How Does Stage 3 Kidney Disease Influence Your Life
At stage 3, the kidneys have been moderately damaged however, you can usually continue normal body functions, so it shouldn’t have a massive impact on your life.
Nevertheless, it does need to be taken seriously, as if you do not receive effective and timely treatment, the kidney condition will worsen, and this can severely shorten your life. Patients with stage 3 kidney disease have suffered a moderate GFR reduction to 30-59 ml/min/m2, and a loss of around half the kidney function.
Creatinine Stages And Risks At Each Stage
Creatinine is a metabolic waste product produced by the metabolic activity of the body muscles. Creatinine is the determining factor to detect whether the kidneys are a function or not. The kidney functions to eliminate most of the creatinine out of the body via urine. When the kidneys are working well they efficiently excrete creatinine but high creatinine levels in the blood show chronic kidney disease .
CKD is a kidney disease that gradually shows its symptoms and is classified into 5 stages according to the severity of kidney failure . The kidney function is measured by Glomerular Filtration Rate . A mathematical formula involving the age, gender, race, and serum creatinine levels is used to calculate GFR. Blood tests are thus ordered to detect the stages of CKD.
Glomerular Filtration Rate: Gfr And Egfr
The main function of the kidneys is to clear water-soluble waste products from the blood. The efficiency of clearance is measured using the GFR
- The GFR is a measure of how much blood is cleaned by the kidneys in one minute. By using a blood test to measure creatinine levels we can calculate the estimated GFR, known as eGFR. We do this using a formula that takes body size into account. The average adult body size is 1.73 m2. A normal GFR is around 100 ml/min/1.73m2
- Because the average normal eGFR is 100, the eGFR can be seen as a percentage of normal kidney function. However, values as low as 60 are considered normal if there is no other evidence of kidney disease
- The eGFR is used to calculate the G stage of CKD
- The eGFR calculation can be inaccurate in people who have much more, or much less muscle than average people of their age, sex, and ethnic origin. For instance, it can be falsely low in body builders, and falsely high in people with anorexia nervosa.
Don’t Miss: Is Watermelon Good For Your Kidneys
Understanding Your Lab Values
People who develop chronic kidney disease may have some or all of the following tests and measurements. If you have kidney disease ask your doctor which tests you will have and how often they will be done. Speak to your doctor about your results. If your numbers are not in the normal range, ask how to improve them.
Serum Creatinine: Creatinine is a waste product in your blood that comes from muscle activity. It is normally removed from your blood by your kidneys, but when kidney function slows down, the creatinine level rises. Your doctor should use the results of your serum creatinine test to calculate your GFR.
Glomerular Filtration Rate : Your GFR tells how much kidney function you have. It may be estimated from your blood level of creatinine. If your GFR falls below 30 you will need to see a kidney disease specialist . A GFR below 15 indicates that you need to start a treatment for kidney failure. Your kidney disease specialist will speak to you about treatments for kidney failure, such as dialysis or kidney transplant.
Blood Urea Nitrogen : Urea nitrogen is a normal waste product in your blood that comes from the breakdown of protein from the foods you eat and from your body metabolism. It is normally removed from your blood by your kidneys, but when kidney function slows down, the BUN level rises. BUN can also rise if you eat more protein, and it can fall if you eat less protein.
COVID-19 patients can become kidney patients.
Do I Need Any Further Tests
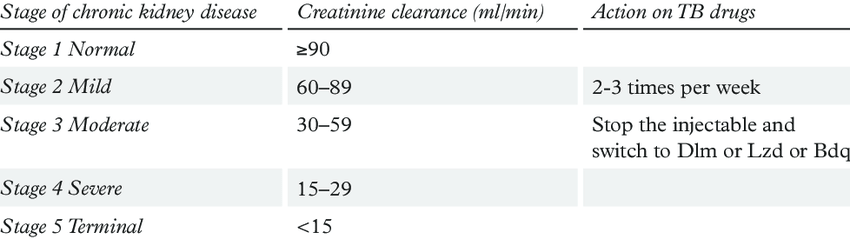
As mentioned, the eGFR test is done to diagnose and monitor the progression and severity of CKD. For example, it should be done routinely at least once a year in people with stages 1 and 2 CKD, and more frequently in those with stage 3, 4 or 5 CKD.
