Hepatorenal Syndrome Type 2
Type 2HRS is characterized by a stable or slowly progressive impairment in renal function in patients with decompensated liver disease who suffer from refractory ascites . Patients usually develop oliguria over a course of several weeks or months, marked by excessive salt and water retention and a slow but steady incline in renal retention parameters . Apart from the time of development, the same specific diagnostic criteria for HRS-AKI also apply for HRS type 2 .
Type 2HRS has been classified as a form of chronic kidney disease in patients with cirrhosis, and . However, type 2HRS or HRS-CKD is challenging to diagnose in clinical practice, as it is a diagnosis by exclusion, yet patients with liver cirrhosis often present with one or several other potential causes for kidney disease. However, according to the ADQI group, CKD due to other causes may develop on top of HRS type 2 . As a result, only a few studies have been published on type 2HRS and data vary substantially. For instance, the reported prevalence among patients with HRS ranges from 16% to 61% . In general, prognosis in HRS type 2 is poor, but more favorable when compared to AKI-HRS .
Liver Disease Rash: A Symptom And A Sign
What is a liver disease rash?Dermatologists find that our skin often shows what is happening inside of the body. A liver disease rash could indicate a further health problem. An example of where this effects your liver would be jaundice, where the skin and the whites of the eyes become yellow. Although yellowing skin is not the only skin change that indicates liver disease, darkening of the skin and bronzing of the skin can point to liver disease or failure and rashes can point to a number of liver health problems.
Whats in this article
- A liver disease rash and hepatitis C
- When does liver disease rash occur?
- Signs & symptoms
- Treatment
A liver disease rash and hepatitis C
Skin rashes may be a sign of hepatitis C, and should not be ignored. Rashes that appear on your skin as a result of hepatitis c show that your body is busy trying to fight the infection on its own. This rash is called urticaria and is the most common rash for those suffering from acute hepatitis c virus. This is a short-term infection, according to the National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse, acute HCV typically lasts for six months or less. Urticaria can also cause the skin to swell, rashes on your face and often comes in rounds that can last for several hours. Urticaria can also develop as a result of certain allergic reactions.
Signs & symptoms
If a rash is due to liver damage skin symptoms may include:
Additional symptoms may include stomach swelling and bleeding that does not stop.
What Is Already Known About This Subject
Renal dysfunction in cirrhosis is common and confers a poor prognosis.
Previous definitions of renal dysfunction in patients with cirrhosis have relied on creatinine thresholds.
AKIN criteria recognise that a small decline in renal function is associated with poor outcomes in general hospitalised patients.
Read Also: Is Aleve Safe For Kidneys
Serum Creatinine Concentration For The Assessment Of Kidney Function In Chronic Liver Disease
Kidney function is evaluated by assessing the glomerular filtration rate , which can be determined by measuring the volume of plasma that can be completely cleared of a given substance over a defined unit of time. The ideal marker for GFR determination is often quoted as having the following characteristics: Appears constantly in the plasma, can be freely filtered at the glomerulus, and does not undergo tubular reabsorption, secretion or extra renal elimination . For many years now, the assessment of GFR has relied on the measurement of the concentration of serum creatinine, which is associated with many problems. Creatinine is a product of the metabolism of creatine, which is produced in the liver from three amino acids, methionine, arginine, and glycine, and stored in muscle to be used as a source of energy once phosporylated. Creatinine does not appear in the plasma at a constant rate it is secreted in the tubule and can undergo extrarenal elimination, thought to involve creatinase in the gut. Serum creatinine concentration displays an exponential relationship with GFR, rendering it specific, but not a sensitive measure of GFR. The creatinine pool is affected by gender, age, ethnicity, nutritional state, protein intake and importantly liver disease .
Treatment For Acute Kidney Failure Caused By Sepsis
When someone has sepsis or septic shock, the doctors work to treat the sepsis, the infection that caused the sepsis, and the damage that the sepsis has done, such as the kidney failure.
