Structure The Kidneys Are Bean
Gerotas fascia is a thin, fibrous tissue on the outside of the kidney. Below Gerotas fascia is a layer of fat.
The renal capsule is a layer of fibrous tissue that surrounds the body of the kidney inside the layer of fat.
The cortex is the tissue just under the renal capsule.
The medulla is the inner part of the kidney.
The renal pelvis is a hollow area in the centre of each kidney where urine collects.
The renal artery brings blood to the kidney.
The renal vein takes blood back to the body after it has passed through the kidney.
The renal hilum is the area where the renal artery, renal vein and ureter enter the kidney.
The nephrons are the millions of small tubes inside each kidney. Each nephron has 2 parts. Tubules are tiny tubes that collect the waste materials and chemicals from the blood moving through the kidney. The corpuscles contain a clump of tiny blood vessels called glomeruli that filter the blood as it moves through the kidney. The waste products are passed through the tubules to the collecting ducts, which drain into the renal pelvis.
Tubular Reabsorption And Secretion
Tubular reabsorption occurs in the PCT part of the renal tubule. Almost all nutrients are reabsorbed, and this occurs either by passive or active transport. Reabsorption of water and some key electrolytes are regulated and can be influenced by hormones. Sodium is the most abundant ion and most of it is reabsorbed by active transport and then transported to the peritubular capillaries. Because Na+ is actively transported out of the tubule, water follows it to even out the osmotic pressure. Water is also independently reabsorbed into the peritubular capillaries due to the presence of aquaporins, or water channels, in the PCT. This occurs due to the low blood pressure and high osmotic pressure in the peritubular capillaries. However, every solute has a transport maximum and the excess is not reabsorbed.
In the loop of Henle, the permeability of the membrane changes. The descending limb is permeable to water, not solutes the opposite is true for the ascending limb. Additionally, the loop of Henle invades the renal medulla, which is naturally high in salt concentration and tends to absorb water from the renal tubule and concentrate the filtrate. The osmotic gradient increases as it moves deeper into the medulla. Because two sides of the loop of Henle perform opposing functions, as illustrated in Figure 22.8, it acts as a countercurrent multiplier. The vasa recta around it acts as the countercurrent exchanger.
What Outside Structure Helps Protect The Kidneys
Each kidney is maintained in place by connective tissue called renal fascia and is protected by a thick layer of adipose tissue called perirenal fat. Each kidney is surrounded by a stiff, fibrous, connective tissue renal capsule that provides support for the soft tissue inside. The renal capsule is closely applied to the kidney by strong ligaments so that no bone or other hard tissue can protrude from within the cavity of the kidney.
The outer portion of the kidney contains many small tubes that carry away waste products from the kidney to be eliminated. These tubes are called ureters. The inner part of the kidney consists of many lobes that function like little batteries to produce blood cells, maintain electrolyte levels, and control hormone production. This area is called the cortex.
The cortex is where most of the disease processes begin. Many cancers are believed to start as abnormal tissues growths that develop within these diseases’ specific cancer types. Tumors can grow slowly at first but eventually they can grow so fast that they block up the urinary tract causing pain, difficulty breathing, and sometimes death. Cancer is primarily treated with chemotherapy and radiotherapy. There are also several new treatments being tested that target the cancer’s genetic material . Genes are the instructions written into each cell’s DNA code that tell it how to behave and what to become.
Read Also: Is Watermelon Good For Ckd Patients
Why Do Men Get Beer Bellies
The thighs, arms, and backside are places where women tend to store fat, whereas the belly is where men do. Men with a beer gut develop visceral fat that bulges outward from their abdominal wall. When your kidneys, liver, and intestines are surrounded by this type of fat, it releases hormones that can interrupt the normal functions of these organs.
