Inclusion And Exclusion Criteria
Discharged AKI cases from between January 1, 2019 and December 31, 2019 from the inpatient database were screened, and a retrospective review of the patients medical records was carried out. The inclusion criteria were as follows: a confirmed diagnosis of AKI, which was defined as any of the following criteria: increase in serum creatinine by 0.3 mg/dL within 48 hours or increase in serum creatinine of 1.5 times from baseline which is known or presumed to have occurred within the 7 days prior US was performed after AKI onset an intervention to relieve the obstruction was not performed before US evaluation and serum creatinine levels had not recovered before US evaluation. Patients aged < 18 years or those who were pregnant or 6 weeks postpartum were excluded.
After the AKI cases were screened, the healthy controls were randomly selected by matching sex and age at a ratio of 2:1 with those in the AKI group. The inclusion criteria of the control group were as follows: sex and age matched with the AKI group renal US kidney evaluation was performed at the hospital between January 1, 2019 and December 31, 2019
Why Texas Childrens Fetal Center
- A single location for expert maternal, fetal and pediatric care. At Texas Childrens Hospital, mother and baby receive the specialized care required for fetal echogenic kidneys and congenital kidney conditions all in one location, including the highest level NICU, if needed.
- A skilled, experienced team with proven outcomes. We have a dedicated team of maternal-fetal medicine specialists, fetal imaging experts, genetic counselors, neonatologists, and pediatric nephrologists and urologists who work in concert to care for you and your baby every step of the way, using proven protocols weve developed over the years. With their combined expertise and unified approach, this team offers the best possible care for pregnancies involving echogenic kidneys.
- We care for your childs needs at every stage of life. Our comprehensive approach starts with your first prenatal visit and continues through delivery, postnatal care, and childhood, thanks to one of the nations leading teams of fetal and pediatric specialists.
What Is Increased Pancreatic Echogenicityglands Causes Symptoms And Treatment Methods
- What is the echogenicity of the pancreas in normal andpathology?
- What caused the local echogenicity of the pancreasglands?
- Increased echogenicity of the pancreas.Treatment
Increased echogenicity of the pancreas: what is it? UnderThis concept refers to diffuse changes in the tissues of an organ,which are fixed by ultrasound.
Also Check: How Often Do People Get Kidney Stones
Case Reporttransient Hyperechoic Renal Cortex Caused By Dehydration And Induced Acute Renal Failure In Two Patients With Intra
Increased renal cortical echogenicity can be seen in patients with various underlying renal abnormalities. However, there are no reports of hyperechoic cortex associated with volume depletion until now. Here, we describe two cases of hyperechoic cortex caused by severe dehydration due to liver abscess and acute salmonellosis which lead to nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. After administering large amounts of fluid supplements, the renal functions dramatically recovered and the echogenicity of the renal cortex returned to normal. Redistribution of renal blood flow and cortical ischemia may play a role in changes in echogenicity that occur in the renal cortex. Additionally, studies on increased renal cortical echogenicity and dehydration are reviewed.
