Does Too Much Whey Protein Cause Side Effects
Whey protein is one of the most popular supplements on the planet.
But despite its many health benefits, theres some controversy surrounding its safety.
Some claim that too much whey protein can damage the kidneys and liver and even cause osteoporosis.
This article provides an evidence-based review of whey proteins safety and side effects.
Renal Function Following Long
This randomized controlled study investigated if low carb diets have any risks to kidney function .
68 participants were equally split into two groups, and they were put on one of two diets
- Diet 1: Very low carbohydrate
- Diet 2: High carbohydrate diet
As shown, both diets contained a respectable amount of protein, but the VLC diet provided significantly more than current recommendations at 35% of energy.
Full health markers for kidney health were taken before and after the study.
After a period of 12-months, there were no changes in either group to serum creatinine or glomerular filtration rate .
In short, this study showed very high protein diets dont adversely affect kidney health in individuals with abdominal obesity.
Compared with higher carbohydrate diets, there is no adverse effect from low carb, high protein diets.
Key Point:
Can Eating Too Much Protein Affect Your Kidneys
While no major studies link high protein intake to kidney disease in healthy people, excess protein does force your kidneys to work harder and can cause problems for people with existing medical conditions. Kidney disease aside, the healthiest diet is a varied one that contains a balance of nutrients. Women only need about 46 grams of protein per day, while men need about 56 grams — but most Americans consume more, notes the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Read Also: Why Do My Kidneys Hurt So Much
Can Eating Too Much Protein Be Bad For You
Answered under the premise that protein shakes are a direct protein supplement to diet, ignoring their detailed composition and basing answer on the above title. As with ALL supplements, read and understand the ingredients list and what makes those ingredients up. Look for full disclosure of ingredients on the labels and you can always check most supplements on labdoor.com.
Click the next link for a comprehensive answer tailored to Whey Protein
Protein Intake And Kidney Function
So, can high protein diets cause kidney damage?
Not according to the evidence.
Although it was theorized that long-term high protein consumption would cause side effects, clinical trials on human participants do not support this hypothesis.
In recent years, there have been several studies that investigated this issue, and they all show no link between protein intake and adverse markers of kidney health.
However, some studies suggest that keeping protein intake at a moderate level may help people with pre-existing kidney disease .
Also Check: Does Iced Tea Cause Kidney Stones
What Foods Are Rich In Protein
Except for isolated fats and sugars, almost every food contains protein.
Among these, those with the highest protein density are predominantly animal foods.
While animal foods tend to be the best sources of protein, a few plant foods can be high in the macronutrient too .
The following foods are the most concentrated sources of dietary protein
- Beans
Key Point:
How Kidneys Are Damaged
Many different diseases, drugs, toxins, and inherited disorders can lead to kidney damage.
However, by far the two most common causes of kidney disease are diabetes and high blood pressure, both of which can damage the kidneys delicate blood vessels and tissues.1
When the root causes of these two diseases are not addressed, chronic kidney disease and ultimately kidney failure can be the result. In the US, diabetes causes 44%, and high blood pressure causes 29% of all cases of end-stage kidney failure requiring dialysis or a kidney transplant.2
Why does this happen?
In the case of diabetes, high blood sugars over long periods of time can cause glucose to bind to vital proteins in the bloodstream. This process, known as glycation, results in the formation of advanced glycation end-products . AGEs can cause abnormal changes to proteins and to receptors that ultimately injure the filtering segments of the kidney. This glycation creates a vicious cycle of additional injuries to tissues that results in progressive kidney damage, called diabetic nephropathy.3
With high blood pressure, the problem is simply too much pressure. Exposing the delicate filtering portion of kidneys to blood that is moving too hard and fast causes scarring, which damages the kidneys. This results in a loss of kidney function, leading to chronic kidney disease or eventually kidney failure.4
Takeaway:
You May Like: What Color Are Kidney Stones When You Pass Them
Effect On Kidney Function
Excessive protein intake has an effect on accelerating the development of chronic kidney disease, according to the findings of a study published in the American Journal of Kidney Diseases that investigated the effect of a high-protein diet on kidney function 5.