Renal Sinus Fat And Additional Metabolic Risk Factors
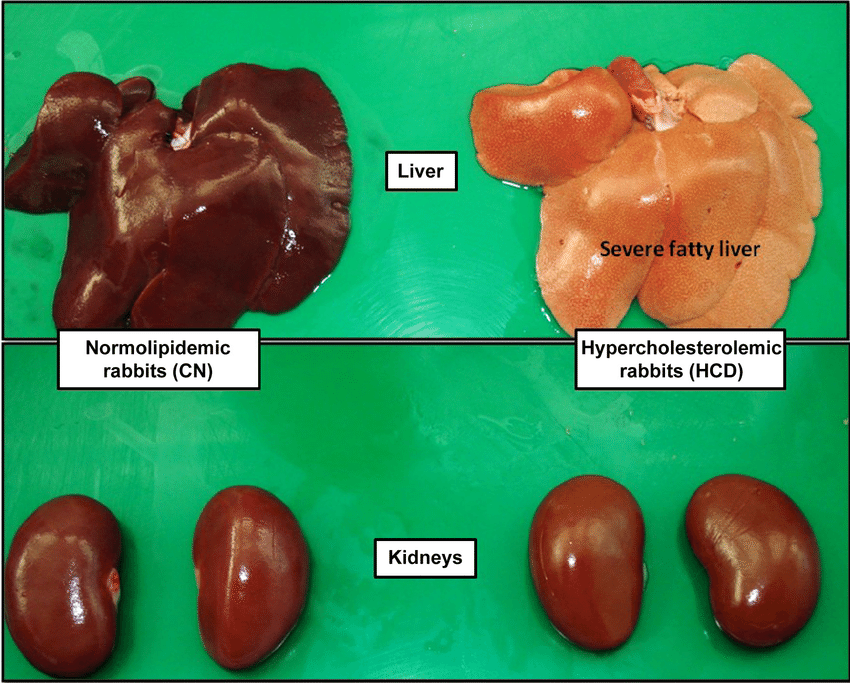
Fatty kidney was associated with an increased odds ratio for diabetes after age-and sex- adjustment , which was attenuated after adjustment for VAT similar results were observed for fasting blood glucose . Similarly, fatty kidney was associated with an increased odds ratio for high triglycerides but not after adjustment for VAT .
Recommended Reading: How Do You Know If You Have Bad Kidneys
What Are The Kidney Coverings
The renal capsule is a thin membranous sheath that wraps around the outside of each kidney. The capsule is made up of strong fibers, mostly collagen and elastin , which assist to maintain the kidney mass and protect it from harm. The renal capsule contains two sets of blood vessels that supply oxygen and nutrients to the kidneys and remove waste products.
The outermost layer of the kidney is called the cortex. The cortex consists of many lobes that appear gray on an x-ray image or at autopsy. It is made up of millions of tightly packed cells that produce hormones, enzymes, and other substances that regulate many parts of the body. The cortex is where most diseases affecting the kidney first become apparent.
The middle layer of the kidney is called the medulla. The medulla lies beneath the cortex and contains large numbers of elongated structures called nephrons. Each nephron is the site of filtration in the kidney, where urine is formed after passing through several layers of tissue. The medulla provides nourishment to the kidney by supplying it with water and minerals from the blood. It also removes waste products from the blood that would otherwise be removed by the liver before they can be eliminated in urine.
The innermost layer of the kidney is called the pyelum. The pyelum is the part of the kidney that produces urine.
What Structures Are Found In The Renal Hilum
The renal hilum is the entry and exit site for structures servicing the kidneys: vessels, nerves, lymphatics, and ureters. The medial-facing hila are tucked into the sweeping convex outline of the cortex. Emerging from the hilum is the renal pelvis, which is formed from the major and minor calyxes in the kidney.
