Treatment Of Protein In Urine
The treatment of proteinuria depends on the cause of the problem. If what generates it is a secondary disease, you should treat it so that the presence of protein in the urine ceases.
Most commonly, doctors prescribe medications of two types when the underlying disease is diabetes or hypertension. The first are the angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, we know them as ACE, for their acronym in English. The second are the angiotensin receptor blockers, or ARB.
Both medications are usually prescribed when the underlying disease is diabetes or hypertension. However, even if these health problems are not present, doctors also order such drugs to prevent kidney damage. In any case, the presence of proteins in the urine is always a reason for medical consultation.
Dont forget to what too much protein in urine means and how to treat it with your friends and family on your social networks!
Abnormal Levels Of Urine Albumin
Technically, microalbuminuria is defined as urinary excretion of albumin between 30 and 300 milligrams of albumin per day. You also might see it defined as between 20 and 200 micrograms per minute.
Values less than that are not technically microalbuminuria. Values higher than that would be called simply albuminuria or sometimes macroalbuminuria or proteinuria.
What Is The Difference Between Micro
Albumin is a type of protein found in large amounts in the blood. Because it is a small molecule in size, it is one of the first proteins able to pass through the kidneys into the urine when there are kidney problems. This presence of small amounts of albumin in the urine is the condition called micro-albuminuria. It is important to note that some physiologic conditions may cause micro-albuminuria, such as an episode of exercising. If your urine micro-albumin is elevated, it would be worth repeating after a day or two of no exercising.
As kidney damage progresses and the amount of albumin in the urine increases, the name of the condition changes from micro-albuminuria to macro-albuminuria or proteinuria.
Recommended Reading: Can Kidney Stones Increase Blood Sugar
Changes In Albuminuria Predict Changes In Renal Outcome
Not only the level of urinary albuminuria excretion itself but also changes in urinary albumin excretion over time predict renal risk changes. Regression or progression of albuminuria frequently occurs, as shown in studies of patients with type 2 diabetes and in the general population.35,36 Patients with type 2 diabetes in whom albuminuria declined by more than 50% over 2 years follow-up had a subsequent mild eGFR decline .37 In contrast, in subjects in whom albuminuria stayed high, long-term renal function decline was substantial . These data imply that albuminuria should be regularly measured to monitor the individual renal risk prediction.
Vitamin D Therapy Of Chronic Kidney Disease
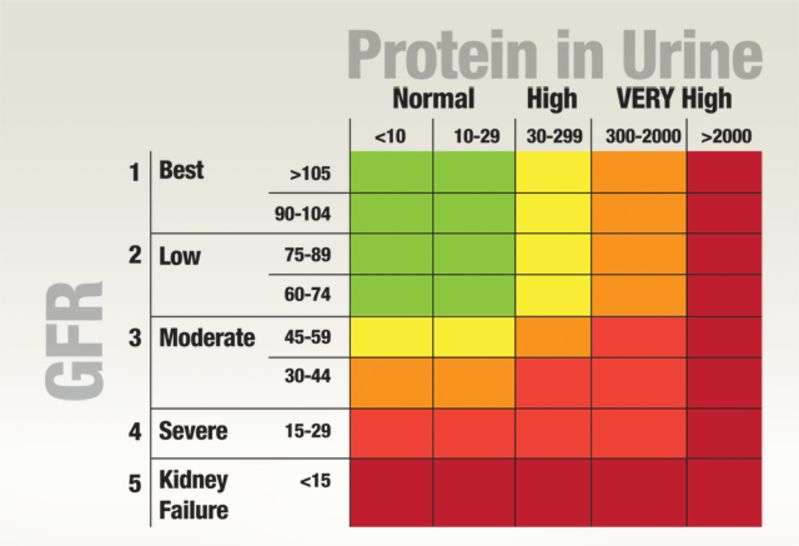
Albuminuria is a major risk factor for progressive renal function decline and is believed to be the initial step in an inevitable progression to proteinuria and renal failure in humans. Thus reduction of albuminuria is a major therapeutic target in the management of CKD. A number of epidemiological and clinical studies have demonstrated potent antiproteinuric activity of vitamin D and vitamin D analogs. In a large cohort cross-sectional analysis of the NHANES data, vitamin D insufficiency was found to be associated with increased prevalence of albuminuria , suggesting that vitamin D has an intrinsic antiproteinuric property. A post hoc analysis of the Effect of Strict Blood Pressure Control and ACE Inhibition on Progression of CKD in Pediatric Patients cohort showed that normal serum 25D levels are associated with less proteinuria and greater preservation of renal function in children with CKD . Moreover, vitamin D deficiency was found to be independently associated with a higher risk of disease progression of diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes and CKD .
