Functions: Circulation Of Oxygen Nutrients Hormones Ions And Fluids Removal Of Metabolic Waste
The cardiovascular system includes the heart, blood vessels and blood. All these are involved in essential functions of the body such as circulation of oxygen, nutrients, hormones, fluids and ions to the cells. It also removes the metabolic wastes and oxygen from the cells. Major loss of blood, called hemorrhage, is life-threatening.
The cardiovascular system helps in the transport of the oxygen from the alveoli in the lungs to the heart as it is carried in the blood. The heart then pumps the oxygenated blood to respiring cells around the body. In exchange, carbon dioxide moves from the body to the alveoli for removal via blood. This transport is done by the hemoglobin present in the red blood cells.
The nutrients are absorbed in the blood circulation from the small intestine. They are transported to different cells of the body for use in the production of the energy and other necessary molecules.
Hormones are released from the endocrine glands into the blood, and they move in the blood to reach their target cells, tissues or organs. For example, insulin is released from the pancreas and is moved around the body affecting all cells.
Fluids, ions and waste travel in the blood and reach the kidney. They help to regulate the amount of material and water excreted in the urine. For example, the waste product urea moves through the blood to reach the kidney for excretion in the urine.
Practice Questions
How Can I Keep My Urinary System Healthy
You cant prevent most urinary tract problems. But you can try to keep your urinary system healthy with proper hygiene and a healthy lifestyle. To help your urinary system work the way it should, you can:
- Drink plenty of water: Staying hydrated will flush out your system and can help you prevent kidney stones and UTIs. You can try drinking cranberry juice to ward off a UTI. Compounds in cranberries may stop bacteria from growing.
- Eat a healthy diet: Low sodium, high-calcium foods may prevent kidney stones.
- Wipe the right way: Women should always wipe front to back after using the toilet. Proper wiping reduces the risk of bacteria getting into the vagina and causing a UTI.
- Empty your bladder after sex: If youre a woman, you should use the bathroom after having sex. Peeing promptly can clear out bacteria and reduce your risk of a UTI.
- Practice safe sex: Protect yourself from an STI with a condom. But be careful with spermicides because they can cause bacteria to flourish.
- Do pelvic floor exercises: Also called Kegel exercises, these can reduce your risk of urinary incontinence by strengthening the muscles in your pelvic floor.
The Wastes Of The Body
Waste Materials.The chemical changes in the body have been compared to what goes on in a furnace, where coal is burned and heat is given off to warm a house or to run an engine. As a result of the burning of fuel in the furnace, certain waste materials are formedunburned clinkers, ash, and gases. The clinkers and ash drop into the ash pan and are removed the gases pass off by way of the chimney. So in our bodies, as a result of the oxidation or burning of the food, waste products are formed. The carbohydrates and fats become carbon dioxide and water. The proteins change into other waste products, such as urea. The in-digestible remainder which cannot be taken into the body is left in the intestines, somewhat as the clinkers are left in the ash pan.
Wastes from the Intestines.Most of the material which is discharged from the intestines has never really been made a part of the living body. You remember that the alimentary canal runs from the mouth to the lower opening of the large intestine. As the food passes through the alimentary canal, the usable parts which the body needs are absorbed through the walls into the blood stream, and the indigestible material remains finally in the large intestine, from which it must be discharged.
The Process of Excretion.The real wastes of the body are the substances formed by the life processes in the cells.
QUESTIONS FOR DISCUSSION AND REVIEW
3. What are the organs of excretion by which the wastes are removed from the blood?
Read Also: How Much Money Is A Kidney Worth
What Are Some Of The Causes Of Chronic Kidney Disease
Chronic kidney disease is defined as having some type of kidney abnormality, or “marker”, such as protein in the urine and having decreased kidney function for three months or longer.
There are many causes of chronic kidney disease. The kidneys may be affected by diseases such as diabetes and high blood pressure. Some kidney conditions are inherited .
Others are congenital that is, individuals may be born with an abnormality that can affect their kidneys. The following are some of the most common types and causes of kidney damage.
Diabetes is a disease in which your body does not make enough insulin or cannot use normal amounts of insulin properly. This results in a high blood sugar level, which can cause problems in many parts of your body. Diabetes is the leading cause of kidney disease.
High blood pressure is another common cause of kidney disease and other complications such as heart attacks and strokes. High blood pressure occurs when the force of blood against your artery walls increases. When high blood pressure is controlled, the risk of complications such as chronic kidney disease is decreased.
Glomerulonephritis is a disease that causes inflammation of the kidney’s tiny filtering units called the glomeruli. Glomerulonephritis may happen suddenly, for example, after a strep throat, and the individual may get well again.However, the disease may develop slowly over several years and it may cause progressive loss of kidney function.