You May Like: Is Watermelon Good For Your Kidneys
How Can I Increase My Kidney Size
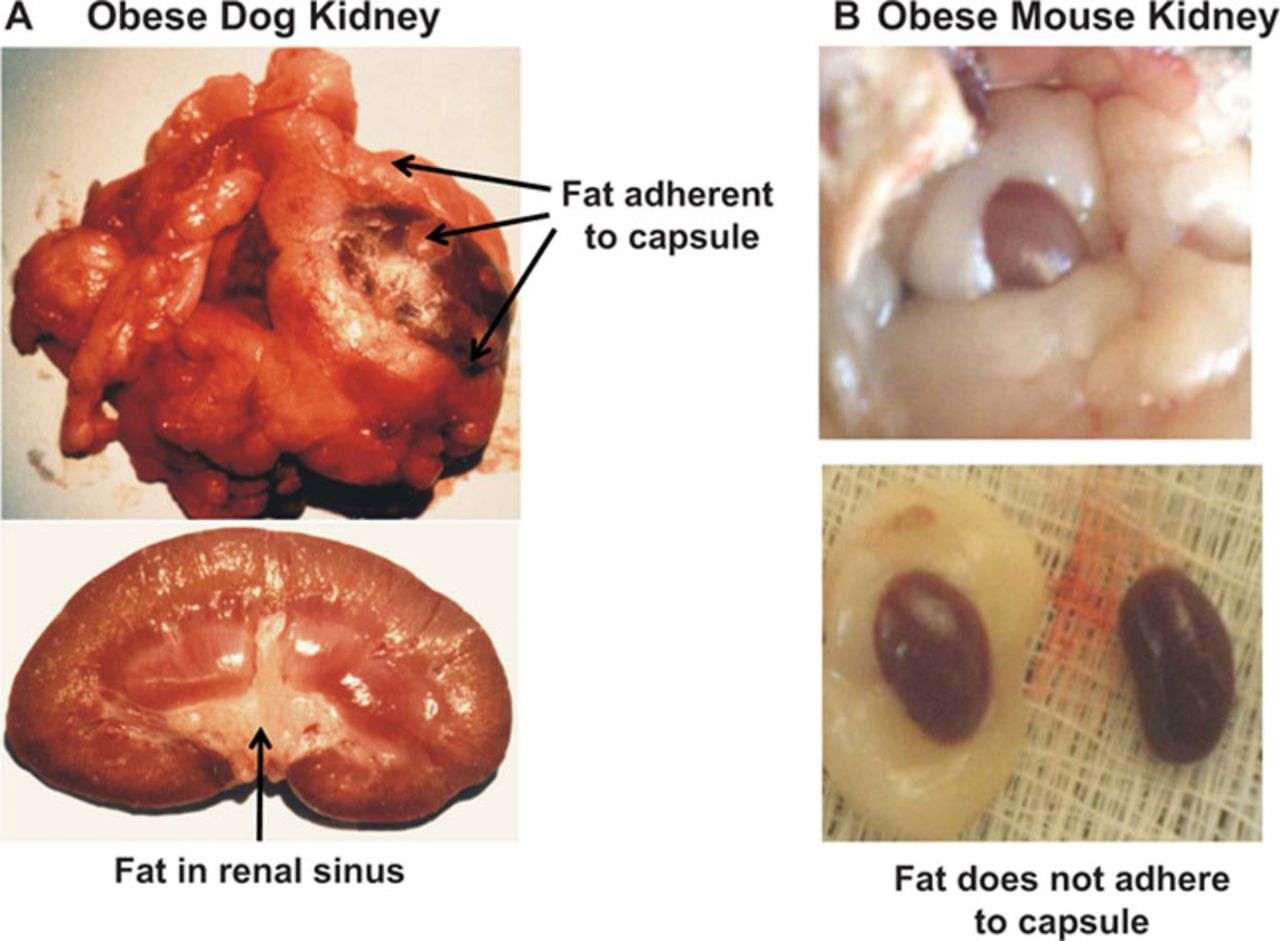
Why Is There Fat Around The Kidneys
Each kidney is held in place by connective tissue, called renal fascia, and is surrounded by a thick layer of adipose tissue, called perirenal fat, which helps to protect it. A tough, fibrous, connective tissue renal capsule closely envelopes each kidney and provides support for the soft tissue that is inside.
Also Check: Tamsulosin Hcl 0.4 Mg Capsule For Kidney Stones
What Are The Anatomical Structure Of The Kidney And Nephron
The nephron is the minute or microscopic structural and functional unit of the kidney. It is composed of a renal corpuscle and a renal tubule. The renal corpuscle consists of a tuft of capillaries called a glomerulus and a cup-shaped structure called Bowmans capsule. The renal tubule extends from the capsule.
What Is Perinephric Fat
Perinephric fat, also known as perirenal fat or the adipose capsule of the kidney, is a layer of fatty material that surrounds the kidneys. It plays an important role because it helps to cushion and protect the kidneys. Evaluation of this layer of tissue can be done either by ultrasonography or computed tomography scanning. Pathologic processes such as infection and cancers can affect this type of fat.
The human kidneys are surrounded by perinephric fat, which is composed of adipose tissue a collection of fat cells bound together by connective tissue and supplied by blood vessels. This layer of tissue is found outside of the outer surface of the kidney, but under a layer of connective tissue called the renal fascia. Typically, it is less than 1 inch in thickness.
You May Like: What Std Causes Kidney Pain
What Is The Role Of The Fatty Tissue Surrounding The Kidney
Kidneyskidneytissuesurroundedadipose tissuetissuekidneytissue
. Beside this, what is the function of the fat surrounding the kidney?
