Polycystic Kidney Disease Symptoms
Most individuals present with complications of polycystic kidney disease. However, increasing numbers are being detected by screening individuals who have an affected relative.
Complications associated with renal disease
- Impaired urine concentrating capacity is a common early presentation with problems associated with excessive water and salt loss such as nocturia.
- Loin pain is the most common symptom, reported by about 60% of affected adults. It can be caused by renal haemorrhage, stones and urinary tract infections . However, chronic loin pain, without an obvious identifiable cause beyond the cysts themselves, develops in a proportion of patients.
- Hypertension is a common presenting feature. 10-15% of affected children are hypertensive, and 50% of affected adults have normal renal function. Hypertension is associated with left ventricular hypertrophy.
- Bilateral kidney enlargement – abdominal examination may reveal enlarged and palpable kidneys.
- Gross haematuria following trauma is a classic presenting feature of ADPKD. It occurs in 30-50%. Renal colic due to clots in the collecting system can be severe. Usually the bleeding is quite brief, reverting to microscopic levels in a few days.
- UTI and pyelonephritis may be presenting features.
- Renal stones are twice as common as in the general population. Uric acid stones are more common than calcium oxalate stones.
- Patients sometimes present with kidney failure, usually in the fourth to sixth decade of life.
Growth Factor And Cytokine Signaling Pathways
Cell proliferation and cell cycle modifying pathways can affect cystogenesis, particularly through inhibition of ERB, Src, CDK and STAT3/STAT6 signaling. Promising results have been noted with the CDK inhibitor, roscovitine. It produced a sustained effect after one administration, halting progression of cystic kidney disease in two mouse models . EGF signaling has been linked to cystogenesis, and its inhibition by EKI-785 or EKB-569 slowed the progression of PKD in one rat model. SKI-606, also known as bosutinib, is a Src-kinase specific inhibitor that has been shown to interfere with renal cyst formation in two rodent models of PKD and has recently entered a phase II randomized clinical trial . Similarly, an experimental drug called KD019 is under investigation in a phase Ib/IIa trial in ADPKD patients . KD019 is a multispecific inhibitor of a number of cytoplasmic and receptor tyrosine kinases, simultaneously targeting EGFR, HER2, Src, VEGFR and EphB4R, while having weak activity against other kinases, and has so far only been studied in the context of non-small-cell lung cancer . Finally, preliminary experimental data on curcumin and pyrimethamine suggest activity against STAT3 and STAT6 signaling in laboratory models of PKD, but more research including human study data need to be obtained in order to establish their true therapeutic potential .
Kidney Failure And Transplant Options
One of the most serious complications of PKD is kidney failure. This is when the kidneys are no longer able to:
- filter waste products
- maintain fluid balance
- maintain blood pressure
When this occurs, your doctor will discuss options with you that may include a kidney transplant or dialysis treatments to act as artificial kidneys.
If your doctor does place you on a kidney transplant list, there are several factors that determine your placement. These include your overall health, expected survival, and time you have been on dialysis.
Its also possible that a friend or relative could donate a kidney to you. Because people can live with only one kidney with relatively few complications, this can be an option for families who have a willing donor.
The decision to undergo a kidney transplant or donate a kidney to a person with kidney disease can be a difficult one. Speaking to your nephrologist can help you weigh your options. You can also ask what medications and treatments can help you live as well as possible in the meantime.
According to the University of Iowa, the average kidney transplant will allow kidney function from 10 to 12 years.
You May Like: Apple Cider Vinegar For Kidney
How Can Polycystic Kidney Be Reversed With Ayurvedic Treatment
Ayurvedic diagnosis and healing way to counteract PKD!
As per Ayurvedic theories, the unbalancing in any of the Tri-Doshas of the human body can result in health-related problems. These Tri-Doshas are Vata, Pitta, and Kapha. Apart from that, there are some biological energies. A specific balance of Tri-Doshas and other vital energies is a must for good health.