How Do My Kidneys Work
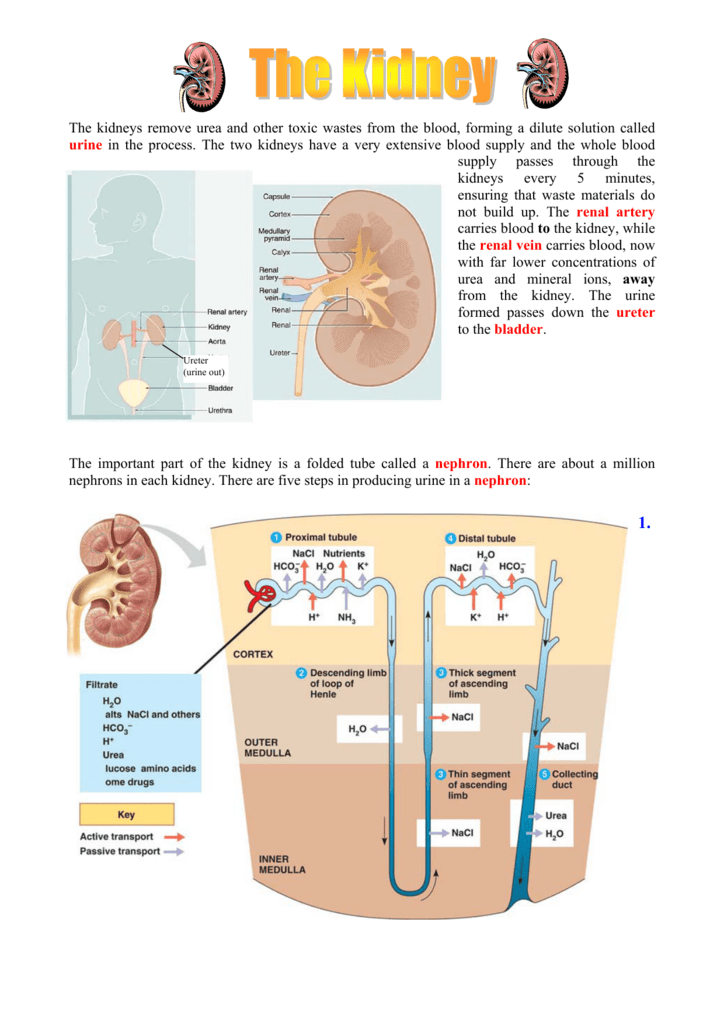
Each of your kidneys is made up of about a million filtering units called nephrons. Each nephron includes a filter, called the glomerulus, and a tubule. The nephrons work through a two-step process: the glomerulus filters your blood, and the tubule returns needed substances to your blood and removes wastes.
Read Also: Is Honey Good For Kidney Health
What Clinical Trials Are Open
Clinical trials that are currently open and are recruiting can be viewed at www.ClinicalTrials.gov.
This content is provided as a service of the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, part of the National Institutes of Health. The NIDDK translates and disseminates research findings to increase knowledge and understanding about health and disease among patients, health professionals, and the public. Content produced by the NIDDK is carefully reviewed by NIDDK scientists and other experts.
How Does The Urinary System Clean My Blood
Your kidneys are an essential part of filtering your blood. Heres how the urinary system works:
Don’t Miss: Is Seltzer Water Bad For Your Kidneys
Key Points On Human Excretory System
- Human excretory system includes organs that facilitate the removal of nitrogenous wastes from the body.
- The main excretory organs include kidney, ureter, urinary bladder and urethra.
- Kidneys filter the blood and urine is the filtrate obtained.
- Urine passes to the urinary bladder via ureter and is expelled out of the body. This is known as micturition.
- Kidneys also regulate the osmotic pressure of a mammals blood through excessive purification and filtration. This is known as osmoregulation.
This was a detailed analysis of the human excretory system.
For more information on Human Excretory System, organs involved, mechanisms and diagrams, keep visiting BYJUS website or download BYJUS app for further reference.
Disorders Of The Excretory System
- Malfunctioning of kidneys can lead to accumulation of urea in blood, a condition called uremia, which is highly harmful and may lead to kidney failure. In such patients, urea can be removed by a process called hemodialysis.
- Blood drained from a convenient artery is pumped into a dialyzing unit after adding an anticoagulant like heparin. The unit contains a coiled cellophane tube surrounded by a fluid having the same composition as that of plasma except the nitrogenous wastes.
- The porous cellophane membrane of the tube allows the passage of molecules based on concentration gradient. As nitrogenous wastes are absent in the dialyzing fluid, these substances freely move out, thereby clearing the blood.
