Progression Of Renal Disease
In the allopurinol group, there was no significant change in eGFR after 24 months , whereas in the control group, there was worsening by the end of the study . In the control group, eGFR decreased 3.3 ± 1.2 ml/min per 1.73 m2, and in allopurinol group, eGFR increased 1.3 ± 1.3 ml/min per 1.73 m2 after 24 months .
We have evaluated the correlation between UA levels and eGFR in the whole data and within each experimental group. There is a significant inverse correlation between UA levels and eGFR in all cases. The change in UA levels at 24 months has been plotted against the change in eGFR , and we found a significant inverse correlation between changes .
Allopurinol treatment slowed renal disease progression in comparison with control groups in a cox regression model adjusted for age, gender, diabetes, UA, hs-CRP levels, renin-angiotensin system blockers, CKD etiology, and albuminuria .
Allopurinol Tablets & Kidney Disease
Allopurinol tablets are the most important weapon in any gout patients arsenal.
Also, they could be more important, if you also suffer from kidney disease.
Because, gout related research from Y P Siu and colleagues investigates allopurinol tablets and kidney disease. Specifically, it looks at in patients with high uric acid levels and impaired kidney function.
They recognized that high uric acid is associated strongly with the development of high blood pressure and kidney disease. So, they thought allopurinol might benefit gout patients with chronic kidney disease.
First, they conducted a randomized controlled trial with 54 patients. All had high uric acid levels and chronic kidney disease. Half were treated with allopurinol tablets . While the other half continued with normal treatment.
Next, patients were assessed after 12 months. Then, 46% of normal patients had significant kidney deterioration or started dialysis. But, only 16% of those treated with allopurinol got worse.
Finally, the authors conclude:
Allopurinol therapy significantly decreases serum uric acid levels in hyperuricemic patients with mild to moderate chronic kidney disease. Its use is safe and helps preserve kidney function during 12 months of therapy compared with controls. Results of this study need to be confirmed with an additional prospective trial involving a larger cohort of patients to determine the long-term efficacy of allopurinol therapy and in specific chronic kidney disease subpopulations.
Dosage For Elevated Serum Uric Acid Levels Due To Cancer Treatments
Adult dosage
600800 mg per day for 2 or 3 days.
Child dosage
600800 mg per day for 2 or 3 days
Child dosage
300 mg per day. Your doctor will adjust your dose as needed based on your serum uric acid level.
Child dosage
150 mg per day. Your doctor will adjust your childs dose as needed based on your serum uric acid level.
Senior dosage
The kidneys of older adults may not work as well as they used to. This can cause your body to process drugs more slowly. As a result, more of a drug stays in your body for a longer time. This raises your risk of side effects.
Your doctor may start you on a lowered dose or a different dosing schedule. This can help keep levels of this drug from building up too much in your body.
Special considerations
- For people with kidney disease: Depending on how well your kidneys are working, your doctor will lower your dose. Your doctor will decide your dosage based on your creatinine clearance. This is a test that measures your kidney function.
Read Also: Do Kidney Stones Hurt After They Pass
A Multicenter Clinical Trial Of Allopurinol To Prevent Kidney Function Loss In Type 1 Diabetes
| The safety and scientific validity of this study is the responsibility of the study sponsor and investigators. Listing a study does not mean it has been evaluated by the U.S. Federal Government. Read our disclaimer for details. |
| First Posted : December 20, 2013Results First Posted : November 20, 2020Last Update Posted : December 4, 2020 |
| Diabetic NephropathiesCoronary Artery Disease | Drug: AllopurinolDrug: Placebo | Phase 3 |
Thirty-one of the 530 participants in this study were recruited as part of a pilot study and transferred to the main study when this was funded. Eligibility criteria for the pilot study were the same as those for the main study, with the exception of a wider estimated GFR interval at entry in the run-in period ml/min/1.73 m2) and the additional requirement of a measured GFR between 45 and 99 ml/min/1.73 m2 at the end of the run-in period. Pilot subjects joined the main study at a time point corresponding to the time elapsed from randomization in the pilot. Thus, they were exposed to the study medication for the same length of time as participants who were directly enrolled in the main study. Outcomes measures were those of the main study, regardless of whether participants were transferred from the pilot or were directly enrolled in the main study.
