Cortical Echogenicity And Advanced Irreversible Chronic Kidney Disease
Renal echogenicity discriminatory capacity to identify advanced and irreversible CKD is shown in figure 2. Elevated renal echogenicity with best discriminatory capacity was a kidney/liver ratio greater than 1.15. Using this cutoff, 65 patients had elevated renal echogenicity. Renal echogenicity had a moderate sensitivity and good specificity in identifying advanced CKD. In comparison to histopathological parameters, it had a better sensitivity than tubular atrophy and inflammatory infiltrate, but was worse than sclerosed glomeruli percentage and interstitial fibrosis. As expected, the opposite was verified in relation to specificity table 3.
Fig. 2.
Discriminatory capacity of quantitative renal echogenicity in identifying advanced chronic kidney disease.
We also compared cortical echogenicity performance against IF/II index . They had very similar discriminatory capacity table 3. Except by the better, but not statistically significant, sensitivity of the IF/II index, renal echogenicity was comparable to this histopathology index.
When analyzing only patients with eGFR less than 30 mL/min/1.73m2 at the renal biopsy, the PPV increased to 92.1% . In fact, in this subgroup, only three patients with increased renal echogenicity did not have advanced CKD confirmed after a 6 months follow-up: two patients had an eGFR between 30-40 mL/min/1.73m2 and another one had an eGFR close to 50mL/min/1.73m2.
Histopathology And Sonographic Evaluation
Patients had a mean renal length of 10.3±1.12 cm and a mean parenchymal thickness of 16.4±0.5 mm. Mean kidney/liver echogenicity ratio was 1.06±0.29. In relation to histopathological parameters used to evaluate chronicity, some degree of interstitial fibrosis was disclosed in 66 patients, tubular atrophy in 70 and inflammatory infiltrate in 53 . Eighty-three patients had more than 30% of globally sclerosed glomeruli.
As expected, there was a positive correlation between all histopathological parameters evaluated. The strongest correlation was found between interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy and the weakest was found between sclerosed glomeruli and inflammatory infiltrate . Renal echogenicity was inversely correlated with renal length , but not with parenchymal thickness . Renal echogenicity correlated with all histopathological parameters . Moreover, renal echogenicity was directly correlated with 24h-proteinuria and inversely with eGFR at follow-up and serum albumin .
Table 2.
Spearman correlation coefficients for the relationships between cortical echogenicity and pathologic parameters
What Is Meant By Echogenicity Of Kidneys
Answered by: Dr Ashutosh Singh | Consultant Nephrologist, Knoxville, USA
Q: I am a 51 years old male with increased cortical Echogenicity of right kidney. What does this imply? I also had elevated alkaline phosphatase in my liver. My shoulder, wrist and finger joints hurt badly. How can I be treated?
Echogenicity of kidneys means ability of various anatomical parts of kidney to generate echo signals on ultrasound examination. There is increased correlation between increased echogenicity of the kidney and chances of underlying kidney disease. Beyond this, there is no use unless one does further tests including serum creatinine and urine studies to ascertain any evidence of kidney disease. Elevated alkaline phosphatase could indicate various diseases including liver and bone disease. You should seek complete evaluation by your family physician.
Recommended Reading: Kidney Failure Kidney Disease Ribbon Tattoos
Bilateral Renal Parenchymal Disease Reported On Ultrasound Scan What Next
This is a common situation that I as a nephrologist face. An apparently healthy person who recently underwent an executive health check-up and was found to have bilateral renal parenchymal disease- grade1 on the ultrasound scan. Everything else is perfectly normal. The only problem is that the apparently healthy person is now extremely anxious with hundreds of questions whizzing through his/her mind :
- is it dangerous?
- do I need to be on a specific diet for it?
- will it worsen to renal parenchymal disease grade 2 and above?
- how well are my kidneys working?
- do I need any other tests?
This post attempts to answer these questions in a simple and straightforward manner.
