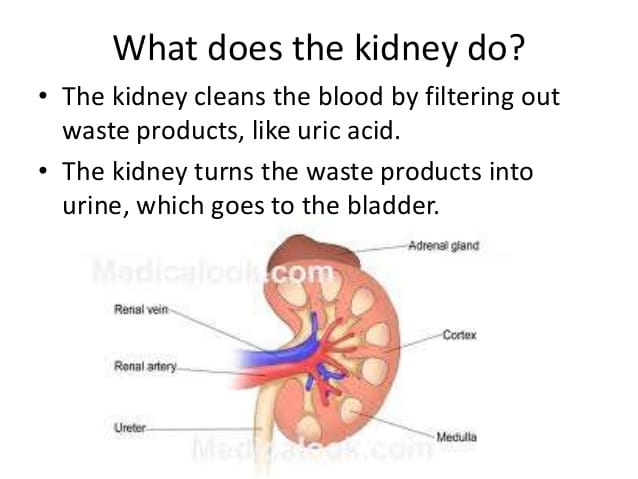
The Kidneys Are Composed Of Three Main Sections
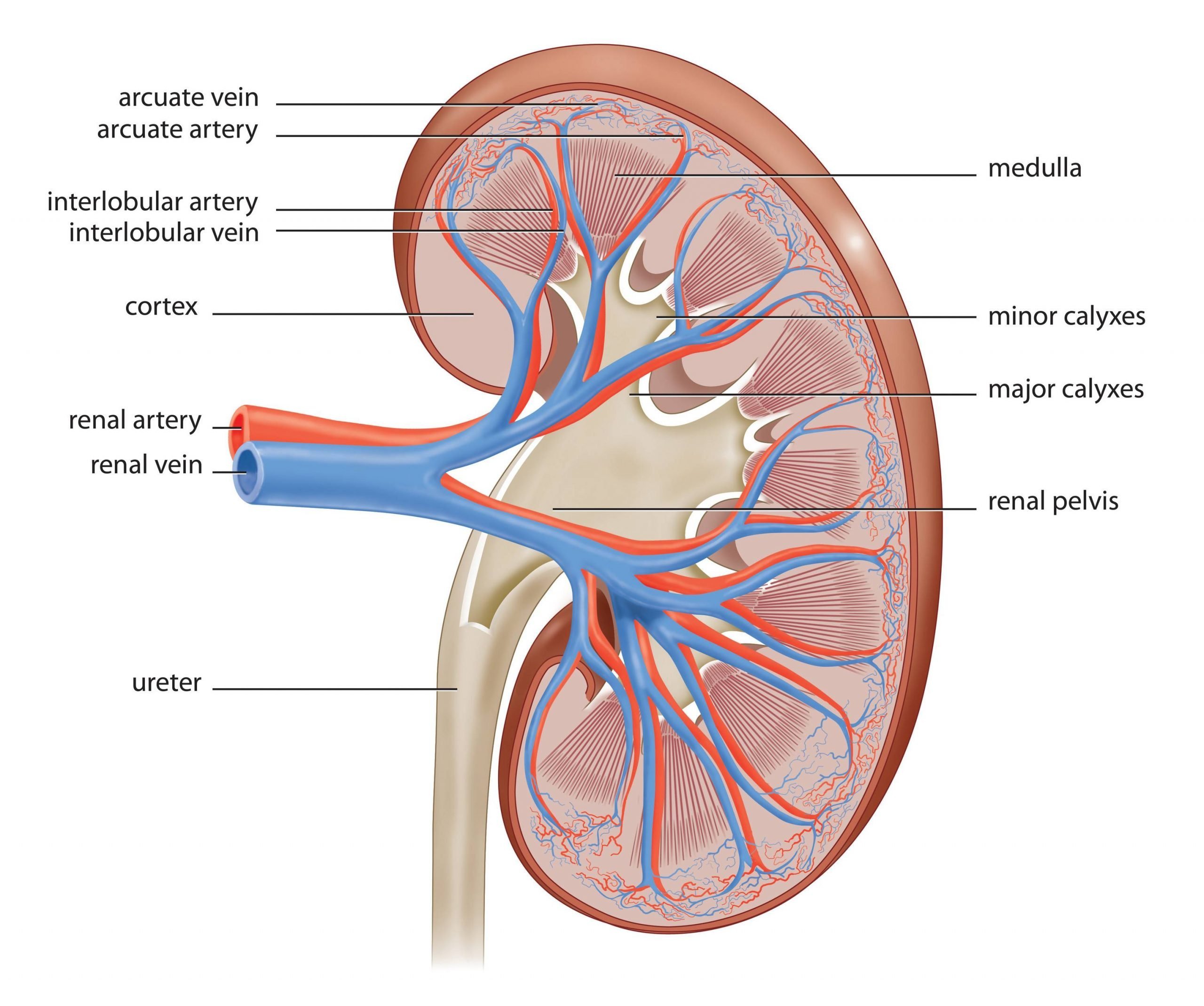
Each kidney consists of an outer renal cortex, an inner renal medulla, and a renal pelvis. Blood is filtered in the renal cortex. The renal medulla contains the renal pyramids, where urine formation takes place. Urine passes from the renal pyramids into the renal pelvis. This funnel-shaped structure occupies the central cavity of each kidney and then narrows as it extends out to join the ureter. Urine drains from the renal pelvis into the ureter.
