What Conditions And Disorders Affect The Renal Arteries
Deposits of fat and cholesterol can build up in the renal arteries. These plaque deposits can lead to atherosclerosis and renal artery stenosis .
Blood flows more slowly through narrowed renal arteries. As a result, pressure builds up in blood vessels throughout the body. Renal artery stenosis can lead to:
Overview Of Blood Vessel Disorders Of The Kidneys
, MD, Loma Linda University School of Medicine
). When blood flow in the arteries supplying the kidneys is completely blocked, the entire kidney or a portion of the kidney supplied by that artery dies . Kidney infarction can lead to the inability of the kidneys to process and excrete the body’s waste products . Kidney failure is the inability of the kidneys to adequately filter metabolic waste products from the blood. Kidney… read more ).
Mechanisms Of Microvascular Rarefaction
Reductions in MV number have been observed in several diseases, as we will discuss in later sections of this overview. In the kidney, there is supporting evidence showing that MV rarefaction accompanies glomerulosclerosis and tubulointerstitial fibrosis . Although rarefaction could theoretically occur in any vessel, it usually first compromises the capillaries and arterioles. The majority of the chronic degenerative disease processes that disrupt the function and structure of the organs are characterized for large alterations in MV number that correlate and accelerate the development and progression of tissue fibrosis. The underlying forces pushing the vessels to regress and disappear are multifactorial . The initiating triggers of MV regression are largely unresolved and could be the result of a combined activation of signaling pathways, the withdrawal of survival factors, and changes in vessel perfusion . Although we may tend to think of MV rarefaction as the consequence of one or several outside of the vessel events, the process sometimes is initiated within the vessels by changes in vascular shape and dynamics of blood circulation, which could be promoted by substances generated and released by vascular endothelial cells. For example, recent studies have suggested that vascular dropout after acute or chronic kidney injury results from endothelial phenotypic transition and apoptosis combined with an impaired regenerative capacity .
Recommended Reading: Can Kidney Cancer Spread To Bones
What Is A Renal Angiogram
A renal angiogram is an imaging test to look at the blood vessels in yourkidneys. Your healthcare provider can use it to look at the ballooning of ablood vessel , narrowing of a blood vessel , orblockages in a blood vessel. He or she can also see how well blood isflowing to your kidneys.
For the test, the radiologist injects a contrast dye into the artery thatbrings blood into the kidney. Then he or she uses X-ray images to watch thedye as it flows through the blood vessels in the kidneys.
X-rays use a small amount of radiation to create images of your bones andinternal organs. A renal angiogram is one type of X-ray.
Fluoroscopy is used during a renal angiogram. Fluoroscopy is a kind ofX-ray movie.
What Are The Risks Of A Renal Angiogram
You may want to ask your healthcare provider about the amount of radiationused during the test. Also ask about the risks as they apply to you.
Consider writing down all X-rays you get, including past scans and X-raysfor other health reasons. Show this list to your provider. The risks ofradiation exposure may be tied to the number of X-rays you have and theX-ray treatments you have over time.
Tell your healthcare provider if you:
- Are pregnant or think you may be pregnant. Radiation exposure during pregnancy may lead to birth defects.
- Are allergic to or sensitive to any medicines, contrast dye, or iodine. Because contrast dye is used, there is a risk for allergic reaction to the dye.
- Have kidney failure or other kidney problems. In some cases the contrast dye can cause kidney failure. You are at higher risk for this if you take certain diabetes medicines.
Possible complications of a renal angiogram include:
- Temporary kidney failure
- Damage to an artery or an artery wall. This can cause blood clots.
You may have other risks depending on your specific health condition. Besure to talk with your provider about any concerns you have before theprocedure.