When it comes to kidney disease, the formation of urine occurs in the intestine itself through the filtration process that takes place in the kidneys. Apart from Tri-doshas, an imbalance of Agni disturbs natural urine formation. Malformation in urine leads to wastes accumulation in the body. This accumulation is called Ama Sanchaya in Ayurveda. The condition of Ama accumulation causes
- tiredness
- puffiness around the eyes
- disturbed electrolytes balance
Mutravaha Srotas is also imbalanced when you have any kidney problem. Polycystic kidney disease is one of the fatal kidney problems. As all the three doshas and Mutra Vaha Srotas are involved in kidney diseases, therefore, treating kidney disease is challenging, and a patient has to be consistent and dedicated to the treatment.
Ayurvedic treatment for PKD mainly combines some herbal formulations, age-old therapies, a kidney health-supporting diet and a few alterations in day-to-day life.
Some Ayurvedic herbs used in Polycystic kidney disease Ayurvedic treatment are as below
Treatment Prospects For Autosomal
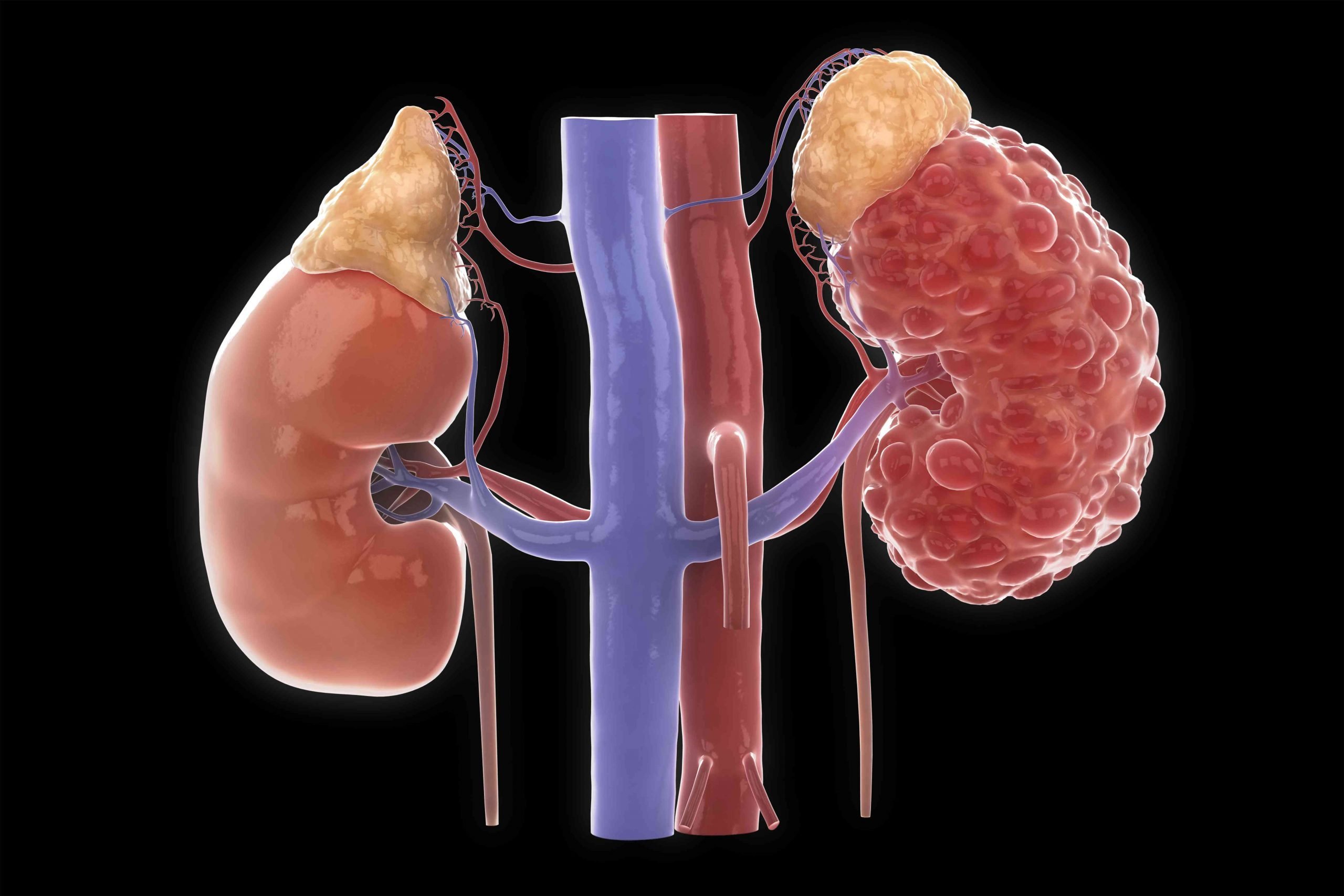
Treatment prospects for autosomal-dominant polycystic kidney disease. An increased understanding of the molecular genetic and cellular pathophysiologic mechanisms responsible for the development of autosomal-dominant polycystic kidney disease , made possible by the advances in molecular biology and genetics of the last three decades, has laid the foundation for the development of effective therapies. As the concept that a polycystic kidney is a neoplasm in disguise is becoming increasingly accepted, the development of therapies for ADPKD may benefit greatly from the expanding body of information on cancer chemoprevention and chemosuppression. This review summarizes the observations that already have been made and discusses therapies for PKD that deserve investigation.