- The cleared blood is pumped back to the body through a vein after adding anti-heparin to it. This method is a boon for thousands of uremic patients all over the world.
- Kidney transplantation is the ultimate method in the correction of acute renal failures . A functioning kidney is used in transplantation from a donor, preferably a close relative, to minimise its chances of rejection by the immune system of the host. Modern clinical procedures have increased the success rate of such a complicated technique.
- Renal calculi: Stone or insoluble mass of crystallised salts formed within the kidney.
- Glomerulonephritis: Inflammation of glomeruli of kidney.
Recommended Reading: Pomegranate Kidney Stones
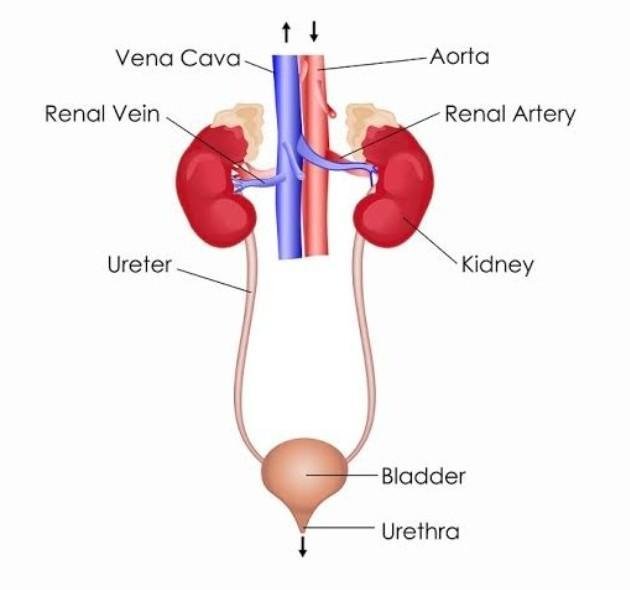
How Do Kidneys Work:
As blood flows through the body it picks up waste and carries this to the kidneys using the kidney arteries. The waste in your blood comes from the normal breakdown of active tissues and from the food you eat. Your body uses food for energy and selfrepair. After the body has taken what it needs, from the food, the waste is sent to the blood. The kidneys filter out the waste products and excess fluids from the body and dispose of them in the form of urine, via the bladder. The clean blood flows back to the other parts of the body. If your kidneys did not remove this waste, it would build up in the blood and cause damage to your body.
The actual filtering occurs in tiny units inside your kidneys called nephrons. Each kidney contains about a million nephrons. In the nephron, a glomerulus intertwines with a urine collecting tube called tubules. A complicated chemical exchange takes place, as waste materials and water in your blood enter your urinary system.
In addition to removing waste, the kidneys have other important functions. These are carried outwith the help of three hormones, which are released in the kidneys.
What Happens During A Kidney Urine Test
You complete 24-hour urine tests at home. For a 24-hour urine test, your provider will give you a container to collect urine. On the day of the test:
Don’t Miss: Can Seltzer Water Cause Kidney Stones
The Heart Receives And Transforms Vitiated Blood
Cardiac veins
Vessels that remove metabolic wastes and deoxygenated blood away from the heart and usually do not collect occlusive material blocking blood flow.
-
The great cardiac vein: main tributary of the coronary sinus. Moves blood away from the anterior aspect of the heart and runs with the LAD.
-
The middle cardiac vein: accompanies the posterior interventricular vein. Moves blood from the posterior interventricular septum, the posterior wall of the left and right ventricles.
-
The small cardiac vein: accompanies the AM. Removes blood from the right ventricle into the right atrium.
-
The left posterior vein: one of the main tributaries of the coronary sinus. Moves blood away from the inferior wall of the left ventricle.
-
The oblique vein: main tributary of the coronary sinus. Removes blood from the posterior wall of the left atrium.
Byung-Soo Kim, … Anthony Atala, in, 2000
What If My Test Results Show Early Kidney Disease
If a test shows irregular results, your healthcare provider will follow up with you about treatment options. You may receive medications to control blood pressure. Or you may follow up with a nephrologist .
If your test results are atypical, your provider will likely order more frequent kidney function tests in the future. Regular testing helps your provider track your health and any underlying conditions.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Kidney function tests check how well your kidneys are working. Healthy kidneys assist with removing waste from your body. Conditions such as diabetes or high blood pressure can affect your kidney function. You may also need a kidney function test to diagnose or rule out an infection. Kidney function tests include blood tests or urine tests. Typically, your provider gives you your results the same day or within a few days.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 07/14/2021.