Certain things can make a renal angiogram less accurate. These include:
- Having contrast dye still in your body from a recent imaging test
- Gas or stool in the intestines
Recommended Reading: Is Hummus Good For Kidney Stones
Blood Flow Through Afferent Arteriole
The afferent arteriole serves as the incoming blood vessels which supply blood to the glomerulus. This helps to regulate the BP inside the kidneys. The afferent arteriole is wider than the efferent arteriole. This results in the blood rushing inside the glomerulus and exit through a narrow pathway. When the blood enters the narrow blood vessels inside the kidneys, they are pressurized. This pressure creates plasma, which is a yellow fluid of the blood consisting of electrolytes, water, and proteins, to pass through the glomerulus. The plasma that remains after filtration is called the filtrate.
More About The Nhlbi Sbir And Sttr Programs
The NHLBI Small Business Innovation Research and Small Business Technology Transfer programs support research and development on the next generation of commercially promising technologies and products to prevent, diagnose, and treat heart, lung, blood, and sleep-related diseases and disorders. For more information on NHLBIs small business programs, visit
Read Also: Which Side Is The Kidney On Your Body
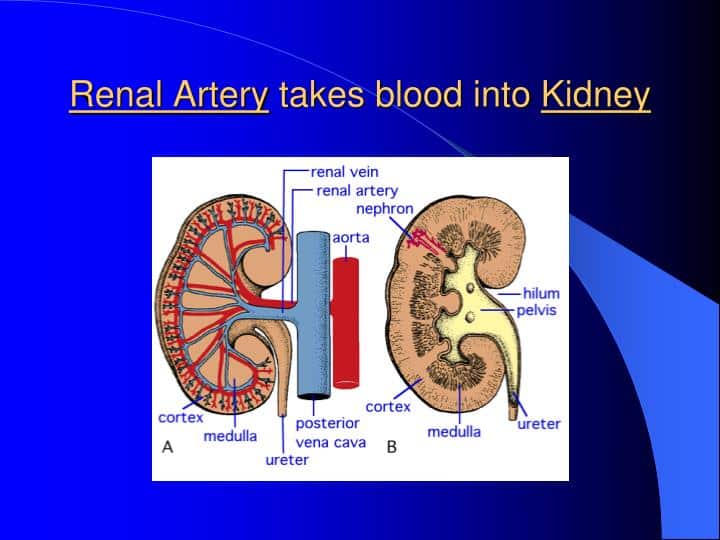
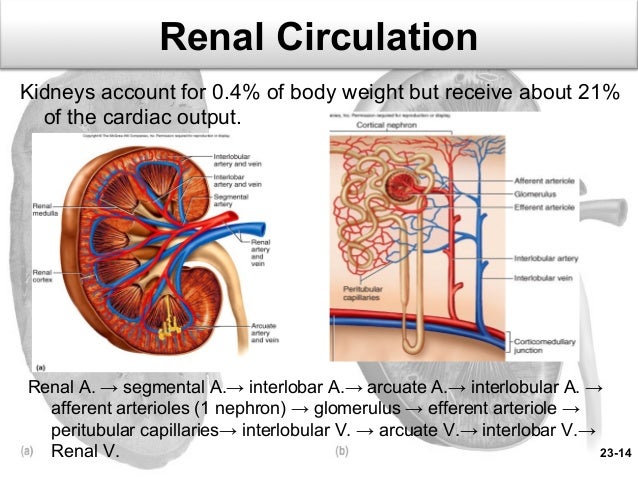
Blood Flow Through Renal Artery
As and when the blood arrives at the kidney, the filtration process starts. The blood gets into the kidney at the hilum via the renal artery. This renal artery later divides into two arteries. These are arcuate arteries that later branch into interlobular arteries. These branches further run inside the renal pyramids and renal column and, finally, into the afferent arteriole.
When Should I Talk To A Doctor
You should call your healthcare provider if you experience:
- Blood in urine.
- Inability to pee or frequent urge to pee.
- Nausea, vomiting and weight loss.
- Unexplained fatigue or headaches.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
The renal arteries send a large volume of blood to the kidneys every day for filtering. These arteries play a critical role in kidney health. Plaque can build up in them, causing renal artery stenosis. This condition slows blood flow and affects kidney function. You may develop high blood pressure thats difficult to treat. Your healthcare provider can help you improve your diet and lifestyle to lower the risk of kidney disease.