The renal capsule is a tough fibrous layer surrounding the kidney and covered in a layer of perirenal fat known as the adipose capsule of kidney. The adipose capsule is sometimes included in the structure of the renal capsule. It provides some protection from trauma and damage.
Also Know, what is the hilus of the kidney? structure of human kidneya deep vertical cleft, the hilus, which leads to a cavity within the kidney known as the renal sinus. The hilus is the point of entry and exit of the renal arteries and veins, lymphatic vessels, nerves, and the enlarged upper extension of the ureters.
In this way, what is perirenal fat and what is its function?
It’s the fatty cushion that prevents kidney from being damaged or even rupturing due to trauma/injuries.
What is the outer covering of the kidney called?
The outer portion of the kidney, located in between the renal capsule and the renal medulla, is the renal cortex.
What Is Another Name For The Renal Capsule
Bowmans capsule, also called Bowman capsule, glomerular capsule, renal corpuscular capsule, or capsular glomeruli, double-walled cuplike structure that makes up part of the nephron, the filtration structure in the mammalian kidney that generates urine in the process of removing waste and excess substances from the
Recommended Reading: Ginger Tea Dissolves Kidney Stones
What Is The Function Of The Perirenal Fat Capsule That Surrounds The Kidney
Each kidney is held in place by connective tissue, called renal fascia, and is surrounded by a thick layer of adipose tissue, called perirenal fat, which helps to protect it. A tough, fibrous, connective tissue renal capsule closely envelopes each kidney and provides support for the soft tissue that is inside.
Surface Mark Of Kidney On The Back
Its done inside parallelogram of Morris that is drawn in the following manner:
- First 2 horizontal lines are drawn 1 at the level of spine of T11 and other in the level of spine of L3.
- Afterward 2 vertical lines are drawn, 1 2.5 cm away and other 9 cm far from the posteromedian plane.
- The middle of hilum of the every kidney is located roughly at the lower border of L1.
Recommended Reading: Kidney Transplant Tattoo Ideas
Overall Study Sample Characteristics
Renal sinus fat ranged from the lower limit of detection in 133 participants to 4.89cm2 with a median value of 0.31cm2. The prevalence of fatty kidney was 30.9% in the overall sample . Individuals with fatty kidney were older, had a higher BMI, and a more adverse metabolic risk factor profile when compared to individuals without fatty kidney. The prevalence of hypertension, CKDcys, CKDcrea, and microalbuminuria were also significantly higher among those with as compared to those without fatty kidney . Age- and sex-adjusted correlations of renal sinus fat with adiposity measures and continuous covariates are presented in . Renal sinus fat was correlated with all covariates examined except UACR , with the strongest correlations observed for other adiposity measures and age.
Which Part Of The Human Body Is Bowman’s Capsule Found
The Bowman’s capsule is found in the outer part of the kidney, the cortex. Essentially, the capsule is a sealed, expanded sac at the end of the tubule, the rest of which elongates into a twisted and looped tubule in which urine is formed. Figure 9.2. Structural overview of a nephron, the functional unit of the kidney.
Also Check: Aleve And Kidney Problems
Abdominal Fat Distribution Patterns And Ckd
The prevalence of CKDcrea and CKDcys by fat distribution pattern category is presented in . The highest prevalence of both conditions was observed among individuals with fatty kidney and high VAT. The prevalence of CKDcys , but not CKDcrea varied across all four distribution categories. Among those with high VAT, the prevalence of CKDcys and CKDcrea were higher among those with fatty kidney when compared to those without fatty kidney .
Prevalence of Chronic Kidney Disease by Fatty Kidney and Abdominal Visceral Adipose Tissue Distribution Patterns
CKDcys is defined as eGFR< 60 mL/min/1.73m2, based on the Cystatin-C only CKD-EPI equation. CKDcrea is defined as eGFR< 60 mL/min/1.73m2, based on the modified MDRD Study Equation. Not fatty kidney and normal VAT Fatty kidney and Normal VAT Not fatty kidney and high VAT Fatty kidney and high VAT . For comparison, CKDcys and CKDcrea status at the 7th Offspring exam cycle are presented. P-values are adjusted for age and sex. CKDcrea available in 2943 participants . CKDcys available in 1206 participants with cystatin-C measures .