- Previous article in issue
Also Check: Is Apple Cider Vinegar Bad For Your Kidneys
The Role Of Adh In Pkd
ADH helped life evolve from oceans to land, eons ago. If it weren’t for ADH, many living organisms would be unable to withstand the harsh dehydrating influence of the warmer land surface under a blazing sun.
Produced by a part of the brain called the hypothalamus, ADH is a hormone that acts on the kidneys and makes them retain and conserve water. It is what makes urine look dark and concentrated when you have not had enough water to drink or spent a day outside in the hot sun. It can, therefore, influence how much water needs to be excreted and how much must be “recycled” to meet the body’s needs .
How does ADH fit into the discussion on CKD? Studies have shown that ADH is one of the major promoters of cyst growth in PKD. In other words, if you could somehow lower ADH levels, or block its action on the cysts, it might be possible to slow down cyst growth and the inexorable progression of PKD.
Ayurveda Treatment For Polycystic Kidney Disease
Ayurvedic treatment in polycystic kidney disease becomes an ideal choice to go for. Ayurveda originated in India, however today it is a globally popular concept for its results. Ayurveda is holistic in nature, i.e., it not just accounts for the symptoms of a disease but also caters to other factors such as conditions of mind, body and soul.
Ayurveda treatment in polycystic kidney diseasealso makes it the ideal treatment alternative as it has no side effects on the body. Unlike other treatment alternatives such as Dialysis and kidney transplant, it is affordable and result-oriented.
Also Check: Is Ibuprofen Metabolized In The Kidneys
What Is The Polycystic Kidney Disease Treatment
Because polycystic kidney disease can lead to renal failure, treatment for ADPKD focuses on decreasing kidney function decline and includes the following steps:
- Lifestyle changes
- Avoid contact sports that can result in internal bleeding due to direct trauma.
Medications-
- Medication for high blood pressure
- ACE inhibitors
- Angiotensin II receptor inhibitors
- Urinary tract infection treatment
- Ciprofloxacin, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, clindamycin, and chloramphenicol are some of the antibiotics used.
Pain management-
- Stay away from nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines
- Large cysts may necessitate surgery.
- Tolvaptan is a drug that is used to decrease the decline of kidney function in adults who are at risk of developing ADPKD quickly.
End-stage renal disease is treated with renal replacement therapy
- Hemodialysis
- Peritoneal dialysis
- Kidney transplantation
Intracranial aneurysms and their treatmentbecause treatment for people with ADPKD is difficult, aneurysm surveillance is required.
Polycystic kidney disease is a more advanced stage of kidney disease. Proper and quick treatment is necessary to avoid any life-threatening reasons. Polycystic kidney disease can be effectively treated with Ayurvedic kidney treatment for the rest of one’s life.
Are There Different Types Of Polycystic Kidney Disease
There are two types of polycystic kidney disease:
- Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease : ADPKD is the most common form of PKD. Its usually diagnosed in adulthood, between the ages of 30 and 50. ADPKD is usually diagnosed in adulthood, between the ages of 30 and 50, but it may occur in early childhood or adolescence.
- Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease : ARPKD is a rare form of PKD, also called infantile PKD. It causes abnormal kidney development in the womb or soon after birth.
You May Like: Is Aleve Hard On Your Kidneys
What Causes Polycystic Kidney Disease
People who have PKD were born with it. PKD is almost always inherited from a parent or from both parents. People of all genders, ages, races, ethnicities and nationalities can have PKD. Men and women get PKD equally as often. If you have a blood relative with PKD, you are more likely to have PKD or carry the gene that causes it. If you carry the gene that causes PKD but you do not have the disease, you are called a carrier. This is possible with autosomal recessive PKD.
Genetic Counselling For Polycystic Kidney Disease
If you or a family member have been diagnosed with PKD, or if PKD runs in your family, it can be helpful to speak to a genetic counsellor. Genetic counsellors are health professionals qualified in both counselling and genetics. As well as providing emotional support, they can help you to understand PKD and what causes it, how it is inherited, and what a diagnosis means for your health, lifestyle, and plans for the future. Genetic counsellors are trained provide information and support that is sensitive to your family circumstances, culture and beliefs.
If PKD runs in your family, a genetic counsellor can explain what genetic testing options are available to you and other family members. You may choose to visit a genetic counsellor if you are planning a family, to find out your risk of passing that condition on to your child, or to arrange for prenatal tests.
is connected with a wide range of support groups throughout Victoria and Australia and can connect you with other individuals and families affected by MCKD.
Also Check: Can Carbonated Water Cause Kidney Stones
Can Polycystic Kidney Disease Be Treated Naturally
Mr. Luo, at the age of 29, have been upset recently, even though his serum creatinine level reduces from 650 umol/L to 368 umol/L. That makes doctors and nurses so confused.
Mr.Luo has ten-year history of Polycystic Kidney Disease . Having been treated in many hospitals, but he still have relapsing PKD. Hospitalization has been one big part of his life.
Once when he moved, he took things too hard. As a result, a sharp pain occurs in the back. He went to hospital immediately and found kidney cyst rupture. Later, his renal function decreases and now he has to take regular dialysis.
As you know, dialysis is usually a permanent and bring great financial pressure on this family. Fortunately, he came to our hospital and was treated with Traditional Chinese Medicine . His renal function is improved, and he can get rid of dialysis.
It is an exciting thing that Mr.Luo can stop dialysis and come back to work. But he is still upset, since his son is diagnosed with Polycystic Kidney Disease. Even he know this will happen one day, but he cannot face it. What if his son have to stay in hospital, just like him?
Who Gets Polycystic Kidney Disease
- Clinical registry data show prevalence rates of diagnosed cases ranging from 1 in 543 to 1 in 4,000. Approximately 4-7 million individuals are affected in the world and account for 7% to 15% of patients on renal replacement therapy.
- It accounts for about 10% of people on dialysis. Annual incidence rates of end-stage kidney disease caused by ADPKD are between 6-8 per million per year in Europe.
- Sex incidence is equal although males may be slightly more seriously affected.
- There is no racial predilection.
Read Also: Is Pomegranate Juice Good For Your Kidneys
Treatment Of Polycystic Kidney Disease
Currently there is no cure for PKD. However, early detection and treatment can reduce or prevent some of the complications of PKD.Common complications and their treatments include:
- high blood pressure controlling high blood pressure is very important. Antihypertensive medication may be prescribed
- pain may be due to kidney stones, bleeding or infection. Treatment will depend on the cause. Talk to your doctor if you are getting repeated or severe back and kidney pain or headaches. Cysts can sometimes be drained to relieve extreme back and leg pain
- blood in the urine fluids, pain-relieving medication, antibiotics and bed rest may be recommended
- urinary tract infections symptoms may include frequent urination, painful urination and fever. Consult with your doctor immediately about treatment with antibiotics. An untreated urinary tract infection can spread to the kidneys
- kidney failure this is treated by dialysis, which is a procedure to remove waste products and extra water from the body by filtering the blood through a special membrane. A kidney transplant is another treatment option. PKD does not redevelop in the transplanted kidney.