Coming to the most important question first
Clinical Utility Of Ultrasonographic Evaluation In Acute Kidney Injury
Caijie Liu, Xiuzhen Wang
Department of Ultrasound, First Affiliated Hospital of Jinzhou Medical University, Jinzhou 121001, China
Contributions: Conception and design: C Liu Administrative support: X Wang Provision of study materials or patients: C Liu Collection and assembly of data: C Liu Data analysis and interpretation: C Liu, X Wang Manuscript writing: All authors Final approval of manuscript: All authors.
Correspondence to:
Background: This study aimed to evaluate ultrasonography in patients with acute kidney injury and the association of US findings with its clinical characteristics.
Methods: This single-center retrospective study evaluated US in AKI patients. A healthy control group was matched by sex and age at a ratio of 2:1 with the AKI group. The US characteristics were compared between the two groups.
Results: The US characteristics of 111 patients with AKI were evaluated. Compared with the control group, AKI patients had greater kidney length and kidney volume . Patients with AKI also displayed thicker parenchyma than those in the control group, but only the difference in the right kidney was found to be significant. Of the 111 AKI patients, 38 had positive US findings including increased parenchymal echogenicity, increased renal resistance index , and hydronephrosis, while only 5 patients had increased RRI. The cause of AKI was attributed to obstructive nephropathy in eight patients.
Submitted Feb 11, 2020. Accepted for publication May 26, 2020.
Also Check: Is Ginger Tea Safe For Kidneys
What Are The Symptoms/treatment/diet For Renal Parenchymal Disease
Like I said above, renal parenchymal disease refers to how the kidneys look on ultrasound scans. Even though it includes the word disease, it is not a specific disease of the kidney. The treatment/symptoms/diet all depend on how well the kidneys are working. So, they are highly variable from patient to patient and need to be advised on an individual basis.
In summary :
- Bilateral renal parenchymal disease on ultrasound only tells about abnormal appearance of the kidneys
- We need to do kidney function tests/renal function tests to know more about the functioning of the kidneys
- Further tests may be needed to pinpoint the exact causes and extent of kidney disease
Hope this blog post was useful in clarifying your doubts about the topic. Take care!
I have recently started writing about kidney-related topics in the Hindi language. It may be of interest. The first post was all about uric acid in Hindi language. It received a very good response and then I wrote about . Please have a look and provide your feedback.
Howdy! I simply would like to offer you a big thumbs up for the excellent info you have got right here on this post.I am returning to your blog for more soon.
Very useful help slot clear doubt.great
Comparison Of Renal Size Parenchymal Thickness And Renal Volume Between The Aki Group And Control Group
Table 2Full table
In both the AKI and control groups, the right kidney was slightly smaller in size than the left kidney. Kidney length, width, thickness, and volume in the AKI group were greater than those in the control group . In the AKI group, the volume of the left kidney was 146.36 cm3, while the volume of the right was 141.48 cm3. The AKI group also had a thicker renal parenchyma than the control group, but the difference was significant in the right kidney. Figure 6 indicated an enlarged kidney and volume increase in AKI.
Figure 6
Also Check: Does Seltzer Water Cause Kidney Stones
Inclusion And Exclusion Criteria
Discharged AKI cases from between January 1, 2019 and December 31, 2019 from the inpatient database were screened, and a retrospective review of the patients medical records was carried out. The inclusion criteria were as follows: a confirmed diagnosis of AKI, which was defined as any of the following criteria: increase in serum creatinine by 0.3 mg/dL within 48 hours or increase in serum creatinine of 1.5 times from baseline which is known or presumed to have occurred within the 7 days prior US was performed after AKI onset an intervention to relieve the obstruction was not performed before US evaluation and serum creatinine levels had not recovered before US evaluation. Patients aged < 18 years or those who were pregnant or 6 weeks postpartum were excluded.