How Is Medullary Nephrocalcinosis Treated
Preventing further deposition of calcium in the medullary region of the kidney is the primary concern for the treating physician. This will prevent worsening of the condition. The next step towards treatment of Medullary Nephrocalcinosis is to identify the cause of the excess calcium deposits. Once a cause is identified then treatment for that cause is begun immediately to treat Medullary Nephrocalcinosis.
Bringing down the levels of calcium is another challenge for the physician which is done by administration of isotonic sodium chloride which helps in bringing down the levels of calcium in the blood. Potassium and magnesium supplementation along with diuretics and restriction of salt is yet another way to bring down the levels of calcium in the blood and treat Medullary Nephrocalcinosis.
In some cases, with the identification of the cause of Medullary Nephrocalcinosis and prompt treatment, the levels of calcium comes down by themselves thereby treating Medullary Nephrocalcinosis. In some cases where Medullary Nephrocalcinosis is caused by renal tubular acidosis the damage done to the kidneys is basically irreversible.
Thus, it is highly recommended that an individual needs to start immediate treatment once a cause is identified and the diagnosis is confirmed of Medullary Nephrocalcinosis.
Also Read:
Medullary Changes And Corticomedullary Differentiation
The medullary pyramids may be more prominent in many cases of parenchymal disease as the increased cortical reflectivity increases contrast with the echo-poor medullary tissue. In other cases there may be a decrease in the degree of corticomedullary differentiation so that the pyramids are poorly defined or even indistinguishable as separate structures . However, as with cortical reflectivity, there is no correlation with the aetiology of the renal disease.3 In acute conditions involving primarily the medulla, such as acute tubular necrosis, the pyramids can be enlarged due to oedema. Increased medullary reflectivity can be detected in nephrocalcinosis of any aetiology and also in some other conditions such as gout.
-
Renal US shows echogenicity of medullary pyramids in neonate with normal renal function
-
Usually involves tips & central portions of pyramids
-
Bases of pyramids typically remain hypoechoic
-
Diffuse involvement of entire medullary pyramid uncommon
-
May appear as layering gradient of echogenicity, brightest at tips of pyramids
-
Posterior acoustic shadowing typically absent
-
Segmental involvement > diffuse
-
Normal renal cortical echogenicity & size
Nyree Griffin MD FRCR, Lee Alexander Grant BA FRCR, in, 2013
Read Also: Is Almond Milk Bad For Your Kidneys
Hormones Of The Adrenal Glands
The role of the adrenal glands in your body is to release certain hormones directly into the bloodstream. Many of these hormones have to do with how the body responds to stress, and some are vital to existence. Both parts of the adrenal glands the adrenal cortex and the adrenal medulla perform distinct and separate functions.
Each zone of the adrenal cortex secretes a specific hormone. The key hormones produced by the adrenal cortex include:
Renal Nerve Anatomy/autonomic Innervation
The kidney receives autonomic supply via both the sympathetic and parasympathetic portions of the nervous system. The preganglionic sympathetic nervous innervation to the kidneys arises from the spinal cord at the level of T8-L1. They synapse onto the celiac and aorticorenal ganglia and follow the plexus of nerves that run with the arteries. Activation of the sympathetic system causes vasoconstriction of the renal vessels. Parasympathetic innervation arises from the 10th cranial nerve , the vagus nerve, and causes vasodilation when stimulated.
