Guideline 1: Use Of Diuretics In Ckd
Diuretics are useful in the management of most patients with CKD. They reduce ECF volume lower blood pressure potentiate the effects of ACE inhibitors, ARBs, and other antihypertensive agents and reduce the risk of CVD in CKD. Choice of diuretic agents depends on the level of GFR and need for reduction in ECF volume.
12.1 Most patients with CKD should be treated with a diuretic .
12.1.a Thiazide diuretics given once daily are recommended in patients with GFR 30 mL/min/1.73 m2
12.1.b Loop diuretics given once or twice daily are recommended in patients with GFR < 30 mL/min/1.73 m2
12.1.c Loop diuretics given once or twice daily, in combination with thiazide diuretics, can be used for patients with ECF volume expansion and edema .
12.1.d Potassium-sparing diuretics should be used with caution:
12.1.d.i In patients with GFR < 30 mL/min/1.73 m2
12.1.d.ii In patients receiving concomitant therapy with ACE inhibitors or ARBs
12.1.d.iii In patients with additional risk factors for hyperkalemia .
12.2 Patients treated with diuretics should be monitored for:
12.2.a Volume depletion, manifest by hypotension or decreased GFR
12.2.b Hypokalemia and other electrolyte abnormalities .
12.2.c The interval for monitoring depends on baseline values for blood pressure, GFR and serum potassium concentration .
12.3 Long-acting diuretics and combinations of diuretics with other antihypertensive agents should be considered to increase patient adherence .
How Do I Know If I Need Water Pills
You can start a diuretic if you have signs of fluid retention. Signs of excess fluid include swelling in the ankles, legs, or a feeling of fullness in the stomach. Your doctor may tell you to take more diuretics if you gain weight.
How long are you on diuretics?
The effect will last for around 6 hours, so if you are taking the tablets twice a day, be sure to take the last dose in the afternoon at least 8 hours before going to bed.
Are there any side effects to taking a diuretic?
If you take a thiazide diuretic, your potassium levels may drop too low , which can lead to life-threatening heart rhythm problems. If you take a potassium-sparing diuretic, you may have too much potassium in your blood. Other possible side effects of diuretics include: Types of blood pressure medications.
What is the best diuretic for your health?
1 Coffee. Coffee is a very popular drink that has been linked to impressive health benefits. 2 dandelion extract. It has been suggested as a potential diuretic due to the high potassium content of the dandelion plant . 3 Horsetail. 4 Parsley. 5 hibiscuses. 6 Caraway. 7 green and black tea. 8 Nigella Sativa.
Is it good to take diuretics to lose weight?
Which Diuretic Is Best For Kidneys
A loop diuretic is generally the diuretic of choice in patients with renal insufficiency. Although a thiazide-type diuretic will initiate diuresis in patients with mild renal insufficiency, the response in patients with a GFR of < 50 ml/min/1.73 m2 is less than that seen with a loop diuretic.
What is the safest diuretic?
TUESDAY, Feb. 18, 2020 Patients taking a common diuretic to help lower blood pressure may be better off with a similarly effective but safer one, a new study suggests. Current guidelines recommend the drug chlorthalidone as the first-line diuretic.
