What Is Dorsal And Ventral
Dorsal and ventral are paired anatomical terms used to describe opposite locations on a that is in the anatomical position. The anatomical position of a human body is defined as a standing upright with the facing forward, arms down at the sides with the palms turned forward, and feet parallel facing forward. On a human body, dorsal refers to the back portion of the , whereas ventral refers to the front part of the . The terms dorsal and ventral are also often used to describe the relative location of a part. For example, the stomach is ventral to the , which means that the stomach is located in front of the spinal cord.
What Is The Difference Between Dorsal And Ventral
The main difference between dorsal and ventral is the area of the to which they refer. In general, ventral refers to the front of the , and dorsal refers to the back. These terms are also known as anterior and posterior, respectively.
However, for certain parts of the , the uses of ventral and dorsal differ from the standard definition. For instance, the dorsal part of the is the area that is closest to the abdomen when erect. Similarly, for the feet, the dorsal side is the top of the foot, or the area facing upwards when standing upright.
Join millions of students and clinicians who learn by Osmosis!
Secretion Of Active Compounds
The kidneys release several important compounds, including:
- Erythropoietin: This controls erythropoiesis, which is the production of red blood cells. The liver also produces erythropoietin, but the kidneys are its main producers in adults.
- Renin: This enzyme helps manage the expansion of arteries and the volumes of blood plasma, lymph, and interstitial fluid. Lymph is a fluid that contains white blood cells, which support immune activity, and interstitial fluid is the main component of extracellular fluid.
- Calcitriol: This is the hormonally active metabolite of vitamin D. It increases both the amount of calcium that the intestines can absorb and the reabsorption of phosphate in the kidney.
A range of diseases can affect the kidneys. Environmental or medical factors may lead to kidney disease, and they can cause functional and structural problems from birth in some people.
Recommended Reading: Will A Muscle Relaxer Help Pass A Kidney Stone
Standing Paralumbar Fossa Celiotomy
The abdominal cavity can be approached via a standing paralumbar fossa celiotomy on the right or left side of the abdomen. The incision should be made in the caudal third of the fossa to facilitate exteriorization of the uterus . The celiotomy should be large so that delivery of the uterus is more easily accomplished. If the right side is elected, the incision should not extend too far ventrally so there is no problem with intestines prolapsing out of the surgical incision. A sharp skin incision approximately 40cm long is made in the skin and continued through the subcutaneous tissue as well as the internal and external abdominal oblique muscles. The peritoneum and transversus abdominis should be tented with a forceps and incised with