B. Bikbov, … G. Remuzzi, in, 2014
Recommended Reading: Can Kidney Infection Cause Diarrhea
What Does The Test Measure
A urine albumin test is a measurement of the protein albumin. Albumin is a common protein in the blood that helps keep fluid from leaking out of blood vessels. Albumin also helps carry substances, including enzymes and vitamins, through the body.
While albumin is supposed to be found in the blood, very little albumin should enter the urine if the kidneys are functioning properly. Different types of urine albumin tests are designed to detect albumin in the urine:
- A urine dipstick test is a test in which a test strip turns a different color based on the amount of albumin in the sample.
- A 24-hour urine sample requires collecting all of your urine for a full day. The laboratory then measures the total amount of albumin in that complete sample.
- An albumin-to-creatinine ratio test measures both albumin and creatinine in a one-time sample, also known as a spot urine sample. Creatinine is a chemical byproduct of normal muscle activity, and it is normally removed from the body in urine. Total daily creatinine production is relatively consistent, so an albumin-to-creatinine ratio test is a way to estimate your total daily urine albumin level without having to do a full 24-hour urine sample.
A dipstick test does not provide an exact measurement of albumin.
A 24-hour urine sample provides an albumin measurement that is typically listed as milligrams per 24 hours .
Questions For Your Doctor About Test Results
To improve your understanding of your urine albumin test, you can bring up some of the following questions when discussing the test result with your doctor:
- Which type of urine albumin test did I have?
- What was my result? Was it normal or abnormal?
- How do you interpret my test result? What do you think is the most likely explanation for the test result?
- Should I repeat this test? If so, how often?
- How accurate is the urine albumin test that I had?
- Do you suggest any other tests for follow-up? What are the pros and cons of the different follow-up test options?
Don’t Miss: Is Watermelon Kidney Friendly
How Do Doctors Treat Protein In The Urine
Doctors treat the cause of protein in the urine:
- If you have diabetes, your doctor will help create a treatment plan to keep it under control and slow down damage to your kidneys. They may recommend that you:
- Check your blood sugar often
- Take certain medicines
- Follow a diabetes-friendly eating plan
- Be active most days of the week
- If you have high blood pressure, your doctor may prescribe a medicine to help lower your blood pressure and slow down damage to your kidneys. The types of medicine are:
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, which are a group of medicines that lower blood pressure. They widen your blood vessels, help your kidneys get rid of extra water and lower the hormones that raise blood pressure.
- Angiotensin receptor blockers , which are a group of medicines that lower blood pressure. They widen your blood vessels.
- If you do not have diabetes or high blood pressure, your doctor may still prescribe an ACE inhibitor or an ARB to slow down damage to your kidneys.
Drinking water will not treat the cause of protein in your urine unless you are dehydrated. Drinking water will dilute your urine , but will not stop the cause of your kidneys leaking protein.If you have protein in your urine, talk with your doctor to choose the best treatment option for you.
What Do The Test Results Mean
Many things can affect the results of laboratory tests. These include the method that each laboratory uses to do the test. To find out what the results mean, it is advisable to attend with the health care provider.
A normal amount of albumin in the urine is less than 20 mg per day. An amount of normal total protein in the urine is less than 150 mg a day.
If the test shows high levels of albumin in the urine or an increase in albumin in the urine, it could mean that there is kidney damage or disease.
If the patient has diabetes, a possible cause of an increase in urinary albumin is diabetic nephropathy, or kidney disease.
You May Like: Seltzer Kidney Stones
Further Tests For Nephrotic Syndrome
Sometimes, further tests may be required. These may include:
- ultrasound an examination of the kidneys using sound waves to outline the structure of the organs
- computed tomography scan uses x-rays and digital computer technology to create detailed two- or three-dimensional images of the internal organs and tissues
- magnetic resonance imaging uses a strong magnetic field and radio waves to provide clear and detailed pictures of internal organs and tissues.