Identification Of Research Areas
Data from the literature were thematically analysed by the leaders and fellows of each literature review team to identify general issues with the currently available data with regard to gout and gout studies in people with concomitant CKD as well as specific issues with individual medications.
The research areas and general requirements for studies identified were agreed on by the leaders and fellows of each literature review team and then circulated to all authors of this Consensus Statement. Agreement was reached by consensus of all authors via e-mail, and final approval was granted by the G-CAN Board. No effort was made to prioritize the research areas.
You May Like: Which Side Is Your Kidney On
Drugs Used To Manage Gout Flares
NSAIDs are generally contra-indicated in people with CKD, and the published literature in gout generally aimed to show the potential for renal-related adverse effects in people with CKD. Although NSAIDs have well-established adverse effects, there has been some suggestion that these drugs could be used in those with end-stage renal disease for short periods of time.
There are a small number of randomized controlled trials of colchicine for treatment of gout flares, and none of these reported outcomes stratified by renal function. Pharmacokinetic studies have indicated that clearance of colchicine is decreased in those with severe kidney impairment and that there is minimal clearance of colchicine by haemodialysis. Thus, the recommendations for use of colchicine in CKD remain largely empirical.
Allopurinol For Gout An Unlikely Contributor To Kidney Disease
NEW YORK Allopurinol does not appear to contribute to decline in kidney function and may actually protect renal function in patients with gout, according to a large population-based study.
You Might Also Like
Gout affects around 4% of Americans and often occurs alongside chronic kidney disease , Dr. Tuhina Neogi from Boston University School of Medicine and colleagues note in an article online Oct. 8 in JAMA Internal Medicine.1
Despite no firm data suggest allopurinol harms renal function in patients with gout, clinicians are often cautious about using it in patients with gout and CKD, either lowering the dose or stopping it entirely when a patient exhibits kidney function decline, leading to worse gout outcomes, they point out.
The researchers used data from a primary care database in the U.K. to explore the risk of CKD in association with allopurinol use in patients with newly diagnosed gout. The created two propensity-matched cohorts of 4,760 patients who initiated allopurinol and 4,760 who did not.
Covariates were well balanced between allopurinol initiators and nonusers, with a mean age of 57, mean BMI of 30, and mean glomerular filtration rate of 77 mL/min. Overall, 71% of users and nonusers had CKD stage 2 or estimated GFR 60 mL/min to 89 mL/min the remaining 29% had CKD stage 1 or eGFR of 90 mL/min or more. As expected, males made up the majority of both cohorts .
Recommended Reading: Where Does It Hurt If Kidney Infection
Literature Search Outcomes And Study Features
A total of 1,233 titles were identified during the initial search, 1,202 of which were excluded upon screening of titles and abstracts. Following a full-text review of 31 studies, 16 RCTs involving 1,943 patients were included in the final network analysis . Details on the 16 RCTs and the features of patients are summarized in Table 1 and Table 2, respectively. All studies included patients with CKD and hyperuricemia, except for one in which patients with normal uric acid levels were not excluded therapeutic outcomes of febuxostat vs. benzbromarone, allopurinol, placebo, or usual therapy, and allopurinol vs. benzbromarone, or placebo/usual therapy were reported in one , two , five , one , and seven studies, respectively. Relationships between different therapies are presented in network plots . The area of each circle represents the numbers of included patients, and the thickness of lines connecting them shows the number of articles comparing the two connected therapies.
FIGURE 1. Flowchart of the study selection procedure.
TABLE 1. Study characteristics of included studies.
TABLE 2. Baseline characteristics of included patients.
FIGURE 2. Network plots for relations between different therapies. The width of lines is proportional to the number of studies comparing every pair of interventions. The size of each circle is proportional to the sample size of each therapy.