scissors. A finger should be inserted into the abdomen and the peritoneum should be swept for any adhesions before the incision is extended. The peritoneum can be left open or closed with the transversus abdominis. The external and internal abdominal muscles are closed next, followed by the skin. A simple continuous pattern using an absorbable suture material can be used on all muscle layers. The skin is usually apposed with an interlocking pattern by using a nonabsorbable suture. It is recommended the most ventral portion of the skin incision be closed with interrupted skin sutures, so the incision can be drained ventrally if necessary.
Danielle L. Brown, … John M. Cullen, in, 2017
What Is The Function Of The Peritoneum
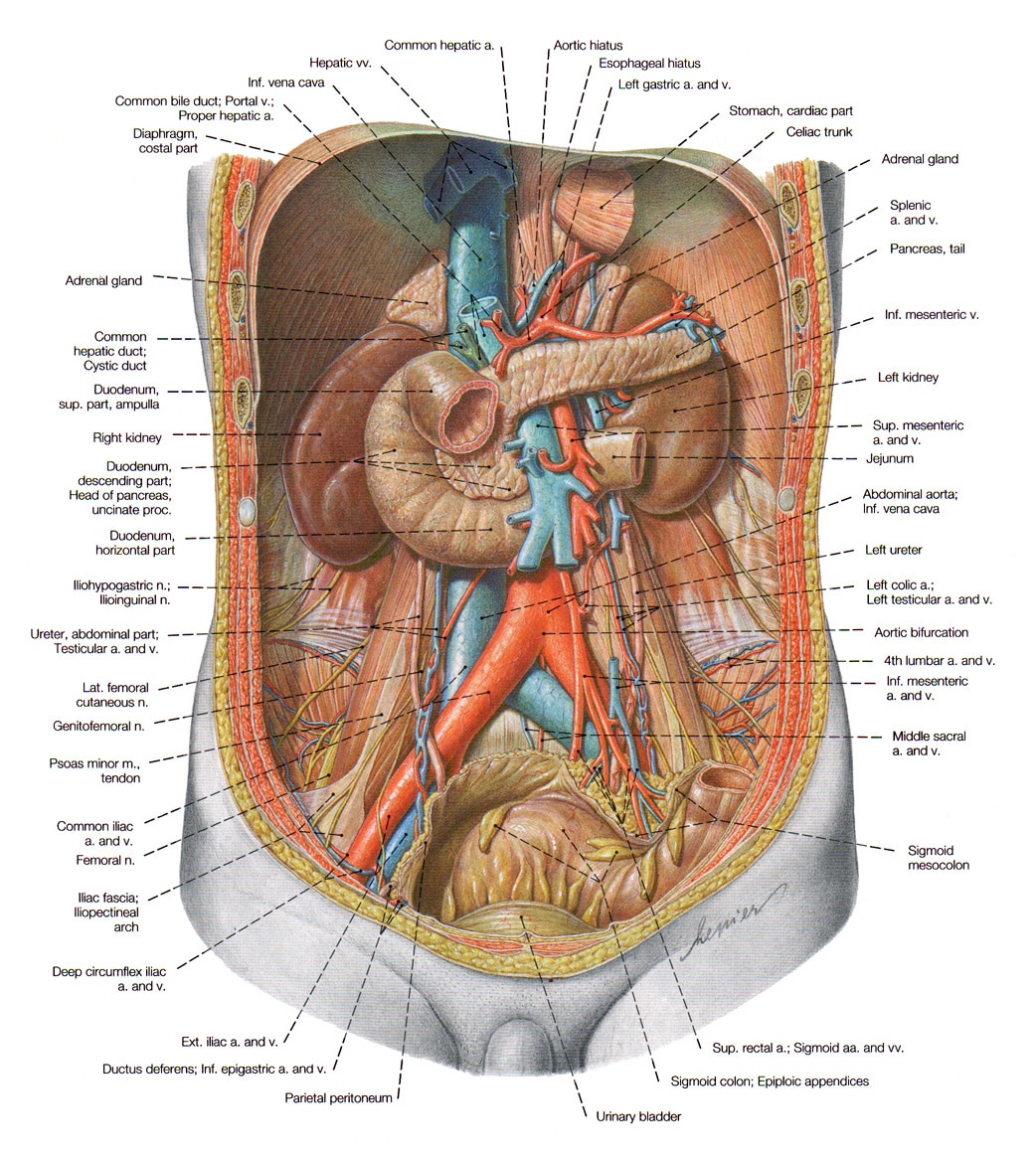
Your peritoneum has several functions, some of which researchers are still learning about. It provides:
- Insulation. Layers of the peritoneum contain fat that warms and protects your organs.
- Lubrication. Peritoneal fluid lubricates your organs inside of your peritoneal cavity .
- Structure. Ligaments in your peritoneum connect your organs to each other and attach your intestines to your back abdominal wall.
- Blood, lymph and nerve supply. Nerves and vessels run through the layers of your peritoneum.
- Immunity. Your peritoneum serves as a barrier to injury and pathogens in your abdominal cavity. It recognizes invasive particles and sends in white blood cells to target them. It filters fluids in your peritoneal cavity and drains waste products away. The tissue also has rapid healing properties to repair its own injuries. Researchers are still exploring these properties.
Don’t Miss: Is A Keto Diet Good For Someone With Kidney Disease
Organ Systems Working Together
Organ systems often work together to do complicated tasks. For example, after a large meal is eaten, several organ systems work together to help the digestive system obtain more blood to perform its functions. The digestive system enlists the aid of the cardiovascular system and the nervous system. Blood vessels of the digestive system widen to transport more blood. Nerve impulses are sent to the brain, notifying it of the increased digestive activity. The digestive system even directly stimulates the heart through nerve impulses and chemicals released into the bloodstream. The heart responds by pumping more blood. The brain responds by perceiving less hunger, more fullness, and less interest in vigorous physical activity, which preserves more blood to be used by the digestive system instead of by skeletal muscles.
Communication between organs and organ systems is vital. Communication allows the body to adjust the function of each organ according to the needs of the whole body. In the example above, the heart needs to know when the digestive organs need more blood so that it can pump more. When the heart knows that the body is resting, it can pump less. The kidneys must know when the body has too much fluid, so that they can produce more urine, and when the body is dehydrated, so that they can conserve water.