Clinical trials have begun in Australia to test medication that alters the production of fluid by the kidney and appears to slow down cyst formation.
Clinical trials have begun in Australia to test medication that alters the production of fluid by the kidney and appears to slow down cyst formation.
Diagnosis And Genetic Counselling
Because until now early diagnosis was primarily associated with disadvantages, screening in children was limited to measurement of blood pressure, in order to provide prompt identification of the most important factor in progression that could be influenced . The availability of specific therapies means it is likely that there will be a paradigm shift, as high-risk patients can be identified in childhood and adolescence and may particularly benefit from early treatment . Ultrasound can be used to diagnose ADPKD in young patients aged between 15 and 29 years, with more than 96% accuracy it is not possible to rule out the disease, however . Currently still of minor significance, genetic diagnosis will become more important if better correlations between genotype and phenotype can be identified in the future, and if there are consequences for treatment before ADPKD becomes manifest. Costs have fallen significantly as a result of high throughput, and unambiguous diagnosis is possible in 90% of cases . The question of genetic counseling for those who wish to undergo preimplantation diagnostics remains difficult. Technically possible, but associated with complications and errors, in Germany this decision is made by ethics committees established specially for this purpose and is currently reserved for serious hereditary diseases.
You May Like: Does Drinking Pop Cause Kidney Stones
Drink Plenty Of Fluids
Drink plenty of fluids, especially plain water, to keep your kidneys healthy. This is especially important if you notice blood in your urine. Staying hydrated can also reduce the potential for obstructive clots forming in the urinary tract.
It is also wise to avoid excessive caffeine with ADPKD. Studies have found that too much caffeine may encourage faster kidney cyst growth and increased kidney size.
One study reported in 2018 in BMC Nephrology looked at the effect of caffeine on ADPKD. It found that excessive caffeine intake was linked to slightly faster kidney growth, but they didnt feel the caffeine created a significant detrimental effect on disease progression.
Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease
NORD gratefully acknowledges Jared Grantham, MD, University Distinguished Professor, emeritus, Kidney Institute, University of Kansas Medical Center, for assistance in the preparation of this report.
Synonyms of Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease
- ADPKD
Subdivisions of Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease
- ADPKD1
- ADPKD2
General Discussion
Signs & Symptoms
The specific symptoms and their severity can vary greatly from one person to another, even among members of the same family. Most affected individuals develop symptoms between the third and fifth decades of life. However, symptoms may occur during childhood or even in infancy. Some affected individuals never develop obvious symptoms and may be diagnosed with ADPKD incidentally in the eighth or ninth decade of life. ADPKD is a highly variable, multisystem disorder it is important to note that affected individuals will not have all of the symptoms discussed below.
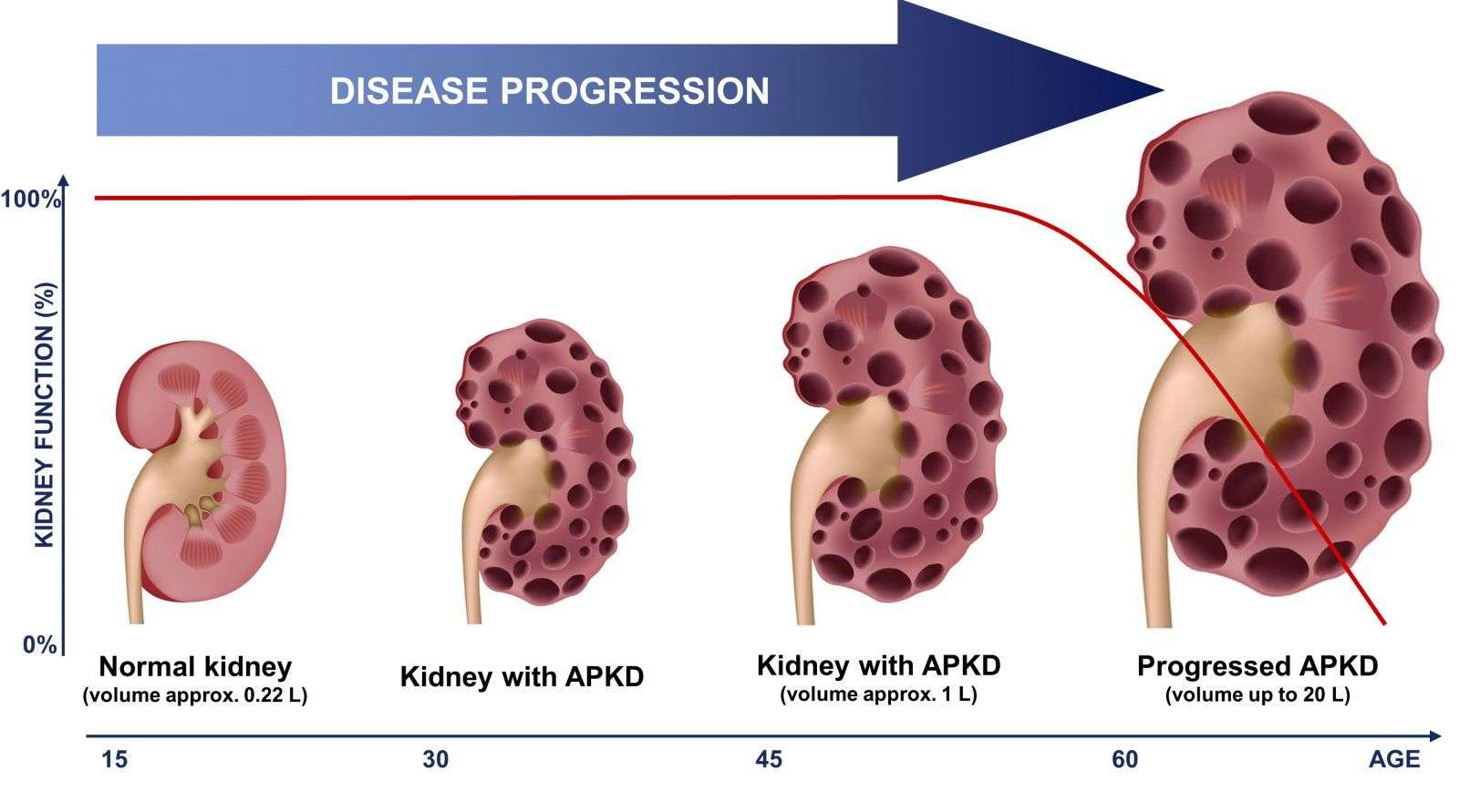
KIDNEY DISEASE The characteristic finding of ADPKD is the development of fluid-filled sacs in the kidneys. All individuals with ADPKD develop cysts in the kidneys, but the number, size, progression and severity of cyst development varies greatly from one person to another. In most cases, renal cysts continue to grow and multiply, potentially causing a variety of symptoms including abnormal enlargement of the kidneys, high blood pressure , flank pain, hematuria, poor function of the kidneys and, potentially, kidney failure.
Causes
Related Disorders
Also Check: Is Vinegar Good For Kidneys
New Study Shows Polycystic Kidney Disease Can Be Treated By Ketogenic Diet
Genetically linked but common polycystic kidney disease has long been perceived to be progressive and irreversible, sentencing patients to a slow and often painful decline as fluid filled cysts develop in the kidneys, grow and multiply and disrupt the organ from functioning properly. Once the kidneys fail, PKD patients often need dialysis or have to undergo a kidney transplant. To escalate issue, a host of other PKD-related conditions and complications add to the patients health burden, including high blood pressure vascular problems and cysts in the liver. Then there is high medical cost involved and also a reduced quality of life. Each year, about 9.2 million people globally are diagnosed with polycystic kidney disease . There is only one drug to date that is able to only slow the progression but not stop it and it does not work in about 60% of the cases.
A recent study by the University of California, Santa Barbara has discovered that simple manner to treating polycystic kidney disease is simply through diet.
Biochemist Thomas Weimbs, co-author commented, Its surprisingly effective, much more effective than any drug treatment that weve tested, and it involves just a diet and fasting. Theres a way of avoiding the development of the cysts through dietary interventions that lead to ketosis.
But the key to success with diet-related issues is consistency. Ask virtually any dieter and theyll tell you that staying on track is the difficult part.