You May Like: Is Mio Bad For Your Kidneys
Data Preprocessing Analysis And Differential Features Screening
Data extraction was performed by Profiling Solution Software . After the data pretreatment,, a matrix containing grouping information, sample names, retention times and normalized peak intensities were obtained. Mass spectrometry total useful signal method was used for the normalization of signal intensities. OPLS-DA was performed by SIMCA-P software. Features were treated as differential if the following conditions were met. First, variable importance in the projection value should be greater than 1.0 in OPLS-DA constructed between control and each experimental group. Second, confidence intervals on VIP column plot should be positive. Third, adjusted p value of Wilcoxon Mann-Whitney Test and stricter false discovery rate correction based on Benjamini-Hochberg method should be lower than 0.05. After the feature screening process, those differential features were prepared for metabolite identification.
Renal Medullary Vasoconstriction In Normotensive Rats
Fig. 4.Chronic influence of renal medullary interstitial infusion of the nitric oxide synthase inhibitor l-NAME on renal medullary blood flow , daily sodium balance , and mean arterial blood pressure in conscious Sprague-Dawley rats. Vertical dashed lines indicate the l-NAME infusion period. * Significant difference from control .
Recommended Reading: Does Carbonation Cause Kidney Stones
Renal Medullary Oxygen Consumption And Po2
There are clearly a large number of factors capable of influencing perfusion of the renal medulla. Although a fairly extensive understanding of the effects of the different circulating and local systems currently exists, a complete understanding of the factors that lead to the stimulation or inhibition of the different systems in health and disease is currently lacking. This is particularly true in the case of the different autocrine and paracrine agents, the regulation of which is just beginning to be elucidated. In addition, a number of different local or circulating factors, including different metabolites of arachidonic acid, various fibrinolytic factors, and other paracrine and autocrine factors that affect vascular tone, capillary permeability, and/or blood coagulation all have the potential to affect hemodynamics in the renal medullary circulation and, through the mechanisms reviewed below, influence fluid and electrolyte homeostasis and arterial blood pressure.
Nephrons: The Basic Functional Units Of Blood Filtration And Urine Production
Each kidney contains over 1 million tiny structures called nephrons. The nephrons are located partly in the cortex and partly inside the renal pyramids, where the nephron tubules make up most of the pyramid mass. Nephrons perform the primary function of the kidneys: regulating the concentration of water and other substances in the body. They filter the blood, reabsorb what the body needs, and excrete the rest as urine.
Read Also: Is Watermelon Good For Kidneys
Loss Of Renal Medullary Hypertonicity
- a.
-
The normal hypertonicity of the renal medulla is crucial for elaboration of highly concentrated urine. When medullary hypertonicity is decreased, the osmotic gradient necessary for movement of water from the collecting ducts into the interstitium and back into the bloodstream is disrupted, causing inappropriately dilute urine.
- b.
-
Although the major cause of impaired concentrating ability in chronic renal disease is the necessity to excrete the daily solute load with a decreased number of functional nephrons, several renal diseases are associated with structural abnormalities that also can contribute to impaired concentrating ability.
- c.
-
Renal medullary washout of solute.
-
Long-standing PU/PD of any cause can result in loss of medullary solutes necessary for normal urinary concentrating ability.
-
Structural lesions need not be present for impaired concentrating ability to occur.
-
Increased medullary blood flow associated with long-standing PU/PD can accelerate removal of solutes by the systemic circulation.
-
Aldosterone deficiency in hypoadrenocorticism impairs NaCl reabsorption in the collecting ducts and contributes to medullary washout of solute. This effect explains why dogs with hypoadrenocorticism often have impaired urinary concentrating ability at presentation despite having structurally normal kidneys.
- 1.
-
Lack of adequate physiologic stimuli for ADH release.
- a.
-
Chronic hypotonicity of body fluids .
- b.
-
Volume expansion .