- Previous article in issue
Comparison Of Renal Size Parenchymal Thickness And Renal Volume Between The Aki Group And Control Group
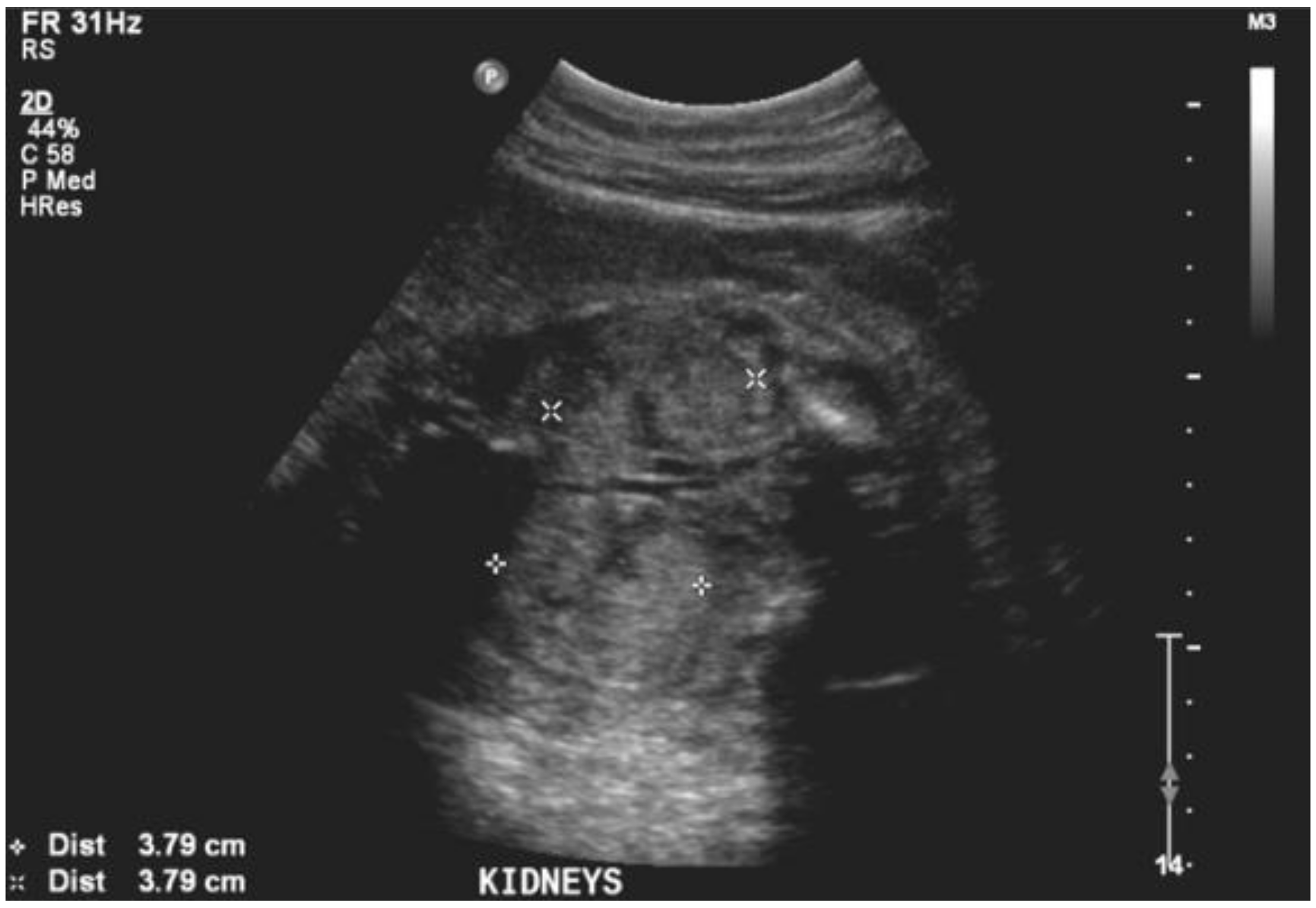
Table 2Full table
In both the AKI and control groups, the right kidney was slightly smaller in size than the left kidney. Kidney length, width, thickness, and volume in the AKI group were greater than those in the control group . In the AKI group, the volume of the left kidney was 146.36 cm3, while the volume of the right was 141.48 cm3. The AKI group also had a thicker renal parenchyma than the control group, but the difference was significant in the right kidney. Figure 6 indicated an enlarged kidney and volume increase in AKI.
Figure 6
Also Check: Does Seltzer Water Cause Kidney Stones
Also Check: Can Diabetes Cause Kidney Stones
Ultrasonography In Acute Kidney Injury
Andrew A. Moses, MD MA Hilda E. Fernandez, MD
Division of Nephrology, Department of Medicine, Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons, Columbia University, New York, NY
DOI:
Introduction
Table 1. Stages of AKI as defined by KDIGO.
