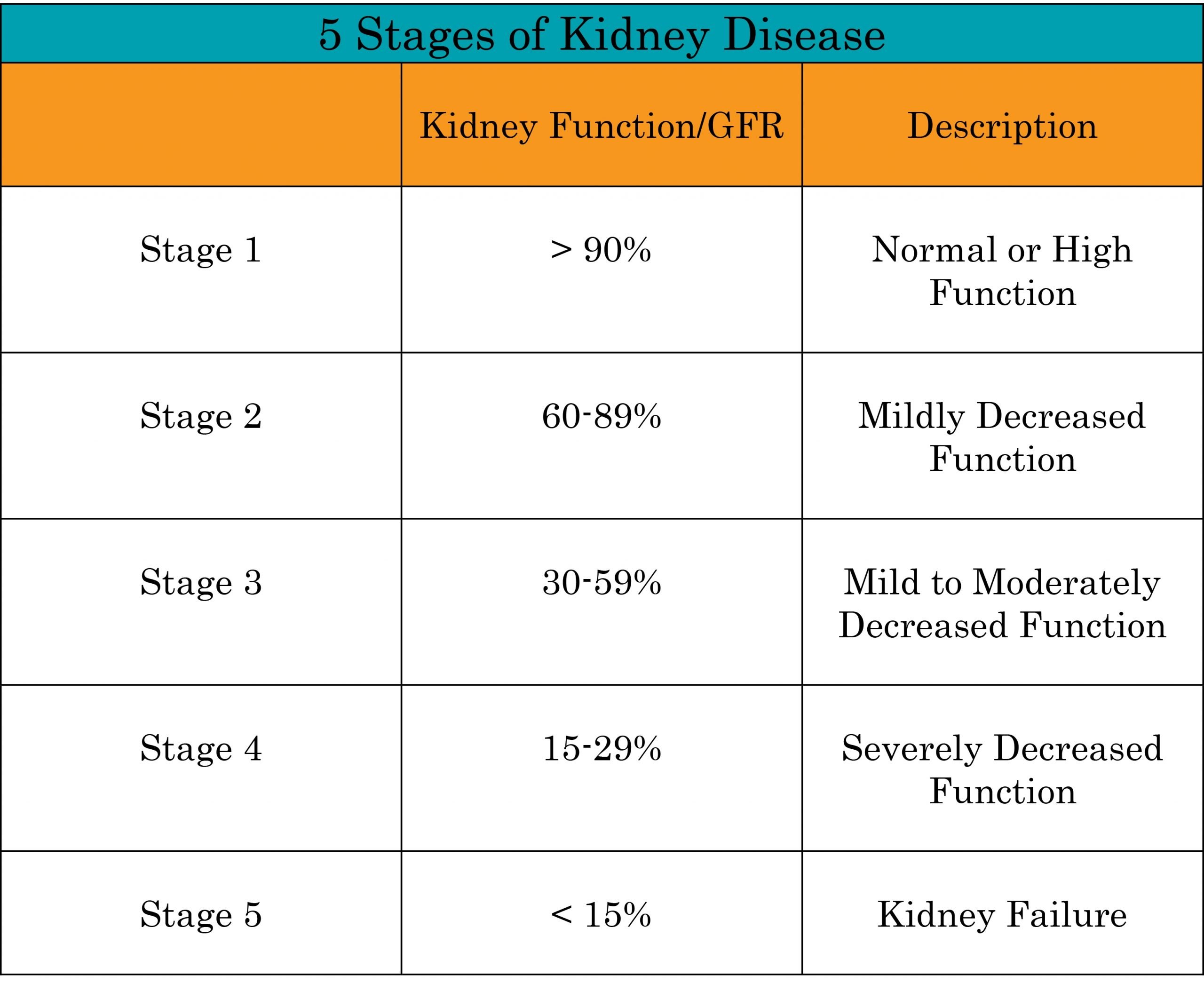
What Are The Ckd Stages
Your kidneys keep a healthy balance between water, salts, and minerals like sodium, calcium, and potassium. They also make hormones that control your blood pressure, keep your bones strong, and help make red blood cells.
Your kidneys also filter extra fluid and waste from your body through units called nephrons. Each nephron has a glomerulus, which filters your blood, and a tubule, which removes the waste and returns what you need back to your blood.
Your kidneysâ filtering speed is called the glomerular filtration rate . If your kidneys are damaged, this GFR will be lower. Blood tests show your estimated glomerular filtration rate and different stages of damage.