Drugs Used For Flare Prophylaxis
Although the medications used for flare prophylaxis are the same as those used to treat flares, they are generally used at lower doses and for longer periods of time . A post hoc analysis of three phase III RCTs in people starting febuxostat who also received prophylaxis with colchicine included participants with an eGFR of < 30ml/min/1.73m2 but again the results were not stratified by renal function. Long-term use of colchicine in the general population has been associated with bone marrow suppression and neuromyotoxicity, but whether these effects are increased in those with gout and CKD is unknown. Whereas short-term courses of glucocorticoids can be considered to have an acceptable riskbenefit profile, long-term use of glucocorticoids for flare prophylaxis can be associated with an increased risk of glucocorticoid-related adverse events, particularly infections, as seen in other rheumatic diseases,. This risk could be particularly concerning in a population that is already at high risk of severe infections, such as those with CKD. Whether the gout flare rate when starting ULT is the same in those with CKD as in those without, and whether prophylaxis is always required, are unknown, although a recent study of incremental use of febuxostat suggested that prophylaxis might not be required when a dose-escalation approach is used.
Read Also: How Many Kidney Transplants Per Year
Medicines For Gout Prevention And Complications
Your doctor can prescribe medicines to help keep a healthy level of uric acid in your body, which can prevent future gout attacks and the complications from gout. When you have gout, your body either makes too much uric acid or cannot get rid of enough of it, which causes it to build up.Some medicines are safe to take when you have kidney disease, but some are not. Talk to your doctor about which medicines are safe for you.
Allopurinol
Allopurinol is a medicine for people who make too much uric acid. It is the most common medicine used to treat chronic gout. Your doctor can tell you if allopurinol is safe for you to take if you have kidney disease.
Probenecid
Probenecid is a medicine that works for people who cannot get rid of enough uric acid. It works to remove extra uric acid through your urine. Probenecid can increase your risk of kidney stones. Probenecid is not safe to take for many people with kidney disease, so talk to your doctor for more information about probenecid.
Pegloticase
Pegloticase is an infusion medicine given by injection into your vein at a doctor’s office, usually every two weeks. It is used for severe chronic gout when other medicines do not work. Pegloticase can quickly bring your uric acid down to a lower level than most medicines can. Talk to your doctor about whether pegloticase is safe for you.
Medicines For Gout Attacks
The main goal of treatment during a gout attack is to decrease pain and swelling. Some medicines are safe for people with kidney disease, and some are not. Talk to your doctor about which medicines make the most sense for you to try.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
NSAIDs are medicines that decrease pain and swelling. Some NSAIDs are available over the counter, like ibuprofen and naproxen sodium. Stronger NSAIDs like indomethacin and celecoxib must be prescribed by a doctor.Taking NSAIDs can lead to kidney disease in time or make kidney disease worse. NSAIDs may not be recommended when you have kidney disease even for the treatment of gout attacks.
Colchine
Colchine is a medicine that can relieve pain. Your doctor may recommend taking colchine during a gout attack, or low doses of colchine every day if you have chronic gout. Colchine may not be recommended for people with kidney disease. Talk to your doctor about whether colchine is right for you.
Corticosteroids, also known as steroids
Steroids are strong medicines used to decrease swelling and pain. Steroids are usually only given for gout if you cannot take NSAIDS or colchine. Steroids can be taken as a pill or given as an injection. Talk to your doctor about whether steroids are safe for you.
You May Like: How To Pass A Kidney Stone Without Surgery
What Is The Mechanism Of Action Of Allopurinol
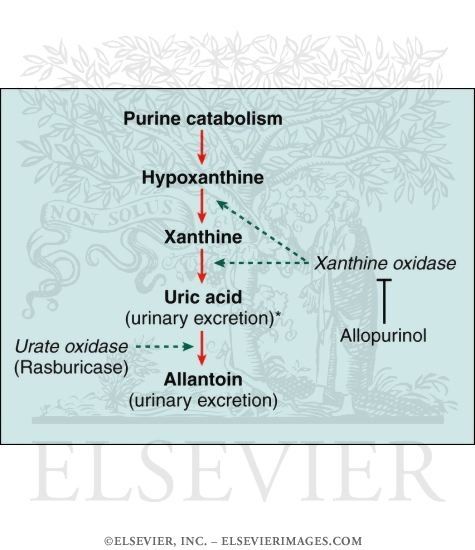
Allopurinol belongs to a family of drugs known as xanthine oxidase inhibitors. It works by lowering the body’s synthesis of uric acid. Gout attacks and kidney stones can be caused by high uric acid levels. Allopurinol is used to prevent gout episodes rather than to treat them once they occur. It may also be used to reduce the risk of future problems with kidney function or damage.