After the AKI cases were screened, the healthy controls were randomly selected by matching sex and age at a ratio of 2:1 with those in the AKI group. The inclusion criteria of the control group were as follows: sex and age matched with the AKI group renal US kidney evaluation was performed at the hospital between January 1, 2019 and December 31, 2019
Disorders Of The Medulla/pyramids
Acute Tubular Necrosis
Acute tubular necrosis is one of the most common causes for ARF in hospital patients.8,9 The injury is usually due to a combination of cellular ischemia and direct tubular epithelial cell injury induced by nephrotoxins. The tubules are more vulnerable to ischemia because of their relatively high metabolic rate and the relatively poor blood supply with low oxygenation when compared with the more luxuriant flow to the cortex and glomeruli. In addition, sloughing of cells and debris into the tubular lumen leads to obstruction by proteinaceous casts. There are several factors which may contribute to the development of this disorder, including ischemia and hypotension, drugs and toxins, sepsis and myoglobinuria/hemoglobinuria. In any individual case, more than one factor is often involved.
Fig. 3.6 Echogenic foci in the region of the medullary pyramids in a patient with medullary sponge kidneys. A little patchy shadowing is visible but this is not a strong feature
Renal Papillary Necrosis
Medullary Sponge Kidney
Nephrocalcinosis
Hyperechogenic medullae are not always the result of nephrocalcinosis and may be seen in patients with gout and in primary hyper-aldosteronism in which chronic hypokalemia results in changes within the tubules and adjacent interstitial tissues.
Recommended Reading: Ginger Benefits For Kidneys
Pediatric Series: Kidney Echogenicity In Children: Clinical Correlation Required
Ultrasonography of the kidneys is one of the most common imaging modalities performed in children in the nephrology clinic. The routine use of prenatal ultrasound in pregnancy care has additionally provided nephrologists with a view into the kidneys and urinary tract as they develop in utero, allowing both families and care teams to prepare for complications related to the kidney that may arise after birth. Increased echogenicity of the kidneys, while non-specific, is one of the most common imaging findings on kidney ultrasound it may be a transient finding, or a harbinger of serious kidney disease that warrants evaluation by a pediatric nephrologist.
The echogenicity of a kidney, or any organ for that matter, refers to how bright it appears on grayscale imaging by ultrasound. These images are produced when the ultrasound machine operates in two-dimensional brightness mode , in which reflected echoes appear as bright dots. Tissue that most strongly reflects sound waves is hyperechoic and appears white , whereas fluid, such as from simple cysts or urine in the collecting system, reflects the weakest and appears black in color. Traditionally, the brightness of the kidneys on ultrasound has been described in relation to that of the liver, which has intermediate echogenicity, and is used as an internal comparison .
- Determine whether the echogenicity is patchy or diffuse
- Its location within the kidney
- Is it primarily cortical
- medullary ?
Post by
Clinical And Laboratory Data
Laboratory data about renal function, 24h-urine protein excretion rate, and serum albumin were collected from patients on the three days before and between three and six months after the renal biopsy was performed. Patients were considered as having irreversible advanced CKD if they had: eGFR less than 30mL/min/1.73m2 at renal biopsy which was maintained after a six-months follow-up. Patients with eGFR less than 30 mL/min/1.73m2 at renal biopsy, but not at 6 months of follow-up were considered as having AKI or acute-on-CKD. Patients with an eGFR higher than 40 mL/min/1.73m2 at renal biopsy and less than 30mL/min/1.73m2 after three to six months were considered as rapid progression and not as irreversible advanced CKD. Patients in whom it was not possible to perform this evaluation due to unavailable data about renal function were excluded. Estimated glomerular filtration rate was calculated using CKD-EPI equation .
You May Like: Does Flomax Hurt Your Kidneys
What Is The Echogenicity Of The Renal Pyramids
4.7/5renal pyramidsrenalechogenicseen here
Echogenicity, therefore, refers to how bright or dark something appears in the gray-scale image the brighter something appears, the more echogenic it is. With regard to the kidney, echogenicity generally refers to how bright or dark the kidney parenchyma appears in comparison to the liver.
Similarly, what is echogenic medullary pyramids? Echogenic medullary pyramids, irrespective of medullary nephrocalcinosis. Description : The right kidney is normal in size, but exhibits increased echogenicity of the medullary pyramids. No obvious acoustic shadowing is noted from the echogenic foci.