The CKD stages are as follows:
- Stage 1 CKD, mild kidney damage with an eGFR above 90 milliliters or greater per minute
- Stage 2, mild damage with 60 to 89 milliliters per minute
- Stage 3a, moderate damage with 45 to 59 milliliters per minute
- Stage 3b, moderate damage with 30 to 44 milliliters per minute
- Stage 4, severe damage with 15 to 29 milliliters per minute
- Stage 5, kidney failure with less than 15 milliliters per minute, a level at which the kidneys are no longer working
Stage 5 CKD is also called end-stage renal disease. At this stage, you will need dialysis or a kidney transplant. Not everyone has CKD that worsens, though.
Recommended Reading: Pineapple Juice And Kidney Stones
What Causes Chronic Kidney Disease
CKD is usually caused by other conditions that strain the kidneys, but some lifestyle habits and other factors can also raise your risk.
Some chronic kidney disease causes include:
- Kidney stones that keep coming back
- Enlarged prostate
- Drinking less alcohol
- Controlling your blood sugar, if you have diabetes
Some doctors might recommend eating a low-protein diet, too. Along with filtering blood and waste, your kidneys also filter protein. Eating low amounts of protein can ease the strain on your kidneys and might stop the disease from worsening. However, evidence for the effectiveness of this diet for CKD is weak.
Show Sources
American Kidney Fund: âChronic Kidney Disease Symptoms, Treatment, Causes & Prevention,â âStages of Chronic Kidney Disease .â
Mayo Clinic: âProtein in urine.â
Medscape: âChronic Kidney Disease .â
National Health Service: âChronic kidney disease.â
National Institutes of Health National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases: âYour Kidneys & How They Work.â
Ckd Symptoms At Stages 3 And 4
Most people only begin to experience symptoms once they reach stage 3. The most common initial symptoms are:
- Swelling, or edema, in your hands, legs, feet, or ankles as the body is unable to get rid of extra fluid and salt
- Changes in urination habits, peeing more or less than normal
- Kidney pain felt in the back
Additionally, you may have:
- Higher protein levels in urine
- Blood or excessive bubbles in your urine
- Urinary tract infections
- Sleep problems due to muscle cramps or restless legs
- Anemia
Also Check: Is Watermelon Good For Kidney Disease
The Five Stages Of Chronic Kidney Disease
Topics
Chronic kidney disease happens gradually in five stages. The American Kidney Fund explains what to expect during each stage.
Chronic kidney disease occurs when a person experiences a gradual, usually permanent, loss of kidney function over a period of months to years. CKD is divided into five stages* of increasing severity, based on the kidneys ability to cleanse the blood of toxic waste and excess fluid.
As explained by the American Kidney Fund, doctors measure how well the kidneys filter waste with anestimated glomerular filtration rate . eGFR is the number given when testing the blood for creatinine, a muscle waste product. eGFR helps gauge how much blood is being filtered through the kidneys and what the most appropriate course of treatment may be.
What Is Kidney Transplantation
Kidney transplantation involves placing a healthy kidney into your body where it can perform all of the functions that a failing kidney cant. Kidneys for transplantation come from two sources: living donors and deceased donors. Living donors are usually immediate family members or sometimes spouses. This is possible because a person can live well with one healthy kidney.
Also Check: Is Apple Cider Vinegar Good For The Kidneys
Do I Need Any Further Tests
As mentioned, the eGFR test is done to diagnose and monitor the progression and severity of chronic kidney disease. For example, it should be done routinely at least once a year in people with stages 1 and 2 CKD, and more frequently in some people with stage 3 and in everyone with stage 4 or 5 CKD.
You are likely to have routine urine dipstick tests from time to time to check for blood and protein in the urine. Also, blood tests may be done from time to time to check on your blood level of chemicals such as sodium, potassium, calcium and phosphate. The need for other tests then depends on various factors and your doctor will advise. For example:
- An ultrasound scan of the kidneys or a kidney biopsy may be advised if certain kidney conditions are suspected. For example, if you have a lot of protein or blood in your urine, if you have pain that seems to be coming from a kidney, etc.
- A scan or having a sample taken is not needed in most cases. This is because most people with chronic kidney disease have a known cause for the impaired kidney function, such as a complication of diabetes, high blood pressure or ageing.