If the kidneys are not working efficiently enough to filter toxins and allow urine to flow, an artificial way of filtering the kidneys, dialysis, will be needed. Dialysis is not a cure. Instead, it gives the doctors a way to clean the blood while they try to get everything else under control. There are two types of dialysis, hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis. Peritoneal dialysis is generally to manage chronic kidney failure. But it can be used for acute kidney failure where hemodialysis isnt possible, in areas with limited resources. For example, peritoneal dialysis has been used in Africa for patients who have malaria-associated acute kidney injury.
With hemodialysis, a machine, called a hemodializer, is the artificial kidney. A catheter placed into the patients vein leads to the other end of the catheter in the hemodializer. When the process starts, blood flows a few ounces at a time, from the patients body to the machine. The machine filters it and sends the blood back through the catheter to the body.
Dont Miss: Is Apple Cider Vinegar Good For Kidneys
Recommended Reading: Can Apple Cider Vinegar Hurt Your Kidneys
What Are The Causes Of Liver Failure
Liver failure occurs when damage to the organ causes it to improperly function and shut down. Acute liver failure is a sudden condition, often brought on by overdose or poisoning. Chronic liver failure is the result of a long-term, progressive degeneration, and is frequently caused by alcohol abuse, malnutrition, and cirrhosis. Other causes of liver failure include certain diseases, such as hepatitis and hemochromatosis.
Some causes of liver failure are sudden, one-time conditions that cause the organ to overload and shut down. One of the most common causes of liver failure is acetaminophen overdose, which occurs when a person takes too many over-the-counter painkillers that contain acetaminophen. Certain prescription medicines and homeopathic herbal supplements are also known to cause liver failure, and may need to be avoided by anyone with a history of liver problems. Ingesting toxic substances, such as poisonous mushrooms, can also overload the liver and is one of the most dangerous causes of liver failure.
How Do Vets Treat Liver And Kidney Disease
Your vet will conduct blood tests and an ultrasound or x-ray to assess the extent of the problem and establish whether it originates with the liver or is a sign of another issue like cancer.
Expect fluid therapies, antibiotics, or, in extreme cases, surgery to remove cysts, gallstones or cancerous parts of the liver. They may also recommend dialysis and changes in their meal plan, supplements and fluid intake.
The more quickly you consult with a vet, the more quickly your dog will be on the road to recovery.
Like all health concerns, keep up-to-date on signs, symptoms and treatments for liver and kidney failure in dogs. Nobody wants to say good-bye to their pets before its their time to go.
Your pets are counting on you for care be sure youre doing everything you can to show them your love by keeping them as healthy as can be.
You May Like: Is Tea Good For Kidneys
Organ Dysfunction: Treating Patients With Ckd And Liver Disease
Jeannette Y. Wick, RPh, MBA, FASCPPharmacy Times
Because the renally and hepatically impaired are often not included in clinical trials, drug regimens for these populations can be challenging.
Because the renally and hepatically impaired are often not included in clinical trials, drug regimens for these populations can be challenging.
Every human tissue has the potential to metabolize drugs. Safe medication use, however, is usually most dependent on the condition of patients kidneys and livers. Organ dysfunction may decrease drug or drug metabolite excretion in phase 1 or phase 2 drug metabolism reactions , leading to accumulation and potential toxicity.
When evaluating whether to prescribe a drug, the parent compound isnt the sole concern some hepatically-reduced drug metabolites are excreted renally. Kidney and liver failure are quite different, but have at least 3 things in commonthey increase in incidence with age, one may lead to the other, and they often challenge prescribers when medication therapy is indicated.3
Drug Metabolism
The FDA has approved many drugs with little pharmacokinetic /pharmacodynamic information in these special patient populations. In organ dysfunction patients, a specific challenge is use of newand potentially better or targeted pharmacologic agents in organ dysfunction patients. Gathering organ dysfunction data has traditionally been a post-marketing function.4,5
Kidney Dysfunction
Measuring Renal Failure
Liver Disease
Abscess
Kidney Disease Outcome Quality Initiative Criteria For Staging Chronic Kidney Disease
The definition and classification of chronic kidney disease was established in 2002 by the Kidney Disease Outcome Quality Initiative group in the USA . There were numerous factors prompting the group to establish clarity for the definition of chronic renal failure, which was already an extensive health care burden. With up to 100,000 new patient cases per year reaching end-stage renal disease, something had to done to try and detect kidney disease earlier.