In a normal, healthy individual, protein drinks are likely safe. But if you have preexisting problems, such as reduced kidney function, you may be at risk of kidney damage if you use Boost excessively over long periods. Your body may not be able to properly eliminate the accumulation of the waste products from protein metabolism, according to the Mayo Clinic47.
- Excessive protein intake has an effect on accelerating the development of chronic kidney disease.
Protein And Body Weight Reduction
Oftentimes, clients looking for weight loss will consider a low-carb, high-protein diet. When successful, people sometimes think its the absence of carbs from the daily calories that achieved the results. However, meeting the right protein requirements is beneficial in two ways. The first is that protein consumption reduces clients appetite. This is because calories from protein take longer to breakdown than most carbs and fats. Consequently, clients will feel fuller longer when eating a diet consisting of high-quality proteins. This result of appetite reduction is commonly called spontaneous reduction in calorie intake. All it means to your client is theyll be feeling fuller longer and therefore less likely to eat and snack at unnecessary times.
We already mentioned the need for protein to support the maintenance and growth of lean mass. Clients who have more muscle tissue have a higher resting metabolic rate because muscle burns more calories than fat to survive. A higher resting metabolic rate means more calories burned each day. Basic weight loss principles tell us more calories burned means more weight lost. So, this is the second reason why daily protein intake is important for body fat reduction.
You likely already know some of this, but you need to be able to convince your clients and people who ask you for fitness and nutrition advice. Tell them why getting enough high-quality protein is so important:
Also Check: How To Protect Your Kidneys From Further Damage
Signs That You’re Eating Too Much Protein
Most people don’t have to worry about serious health risks from eating too much protein, but you may experience minor side effects:
Bad breath: Excess protein can sometimes cause bad breath, due to bacteria breaking down the protein and emitting odors that can smell like cabbage or rotten eggs.
GI issues: Eating too many protein-rich foods may also mean you’re missing out on other essential nutrients like fiber, since protein-rich animal products don’t contain fiber. A low-fiber diet can cause digestive issues ranging from constipation, diarrhea, mild nausea, or fatigue after meals. It can also change your microbiome, the colony of beneficial bacteria and microorganisms that live in your gut.
Loss of appetite: Eating a lot of protein can also decrease appetite, says Fear, since it keeps you feeling full for longer. That can make it useful for weight-loss goals.
Weight gain: However, eating too much of anything can still lead to weight gain, so if you’re consuming too many calories in the form of protein, those excess calories will be stored as fat and lead to weight gain.
Higher Protein Intake Is Not Associated With Decreased Kidney Function In Pre
In this study, 355 pre-diabetic men and women were split into following two different dietary systems
- A moderate protein diet: 15% of energy
- A high protein diet: 25% of energy
The higher protein diet worked out at 1.6 grams protein per kilogram of body weight.
Throughout the study, lab tests demonstrated increased serum urea and urea excretion were consistent with increased protein intake.
After a 12-month period, there were no indications that the participants on higher protein diets had experienced any adverse effects on kidney function.
Interestingly, there was even a slight indication of improved kidney function with increasing protein intake.
In short, the study found no detrimental effects of a high protein diet on kidney health and no negative changes to any health markers.
Key Point:
Don’t Miss: How Long To Live With Kidney Disease
Can Too Much Protein Be Harmful To Your Kidneys
Increased muscle mass, strong bones, and encouraging a healthy metabolism are just some of the benefits associated with a high protein intake and are notably why protein tends to play a vital role in those who lift weights or are trying to gain muscle.
And while adding protein to our diets has important benefits for us all , too much protein can potentially be harmful to the kidneys with studies showing that a high protein diet can cause kidney stones and can worsen kidney function in those already living with kidney disease.