References
Also Check: Does Red Wine Cause Kidney Stones
Who Can Help Me With A Urinary Problem
Your primary doctor can help you with some urinary problems. Your pediatrician may be able to treat some of your childs urinary problems. But some problems may require the attention of a urologist, a doctor who specializes in treating problems of the urinary system and the male reproductive system. A gynecologist is a doctor who specializes in the female reproductive system and may be able to help with some urinary problems. A urogynecologist is a gynecologist who specializes in the female urinary system. A nephrologist specializes in treating diseases of the kidney.
Secretion Of Active Compounds
The kidneys release a number of important compounds, including:
- Erythropoietin: This controls erythropoiesis, or the production of red blood cells. The liver also produces erythropoietin, but the kidneys are its main producers in adults.
- Renin: This helps manage the expansion of arteries and the volume of blood plasma, lymph, and interstitial fluid. Lymph is a fluid that contains white blood cells, which support immune activity, and interstitial fluid is the main component of extracellular fluid.
- Calcitriol: This is the hormonally active metabolite of vitamin D. It increases both the amount of calcium that the intestines can absorb and the reabsorption of phosphate in the kidney.
Don’t Miss: Is Pomegranate Juice Good For Your Kidneys
Pathophysiology Of Renal Ischemia
Ischemia starves the tissue of oxygen and nutrients and causes accumulation of metabolic waste products. At the cellular level, the biochemical changes occurring during ischemia induce rapid anaerobic glycolysis, resulting in accumulation of lactic acid that lowers intracellular pH36 and lysosomal instability with activation of lytic enzymes. One of the cell functions requiring the most energy is sodium and water homeostasis via the sodium-potassium pump. In hypoxic conditions, this pump fails, and cellular, mitochondrial, and nuclear swelling and eventual rupture can occur.37
In response to renal ischemia, cytoprotective mechanisms, such as a rapid decrease of cellular metabolic activity,38 are activated as well. However, in cadaveric donor kidneys, the expression of genes encoding for factors relevant to the adaptive graft response, such as heme-oxygenase-1 , vascular endothelial growth factor , and Bcl-2, is lower than normal.39 This reflects a defective adaptation against ischemia/reperfusion injury that would affect graft function in the short term.
Rochelle Coleen Tan Dy, in, 2018
What Do The Results Of My Kidney Function Test Mean
Kidney function test results can tell you whether your kidneys are functioning typically or not. Most function tests look for two measurements:
- GFR of less than 60 could indicate kidney disease.
- Urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio of more than 30 milligrams per gram could be a warning sign of kidney disease.
Read Also: Bleeding Kidney Symptoms
Kidney Structure And Function
Figure 1. Depiction of mammalian kidney, showing blood vessels and tubules within cortex, outer medulla, and inner medulla. Two nephrons are depicted: one short-looped nephron descends into outer medulla, but returns to the cortex before entering inner medulla the long-looped nephron extends into the inner medulla. Segments along the nephron are abbreviated: B, Bowman’s space within the glomerulus PT, proximal tubule DTL, descending thin limb ATL, ascending thin limb TAL, thick ascending limb MD, macula densa DT, distal tubule CCD, cortical collecting duct OMCD, outer medullary collecting duct and IMCD, inner medullary collecting duct. From Berne, R. M. Levy, M. N. Principles of Physiology, 3rd Ed. Mosby, 1999.
Mechanism Of Excretion In Humans
The process of excretion in humans takes place in the following steps:
Urine Formation
The urine is formed in the nephrons and involves the following steps:
-
Glomerular Filtration
-
Secretion
Glomerular Filtration
It is the primary step in urine formation. In this process, the excess fluid and waste products from the kidney are filtered out of the blood into the urine collection tubules of the kidney and eliminated out of the body.
The amount of filtrate produced by the kidneys every minute is known as Glomerular Filtration Rate .
Tubular Reabsorption
It is the absorption of ions and molecules such as sodium ions, glucose, amino acids, water etc. Water involves passive absorption, while glucose and sodium ions are absorbed by an active process.
Secretion
Potassium ions, hydrogen ions, and ammonia are secreted out to maintain the equilibrium between the body fluids.
The functions of the various tubules involved in the process are:
-
Glomerulus- filters the blood
-
Proximal Convoluted Tubules – reabsorb water, ions and nutrients. They remove toxins and help in maintaining the ionic balance and pH of the body fluids by secretion of potassium, hydrogen and ammonia to filtrate and reabsorbing bicarbonate ions from the filtrate.
-
Descending Loop of Henle- is permeable to water and the filtrate gets concentrated as it is impermeable to electrolytes.
-
Collecting Duct- a large amount of water is reabsorbed from the filtrate by the collecting duct.
Micturition
Explore more: Micturition
Don’t Miss: What Laxative Is Safe For Kidneys