Richard W. Nelson, in, 2015
Brief Overview Of Morphology And Function Of Mature Renal Medulla
The medulla of the adult kidney has a modified cone shape with a broad base adjacent to renal cortex and the narrow apex termed papilla. The mature renal medulla consists of the medullary collecting ducts, loops of Henle, vasa recta and the interstitium . The main function of the medulla is to regulate concentration of the urine. The urine flows from the collecting ducts into the renal calyces and pelvis, which undergoes unidirectional peristaltic movements to allow drainage of the urine into the downstream ureter and bladder. In addition, the renal papilla is a niche for adult kidney stem cells which may play a role in repair after ischemic kidney injury.,
Recommended Reading: 4mm Kidney Stone Actual Size
Development Of Medullary Vasculature
Anatomical development of vasa recta
Vasa recta are straight capillaries that branch off the efferent arterioles of juxtamedullary nephrons, enter the medulla and surround the LOH. These vessels play an important role in the maintenance of mass balance and osmotic gradient in the medulla by returning the NaCl and water reabsorbed in the LOH and medullary collecting tubule to the systemic circulation. The vasa recta function as countercurrent exchangers to delay the washout of NaCl and urea and prevent the excess accumulation of water in the inner medulla. In the developing rat kidney, vasa recta bundles grow centrally into the medulla around the previously developed collecting ducts.
Factors that control angiogenesis of vasa recta
Angiogenic factors
Embryonic blood flow and oxygenation
What Is The Function Of The Medullary Pyramid In The Kidney
4.2/5ureterbladderread here
The renal medulla is the interior portion of the kidney where the primary functions of the organ occur: the filtering of waste materials and elimination of fluid from the body. The kidney filters blood and sends waste materials to the bladder to become excreted urine.
Subsequently, question is, what is a medullary pyramid? Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy. The medullary pyramids are paired white matter structures of the brainstem’s medulla oblongata that contain motor fibers of the corticospinal and corticobulbar tracts known together as the pyramidal tracts. The lower limit of the pyramids is marked when the fibers cross .
Also to know, where is the medullary pyramid in the kidney?
The renal papilla is the location where the renal pyramids in the medulla empty urine into the minor calyx in the kidney. Histologically it is marked by medullary collecting ducts converging to form a papillary duct to channel the fluid.
How many pyramids are there in kidney?
Renal pyramids are kidney tissues that are shaped like cones. Another term for renal pyramids is malpighian pyramids. Between seven and eighteen pyramids exist in the innermost part of the kidney, which is called the renal medulla in humans, there are usually only seven of the pyramids.
You May Like: Do Multivitamins Cause Kidney Stones
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Medullary Sponge Kidney
Many people with medullary sponge kidney have no symptoms. The first sign that a person has medullary sponge kidney is usually a UTI or a kidney stone. UTIs and kidney stones share many of the same signs and symptoms:
- burning or painful urination
- fever and chills
- vomiting
People who experience these symptoms should see or call a health care provider as soon as possible.
Diagnosis Of Medullary Sponge Kidney
Since medullary sponge kidney may not cause symptoms, the condition is often diagnosed during medical investigations for other problems. The presence of kidney cysts and kidney stones may suggest medullary sponge kidney. However, conditions other than medullary sponge kidney can cause kidney stones , so these must be ruled out before medullary sponge kidney is diagnosed.
Tests used to diagnose medullary sponge kidney may include:
- renal ultrasound scan of the kidneys. This is normal in medullary sponge kidney unless stones have formed
- computed tomography scan to detect the presence of cysts, if other tests are inconclusive or if more information is needed.
Kidney stones may be seen in the bladder, ureters or kidneys. In severe cases, imaging may reveal multiple large cysts and clusters of broad kidney stones.
Recommended Reading: Bleeding Kidney Treatment
How Can I Strengthen My Adrenal Glands
healthyvitaminsfoodsvitaminshealthy adrenal glandsHow Adrenal Glands Work to Produce Cortisol
Nephrotoxicity Induced By Cisplatin
Body weight, kidney coefficient, blood urine nitrogen and serum creatinine of rats in different groups have been reported in our previous study. The results demonstrated that low-dose cisplatin induced slight kidney damage, and medium- or high-dose cisplatin induced significant renal function decline. It should be noted that the initial numbers of rats were 13, 13, 16 and 26 for group C, L, M and H, respectively. Eventually, 2, 3 and 10 rats in group L, M and H died, and the final numbers of animals were 13, 11, 13 and 16 for group C, L, M and H, respectively.
Not only the macroscopic indicators but also microscopic morphology were significantly changed after cisplatin administration. showed the representative pathological examination results of cortex and medulla in different groups. No abnormal changes were observed in control group , and only slight tubular expansion could be observed in medulla in low-dose cisplatin group . But remarkable abnormal histological changes can be observed in both cortical and medullar part in medium-dose cisplatin group and high-dose cisplatin group . The damages manifested tubular necrosis, tubular expansion, renal epithelial casts and interstitial infiltration of inflammatory cells.
Figure 1: Nephrotoxicity was induced by cisplatin.