You May Like: What Is Chronic Kidney Disease Stage 4
Are There Differences Among Diuretics
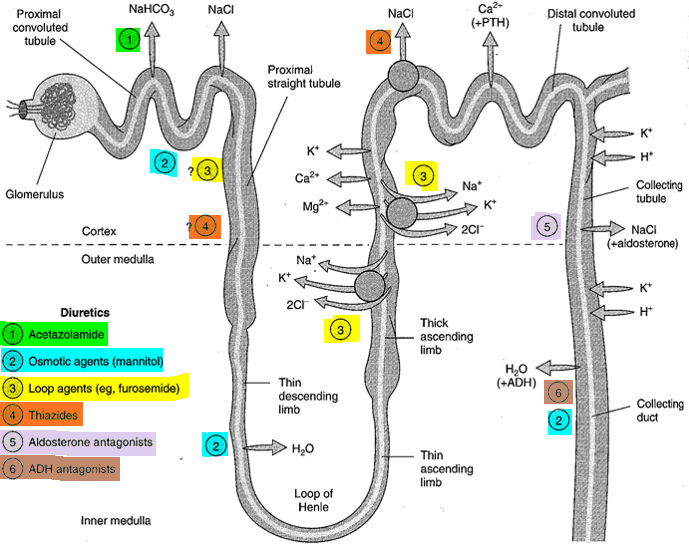
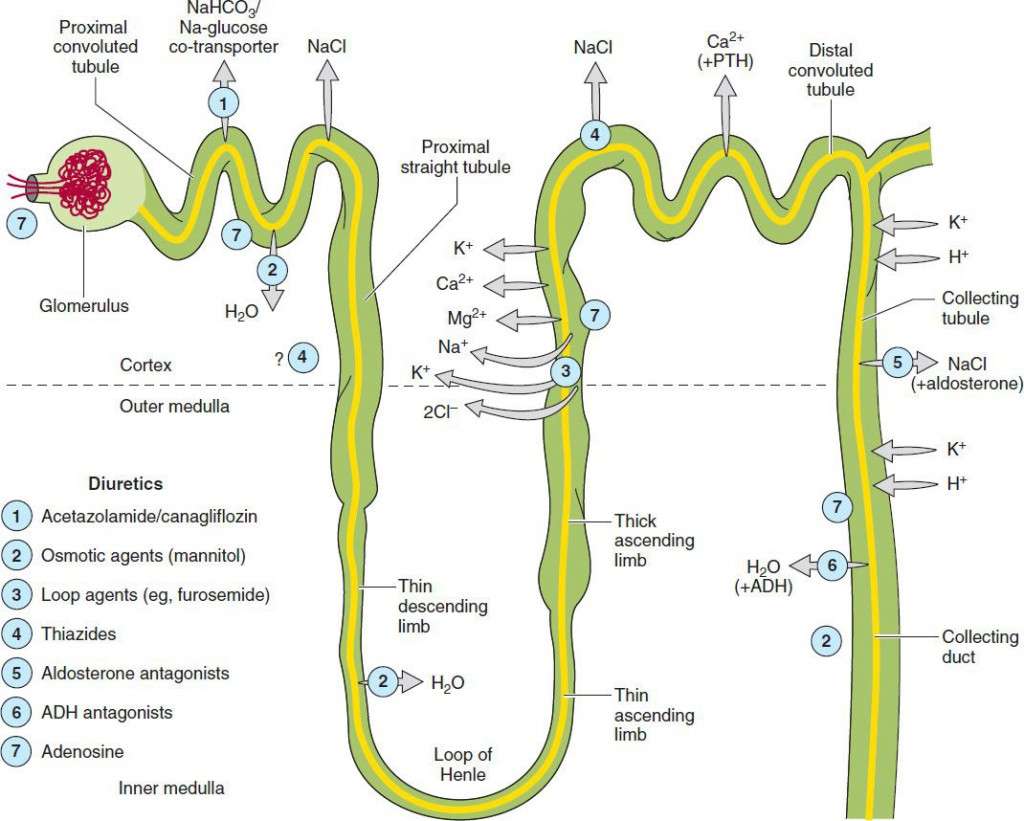
A major difference among diuretics is the level of potency. Potency variation is due to the differences in the sites of action of diuretics on the kidney structure.
- Loop diuretics are the most potent diuretics as they increase the elimination of sodium and chloride by primarily preventing the reabsorption of sodium and chloride. The high efficacy of loop diuretics is due to the unique site of action involving the loop of Henle in the kidneys.
- Thiazide diuretics increase the elimination of sodium and chloride in approximately equivalent amounts. They do this by inhibiting the reabsorption of sodium and chloride in the distal convoluted tubules in the kidneys.
- In the distal tubule, potassium is excreted into the forming urine coupled with the reabsorption of sodium. Potassium-sparing diuretics reduce sodium reabsorption at the distal tubule, thus decreasing potassium secretion. Potassium-sparing diuretics when used alone are rather weak, hence they are used most commonly in combination therapy with thiazide and loop diuretics.
- Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors work by increasing the excretion of sodium, potassium, bicarbonate, and water from the renal tubules
- Osmotic diuretics are low-molecular-weight substances that are filtered out of the blood and into the tubules where they are present in high concentrations. They work by preventing the reabsorption of water, sodium, and chloride.
How Do Diuretics Affect The Kidneys
4.3/5Diureticscausekidneyscause
In this regard, do Diuretics cause kidney damage?
Diuretics. Water pills like hydrochlorothiazide and furosemide, used for high blood pressure and edema, can cause dehydration and can also lead to swelling and inflammation of the kidneys. The following tips can help prevent the risk of kidney damage.