Donât Miss: What Eases Kidney Stone Pain
What Medical Treatments Involve The Peritoneum
- Peritoneal dialysis. The peritoneum is so effective at filtering waste products that sometimes healthcare providers use it as a method of dialysis to treat people living with kidney failure. Dialysis does the work of your kidneys by removing waste products and excess fluid from your blood. During the process, you or your healthcare provider fill your peritoneal cavity with a fluid solution. Your peritoneum filters the fluid, and later, you or your healthcare provider drain it out.
- Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy . HIPEC is a new, targeted form of chemotherapy that takes advantage of the absorbent properties of your peritoneum. Its a concentrated, heated chemotherapy solution thats delivered directly into your peritoneal cavity. If you have localized cancer in your peritoneal cavity, HIPEC can treat it locally. This is a unique alternative to traditional chemotherapy, which is delivered systemically through your bloodstream and is associated with many side effects. It may also be more effective.
- Cytoreductive/debulking surgery. Cancer in your abdominopelvic cavity will usually be treated with surgery, as well as chemotherapy. Cytoreductive or debulking surgery attempts to remove as many cancer cells as possible, wherever theyre found. Sometimes, that means removing part or all of your peritoneum . The most common part affected is your omentum. Certain types of cancer tend to spread there first, and sometimes, an omenectomy removes it.
Also Check: What Helps Pass A Kidney Stone Faster
Where Are The Kidneys And Liver Located News Medical
- Highest rating: 3
- Low rated: 3
- Summary: The kidneys are bean-shaped organs located in the upper retroperitoneal region of the abdomen. That is, they are located behind the smooth peritoneal lining of
See Details
- Highest rating: 3
- Low rated: 3
- Summary: The abdominal cavity holds digestive organs and the kidneys, and the pelvic cavity holds reproductive organs and organs of excretion. Dorsal Cavity. The dorsal
See Details
What System Is The Kidney Part Of
| Thyroid gland Parathyroid gland Adrenal glands Pituitary gland Pancreas Stomach Pineal gland Ovaries Testes | |
| Urinary | Kidneys Ureters Bladder Urethra |
Likewise, how does the kidney work with other systems? The excretory system is a close partner with both the circulatory and endocrine system. The circulatory system connection is obvious. Blood that circulates through the body passes through one of the two kidneys. Urea, uric acid, and water are removed from the blood and most of the water is put back into the system.
Also to know is, is the kidney part of the digestive system?
Wikijunior:Human Body/Digestive System/Kidneys. Kidneys are pairs of organs located in the back of the abdominal cavity. Each kidney is important to keep your body balanced and well suited.
What organs are part of two systems?
Answer and Explanation:
Recommended Reading: How Do The Kidneys Compensate For Acid Base Imbalances
What Are The Six Body Cavities
Anatomical terminology for body cavities: Humans have multiple body cavities, including the cranial cavity, the vertebral cavity, the thoracic cavity , the abdominal cavity, and the pelvic cavity.
Which is the most protective body cavity?
The cranial cavity is the most protective body cavity. It surrounds the brain in bone, soft tissue, and a protective layer of liquid which reduces the strain and damage from impacts. The vertebral cavity is similar, but has gaps were the nerves must enter or exit.
Which body cavity is divided into four quadrants?
The abdominal cavity in the human body has four parts or quadrants, located inside our abdomen. First, the upper-right quadrant consists of the liver, stomach, duodenum, pancreas, colon, transverse colon and right kidney.
What body cavity contains the liver and stomach?
The abdominopelvic cavity is a body cavity that consists of the abdominal cavity and the pelvic cavity. It contains the stomach, liver, pancreas, spleen, gallbladder, kidneys, and most of the small and large intestines. It also contains the urinary bladder and internal reproductive organs. Click to see full answer.
What is the major body cavity?
The body has two major cavities: dorsal , including the cranial and spinal cavities ventral , including the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities.