| Stage of AKI | ||
| < 0.5mL/kg/h for 12 hours | ||
| 3 | 3.0 times baseline OR Increase in serum creatinine to 4.0 mg/dL OR initiation of kidney replacement therapy OR in patients < 18 years, decrease in GFR to < 35 mL/min per 1.73 m2 | < 0.3 mL/kg/h for 24 hours OR Anuria for 12 hours |
Kidney Imaging
Ultrasonography can also assist in distinguishing AKI from chronic kidney disease . Often in CKD, the kidney length decreases, and severe CKD can be characterized by a combined kidney length of < 20 cm . Changes in kidney size can also be indicators of other types of chronic disease. Enlargements in kidney size can be associated with deposition-type diseases, most notably amyloidosis, diabetes, lymphomatous invasion, and HIV . In patients with amyloidosis and lymphoma with established kidney disease, changes in size help monitor the progression of disease or treatment response. Early in the progress of these diseases, there is deposition and swelling, but afterward, the kidney shrinks as in other progressive causes of CKD .
Table 2. Summary of ultrasound findings in kidney insufficiency.
| Kidney Insufficiency | |
| Only seen in severe ischemic states | Treatment of underlying shock, poor prognosis |
Pre-renal AKI
Post-renal AKI
Clinical And Laboratory Data
Laboratory data about renal function, 24h-urine protein excretion rate, and serum albumin were collected from patients on the three days before and between three and six months after the renal biopsy was performed. Patients were considered as having irreversible advanced CKD if they had: eGFR less than 30mL/min/1.73m2 at renal biopsy which was maintained after a six-months follow-up. Patients with eGFR less than 30 mL/min/1.73m2 at renal biopsy, but not at 6 months of follow-up were considered as having AKI or acute-on-CKD. Patients with an eGFR higher than 40 mL/min/1.73m2 at renal biopsy and less than 30mL/min/1.73m2 after three to six months were considered as rapid progression and not as irreversible advanced CKD. Patients in whom it was not possible to perform this evaluation due to unavailable data about renal function were excluded. Estimated glomerular filtration rate was calculated using CKD-EPI equation .
4.7/5renal pyramidsrenalechogenicseen here
Echogenicity, therefore, refers to how bright or dark something appears in the gray-scale image the brighter something appears, the more echogenic it is. With regard to the kidney, echogenicity generally refers to how bright or dark the kidney parenchyma appears in comparison to the liver.
Just so, is echogenic kidneys normal?
What is the meaning of increased echogenicity?
Don’t Miss: What Does Chronic Kidney Disease Mean
Symptoms Of Enlarged Kidney
Pain: In the context of having an enlarged kidney, pain can present in the form of burning or pain during urination. It can signify a urinary tract infection, which can be a precursor of an enlarged kidney. Pain is usually localized near the pelvis, over the bladder, or near the lower part of the abdomen. Women will generally feel pain near the opening of the vagina, while men will feel pain at the end of the urethra. Pain may also travel or radiate to the lower back. As the outer covering of the kidney swells, it can lead affected patient to feel nausea and vomiting. Kidney enlargement due to kidney stones can cause severe pain that may last from 20 to 30 minutes.
Swelling: Generally found in the legs of the affected patient and is caused by fluids not being able to pass properly through the diseased kidney. Instead, fluid accumulates and pools in the extremities, like in the legs, making them look puffy or swollen. Swelling may also be seen in the ankles, abdomen, lower back, and face. Swelling found in the legs may also be a sign of heart failure.
What Is The Best Treatment For Nephrotic Syndrome
Nephritic syndrome is a condition where there is swelling present over the hands, feet, face, and abdomen. This is associated with the release of high amounts of protein in urine along with increased levels of cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood. It occurs as a result of damage to the glomeruli of the kidneys that filter the toxins and waste from the body. As a result, healthy proteins from the blood leak into urine and toxins are not fully filtered out from the body. It also leads to the retention of excess water taking place in the body tissues.
Recommended Reading: Do Kidney Stones Cause Headaches
What Causes An Enlarged Kidney
Hydronephrosis: This is the blockage of urine flow, leading to kidney distension. The condition can be caused by a kidney stone, blood clot, prostate enlargement, fecal impaction, injury, infection, radiation, or even a tumor. Pregnant women may also develop hydronephrosis, as an enlarged uterus can create pressure leading to a blockage of urinary output. Symptoms of this condition include excruciating, intermittent flank pain, with chronic forms of hydronephrosis possibly not exhibiting any symptoms at all. Treatment often involves relieving the source of the blockage.