One may also ask, do diuretics improve kidney function? Observational studies with small sample size and short duration have shown that diuretics decrease blood pressure and improve edema in CKD patients but their use, particularly at higher doses, is associated with rise in serum creatinine and several metabolic complications .
Similarly, it is asked, what diuretics are safe for kidneys?
Description of the intervention
Also Check: How Do You Diagnose Kidney Disease
Chronic Kidney Disease Fluid Overload And Diuretics: A Complicated Triangle
-
* E-mail:
Affiliations Discipline of Clinical Pharmacy, School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, University Sains Malaysia, Penang, 11800, Malaysia, Chronic Kidney Disease Resource Centre, School of Medical Sciences, Health Campus, University Sains Malaysia, Kubang Kerain, 16150, Kelantan, Malaysia
-
Affiliation Discipline of Clinical Pharmacy, School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, University Sains Malaysia, Penang, 11800, Malaysia
-
* E-mail:
Affiliation Chronic Kidney Disease Resource Centre, School of Medical Sciences, Health Campus, University Sains Malaysia, Kubang Kerain, 16150, Kelantan, Malaysia
-
Affiliation Discipline of Clinical Pharmacy, School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, University Sains Malaysia, Penang, 11800, Malaysia
-
Affiliations Discipline of Clinical Pharmacy, School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, University Sains Malaysia, Penang, 11800, Malaysia, Chronic Kidney Disease Resource Centre, School of Medical Sciences, Health Campus, University Sains Malaysia, Kubang Kerain, 16150, Kelantan, Malaysia
Rationale: Recommendations For Intiation And Dose Escalation Of Diuretics In Ckd
Strength of Evidence
The choice of diuretics will be dependent upon both the stage of CKD and the ECF volume overload in the patient. The dose ranges for commonly used diuretics are shown in Table 149.
Thiazide diuretics can be used in CKD Stages 1-3 . In the doses recommended in Table 149, thiazides are effective in generating a diuresis in patients with GFR greater than approximately 30 mL/min/1.73 m2.536,543 Whether their nondiuretic properties contribute to blood pressure control in CKD is not known.
Thiazide diuretics differ in their pharmacokinetics. Hydrochlorothiazide should be started at a dose of 25 mg/d in Stage 1-3 CKD, with titration to 50 to 100 mg/d as necessary. Doses as low as 6.25 mg of HCTZ in fixed-dose combination antihypertensive products improve the blood pressure response to other nondiuretic antihypertensive medications such as ß-blockers and ACE inhibitors. Chlorthalidone was used in a dose range of 12.5 to 25 mg/d in ALLHAT. Chlorthalidone is longer-acting than HCTZ, resulting in better blood pressure control, but also a higher incidence of hypokalemia. Chlorthalidone may be effective at a lower GFR than HCTZ.
Loop diuretics are not as effective as thiazide diuretics in lowering blood pressure in CKD Stages 1-3. In CKD Stages 4-5, loop diuretic therapy is a useful adjunct therapy in the treatment of hypertension. Fixed-dose combination antihypertensive products containing a loop diuretic are currently not available in the United States.
You May Like: Can Ejaculating Help Pass A Kidney Stone
What Diuretics Are Safe For Kidneys
Frequentlyadministered potassiumsparing diuretics are triamterene, amiloride, spironolactone and eplerenone. These drugs are further classified as those that inhibit epithelial sodium channels and mineralocorticoid receptor inhibitors.
Which diuretic is best for kidneys?
A loop diuretic is generally the diuretic of choice in patients with renal insufficiency. Although a thiazide-type diuretic will initiate diuresis in patients with mild renal insufficiency, the response in patients with a GFR of & lt,50 ml/min/1.73 m2 is less than that seen with a loop diuretic.
What water pill is safe for kidneys?
Furosemide is given to help treat fluid retention and swelling that is caused by congestive heart failure, liver disease, kidney disease, or other medical conditions. It works by acting on the kidneys to increase the flow of urine.
Can you take diuretics if you have kidney disease?
Diuretics are useful in the management of most patients with CKD. They reduce ECF volume, lower blood pressure, potentiate the effects of ACE inhibitors, ARBs, and other antihypertensive agents, and reduce the risk of CVD in CKD.
What is the safest diuretic?
TUESDAY, Feb. 18, 2020 Patients taking a common diuretic to help lower blood pressure may be better off with a similarly effective but safer one, a new study suggests. Current guidelines recommend the drug chlorthalidone as the first-line diuretic.