The Cockcroft-Gault equation has been widely used to detect renal dysfunction, adjust drug dosing for drugs excreted by the kidneys, and assess the effectiveness of treatments for progressive kidney disease. It has also been used to evaluate patient’s health insurance claims and assign them points, which would prioritize them on the waiting list for a kidney transplant, similar to the way in which the model for end-stage liver disease is now used for liver transplantation. However, there is established evidence that the degree of chronic kidney disease and not just end-stage renal disease is an important risk factor for cardiovascular disease and AKI . Moreover, new treatments, in particular angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors, have been shown to slow the progression of chronic kidney disease by reducing the damaging effects of the proteinuria and raised intra-glomerular pressure encountered with hyper tension .
Table 3 Kidney Disease Outcome Quality Initiative staging criteria for chronic kidney disease
You May Like: Can Kidney Stones Cause High Blood Sugar
Does Protein Itself Raise Urine Calcium
Four studies appear to fit the needs for data in that they are trials of protein loading in a rather pure form, using foods and with considerable care for total nutrition. Of these, one used alkali to offset the protein acid load. The points taken from these additional reports are here.
The Fenton data are in a faded blue, for visual contrast. The protein load studies are in red. The pentagon and diamond are protein load +KCl and the same protein load + K Citrate in a single trial.
In these trials, protein intake was varied over a two fold range, mostly from about 1 to about 2 gm/kg/day.
More or less the data fall on the Fenton plot.
In the one special trial it is obvious that the K Citrate lowered the change in NAE without affecting the change in urine calcium. So it is possible to dissociate a protein effect from its acid base effect within the controlled environment of a trial. Given the modest quantitative changes in NAE it is possible that natural variability of urine calcium excretion might have permitted apparent stability despite the lack of a change in NAE in one point and a significant increase of NAE in the other, but the statistical testing is based on the observed variability and gave a low probability from chance alone.
Essentially the trial of diamonds and pentagons tells us that protein itself has a renal effect on calcium handling.
Assessment Of Chronic Kidney Disease In Patients With Chronic Liver Disease
The reliance on serum creatinine concentration is pivotal to the problems with estimated GFR and the gulf between the original MDRD study population and patients with chronic liver disease. This has been highlighted by a meta-analysis that reviewed creatinine clearance and estimated GFR and demonstrated a mean overestimation of 18.7 ml/min/1.73 m2 . Timed urine creatinine clearance also performs poorly, significantly overestimating GFR in patients with chronic liver disease, particularly at the lower range of GFR measurements . So why use estimated GFR if it performs so poorly? Despite its drawbacks, it is the most cost-effective method of assessing kidney function in the chronic setting and provides greater clarity on the extent of disease if one considers the overestimation and uses the extended version, which incorporates albumin and urea. Serial measures tend to provide greater information than measures in isolation.
Also Check: Kidney Transplant Tattoo Ideas
What Causes A Dogs Liver To Be Enlarged
For example, infections and/or inflammation may lead to generalized symmetrical enlargement of the liver, whereas tumors, hemorrhages, cysts, or rotation of liver lobe may lead to asymmetrical or focal enlargement. That is, only a part of the liver may be enlarged. Symptoms can vary depending on the cause.
How Dermatologists Help Patients With Kidney Disease
Kidney doctors, called nephrologists, often care for patients with kidney disease. When a kidney disease affects the skin, a nephrologist may team up with a dermatologist. Some skin conditions that develop due to kidney disease can be difficult to control. For example, if a patient has extremely itchy skin, it may be impossible to sleep through the night. A board-certified dermatologist can help a patient get some relief. This may involve using the right balance of moisturizers and medication that you apply to the skin. Some patients get relief with a treatment called UVB phototherapy.