Just so, is echogenic kidneys normal?
Echogenic kidneys can be a normal variant but are also seen in association with renal dysplasia, chromosomal abnormality, adult and fetal polycystic disease, Pearlman syndrome, BeckwithWiedemann syndrome, and CMV infection. The incidence of echogenic kidneys has been estimated at 1.6 cases per 1000 sonograms.
What is the meaning of increased echogenicity?
Echogenicity or echogeneity is the ability to bounce an echo, e.g. return the signal in ultrasound examinations. In other words, echogenicity is higher when the surface bouncing the sound echo reflects increased sound waves.
Is Increased Echogenicity Related To A Decrease In Glomerular Filtration Rate Objective Measurements In Pediatric Solitary Kidney Patientsa Retrospective Analysis
-
Affiliation Department of Urology and Urological Science Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea
-
Affiliation Department of Radiology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea
-
Affiliation Department of Radiology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea
-
Affiliation Department of Urology and Urological Science Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea
-
Affiliation Department of Urology and Urological Science Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea
-
Affiliation Department of Urology and Urological Science Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea
Don’t Miss: Can Apple Cider Vinegar Hurt Your Kidneys
The Characteristics Of 111 Patients With Aki
Table 1Full table
The data of 111 AKI patients, with a mean age of 59 years, were analyzed. Among these 111 patients, 83 were male and 28 were female. The average value of the highest serum creatinine level was 379 µmol/L. The etiologies of AKI included volume depletion, heart failure, sepsis, obstructive nephropathy, and ATN . In 33 cases, AKI coexisted with glomerular disease, including IgA nephropathy , focal segmental glomerulosclerosis , lupus nephritis , membranous nephropathy , antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody associated vasculitis , nephrotic syndrome , capillary proliferative glomerulonephritis, post-infectious glomerulonephritis , and diabetic nephropathy . In some cases, AKI was caused by multiple etiologies.
What Does Echotexture Of The Kidney Mean
4.8/5kidneykidneyabout it here
RESULTS: Median renal lengths were 11.2 cm on the left side and 10.9 cm on the right side. Median renal volumes were 146 cm3 in the left kidney and 134 cm3 in the right kidney. Renal size decreased with age, almost entirely because of parenchymal reduction.
Likewise, is echogenic kidneys normal? Echogenic kidneys can be a normal variant but are also seen in association with renal dysplasia, chromosomal abnormality, adult and fetal polycystic disease, Pearlman syndrome, BeckwithWiedemann syndrome, and CMV infection. The incidence of echogenic kidneys has been estimated at 1.6 cases per 1000 sonograms.
Hereof, what is a echogenic kidney?
Kidneys are considered echogenic if the reflectivity of the renal parenchyma is greater than the reflectivity of the liver. Once diagnosed, other sonographic features of aneuploidy, renal anomalies, and CMC infection should be sought.
What is the parenchyma of the kidney?
The renal parenchyma is the functional part of the kidney that includes the renal cortex and the renal medulla. Renal parenchyma disease describes medical conditions which damage these parts of the kidney. These diseases may be congenital, hereditary or acquired.
Don’t Miss: Is Ginger Good For Kidneys
Why Texas Childrens Fetal Center
- A single location for expert maternal, fetal and pediatric care. At Texas Childrens Hospital, mother and baby receive the specialized care required for fetal echogenic kidneys and congenital kidney conditions all in one location, including the highest level NICU, if needed.
- A skilled, experienced team with proven outcomes. We have a dedicated team of maternal-fetal medicine specialists, fetal imaging experts, genetic counselors, neonatologists, and pediatric nephrologists and urologists who work in concert to care for you and your baby every step of the way, using proven protocols weve developed over the years. With their combined expertise and unified approach, this team offers the best possible care for pregnancies involving echogenic kidneys.
- We care for your childs needs at every stage of life. Our comprehensive approach starts with your first prenatal visit and continues through delivery, postnatal care, and childhood, thanks to one of the nations leading teams of fetal and pediatric specialists.