You are likely to have routine urine dipstick tests from time to time to check for blood and protein in the urine. Also, blood tests may be done from time to time to check on your blood level of chemicals such as sodium, potassium, calcium and phosphate. The need for other tests then depends on various factors and your doctor will advise. For example:
- An ultrasound scan of the kidneys or a kidney biopsy may be advised if certain kidney conditions are suspected. For example, if you have a lot of protein or blood in your urine, if you have pain that seems to be coming from a kidney, etc.
- A scan or having a sample taken is not needed in most cases. This is because most people with CKD have a known cause for the impaired kidney function, such as a complication of diabetes, high blood pressure or ageing.
- If the CKD progresses to stage 3 or worse then various other tests may be done. For example, blood tests to check for anaemia and an altered level of parathyroid hormone . PTH is involved in the control of the blood level of calcium and phosphate.
Read Also: What Std Messes With Your Kidneys
Stages Of Kidney Disease
The term chronic kidney disease is used worldwide to mean any form of kidney disease that goes on for more than a few months.
The word ‘chronic’ doesnt necessarily mean ‘serious’ and the word ‘disease’ includes any abnormality of kidney structure or function, whether or not it is likely to cause a person to feel unwell or to develop complications.
Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate
A normal eGFR is 90 ml/minute/1.73 m or more. If some of the glomeruli do not filter as much as normal then the kidney is said to have reduced or impaired kidney function.
The eGFR test involves a blood test which measures a chemical called creatinine. Creatinine is a breakdown product of muscle. Creatinine is normally cleared from the blood by the kidneys. If your kidneys are not working very well and the glomeruli are not filtering as much blood as normal, the level of creatinine in the blood goes up.
The eGFR is calculated from your age, sex and blood creatinine level. An adjustment to the calculation is needed for people with African-Caribbean origin. See the separate leaflets called Routine Kidney Function Blood Test and Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate .
Also Check: Is Celery Juice Good For Kidneys
Securing Hospice Care Services
If you or a loved one is unable to receive treatment for CKD, it may be time to consider hospice care services, as the disease is not fully curable. Reach out to Harbor Light Hospice for more information about CKD or to use Harbor Lights hospice care services for a loved one in the late stages of CKD. The organizations customized hospice care services include the support of nurses, doctors, and mental and spiritual health counselors, who provide comprehensive care for patients and their loved ones as the patient nears the end of their life.
What Is Creatinine And Why Does It Matter
Creatinine is a waste product of the body and is produced mainly through muscle activity. Its normal for everyone to have some creatinine present in their blood. But it cant just stay there.Like other waste products, the creatinine in your bloodstream has to be removed. This is a job for your kidneys: they filter creatinine out from your blood and excrete it from the body in urine.By measuring the amount of creatinine found in someones body, doctors can get an idea of how well their kidneys are functioning. The special thing about creatinine is that it is produced at a constant rate, and filtered almost freely by the kidneys. This means that the creatinine in your body is at an equilibrium. When the kidneys are damaged, they filter waste materials less efficiently. This means the amount of creatinine in the blood usually increases.Think of it this way. When you run the tap of a kitchen sink without plugging the drain, a small layer of water will collect. But the sink will not flow over. However, when you partially plug the drain, the water level will rise. It will continue to rise until a new, higher equilibrium is reached. Your muscles are like the tap, the kidneys are like the drain and the creatinine levels in your blood are like the water. If your kidneys become damaged, the creatinine starts to increase.