The Need To Monitor Kidney Function With Certain Drugs
Experts have suggested that after the initial assessment of kidney function, physicians should consider regular monitoring after starting or increasing the dosage of drugs associated with nephrotoxicity, especially those used chronically in patients with multiple risk factors for impaired kidney function, Dr. Naughton noted. If there is any sign of kidney harm, the provider should review the medications you are taking in order to identify which one is causing the problem.
If multiple medications are present and the patient is clinically stable, physicians should start by discontinuing the drug most recently added to the patients medication regimen. Once that has been taken care of, further harm to the kidneys may be minimized by keeping blood pressure stable, staying hydrated, and temporarily avoiding the use of other medications that may cause nephrotoxicity.
These safety tips can ensure you get the care you need while keeping your kidneys safe. That way, they can tend to essential functions like keeping things flowing .Originally published May 11, 2017
Read Also: Where Do Kidney Stones Come Out
What Are The Drug Interactions Of Diuretics
Thiazide diuretics given concurrently with antidiabetic drugs causes a decreased blood level of antidiabetic drugs, hence doses of antidiabetic drugs may need to be increased.
- Among patients taking digoxin , low levels of potassium caused by concurrent digoxin and diuretics may cause weakness, cramps, and irregular heartbeats.
- Lithium given concurrently with diuretics may induce lithium toxicity due to decreased renal elimination of lithium. Lithium levels should be monitored to ensure safety.
- Potassium-sparing diuretics given with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs have been associated with severely elevated levels of potassium . Severe hyperkalemia may present as muscle weakness, fatigue, and slow heart rate . It is important to monitor potassium blood levels and to have an electrocardiogram performed.
- Diuretics are often prescribed with other medications for high blood pressure and heart disease. This may increase the effects of these medications, potentially causing electrolyte abnormalities .
How The Intervention Might Work
Diuretics trigger a range of mechanisms, including braking phenomenon. Braking phenomenon leads to postdiuretic sodium retention. Presence or absence of sodium retention leads to two different phenomena . There can be no tendency to retain sodium in that case the normal Sshaped dose response relationship is observed. The Sshaped response curve indicates that the optimal dose led to maximum diuretic response and additional doses will not increase the effect. Where there is a tendency to retain sodium, the Sshaped curve shifts right and down, indicating that the optimal dose did not result in an appropriate dose response. This effect is termed diuretic resistance, and hence, a higher dose may be required . The site of action for all diuretics is in the luminal space. Glomerular filtration has a minor role in diuretic entry into the urinary compartment, largely because all diuretics are bound to protein .
Diuretics will lower blood pressure and potentiate the effects of ACEis, ARBs and other antihypertensive agents, including calciumchannel blockers by reducing extracellular fluid volume . Dosing is empiric and frequently determined by the elimination of oedema for CKD stage 4 to 5. Spironolactone leads to natriuretic response in patients with cirrhosis and ascites or heart failure, particularly used with a loop or a thiazidetype diuretic or both .
Recommended Reading: What Side Do You Lay On For Kidney Stones
Why It Is Important To Do This Review
CKD is an important, common condition that can complicate other comorbidities and itself lead to increased morbidity and mortality. This review intends to systematically assess the benefits and harms of diuretics for people at all stages of CKD. Diuretics are important class of drugs but there is little evidence to guide clinicians regarding which diuretics are most effective, safest in these patients, or when switching should occur from one type of diuretic to another in this population.
There is limited evidence about the appropriate time to convert from one class of diuretic to another. There is need to assess existing differences for controlling blood pressure for loop diuretics without any effect on volume loss. Furthermore, there is limited information available for titrating dose appropriately for blood pressure control.
The safety and efficacy of diuretics alone or in combination need to be addressed. The safety issue of combining loop diuretics with thiazide diuretics compared with higher doses of loop diuretics has not been addressed, nor is the safety and efficacy of use of loop diuretics in patients on haemolysis known.
The body of evidence concerning the blood pressurelowering response of loop diuretics compared with ACEis is insufficient. There is limited evidence relating to adverse events associated with diuretics among people at all stages of CKD . Hence, a systematic review is required to investigate these issues to better inform clinical decision making.