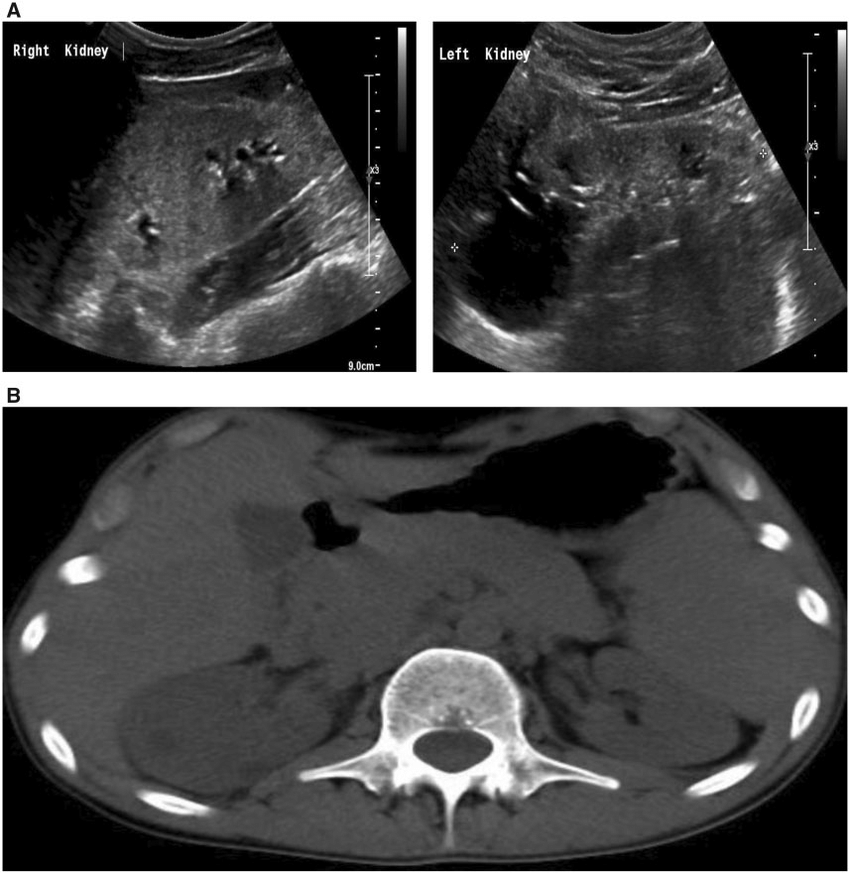
What Is The Significance Of Increased Renal Echogenicity On Ultrasound
When the right kidney is more echogenic than the normal liver and the left kidney is isoechoic or more echogenic than the normal spleen, the kidneys can be characterized as being abnormally echogenic.
Increased renal echogenicity is an indication of parenchymal disease but is nonspecific for the type of parenchymal disease, which may include acute or chronic glomerulonephritis, acute interstitial nephritis, diabetes mellitus, systemic lupus erythematosus, HIV nephropathy, and amyloidosis.
Percutaneous renal biopsy is therefore frequently required for a definitive diagnosis.
Recommended Reading: Is Tea Good Or Bad For Your Kidneys
Histopathology Parameters And Advanced Irreversible Chronic Kidney Disease
Initially, each histopathological parameter was evaluated separately in relation to its discriminatory capacity to identify advanced CKD . Generally, they had moderate to good discriminatory capacity and similar capacity when compared to each other. The only trend in statistical difference was between the discriminatory capacities of interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy . The score with best discriminatory capacity was grade 3 or higher in all histopathological parameters and more than 30% of sclerosed glomeruli. These scores were used to calculate sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values for each parameter, as shown in Table 3.
Table 3.
Discriminatory capacity, sensitivity, specificity, predictive positive and negative values of each simple or combined histopathology parameter and renal echogenicity. IF/II index: composite index adding interstitial fibrosis and inflammatory infiltrate
Table 4.
Multivariate analysis with advanced chronic kidney disease after 6 months follow-up as the dependent variable