You May Like: Celery Juice Kidney
Excess Of Adrenaline Or Noradrenaline: Pheochromocytoma
Pheochromocytoma is a tumor that results in excess production of adrenaline or noradrenaline by the adrenal medulla that often happens in bursts. Occasionally, neural crest tissue, which has similar tissue to the adrenal medulla, may be the cause of overproduction of these hormones. This known as a paraganglioma.
Pheochromocytomas may cause persistent or sporadic high blood pressure that may be difficult to control with regular medications. Other symptoms include headaches, sweating, tremors, anxiety and rapid heartbeat. Some people are genetically predisposed to developing this type of tumor.
Importance Of The Kidney In Blood Pressure Control
To appreciate the importance of renal medullary blood flow in the control of arterial blood pressure, one must first accept the important role of the kidney in the regulation of arterial blood pressure. The theoretical importance of the kidney in the control of arterial pressure and the concept that alterations in renal function lead to adjustments in arterial blood pressure was first introduced by Guyton and colleagues and has been reviewed extensively . Although arterial blood pressure is controlled by many regulatory systems, it is proposed that the kidney, through its ability to regulate extracellular fluid volume, is the dominant long-term controller of arterial pressure.
Similar data have been obtained from clinical studies. It was first demonstrated that mean arterial pressure was significantly higher in patients who received a renal transplant from a donor with a family history of hypertension than in patients whose donor family had a normotensive history . Second, patients who received a transplant from a hypertensive donor had higher blood pressures compared with patients who received kidneys from normotensive donors . Finally, transplantation of a kidney from a normotensive donor produced a sustained normalization of arterial pressure in hypertensive patients who had demonstrated long-standing essential hypertension . These clinical data emphasize the importance of the kidney in the development and maintenance of hypertension in humans and experimental animals.
You May Like: Kidney Transplant Tattoos
Sample Pretreatment For Instrumental Analysis
Frozen renal cortex or medulla were firstly placed into pre-cooled 2mL homogenization tubes containing ceramic beads. Then, pre-cooled methanol was added . The samples were homogenized for three times , with 60s intervals between homogenization steps. After two centrifugations , the supernatant was removed and named as kidney homogenate. For LC-MS analysis, 125L acetonitrile was added to a 25L aliquot of the kidney homogenate. The solution was mixed thoroughly and centrifuged twice , and the supernatant was removed for LC-MS analysis. For GC-MS analysis, 100L methanol was added to a 10L kidney homogenate. The next derivation steps referred to our previous studies,.
What You Need To Know
- Adrenal glands, also known as suprarenal glands, are small, triangular-shaped glands located on top of both kidneys.
- Adrenal glands produce hormones that help regulate your metabolism, immune system, blood pressure, response to stress and other essential functions.
- Adrenal glands are composed of two parts the cortex and the medulla which are each responsible for producing different hormones.
- When adrenal glands dont produce enough hormones, this can lead to adrenal insufficiency .
- Adrenal glands may develop nodules that can be benign or malignant, which can potentially produce excessive amounts of certain hormones leading to various health issues.
Don’t Miss: Is Pomegranate Juice Good For Your Kidneys
How The Kidneys Work
Blood is filtered at high pressure to remove glucose, water, salts and urea.
All the glucose, and some water and salts, are reabsorbed back into the blood. Note that urea is not reabsorbed.
Dr Alice Roberts dissects a pig’s kidney and explains the structure and function of the kidney and urinary system
What Is Renal Medulla
Renal medulla refers to the inner-most part of the kidney. It is composed of 8-12 renal pyramids. Renal pyramids are triangular structures, which consist of densely-packed network of nephron structures. The loops of Henle and the collecting tubules are located in the renal pyramids of the renal medulla. The U-shaped portion of a nephron is called the loop of Henle. It re-filters water, sodium ions, and chloride ions from the filtrate. Renal medulla also contains collecting tubules of the nephrons. Collecting tubules concentrate the final filtrate or urine and transport it to the renal calyces. The distribution of a nephron in the renal cortex and medulla is shown in figure 2.
Figure 2: Distribution of a Nephron in Renal Medulla and Cortex
Since both loop of Henle and collecting tubules reabsorb water from urine, the length of these structures determines the amount of water that is going to be absorbed from the urine. If the two types of tubules are lengthy, a high amount of water is going to be absorbed from the urine.
You May Like: Is Watermelon Bad For Kidneys