The most common side effects of allopurinol include diarrhea, nausea, rash, irritability, and fatigue. Other side effects include headache, dizziness, dry mouth, and light-headedness when standing up quickly or exercising. Allopurinol may cause liver problems such as jaundice or pain when drinking alcohol. People who take aspirin or other medications that contain salicylates should not take allopurinol because it will not relieve them of their need for daily aspirin.
People who take allopurinol or similar medications to lower blood pressure should do so under close supervision from their physician. Combining these drugs with other medications or overthe-counter products that cause acidity in the body may lead to low blood pressure. Examples of such combinations include Isordil , Zyloprim .
Allopurinol Safe Even With Chronic Kidney Disease
A green light for dosing to achieve the target urate level.
Key points Allopurinol is a safe and effective therapy for lowering urate levels in gout, even in patients with creatinine clearances < 30 mL/min.
High doses of allopurinol are rarely needed to achieve acceptable urate levels in patients with chronic kidney disease.
High doses are more likely necessary in gout patients with normal kidney function.
BackgroundAccording to Stamp and colleagues in New Zealand, “The use of allopurinol in people with chronic kidney disease remains one of the most controversial areas in gout management.”1
Allopurinol remains the first-line drug for lowering urate in patients with gout and is prescribed in escalating doses to a target urate level. In patients with poor kidney function, the American College of Rheumatology and the European League Against Rheumatism have conflicting recommendations with regards to allopurinol dosing: the ACR recommends dose escalation and EULAR dose restriction.
Previous studies that have looked at urate-lowering therapy have not included patients with chronic kidney disease. The authors sought to determine the effect of baseline kidney function on the safety and efficacy of allopurinol escalation therapy. They recently published their findings in Arthritis Research & Therapy.
All groups saw a reduction in serum urate below 6 mg/dL by month 24.
Read Also: How To Measure For A Kidney Lazy Susan
Role Of Combination Ult
Combination therapy with a XOI and a uricosuric can be very effective, and if uricosuric toxicity is a consequence of urate concentration within renal tubules then combination therapy could theoretically ameliorate such toxicity. However, as uricosuric treatment is usually not considered for patients with advanced CKD this approach is largely untested.
Does Colchicine Have Any Effect On Kidneys
In my response, I said that the answer to Does colchicine affect kidneys is similar to allopurinol. Because there is conflicting evidence. But it is clear that experts need to consider the exact nature of the patients kidney disease. Also, the colchicine research indicates the importance of dose. Which I didnt pick up on in the debate about allopurinol with kidney disease.
Whenever you have two serious illnesses together you must rely on expert investigation and individual case management. Because every case is different. So you will not get the level of care you need from Internet articles.
Also Check: What Eases Kidney Stone Pain
Case 1 Dress Syndrome Accompanied By Acute Liver Failure Due To Allopurinol
A 58 year old woman with diabetes, hypertension, gastric ulcer and gouty arthritis with hyperuricemia and mild renal insufficiency was started on allopurinol and developed fever and rash 17 days later. She had undergone resection of a parathyroid adenoma under enflurane anesthesia shortly after starting allopurinol, but she recovered uneventfully and was sent home on doxycycline, in addition to her usual medications including glibenclamide, indomethacin and cimetidine. One week later, she developed fever, fatigue and rash which became generalized and exfoliative. Allopurinol was stopped and she was admitted for observation. She was markedly febrile and had a generalized erythematous rash. Blood testing showed leukocytosis and eosinophilia. Liver tests, which were previously normal, were mildly elevated on admission, but over the next few days worsened with onset of jaundice . Tests for hepatitis A and B were negative. She subsequently developed progressive prolongation of the prothrombin time followed by confusion, encephalopathy and ascites. Corticosteroids were started. She developed gram negative sepsis followed by multiorgan failure and died. Postmortem liver biopsy showed marked centrilobular necrosis, cholestasis, inflammation and small islands of regenerating hepatocytes.
Key Points
| < 1.2 |