Read Also: Which Is More Painful Gallstones Or Kidney Stones
How Can I Protect My Renal Artery
If a renal artery blockage affects less than 60% of the artery, it may improve with lifestyle and dietary changes. These steps can keep your renal arteries and kidneys healthy:
- Eat a heart-healthy diet low in cholesterol, fat, salt and sugar.
- Exercise most days of the week.
- Limit your intake of protein and potassium if you have kidney disease.
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Quit smoking and using tobacco products.
Are There Special Medications For Hypertension If You Have Kidney Disease
Two types of medications can help lower blood pressure and slow the progression of kidney disease: ACE inhibitors and ARBs.
- ACE inhibitors help to prevent the body from producing as much angiotensin. This helps the blood vessels to relax.
- ARBs keep angiotensin from binding with receptors. This can also help the blood vessels to relax. This is key to slowing the progression of kidney disease.
In addition to these medications, your healthcare professional may prescribe a diuretic to help the kidneys remove excess sodium and fluid from the body.
Also Check: What Foods To Eat With Kidney Disease
What Is Reabsorbed By Active Transport
Active transport, simple diffusion, and enhanced diffusion are some of the mechanisms of solute recovery that are available. The vast majority of filtered chemicals are reabsorbed. Waste products like as urea, NH3, creatinine, and certain medicines are filtered or secreted. Hydration is secreted or reabsorbed as needed to keep the acidbase balance stable.
Changes In Mv Toneendothelial Dysfunction
The integrity of the vascular endothelium plays a pivotal role in the molecular traffic between the blood and surrounding tissue, as well as in many aspects of vascular function such as control of vascular tone, vascular permeability and proliferation, and fluid balance . Endothelial dysfunction is the result of a combination of abnormal vasodilatory response of endothelial cells with an imbalance between substances that determines vascular tone, which are produced by or act on the endothelium. The endothelial cells are both targets and sources of vasoactive substances such as nitric oxide , prostacyclin, angiotensin II, or endothelin-1, to name a few. Furthermore, endothelial dysfunction also plays a role in favoring inflammation and thrombosis via upregulation of adhesion molecules and generation of chemokines. Endothelial dysfunction has been implicated in the pathophysiology of hypertension , coronary artery disease , chronic heart failure , peripheral artery disease , diabetes , and chronic renal disease .
Read Also: What Are The Symptoms Of Bad Kidneys
Structure Of The Kidney
The middle portion of the back is where the kidneys are positioned in the human body. These are superior to the rib cage. Each of the two kidneys has a size of a fist of an adult. They are major filtration organs that eliminate all the waste from the blood. Around one-quarter of the blood is filtered out every minute by the kidney, which sums up to about 150 to 170 litres of the blood per day. This organ has numerous functions, apart from the excretory function. Some of these are controlling the blood pressure , production of red blood cells, controlling the acid level of the blood, and regulation of calcium. There are certain special cells in the filtering tubules of the kidney which can sense the sodium levels. When there is a pressure drop, the sodium levels also fall. When there are high sodium levels in the body, more water will be retained inside the body, which in turn increases the BP. There is yet another mechanism of regulating the BP by the kidneys which is through the hormone renin. Renin is associated with angiotensin I and II and will result in the constriction of the blood vessels, thereby increasing BP.
Which Blood Vessel Of The Kidney Supplies Blood To The Medulla
It is the efferent arterioles of the juxtamedullary glomeruli that supply the renal medulla with nutrients and waste products. As a result, the blood supply is completely postglomerular. The descending vasa recta has an influence on the distribution of blood inside the renal medulla, and it is responsible for this distribution. The vascular bundles are formed by the ascending and descending vasa recta.