How Does Protein Get Into Urine
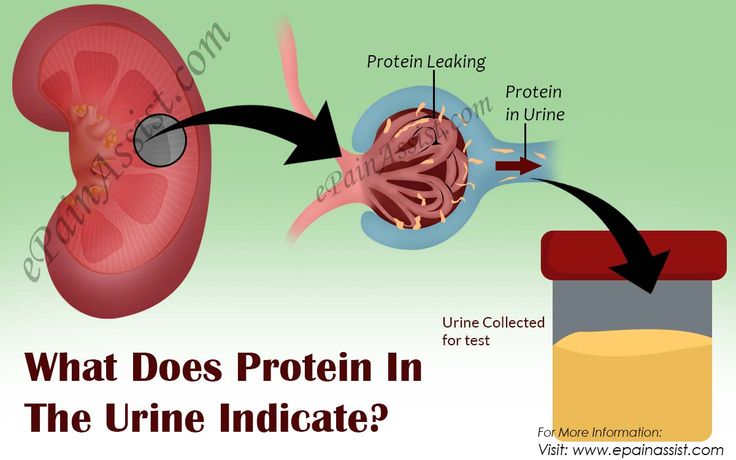
Protein gets into the urine if the kidneys arent working properly. Normally, glomeruli, which are tiny loops of capillaries in the kidneys, filter waste products and excess water from the blood.
Glomeruli pass these substances, but not larger proteins and blood cells, into the urine. If smaller proteins sneak through the glomeruli, tubules recapture those proteins and keep them in the body.
However, if the glomeruli or tubules are damaged, if there is a problem with the reabsorption process of the proteins, or if there is an excessive protein load, the proteins will flow into the urine.
You May Like: Can Drinking Too Many Sodas Cause Kidney Stones
Interaction With Drugs And Medication
Many older people take a regimen of prescription and over-the-counter drugs, often with vitamin and mineral supplements. Protein drinks, like Boost, that are often taken as a meal replacement for weight gain, contain high levels of vitamins and minerals that can add to this mix within the body and cause problems 4. You also shouldn’t drink Boost if you take blood thinners such as Coumadin and warfarin. The high amount of vitamin K in a Boost drink can directly affect the efficiency of these medications, warns AgingCare2.
Does Dietary Protein Affect Kidney Health
Protein is an essential macronutrient and is the building block of life. You need it to repair cells and make new ones.
The basic recommendations for protein intake are 0.8 grams per kilogram of body weight each day .
As we already mentioned, the belief is that too much protein can make your kidneys work harder than they need to since it adds more protein byproduct that needs to be removed.
The truth is, it will increase their workload a bit but its insignificant compared to the work your kidneys already do.
A 2016 study found that over a one-year period, 14 healthy men who alternated between a high protein diet and normal diet had no changes in their kidney function. The high protein diet was about 2.5 to 3.3 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight each day.
This is only the case for individuals with healthy kidneys. You do need to be aware if you deal with chronic kidney disease, as high protein intake can accelerate kidney damage.
Read Also: Does Cranberry Juice Help Flush Your Kidneys
Health Effects Of Protein Intake In Healthy Adults: A Systematic Literature Review
This systematic review analyzed the existing literature on protein intake and a range of different health conditions .
Regarding kidney health, the review found that there is inconclusive evidence that a higher protein intake can affect kidney function.
Among the notable points from this study was the findings of the European Food Safety Authority .
This food safety organization published their findings on protein intake and kidney health in 2012. Markedly, the EFSA deemed that there is insufficient evidence available to justify an upper level of protein intake for optimal kidney function.
On the negative side, this systematic review did find an association between kidney function decline and high protein intake in people with kidney disease.
Overall, the studys position is that there is no conclusive evidence to suggest that high protein diets cause harm.
However, the researchers do stress that they cant rule out high protein intake affecting kidney function in the long term since this research doesnt yet exist.