You May Like: Lithobalance
Impact Of Stage 3 Kidney Disease On Your Health
Depending on how far your kidney disease has progressed, you will fit into one of the five stages of kidney disease. These stages are measured by your glomerular filtration rate or your GFR. Having stage 3 kidney disease means that you will have a GFR between 30 and 59.
Most people who have stage 3 kidney disease will not have any symptoms. However, if you do, it can manifest as swelling in your hands or feet, back pain, or irregular urination patterns.
The more impactful symptoms of kidney disease stage 3 are the health implications of your decreased kidney functioning such as high blood pressure, anemia, and bone disease.
Ultimately, if stage 3 kidney disease goes untreated or progresses further, you will enter into stage 4 kidney disease. Stage 4 kidney disease is severe, as are its symptoms. It is also the last stage of kidney disease before kidney failure at this point, you will need to talk to your doctor to prepare for kidney failure. â
If your kidneys fail, you will either need to have dialysis or a kidney transplant. Dialysis is a treatment that will clean your blood. You will need to think about which kind of dialysis you will want, as there are different types available. The other option, a kidney transplant, is when you find a donor who gives you a healthy kidney from their body. If you get a transplant, you will not need to do dialysis.
Control Other Health Problems
You may have other disorders, such as diabetes and high blood pressure, which can damage your kidneys. One of the goals of your treatment is to make sure these are well-controlled. Ask your healthcare professional what you can do to keep these conditions under control – and do it! Some of the things your healthcare professional may ask you to do:
- Take medications called angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers as part of your therapy. Studies have shown that these medications help to protect your kidney function. You may also need other blood pressure medications to control your blood pressure.
- Lose weight if you are overweight
- Cut down on salt in your diet to control blood pressure
- If you have diabetes, monitor your blood sugar, follow your diet and take your medications as prescribed
Don’t Miss: Is Seltzer Water Bad For Your Kidneys