- If the chronic kidney disease progresses to stage 3 or worse then various other tests may be done. For example, blood tests to check for anaemia and an altered level of parathyroid hormone . PTH is involved in the control of the blood level of calcium and phosphate.
How Common Is Chronic Kidney Disease
About 1 in 10 people have some degree of chronic kidney disease. It can develop at any age and various conditions can lead to CKD. It becomes more common with increasing age and is more common in women.
Although about half of people aged 75 or more have some degree of chronic kidney disease, most of these people do not actually have diseases of their kidneys they have normal ageing of their kidneys.
Most cases of CKD are mild or moderate .
Read Also: Can Apple Cider Vinegar Affect Your Kidneys
Treating Kidney Disease Based On Stages
With information about different stages of kidney disease, you can definitely take steps to slow the progression rate of your kidney disease. However, you can also try certain ways to treat your kidney disease based on different stages.
Stage 1
Your GFR will be 90 or above with in this stage with fewer symptoms. Sometimes, there are no symptoms at all. Still, it is possible to identify kidney damage before the GFR begins to drop. The treatment used in this stage,like eating a healthy diet, taking exercise regularly, stopping smoking, will slow the progression of chronic kidney disease and reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
Stage 2
Your GFR will be between 60 and 89 with evident symptoms and some kidney damage. The kidney function will start to decline in this stage. Your doctor will continue with the same treatment of stage 1, like controlling the blood pressure, taking some medications, to reduce to risk of other health issues.
Stage 3
You will notice moderate decrease in GFR, which may still be between 30 and 59. Kidney damage is usually quite noticeable in this stage with other issues, such as bone problems and anemia. Your doctor will suggest medication option and some lifestyle changes to avoid and treat these complications.
Stage 4
Stage 5
Your GFR will be less 15, which will result in kidney failure. In this stage, you will need to a kidney transplant to maintain life.
What Do The Kidneys Do
As a vital part of the excretory system, the kidneys filter the blood and remove the waste and excess fluids resulting from metabolism. They also regulate electrolytes, such as sodium, potassium, calcium, phosphorus, and water in the body. Waste and other excess fluids then become urine, which is flushed out of the body. Maintaining this balance and removing the bodys waste ensures that the nerves, muscles, and other tissues continue to function normally. Aside from these functions, the kidneys also secrete hormones that aid in several essential bodily functions. These include controlling blood pressure, encouraging the production of red blood cells, and strengthening the bones and muscles through calcium absorption. If the kidneys suffer damage or are affected by diseases or illnesses, it can cause adverse effects on their ability to perform these functions.
Recommended Reading: Does Flomax Hurt Your Kidneys
What Is The Life Expectancy For Stage 5 Kidney Failure Without Dialysis
Supportive, or palliative, care is the choice to not pursue treatmentin this instance, specifically dialysis. This course of action, however, will only allow you to maintain your quality of life. It will not help with nor extend your life expectancy.
Without dialysis, the life expectancy for stage 5 kidney failure is not a hard and fast answer, as it varies depending on each kidney patients unique medical history. Generally, life expectancy without dialysis can be anywhere from days to weeks, which depends on:
- Amount of kidney function
What Is Kidney Failure
Healthy kidneys filter the blood, removing waste and excess salt and water. They also help the body to produce red blood cells, control blood pressure, and maintain strong bones. Kidney failure means kidneys are damaged and unable to perform their usual functions. Kidney failure means:
- Kidney function has dropped below 15 percent of normal
- Kidneys are not functioning well enough on their own for a person to survive
There is no cure for kidney failure, but treatment can help people live longer.
Also Check: Can I Take Flomax Twice A Day For Kidney Stones
Relieving Symptoms And Problems Caused By Chronic Kidney Disease
If chronic kidney disease becomes severe you may need treatment to combat various problems caused by the poor kidney function. For example:
- Anaemia may develop which may need treatment with iron or erythropoietin – a hormone normally made by the kidneys.
- Abnormal levels of calcium or phosphate in the blood may need treatment.
- You may be advised about how much fluid to drink, and how much salt to take.
- Other dietary advice may be given which can help to control factors such as the level of calcium and potassium in your body.
If end-stage kidney failure develops, you are likely to need kidney dialysis or a kidney transplant to survive.
People with stage 3 CKD or worse should be immunised against influenza each year, and have a one-off immunisation against pneumococcus. People with stage 4 CKD should be immunised against hepatitis B.