Polycystic kidney disease: A disorder that is characterized by clusters of fluid-filled sacs called cysts within the kidney. Cysts may also be found elsewhere in the body. Complications of polycystic kidney disease include high blood pressure, pain, urinary tract infections, liver cysts, and kidney failure due to progressive function loss. Treatment of this disorder often involves managing the complications.
Pyelonephritis: An infection of the kidneys that originally stems from a bladder infection or from an infection originating in the blood. Diabetics, pregnant women, and immunocompromised individuals are considered high risk. Signs and symptoms may include enlarged kidneys, tenderness on one or both sides of the lower back, chills, fever, painful and frequent urination, foul-smelling urine, cloudy urine, and spasms causing intense pain. Treatment involves the use of antibiotics to eradicate the infection
When Pancreas Echogenicity Is Rising
Increased susceptibility to ultrasound are suchpancreas diseases:
Article in the topic: Symptoms of pancreatitis in men. How to recognizepancreatic disease
Hyperechoic inclusions in the gland may be temporaryphenomena. The gland echogenicity may be increased for some time.due to such reasons:
You May Like: What Are The Filtering Units Of The Kidney Called
What Is Pancreas Echogenicity
The term echogenicity means the ability of the tissues of an organ to reflectfrom yourself an ultrasound. This ability depends largely ondensity of an organ to which ultrasound is directed.The result of the study is displayed on the monitor of the device in the formPictures with different shades of gray.
The echo density of each organ is different. It is homogeneous andheterogeneous. The denser the body in its structure, the brighter itshade of gray on the ultrasound screen. Ehonegativnost characteristic ofliquids. They are not able to reflect the high frequency sound, they are hispass through themselves. Those pathological formations thatcontain fluid , in medicine they are called anechoic.The concept of anechogenicity refers not only to pathologicalstructures, but also to healthy organs: the gall bladder, heart,ventricles of the brain, intestines, bladder.
to content
What Is The Significance Of Increased Renal Echogenicity On Ultrasound
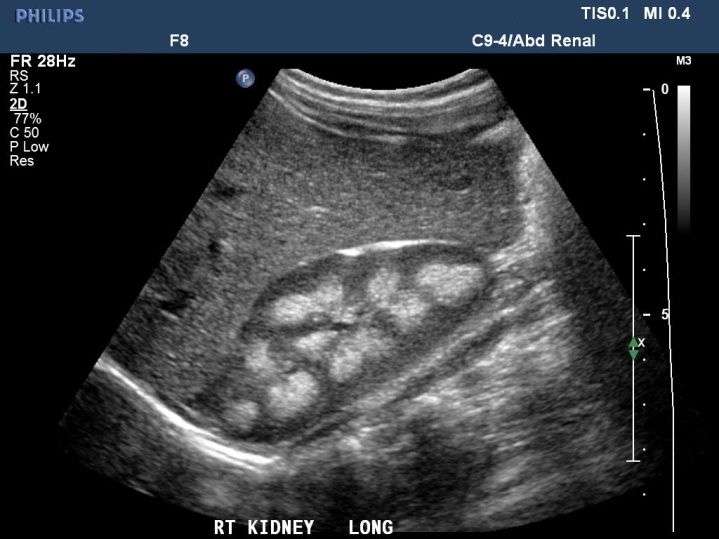
When the right kidney is more echogenic than the normal liver and the left kidney is isoechoic or more echogenic than the normal spleen, the kidneys can be characterized as being abnormally echogenic.
Increased renal echogenicity is an indication of parenchymal disease but is nonspecific for the type of parenchymal disease, which may include acute or chronic glomerulonephritis, acute interstitial nephritis, diabetes mellitus, systemic lupus erythematosus, HIV nephropathy, and amyloidosis.
Percutaneous renal biopsy is therefore frequently required for a definitive diagnosis.
Recommended Reading: Is Tea Good Or Bad For Your Kidneys
You May Like: What To Do If Kidneys Hurt
Stage 1 Of Chronic Kidney Disease
A person with stage 1 chronic kidney disease has kidney damage with a glomerular filtration rate at a normal or high level greater than 90 ml/min. There are usually no symptoms to indicate the kidneys are damaged. Because kidneys do a good job even when theyre not functioning at 100 percent, most people will not know they have stage 1 CKD. If they do find out theyre in stage 1, its usually because they were being tested for another condition such as diabetes or high blood pressure .