Diuretic Mechanism And Uses
Water pills, also known as diuretics, work by affecting the way the kidneys filter the blood. Some of them block the ability of the kidneys to reabsorb sodium and/or potassium, which also pulls extra water into the urine. Others increase the rate at which urine flows through the kidneys. Regardless of their mechanism, water pills increase the amount of water lost through the urine and often are used to treat high blood pressure, kidney disease and congestive heart failure, the Texas Heart Institute explains. Because they eliminate water from the body, they may also cause short-term weight loss.
Recommended Reading: Apple Cider Vinegar For Kidney Infection
Read Also: Are Eggs Bad For Kidneys
What Do Diuretics Do To The Kidneys
Diureticswater pillskidneysThere are three types of diuretics:
- Loop-acting diuretics, such as Bumex®, Demadex®, Edecrin® or Lasix®.
- Potassium-sparing diuretics, such as Aldactone®, Dyrenium® or Midamor®.
- Thiazide diuretics, such as Aquatensen®, Diucardin® or Trichlorex®.
The 8 Best Natural Diuretics to Eat or Drink
- Dandelion Extract. Dandelion extract, also known as Taraxacum officinale or lions tooth, is a popular herbal supplement often taken for its diuretic effects .
- Horsetail.
Also Check: Watermelon Renal Diet
Pathogenesis Of Hypertension In Chronic Kidney Disease
A number of mechanisms contribute to the development of hypertension in CKD and these influence its management . Increase in sympathetic tone, brought about by afferent signals generated by functionally declining kidneys, contributes to the development of hypertension in CKD . As eGFR declines there is an upregulation of the reninangiotensinaldosterone system which promotes salt and water retention . This is compounded by an increased salt sensitivity of BP . Endothelial dysfunction is characteristic of advanced CKD and its association with hypertension is well-established . Increased arterial stiffness is also seen throughout the spectrum of CKD , is implicated in the development of hypertension , and is an independent risk factor for CVD events . Once hypertension has developed, several factors, including increased oxidative metabolism, with resultant relative renal hypoxia, may drive further progression of BP and CKD .
Fig. 1
Pathogenesis and management flow-chart of hypertension in chronic kidney disease. ACEi angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor, ARB angiotensin II receptor antagonist , CCB calcium channel antagonist , CKD chronic kidney disease, RAAS reninangiotensinaldosterone system
You May Like: Which Of The Following Does Not Describe Acute Kidney Failure
Rationale: Review Of Physiology And Pharmacology
A thorough application of the determinants of diuretic response is a prerequisite for the proper use of diuretics in CKD.
Sodium Retention in CKD
Sodium retention occurs when sodium intake exceeds sodium excretion and leads to ECF volume expansion. ECF volume expansion is common in CKD and is an important cause of hypertension . In principle, the mechanism of decreased sodium excretion in CKD is reduced glomerular filtration of sodium, increased tubular reabsorption of sodium, or both. It is useful to think of two patterns of altered pathophysiology:
Sodium retention due to decreased filtered load. In principle, ECF volume expansion could lead to compensatory decrease in tubular reabsorption of sodium, re-establishment of the steady-state of sodium balance, with resultant hypertension, but without other manifestations of ECF volume expansion. It appears that tubular reabsorption is not truly appropriately suppressed. This is the most common pattern observed in CKD.530 Large increases in ECF volume may arise if sodium intake is very high or reduction in GFR is severe .
Use of Diuretics as Antihypertensive Agents
Long-term therapy with thiazide diuretics may also reduce blood pressure by mechanisms other than reducing ECF volume. As a corollary, a blood pressure reduction with thiazide-type diuretics may occur even in the absence of a significant diuresis.
Principles of Diuretic Action
Potentiation of Effects of Antihypertensive Agents by Diuretics
Classes of Diuretics
Fast Facts On Diuretics
Many people use diuretic medications that are prescribed by a doctor. However, some foods and drinks are also considered natural diuretics.
Types of diuretic medications include:
- thiazide diuretics
- potassium sparing diuretics
Thiazides decrease blood pressure at the same time as removing excess fluid, as they relax the blood vessels. They can help in cases of chronic heart failure. Chlorothiazide is an example.
Loop diuretics, for example, furosemide, are used in patients with pulmonary edema, high blood pressure, kidney problems, and heart failure.
Potassium-sparing diuretics do not reduce blood pressure, but they also prevent a loss of potassium. Amiloride is an example. They are considered weak diuretics, and they may be used with thiazides or loop diuretics. They must not be used with potassium supplements.
Some foods, drinks, and spices can act as natural diuretics.
Recommended Reading: Can Kidney Stones Be Life Threatening