Contents
Also Check: What Happens When A Man Passes A Kidney Stone
What Are The Treatment Options For Renal Vascular Disease
If, during a diagnostic angiogram, a physician finds that a patients renal artery or one of its branches is reduced to at least 20% of its normal size, he or she may decide to perform an angioplasty. Angioplasty is a minimally-invasive procedure in which a physician threads a catheter through a leg artery to an occluded blood vessel and inflates a balloon on the tip that expands to force the artery to become wider. He or she may also place a stent at the same point in the artery in order to keep the vessel from collapsing. If angioplasty and stent placement is insufficient to restore circulation to the restricted area, a patient may need to have an invasive, open surgery to remove a blockage or bypass the occluded point altogether.
Patients who have renal artery or vein thrombosis must often take anticoagulants such as Coumadin or Warfarin in order to prevent further clotting and give the body a chance to dissolve the existing clot. Thrombolytic medications actively dissolve clots and may be able to help a patient who has a severe blockage if he is able to restore blood flow to the restricted area within three hours of the initial clot.
Blood Flow Through The Kidneys
This flow happens through major blood vessels such as the renal artery. This renal artery further branches into the tiniest of the nephrons where the blood is filtered out. Nephrons comprise the glomerulus. Later, the filtered blood tends to flow out through the veins.
Blood keeps circulating through the kidneys all throughout the day. However, per day, around 150 quarts of blood are filtered out. But only one or two quarts of that filtered substance become urine.
You May Like: What’s Normal Kidney Function
How And Why Are Kidneys Important
Kidneys are the primary organs that eliminate all the waste products from within the body. The acids produced in the cells as a result of metabolism are removed by the kidneys. Kidneys help maintain the salt, water, and minerals like potassium, calcium, and sodium concentration in the blood. Only when the waste is removed, all other organs in the body can function properly.
How Do I Get Ready For A Renal Angiogram
- Your healthcare provider will explain the procedure to you. Ask him or her any questions you have about the procedure.
- You may be asked to sign a consent form that gives permission to do the procedure. Read the form carefully and ask questions if anything is not clear.
- You’ll be asked to not eat or drink liquids before the procedure. Your healthcare provider will tell you how long to fast. It might be several hours or overnight.
- Tell your provider if you are pregnant or think you may be.
- Tell your healthcare provider if you are allergic to contrast dye or iodine.
- Tell your healthcare provider if you are sensitive to or are allergic to any medicines, latex, tape, or anesthetic drugs .
- Tell your provider about all medicines you are taking. This includes prescriptions, over-the-counter medicines, and herbal supplements.
- Tell your healthcare provider if you have had a bleeding disorder. Also tell your provider if you are taking blood-thinning medicine , aspirin, or other medicines or herbal supplements that affect blood clotting. You may need to stop these medications before the test.
- You may get medicine to help you relax before the test.
- Depending on the site used for injection of the contrast dye, the recovery period may last up to 12 to 24 hours. You may need to spend the night.
- You may need a blood test before the procedure to see how long it takes your blood to clot. You may also need other blood tests.
- Follow any other instructions your provider gives you to get ready.
Don’t Miss: How Much Does A Kidney Go For
Why Might I Need A Renal Angiogram
You may need a renal angiogram to help your healthcare provider findproblems in the blood vessels of your kidneys. These problems may include:
- Bulging of a blood vessel
- Narrowing of a blood vessel
- Spasm of a blood vessel
- An abnormal connection between arteries and veins
- Blood clot
You may also need a renal angiogram to help your provider diagnose:
- Complications from a kidney transplant
You may need a renal angiogram if another test such as a CT scan or MRI didnot give your provider enough information.
Your healthcare provider may have other reasons to recommend a renalangiogram.