What Does It Mean When A Cat Has Elevated Creatinine Levels
Diagnosing Creatinine Levels. If the creatinine levels are more than 2.5 mg per dl, this means that the cat has elevated creatinine levels and this can point to a kidney problem. This means that the kidneys are not able to filter the creatinine as they should and this will result in a high level of toxins in the cats body.
Anemia Parameters And Use Of Esa And Iron
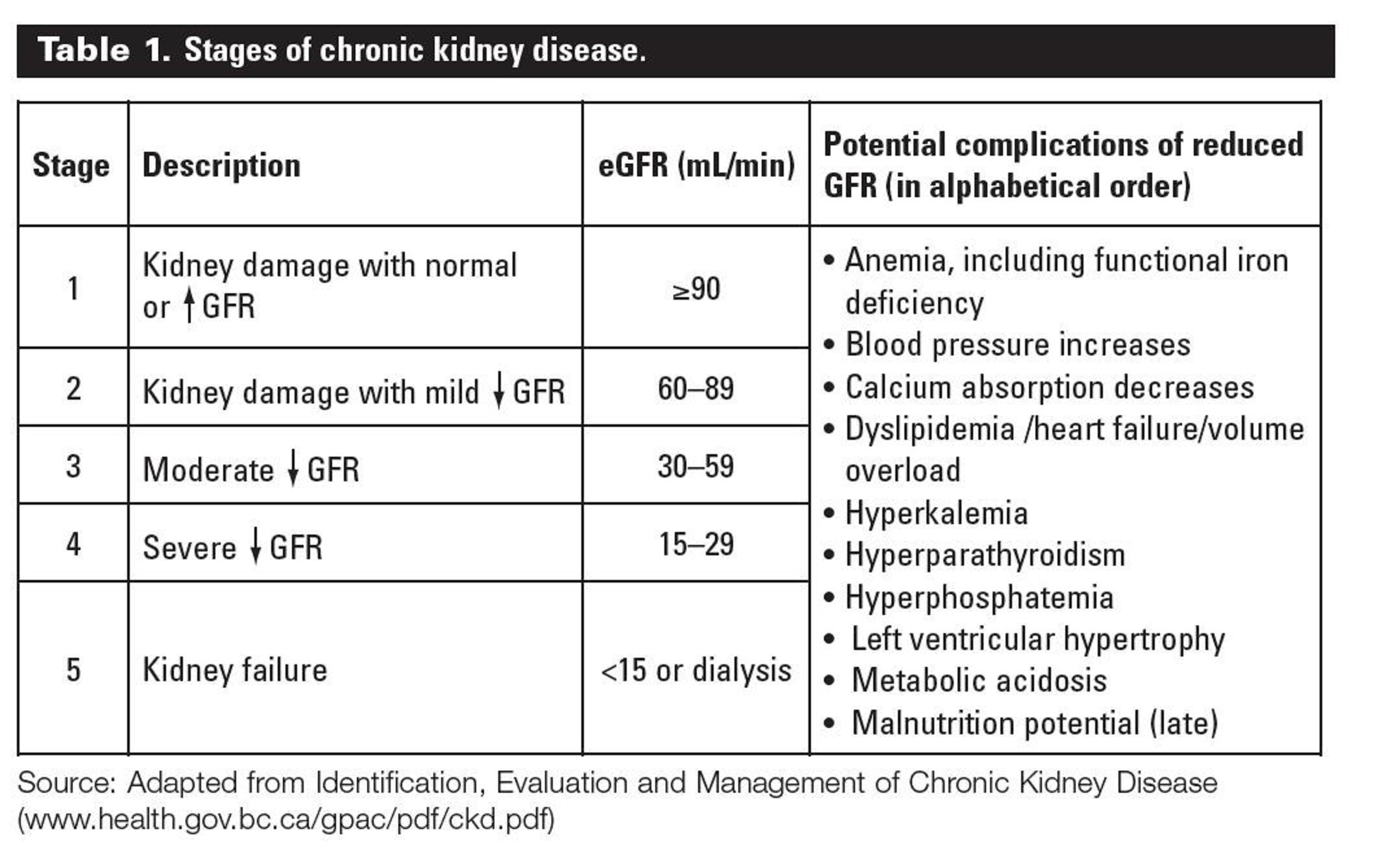
According to the K-DOQI and the European Best Practices Guidelines , anemia was present in 51.3% and 30.5% of the total subjects, respectively. The mean hemoglobin for the cohort as a whole was 12.8 g/dL and the majority of patients had hemoglobin greater than 11 g/dL . The percentage of patients with severe anemia was 1.6% and the percentage of patients with hemoglobin between 9 and 11 g/dL was 11.5%. About 25% of the total cohort was receiving ESA and the mean hemoglobin in this group while receiving this therapy was 12 ± 1.5 g/dL and the range was wide . The mean ferritin level was 150 ng/mL and the percentage of patients with transferrin saturation < 20% was 26.3%. The percentage of patients on oral and IV iron supplementation were 31.9% and 3.0%, respectively.
Table 5 Anemia parameters and the use of ESA and iron
The mean hemoglobin was significantly lower in stage 4 when compared to stage 3 CKD patients . The percentage of patients with hemoglobin greater than 11 g/dL was significantly higher in stage 3 than stage 4 CKD patients . Conversely, the percentage of patients with hemoglobin < 9 g/dL was significantly lower in stage 3 than stage 4 CKD patients . No significant differences were noted in the percentage of patients with hemoglobin between 9 and 11 g/dL between CKD stage 3 and 4 patients .
Figure 3
Percentage of CKD stage 3 and 4 patients with hemoglobin less than 11 as a function of GFR.
Don’t Miss: Renal Diet Orange Juice
Indications For Nephrology Referral
Nephrology consultation is indicated when the estimated GFR is less than 30 mL per minute per 1.73 m2, or earlier if necessary .9,15 Partnership between primary care physicians and nephrologists is key to successful CKD management. The National Kidney Foundation’s suggested multidisciplinary clinical action plan for CKD is available at http://www.kidney.org/professionals/KDOQI/cap.cfm.