The right skin care may also help. If the kidney disease is causing extremely dry skin, these tips from dermatologists may help:
1 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Chronic kidney disease in the United States, 2019. Page last reviewed Mar. 11, 2019. Last accessed Feb. 27, 2020.
ImagesImage 1: Image used with permission of the American Academy of Dermatology National Library of Dermatologic Teaching Slides.
Images 4, 5, 7, 8, 11: Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology
ReferencesAmin A, Burgess EF. Skin manifestations associated with kidney cancer. Semin Oncol. 2016 43:408-12.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Chronic kidney disease in the United States, 2019. Page last reviewed Mar. 11, 2019. Last accessed Feb. 27, 2020.
Galperin TA, Cronin AJ, et al. Cutaneous Manifestations of ESRD. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014 9:201-18.
Read Also: Can Diet Coke Cause Kidney Stones
Diagnosis And Etiology Of Renal Failure
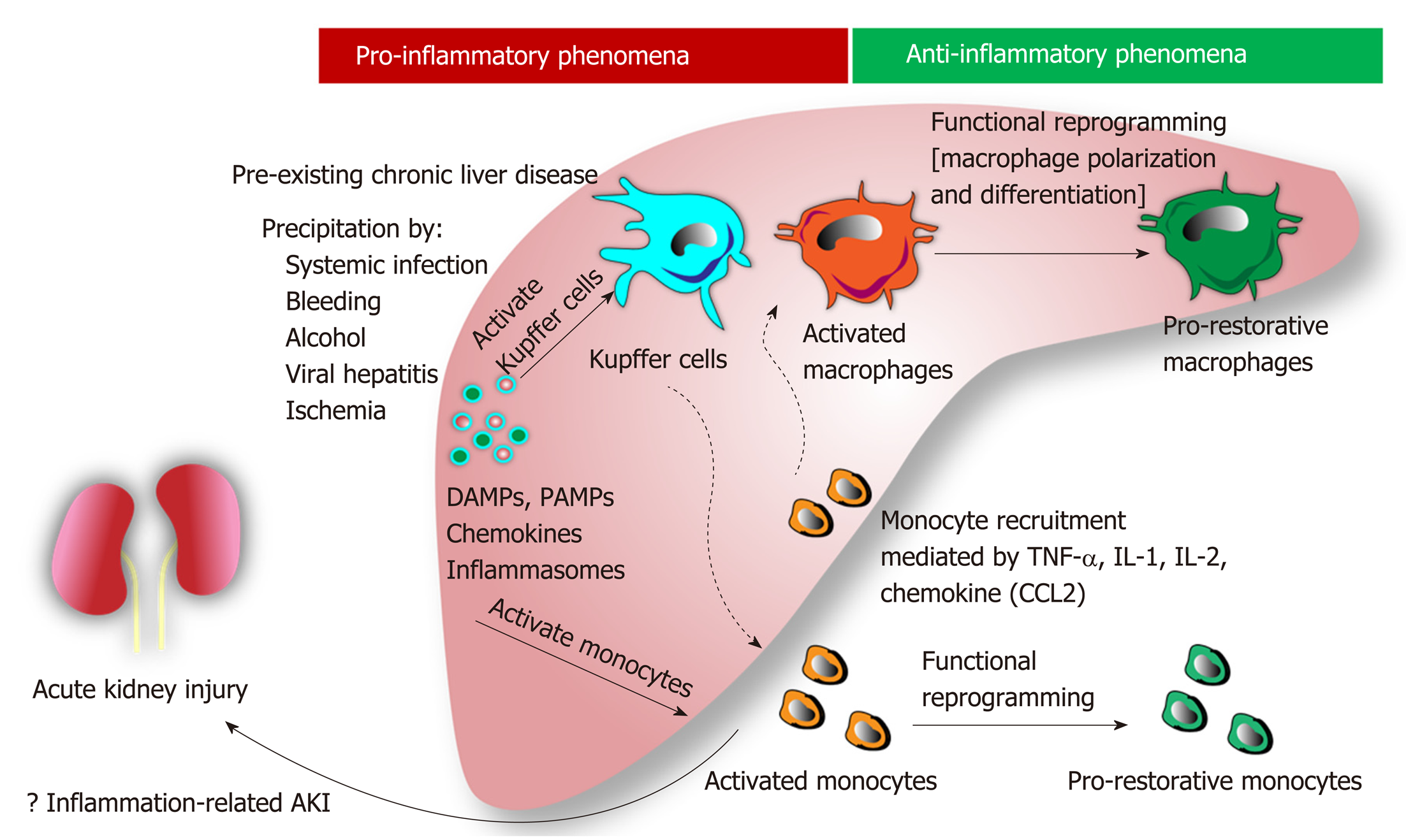
The most common causes of renal injury in patients with cirrhosis are: circulatory dysfunction due to bacterial infection hypovolemia secondary to gastrointestinal bleeding, paracentesis or diuretic use contrast or drug-induced chronic kidney diseases and hepatorenal syndrome .