Symptoms of stage 1 kidney disease
Other ways a person may discover they are in stage 1 CKD include:
- Higher than normal levels of creatinine or urea in the blood
- Blood or protein in the urine
- Evidence of kidney damage in an MRI, CT scan, ultrasound or contrast X-ray
- A family history of polycystic kidney disease
Treating stage 1 kidney disease
Regular testing for protein in the urine and serum creatinine can show whether the kidney damage is progressing. Living a healthy lifestyle can help slow the progression of kidney disease. It is recommended that people in stage 1 CKD:
Living with stage 1 kidney disease
Liver Mass Detection And Characterization
Echogenicity is the dominant factor determining lesion conspicuity on ultrasound. Markedly hypoechoic or hyperechoic lesions may be readily detected and characterized by ultrasound, even when small . Larger masses that have echogenicity similar to adjacent liver may be more difficult to appreciate. Lesion size and body habitus are significant factors that influence lesion detection . On gray scale ultrasound, liver masses are differentiated by internal architecture and are described as cystic, hypoechoic, or hyperechoic relative to the liver. The majority of cystic masses are benign . Hypoechogenicity is a feature of many malignancies. Hyperechoic masses include both benign etiologies, such as hemangioma or focal fat, as well as malignant hepatic neoplasms, such as hepatocellular carcinoma and metastases.
Read Also: Can Kidney Stones Cause Bloating
Pediatric Series: Kidney Echogenicity In Children: Clinical Correlation Required
Ultrasonography of the kidneys is one of the most common imaging modalities performed in children in the nephrology clinic. The routine use of prenatal ultrasound in pregnancy care has additionally provided nephrologists with a view into the kidneys and urinary tract as they develop in utero, allowing both families and care teams to prepare for complications related to the kidney that may arise after birth. Increased echogenicity of the kidneys, while non-specific, is one of the most common imaging findings on kidney ultrasound it may be a transient finding, or a harbinger of serious kidney disease that warrants evaluation by a pediatric nephrologist.
The echogenicity of a kidney, or any organ for that matter, refers to how bright it appears on grayscale imaging by ultrasound. These images are produced when the ultrasound machine operates in two-dimensional brightness mode , in which reflected echoes appear as bright dots. Tissue that most strongly reflects sound waves is hyperechoic and appears white , whereas fluid, such as from simple cysts or urine in the collecting system, reflects the weakest and appears black in color. Traditionally, the brightness of the kidneys on ultrasound has been described in relation to that of the liver, which has intermediate echogenicity, and is used as an internal comparison .
- Determine whether the echogenicity is patchy or diffuse
- Its location within the kidney
- Is it primarily cortical
Post by
What Is Kidney Failure
The kidneys are designed to maintain proper fluid balance in the body, remove waste and eliminate toxins from the blood. The kidneys make urine, which carries away those products of elimination and excess fluid. They also make hormones, which stimulate the making of red blood cells in the bone marrow and strengthen the bones. The term kidney failure describes a situation in which the kidneys have lost the ability to effectively carry out these functions. A build-up of waste levels can cause a chemical imbalance in the blood, which can be fatal if left untreated. Patients with renal failure may develop a low blood count or weak bones over time. Chronic renal failure can be caused by a variety of diseases and means failure of kidney function over time.
Other conditions can result in acute kidney failure, such as a drop in blood flow to the kidneys, blockage of urine flow, or damage from infections, certain medications or contrast materials used in imaging. Acute kidney failure can occur quickly and may leave the kidneys with permanent damage. In many cases, it occurs in patients who are already critically ill and require intensive care.
Symptoms may include:
You May Like: How Do You Treat Low Kidney Function
Lose Weight If Needed
A higher body mass index increases the likelihood that you will have fatty deposits in your liver. When you lose weight, you also lose fat content in your liver. You can encourage weight loss by cutting back on portion sizes, increasing your physical activity, and eating whole foods instead of packaged and processed foods.