Key Point:
So When It Comes To Protein How Much Is Too Much
It’s hard to provide a specific answer since so much is still uncertain and the experts themselves don’t agree. However, for the average person it’s probably best to aim for no more than 2 gm/kg that would be about 125 grams/day for a 140-pound person. New information could change our thinking about the maximum safe amount, but until we know more about the safety, risks and benefits of high protein diets, this seems like a reasonable recommendation.
Don’t Miss: Can Your Kidneys Hurt If You Drink Too Much Water
Protein Does Not Cause Osteoporosis
Some people believe that a high protein intake can contribute to osteoporosis.
The theory is that protein increases the acid load of your body, which then causes the body to take calcium out of the bones to neutralize the acid .
Even though there are some studies showing increased short-term calcium excretion, this effect does not persist over the long term .
In fact, longer-term studies do not support this idea. In one 9-week study, replacing carbohydrates with meat did not affect calcium excretion and improved some hormones known to promote bone health, like IGF-1 .
A review published in 2017 concluded that increased protein intake does not harm the bones. If anything, the evidence pointed to a higher protein intake improving bone health .
Multiple other studies show that a higher protein intake is a good thing when it comes to your bone health.
For example, it may improve your bone density and lower the risk of fractures. It also increases IGF-1 and lean mass, both known to promote bone health .
There are plenty of other potentially helpful nutritional strategies. If you want to learn more, check out this article on 10 natural ways to build healthy bones.
Summary
Long-term studies show that a high protein intake may improve your bone health. It does not cause osteoporosis.
Eating Plenty Of Protein Is A Good Thing
There are many benefits associated with a high protein intake.
- Muscle mass: Adequate amounts of protein have a positive effect on muscle mass and are crucial to prevent muscle loss on a calorie-restricted diet (
- 24 ).
Overall, a higher protein intake is beneficial for your health, especially for maintaining muscle mass and losing weight.
Summary
There are many benefits to a high protein intake, such as weight loss, increased lean mass and a lower risk of obesity.
Don’t Miss: Is Lucozade Bad For Your Kidneys
What Else Causes Protein In Urine
Proteinuria causes are linked to other conditions. Diabetes and high blood pressure are the two leading causes of chronic kidney disease , and kidney damage from those two conditions can result in proteinuria. Lupus, arthritis and other immune system disorders can also cause proteinuria. Protein in the urine can even be a warning sign of pre-eclampsia during pregnancy.
Urinary Effects Of Excessive Protein Intake

The compounds present in your urine are determined, in part, by what you eat. Ketones are an acidic byproduct of high-protein intake. Protein is also about 16 percent nitrogen. As a result, the urine produced by a high-protein eater is acidic, with a higher nitrogen content. Although your bladder is designed to handle any type of urine, it is a good idea to increase your water intake if you are eating a lot of protein. This will help you stay hydrated and dilute urinary substances to protect your bladder in the long run.
Also Check: What Are The Symptoms Of Kidney Stones In A Female
Amino Acids Are Acids Right What About Acidity
Evidence is theoretically sound, but the acidity of excessive amino acids does not appear to be a clinical concern. It’s not potent enough to cause harm to most individuals.
Bone Mineral Density
In looking at large survey research, there appears to be no relation between protein intake and bone fracture risk except for when total calcium intake was below 400mg per 1000kcal daily, although the relation was fairly weak . Other reviews not similar ‘lack of correlation despite logic’ relations.
One intervention study noted that protein intake was actually positively associated with bone mineral density, but this correlation only was shown when the acidic effects of sulfate was controlled for.
Soy protein itself seems to have additional protective effects on bone mass in post-menopausal women, which may be due to the isoflavone content. For more information, please read our FAQ page on Soy Isoflavones.
The role of the Kidneys
Kidneys can acutely increase the Glomerular filtration rate , or the rate of filtration of the blood. They do this in response to dietary protein intake, and the lack of this compensation in some forms of kidney damage are a reason protein intake is controlled for in kidney disease management.
Additionally, the kidneys serve to regulate acid-base balance in the body via the sodium-bicarbonate buffering system. Disorders in acid:base balance can further pathophysiology of renal complications.
The role of Resistance Training