Acute, complex, or severe cardiovascular disease
|
Anemia of CKD |
|
Bone and mineral disorder of CKD |
|
Difficult to manage adverse effects of medications |
|
Hyperkalemia |
|
Refractory proteinuria |
|
Resistant hypertension |
|
Stage 4 CKD |
|
Unexplained decrease in estimated GFR > 30 percent over four months |
CKD = chronic kidney disease GFR = glomerular filtration rate.
Information from references 9 and 15.
Acute, complex, or severe cardiovascular disease
|
Anemia of CKD |
|
Bone and mineral disorder of CKD |
|
Difficult to manage adverse effects of medications |
|
Hyperkalemia |
|
Refractory proteinuria |
|
Resistant hypertension |
|
Stage 4 CKD |
|
Unexplained decrease in estimated GFR > 30 percent over four months |
CKD = chronic kidney disease GFR = glomerular filtration rate.
Information from references 9 and 15.
Read the full article.
- Get immediate access, anytime, anywhere.
- Choose a single article, issue, or full-access subscription.
- Earn up to 6 CME credits per issue.
What Is The Average Creatinine Level In Stage 3 Kidney Disease
In stage 3 kidney disease, patients kidneys are functioning at 30%-59%, so creatinine level rises obviously. In clinic, serum creatinine is a reliable indicator for kidney function level. Here, you may want to know: what is the average creatinine level in stage 3 kidney disease.
Creatinine level and kidney disease stages
Although it is not so exact to divide stages of kidney disease through creatinine, creatinine level indeed can reflect patients illness condition. Here, you can get the average creatinine level in stage 3 chronic kidney disease and other stages:
Stage 1: Normal creatinine level, GFR 90 or more
Stage 2: Creatinine level less than 2mg/dl, GFR 60-89
Stage 3: Creatinine level 2-5mg/dl, GFR 30-59
Stage 4: Creatinine level 5-8mg/dl, GFR 15-29
Stage 5: Creatinine level more than 8mg/dl, GFR less than 15.
Once kidney disease patients creatinine level is higher than the normal, usually doctors prescribe some medications such as diuretic and ketosteril to lower their creatinine. In this case, their creatinine level may be not in accord with the above values. Besides, age, gender, weight, the extent of exercise, female, diet, etc, may also affect creatinine level.
No matter whether your creatinine level is higher or lower than the average value, the most urgent thing you need to do is to reduce your elevated creatinine level.
What should you do?
Several treatment tips can help you solve this problem from the root.
Recommended Reading: Red Wine And Kidney Stones
What Is Chronic Kidney Disease
Chronic kidney disease means that your kidneys are diseased or damaged in some way, or are ageing. As a result, your kidneys may not work as well as they used to. A range of conditions can cause CKD .
Chronic means ongoing, persistent and long-term. It does not mean severe as some people think. You can have a mild chronic disease. Many people have mild CKD.
CKD used to be called chronic renal failure but CKD is a better term, as the word failure implies that the kidneys have totally stopped working. In most cases of CKD this is not so. In most people who have CKD there is only a mild or moderate reduction in kidney function, which usually does not cause symptoms, and the kidneys have not ‘failed’.
Acute kidney injury occurs when the function of the kidneys is rapidly affected – over hours or days. For example, the kidneys may go into AKI if you have a serious blood infection which can affect the kidneys. This is in contrast to CKD where the decline in function of the kidneys is very gradual – over months or years. See the separate leaflet called Acute Kidney Injury.
For more information, see the separate leaflet called What do kidneys do?
Chronic Kidney Disease
Treatment Of Kidney Disease Stage 3
Once you are diagnosed with stage 3 kidney disease, there is no way to treat the damage that has already been done to your kidneys. The following steps for your treatment have to do with treating the issues caused by decreased kidney functioning and preventing further damage.
These treatments include:
You May Like: How Long For Flomax To Work For Kidney Stones