CKD, such as IgA nephropathy, glomerulonephritis or nephrosclerosis are commonly seen in patients with cirrhosis. In most cases, the underlying causes of both conditions are alcoholic liver disease, hepatitis B and C and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis with associated diabetes and/or hypertension. HRS is a functional type of renal failure found only in patients with advanced cirrhosis and ascites. It is reversible either with orthotopic liver transplantation or with pharmacological treatment with splanchnic vasoconstrictors and albumin. HRS is the ultimate result of arterial underfilling due to splanchnic and systemic vasodilation generally with high cardiac output. When the circulatory dysfunction is inadequate to restore hemodynamics, vasoconstrictor mediators are released, resulting in severe renal vasoconstriction.
Acute Kidney Failure Symptoms
Signs that your kidneys have stopped working effectively are caused by the buildup of fluid and toxins in the body. The most obvious sign is a decrease in the amount of urine that is put out, although this isnt always the case. Some people do continue to produce urine, but lab tests will show that the urine is not normal.
Someone with acute kidney injury usually also looks swollen, as the fluid accumulates in the bodys tissues. This swelling is called edema and can come on very quickly.
Other symptoms of acute kidney failure can include:
- Shortness of breath
- Seizures
- Coma
Urine and blood tests tell doctors how well your kidneys are functioning, so many samples are taken during diagnosis and treatment. For example, the doctors test for creatinine, which is created when muscle begins to break down. A BUN test tells you if a substance called urea is building up in the blood, an indicator that the kidneys are not filtering waste properly.
Recommended Reading: Can Kidney Transplant Patients Eat Ginger
How Can Liver Failure Be Prevented
The best way to prevent liver failure is to limit your risk of getting cirrhosis or hepatitis. Here are some tips to help prevent these conditions:
- Get a hepatitis vaccine or an immunoglobulin shot to prevent hepatitis A and B.
- Eat a proper diet from all of the food groups.
- Maintain a heathy weight.
- Do not drink alcohol in excess. Avoid alcohol when you are taking acetaminophen.
- Practice proper hygiene. Since germs are commonly spread by hands, be sure to wash your hands thoroughly after you use the bathroom. Also, wash your hands before you touch any food.
- Don’t share any personal toiletry items, including toothbrushes and razors.
- If you get a tattoo or a body piercing, make sure the conditions are sanitary and all equipment is aseptic .
- Be sure to use barrier protection when having sex.
- If you use illegal intravenous drugs, don’t share needles with anyone.
Show Sources
Mayo Clinic: âAcute liver failure,â âAutoimmune hepatitis,â âCirrhosis,â âHemochromatosis,â âHepatitis A,â âLiver disease.â
Johns Hopkins: âChronic Liver Disease/Cirrhosis.â
CDC: âHepatitis C Questions and Answers for the Public
Oxalosis and Hyperoxaluria Foundation: âOverview of Hyperoxaluria.â
UpToDate: âDrugs and the liver: Metabolism and mechanisms of injury,â âHepatic adenoma.â
The Hepatitis C Trust: âHepatitis C liver damage progression.â
National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism: âAlcohol Alert.â