How Is Chronic Kidney Disease Diagnosed
The doctor will take your complete medical history along with your family history, such as if anyone in your family has or had diabetes, whether you are on any medications , and so on. They will perform a thorough physical examination to see if you have any signs or symptoms of CKD.
A few tests will help your doctor confirm the diagnosis of CKD. These are:
- Kidney function tests: This test will look at your creatinine levels to check if you have trouble with your kidney.
- Blood tests: Low hemoglobin levels are found in CKD.
- Urine test: This will be done particularly to check for the presence of protein or persistent protein in the urine, which is a sign of kidney damage. Other things that the doctor will look for include red blood cells and white blood cells .
- Ultrasonography: To check for any cysts or scarring or size of the kidney.
Don’t Miss: Osteocleanse
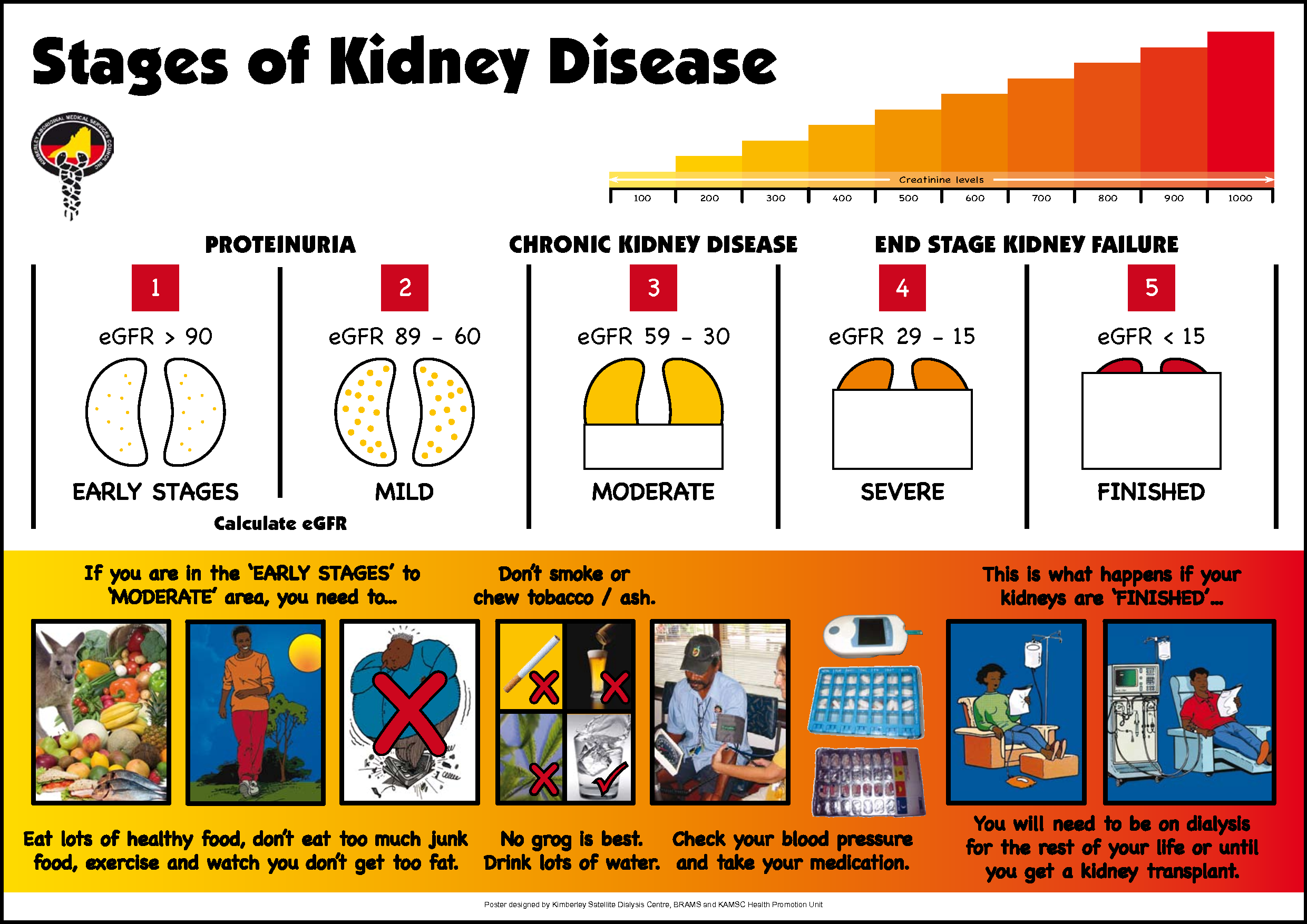
Stages Of Kidney Disease
- Medically reviewed by
Chronic kidney disease is divided into five stages. The stages are based on the eGFR test result and how well your kidneys work to filter waste and extra fluid out of your blood. As the stages go up, kidney disease gets worse and your kidneys work less well. At each stage, it is important to take steps to slow down the damage to your kidneys.
Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate
A normal eGFR is 90 ml/minute/1.73 m or more. If some of the glomeruli do not filter as much as normal then the kidney is said to have reduced or impaired kidney function.
The eGFR test involves a blood test which measures a chemical called creatinine. Creatinine is a breakdown product of muscle. Creatinine is normally cleared from the blood by the kidneys. If your kidneys are not working very well and the glomeruli are not filtering as much blood as normal, the level of creatinine in the blood goes up.
The eGFR is calculated from your age, sex and blood creatinine level. An adjustment to the calculation is needed for people with African-Caribbean origin. See the separate leaflets called Routine Kidney Function Blood Test and Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate .
Don’t Miss: Is Vinegar Good For Your Kidneys
Stage 2 Kidney Disease Dialysis
What Are the CKD Stages? · Stage 1 CKD, mild kidney damage with an eGFR above 90 milliliters or greater per minute · Stage 2, mild damage with 60.
The cost of dialysis consists of many factors.
A person with stage 2 chronic kidney disease has kidney damage with a mild decrease in their glomerular filtration rate of 60-89 ml/min.
Stage 2 kidney disease symptoms darker urine that may range in color between yellow, red, and orange. increased or decreased urination. excessive fatigue. high blood pressure. fluid retention pain in the lower back. muscle cramps at night. insomnia.
The Dialysis Machines Market is expected to grow on an unabashed note in the next decade. With a worldwide shortage of healthcare staff, the healthcare IT solutions comprising web-based staffing.
Kidney infections can cause serious health problems if you don’t get treatment. Learn about common signs of kidney infections and when to see the doctor.
Stage 2 kidney disease means you have an estimated glomerular filtration rate of 60-89 with mild loss of kidney function. At chronic kidney disease.
Our findings demonstrated that RLS is common in Taiwanese dialysis patients. Clinicians should have a high suspicion for the presence of RLS symptoms in patients with ESRD, especially those with type 2 diabetes, anemia, low serum iron status and long duration of dialysis.
At this point, you’ll need dialysis or a kidney transplant. Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center.
Medication To Protect Your Kidneys
- ACE inhibitors and ARBs. If you have high levels of protein in your urine then you may be advised to take medication even if your blood pressure is normal. Two related types of medication have been shown to be beneficial for many people with CKD. This is because they can prevent further worsening of the function of your kidneys. These medicines are called:
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and
- Angiotensin receptor blockers , such as losartan, valsartan, candesartan, telmisartan).
- SGLT2 inhibitors. A group of medicines called the SGLT2 inhibitors were originally used to keep blood sugar under control in type 2 diabetes. However, more recent studies show that some of them can significantly reduce decline in kidney function. These may be recommended whether you have type 2 diabetes or not. The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence has issued new guidance recommending that they should be offered to, or considered for, most people with type 2 diabetes and CKD.
Also Check: Are Grapes Good For Kidney Stones
Being A Living Kidney Donor
If you have two healthy kidneys, you may be able to donate one of your kidneys to enhance or save someone else’s life. Both you and the recipient of your kidney can live with just one healthy kidney.
If you are interested in living kidney donation:
- Contact the transplant center where a transplant candidate is registered.
- You will need to have an evaluation at the transplant center to make sure that you are a good match for the person you want to donate to and that you are healthy enough to donate.
- If you are a match, healthy and willing to donate, you and the recipient can schedule the transplant at a time that works for both of you.
- If you are not a match for the intended recipient, but still want to donate your kidney so that the recipient you know can receive a kidney that is a match, paired kidney exchange may be an option for you.
Another way to donate a kidney while you are alive is to give a kidney to someone you do not necessarily know. This is called living non-directed donation. If you are interested in donating a kidney to someone you do not know, the transplant center might ask you to donate a kidney when you are a match for someone who is waiting for a kidney in your area, or as part of kidney paired donation. You will never be forced to donate.