Blood Vessels Of The Kidney
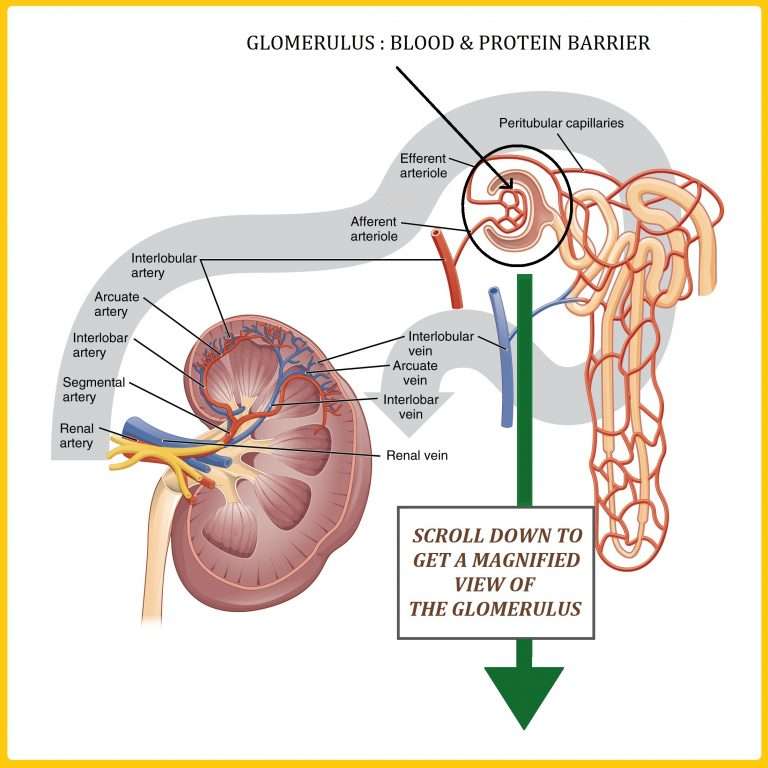
BLOOD VESSELS OF THE KIDNEY
The pathway of blood flow through the kidney is an essential part of the process of urine formation. Blood from the abdominal aorta enters the renal artery, which branches extensively within the kidney into smaller arteries . The smallest arteries give rise to afferent arterioles in the renal cortex . From the afferent arterioles, blood flows into the glomeruli , to efferent arterioles, to peritubular capillaries, to veins within the kidney, to the renal vein, and finally to the inferior vena cava Notice that in this pathway there are two sets of cap-illaries, and recall that it is in capillaries that exchanges take place between the blood and surrounding tissues. Therefore, in the kidneys there are two sites of ex-change. The exchanges that take place between the nephrons and the capillaries of the kidneys will form urine from blood plasma.
Figure 182 shows two views of a vascular cast of a kidney the shape of the blood vessels has been pre-served in red plastic. You can see how dense the vas-culature of a kidney is, and most of these vessels are capillaries.
Read Also: Can Girls Get Kidney Stones
Blood Flow Through Efferent Arteriole
This flow occurs after exiting the glomerulus. This efferent arteriole is the outgoing blood vessel that carries the blood away from the nephrons comprising the glomerular capillaries. The blood later flows into the individual vessels known as the peritubular capillary. This peritubular capillary surrounds the distal and proximal convoluted tubule inside the kidney which later descends to the vasa recta and travels through a venule network that converges into the cortical radiate and arcuate veins.
What Causes Renal Vascular Disease
Many different processes can cause the different types of renal vascular disease.
Causes of renal artery thrombosis and renal vein thrombosis The renal blood vessels can become occluded if a blood clot develops because of trauma, infection, inflammatory disease, or renal artery aneurysm. These clots can develop in both arteries and veins. Pregnancy vein compression due to an abnormally large, adjacent structure such as a tumor or renal artery aneurysm nephrotic syndrome steroid medications and oral contraceptives can all cause clots to develop in the renal veins. Nephrotic syndrome is a condition in which the parts of the kidneys that act as blood filters become damaged and allow too much protein to leak out of the blood and pass into urine.
Causes of renal artery aneurysms Bulges called aneurysms can occur in the arteries supplying the kidneys due to trauma, atherosclerosis, fibromuscular dysplasia, or congenital blood vessel weaknesses.
Read Also: Can You Drink With A Kidney Infection