If I Have Albuminuria Does It Mean I Have Kidney Disease
It may be an early sign of kidney disease, but your doctor will check you again to make sure albuminuria is not caused by something else, like not drinking enough water. If your doctor suspects that you have kidney disease, the test for albumin will be repeated. Three positive results over three months or more is a sign of kidney disease.
You will also be given a simple blood test to estimate GFR. GFR stands for glomerular filtration rate. Your GFR number helps determine how well your kidneys are working.
You may also be given:
-
Imaging tests. . This produces a picture of your kidneys and urinary tract. It can show whether your kidneys have kidney stones or other problems.
-
A kidney biopsy. This can help find out what caused your kidney disease and how much damage to the kidneys has happened.
You May Like: Does Diet Soda Cause Kidney Stones
How Often Do I Need To Have A Test For Albuminuria
People who are at increased risk for kidney disease should have this test as part of routine checkups by a healthcare provider. Those at increased risk include:
-
People with diabetes
-
People with high blood pressure
-
People with a family history of kidney failure
-
People who are 65 years or older
-
Certain ethnic groups including African Americans, Hispanics, Asians, American Indians
How Long Will I Have To Wait For A Transplant If I Need One
The process of getting listed for a kidney transplant often begins after you your evaluation. The average wait time for a kidney from a deceased donor is 3-5 years. If you have a donor who is willing and able to give you a kidney, you can have your transplant as soon as both you and your donor are ready. Learn more about the kidney transplant waiting list and what you can do while you wait.
Don’t Miss: Is Ginger Good For The Kidneys
Chronic Kidney Disease: Detection And Evaluation
DAVID Y. GAITONDE, MD DAVID L. COOK, MD and IAN M. RIVERA, MD, Dwight D. Eisenhower Army Medical Center, Fort Gordon, Georgia
Am Fam Physician. 2017 Dec 15 96:776-783.
Patient information: See related handout on chronic kidney disease, written by the authors of this article.
SORT: KEY RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PRACTICE
The initial evaluation of GFR should include measurement of serum creatinine and estimation of the GFR using a creatinine-based equation.
| Clinical recommendation | Evidence rating | References |
|---|---|---|
|
An early morning spot urine albumin/creatinine ratio is the preferred initial test to measure proteinuria in patients undergoing CKD evaluation. |
||
|
Serum cystatin C should be measured to determine whether decreased GFR represents a false positive in patients who have elevated serum creatinine levels, but no known CKD, no risk factors for CKD, and no albuminuria. |
||
|
CKD should be classified using the estimated GFR and the degree of albuminuria. |
||
|
Patients with CKD should have serum hemoglobin measured at least annually, and more often depending on the severity of CKD. |
||
|
Routine evaluation of bone density should not be performed in patients with an estimated GFR < 45 mL per minute per 1.73 m2 because results may be inaccurate. |
||
|
The evaluation of patients with stage 3a to 5 CKD should include measurement of serum calcium, phosphorus, parathyroid hormone, alkaline phosphatase, and 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels. |
SORT: KEY RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PRACTICE
What Does 100% Albumin In Urine Mean
Albuminuria is a sign of kidney disease and means that you have too much albumin in your urine. Albumin is a protein found in the blood. A healthy kidney doesnt let albumin pass from the blood into the urine. A damaged kidney lets some albumin pass into the urine. The less albumin in your urine, the better.
You May Like: Osteocleanse Reviews
What Does Albumin To Creatinine Ratio Mean
The urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio shows whether you have albumin in your urine. Albumin is a type of protein thats normally found in the blood. Your body needs protein. Its an important nutrient that helps build muscle, repair tissue, and fight infection. But it should be in your blood, not your urine.
What Causes Proteinuria
In many cases, proteinuria is caused by relatively benign or temporary medical conditions.
These include dehydration, inflammation and low blood pressure. Intense exercise or activity, emotional stress, aspirin therapy and exposure to cold can also trigger proteinuria. In addition, a kidney stone in the urinary tract can cause proteinuria.
Occasionally, proteinuria is an early indication of chronic kidney disease, a gradual loss of kidney function that may eventually require dialysis or a kidney transplant. Diabetes and high-blood pressure can damage kidneys and are the number-one and number-two causes of kidney disease.