Mean imputed SBP and eGFRcys within renal sinus fat and VAT tertiles are presented in , respectively . When examining trends across renal sinus fat tertiles within VAT tertiles, we observed that mean SBP is higher and eGFRcys is lower as renal sinus fat increases within each VAT tertile, highlighting the association between renal sinus fat and SBP and eGFRcys.
Distilling The Facts About Horses’ Kidneys
Distilling the facts about kidneysWhere are the kidneys?What do the kidneys do?Waste processing and purificationFluid control and hormone productionKidney trouble
Signs of kidney dysfunction can be difficult to spot but may include:
- Abnormal urination, which may be increased, strong smelling or discoloured
- Weight loss
- Dental tartar and gum inflammation caused by the build up of urea and ammonia circulating in the blood
- Lethargy
- Lack of sheen or a rough coat
How is kidney dysfunction treated?Did you know?
References
You May Like: Apple Cider Vinegar Kidney
Cardiorenal Fat: A Cardiovascular Risk Factor With Implications In Chronic Kidney Disease
- 1Nephrology Department, Hospital Clínico Universitario, Institute of Health Research , Valencia, Spain
- 2Universidad de Valencia, Medicine School, Valencia, Spain
There is a growing interest in the potential role of adipose tissues in cardiac and renal pathophysiology, and determining the mechanisms by which fat compartments around the heart and kidneys influence cardiovascular disease is of clinical importance in both general and high-risk populations. Epicardial fat and perirenal fat have been associated with adverse outcomes in chronic kidney disease patients. Epicardial fat is a rich source of free fatty acids and is capable of secreting inflammatory and pro-atherogenic cytokines that promote atherosclerosis through a local paracrine effect. Recent evidence has demonstrated that perirenal fat has a closer correlation with kidney diseases than other visceral fat deposits in obesity or metabolic disturbances. Moreover, perirenal fat has been reported as an independent risk factor for CKD progression and even associated with cardiorenal dysfunction. Accordingly, these forms of organ-specific fat deposits may act as a connecter between vascular and cardiorenal disease. This review explores the possible links between epicardial and perirenal fat and its significant role as a modulator of cardiorenal dysfunction in CKD patients.
Why Is My Husbands Stomach So Big And Hard
A swollen stomach or feeling hard could be the result of eating too much or drinking too much carbonated drinks, both of which are easily curable. Inflammatory bowel diseases may also contribute to a headache. When you drink a soda too quickly, you may experience a hard stomach from the accumulated gas.
Recommended Reading: Ginger Good For Kidneys
Renal Sinus Fat And Renal Function
Among participants with cystatin-C measurements , 5.9% had CKDcys. Fatty kidney was associated with an increased odds ratio for CKDcys , which persisted after adjustment for BMI and VAT . Fatty kidney was associated with an increased odds ratio for CKDcrea after age- and sex-adjustment but not after multivariable adjustment .
The prevalence of microalbuminuria was 13.4% among individuals with fatty kidney and 6.0% among those without fatty kidney . Fatty kidney was associated with an increased odds ratio of microalbuminuria in age- and sex-adjusted models , which was attenuated and no longer statistically significant after multivariable adjustment .
What Is A Fatty Tumor On The Kidney
A fatty tumor on the kidney, called angiomyolipoma, is a benign mass composed of fat, blood vessels and smooth muscle. A benign tumor is noncancerous and cannot metastasize or spread to other parts of the body but it can grow and destroy other tissue, according to the Canadian Cancer Society.
An angiomyolipoma can be either sporadic, which accounts for 80 percent of cases, or it can be a sign of tuberous sclerosis, notes the Tuberous Sclerosis Alliance. Sporadic angiomyolipomas occur most often in women as a single tumor in one kidney. Tuberous sclerosis, which accounts for 20 percent of angiomyolipomas, can produce multiple tumors that are larger and affect younger people of both sexes in both kidneys.
An accurate diagnosis by ultrasound, CT or MRI of a fatty tumor depends on the fat content, explains the Tuberous Sclerosis Alliance. It can be difficult to differentiate between a malignant tumor and a benign angiomyolipoma. Patients with tuberous sclerosis and renal angiomyolipomas are more likely to develop malignant kidney tumors than people with renal angiomyolipomas and no sign of tuberous sclerosis. Benign fatty tumors often do not require treatment unless they grow larger than 4 centimeters, are malignant or cause an obstruction in the kidney.
Also Check: Tea Good For Kidneys