Functions Of Major Organs And Conditions That Can Damage Them
Table 1: Organ functions and damaging conditions
| Organ | Conditions that may damage the organ | Possible symptoms of organ damage | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brain | Controls all other organs and their functioning |
|
|
| Heart | Pumps blood to deliver a continuous supply of oxygen and other nutrients to other organs |
|
|
| Helps oxygen breathed air to enter the red cells in the blood |
|
|
|
| Kidneys | Filters blood and removes waste products through urine |
|
|
| Liver | Removes waste products and foreign substances from the blood, regulates blood sugar levels, and produces essential nutrients such as albumin |
|
|
Also Check: Do Kidney Stones Cause Headaches
Functions Of The Liver
The liver regulates most chemical levels in the blood and excretes a product called bile. This helps carry away waste products from the liver. All the blood leaving the stomach and intestines passes through the liver. The liver processes this blood and breaks down, balances, and creates the nutrients and also metabolizes drugs into forms that are easier to use for the rest of the body or that are nontoxic. More than 500 vital functions have been identified with the liver. Some of the more well-known functions include the following:
-
Production of bile, which helps carry away waste and break down fats in the small intestine during digestion
-
Production of certain proteins for blood plasma
-
Production of cholesterol and special proteins to help carry fats through the body
-
Conversion of excess glucose into glycogen for storage and to balance and make glucose as needed
-
Regulation of blood levels of amino acids, which form the building blocks of proteins
-
Processing of hemoglobin for use of its iron content
-
Conversion of poisonous ammonia to urea
-
Clearing the blood of drugs and other poisonous substances
-
Regulating blood clotting
-
Resisting infections by making immune factors and removing bacteria from the bloodstream
-
Clearance of bilirubin, also from red blood cells. If there is an accumulation of bilirubin, the skin and eyes turn yellow.
Fundamental Concepts To Which Crystal System Does This Unit Cell Belong 31 What Is
3.2Fundamental Concepts To which crystal system does this unit cell belong? 3.1 What is the difference between atomic structure and crystal structure? What would this crystal structure be called? Crystal Systems Calculate the density of the material, given that its atomic weight is 145 g/mol. 3.2 The accompanying figure shows a unit cell for a hypothetical metal. gix oF OCKI 2ire ebcomreg in z4 ebn doss eosi ba +2 mstera ixa ed 900 Xese 0.40â¦
Don’t Miss: How Do You Know If You Have Kidney Disease
Filtration Reabsorption And Secretion
Nephrons: The Basic Functional Units Of Blood Filtration And Urine Production
Each kidney contains over 1 million tiny structures called nephrons. The nephrons are located partly in the cortex and partly inside the renal pyramids, where the nephron tubules make up most of the pyramid mass. Nephrons perform the primary function of the kidneys: regulating the concentration of water and other substances in the body. They filter the blood, reabsorb what the body needs, and excrete the rest as urine.
Read Also: How To Clean Out Your Kidneys
The Mouth Cavity Pharynx Esophagus And Stomach
- The Mouth.
- Ingestion starts with the mouth. Teeth cut and grind food into smaller particles. Tongue and teeth MASTICATE food breaking it down into smallerparticles. The tongue is composed of SKELETAL muscle covered by mucous membrane, and helps when swallowing. The TASTE BUDS are located in the mucous membrane, when stimulated by food a nervous signalis sent which causes the salivary and gastric glands to secrete saliva. Saliva helps lubricate and moisten food, but also contains ENZYMES that begin to digest food while it is still in the mouth.
- The pharynx
- is a mucusulomembranus sack like structure which acts as a passageway for chewed food, and as an airway during respiration.
- The oesophagus
- is a long narrow mucusulomembranus tube, about 10 inches long. It is very flexible and stretches from the pharynx to the stomach. It propels food down to the stomach by awavelike movement of the esophagus muscles.
- Sphincters
- are bands of ring like muscle that act as gateways to natural openings or âorificesâ at various locations in the body. The muscles close the opening by contracting, and open it byrelaxing. The cardiac sphincter is at the base of the oesophagus near the heart, it relaxes to allow food to enter the stomach.
- The Stomach
- is a muscular, curved pouch like structure. It churns food and mixes it with various lubricating and digestive secretions. Food enters from the esophagus via the cardiacsphincter and is sent to the small intestine via the PYLORIC Sphincter.
Kidney Pain Location And Sensation
Most people tend to associate pain in the area between the ribs and hips as either digestive problems or muscular back pain. However, kidney pain isnt always felt in the same place as the kidneys location.
Dr. Charles Patrick Davis on MedicineNet explains that renal or flank pain can be felt anywhere between the lowest rib and the buttocks. The pain may also radiate to the groin or abdominal area. Depending on the underlying cause of the kidney pain, you may feel the pain in just the left or right side of your back. However, sometimes kidney pain affects both sides of the back.3
Read Also: What Arthritis Meds Are Safe For Kidneys
Also Check: Can Taking Creatine Cause Kidney Problems