Other potentially kidney-harming diseases and medical conditions, which can lead to proteinuria, include:
- Immune disorders like lupus and Goodpastures syndrome
- Acute inflammation of the kidney
- Puffiness around the eyes, especially in the morning
- Foamy or bubbly urine
These are also symptoms of chronic kidney disease. Anyone experiencing these symptoms, especially foamy urine and swelling, should see a doctor immediately.
Read Also: Osteocleanse
How Is A Urine Albumin
An albumin-to-creatinine ratio test is very similar to a protein-to-creatinine ratio test, but the latter measures albumin and all other types of proteins in the urine. In this way, the protein-to-creatinine test has a broader focus than the albumin-to-creatinine test.
A difficulty with protein-to-creatinine tests is that no single laboratory technique can precisely measure each separate type of protein. As a result, there can be more variability in test results, leading to greater use of the urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio test.
Can Dehydration Cause Albumin In Urine
Your urine normally may have a very small amount of protein. Much of this protein is the type called albumin. But many other types of protein may be found in urine. When your body loses large amounts of protein in the urine, it can be because of dehydration, strenuous exercise, fever, or exposure to cold temperatures.
Recommended Reading: Ginger Tea For Kidneys
When Should I Get A Urine Albumin Or Albumin
Urine albumin tests can be used in several different medical contexts.
For diagnosis, they are generally performed if you have signs of possible kidney impairment. Urinary changes, swelling, and unexplained itching are examples of symptoms that can be associated with kidney problems. In these cases, a urine albumin test may be performed along with other kidney function tests.
Screening with a urine albumin test is only recommended for some people. For people without risk factors for kidney disease, the downsides of this testing, including financial costs and potential unnecessary follow-up, are considered to be greater than the potential benefits. As such, this screening is not recommended in the population in general.
Instead, screening is usually reserved for people who are at a higher risk of having kidney problems. Urine albumin testing is recommended for people with diabetes, and this testing may be done every year for people with type 2 diabetes.
Screening is also advised in people with one or more of the following risk factors for kidney disease:
- High blood pressure
- Cardiovascular disease
- Belonging to certain racial or ethnic groups
If you have had an abnormal albumin level in your urine or have been diagnosed with kidney disease in the past, you may have repeat testing to monitor your urine albumin levels. In these cases, the doctor may request 24-hour urine samples to more precisely measure the amount of albumin.
Urine Albumin And Albumin To Creatinine Ratio
Testing.com is fully supported by readers. We may earn a commission through products purchased using links on this page. You can read more about how we make money here.
- Also Known As:
This page was fact checked by our expert Medical Review Board for accuracy and objectivity. Read more about our editorial policy and review process.
-
Select, schedule, and purchase your test
Its simple and conveniently online
-
Visit a Quest Patient Service Center for your appointment
Choose from more than 2,200 locations nationwide
-
Get your confidential results sent directly to you
Access your results online via the secure MyQuest portal
Powered by QuestDirect
Also Check: Can Seltzer Water Cause Kidney Stones
What To Do With High Microalbumin And Diabetes
What to do with high microalbumin and Diabetes? Albumin makes up most of the protein in our plasma and plays an important role in maintaining the plasma colloid osmotic pressure. For diabetics, high microalbumin in urine is an indicator of kidney damages, so regular urine test is very necessary for diabetes patients to have a prompt diagnosis about Diabetic Nephropathy, one of the leading complications of diabetes. Well then, what to do when there are high microalbumin in urine?
Since appearance of microalbumin in urine indicates kidney problem, we need to take some measures to protect kidneys, so as to avoid the further deterioration of illness condition. To achieve this goal, diabetics generally need to act from the following several aspects:
1. Tight control of blood sugar
In cases of Diabetic Nephropathy, kidneys are damaged due to long-term high blood sugar. Kidney is responsible for filtering blood. When blood contains too much glucose, kidneys have to work more hardly to get excess glucose out of the body. GFR is an indicator used to reflect kidney condition. It refers to the blood volume filtered by kidney within a certain time. For diabetics with high level of blood glucose, their kidneys need to filter more blood to lower blood sugar level so with medical tests, we can find their GFR is higher than the normal range. Tight control of blood sugar helps to reduce kidney burn, which is very helpful for protecting residual kidney function.
2. Well-planed diet