What Are The Symptoms Of Anemia Of Inflammation
Anemia of inflammation typically develops slowly and may cause few or no symptoms. In fact, you may only experience symptoms of the disease that is causing anemia and not notice additional symptoms.
Symptoms of anemia of inflammation are the same as in any type of anemia and include
- a fast heartbeat
- shortness of breath
Pathophysiology Of Iron Metabolism In Chronic Kidney Disease
Iron is a vital element in human metabolism. Due to its unique ability to act both as an electron donor and as an electron acceptor , iron plays an imperative part in cellular respiration as well as oxygen transport and storage. However, due to its ability to receive and transfer electrons, iron can cause severe oxidative stress and tissue damage . As iron has an essential role in both energy metabolism and damaging potential, its absorption, transfer, and metabolism are tightly regulated. The regulation of iron is done mainly by adjusting absorption . This is due to the fact that the ability of the body to secrete iron is negligible .
In addition, CKD patients have an absolute iron deficiency. This can arise from an increased rate of blood loss during dialysis . The frequent phlebotomies, and blood remaining in the dialysis tubing, contribute to iron loss . The high rate of iron loss is also due to gastrointestinal bleeding from the combination of gastritis and platelet dysfunction . This is common in both dialysis- and non-dialysis -dependent CKD . Decreased gastrointestinal iron absorption and malnutrition contribute as well.
Due to the combination of reduced iron absorption and increased iron losses, iron deficiency is common among CKD patients who are both ND and dialysis dependent.
How Is Anemia Of Chronic Kidney Disease Diagnosed
Your doctor can check for anemia by doing two blood tests:
- Hemoglobin test. This test measures the level of hemoglobin in your blood. Hemoglobin is the substance in red blood cells that carries oxygen. This is the best test for anemia.
- Hematocrit . A hematocrit test shows your doctor how much of your blood is made up of red blood cells.
Your doctor will repeat these tests to see how well treatment is working.
Recommended Reading: Does Sprite Cause Kidney Stones
Anemia In Cancer Patients
ESAs are effective in raising hemoglobin levels and reducing transfusion requirements in patients with chemotherapy-induced ane-mia. However, there are data linking the use of ESAs to shortened survival in patients who have a variety of solid tumors.
Several mechanisms have been proposed to explain this rapid disease progression, most notably acceleration in tumor growthâ by stimulation of erythropoietin receptors on the surface of the tumor cells, leading to increased tumor angiogenesis.,
For these reasons, treatment of renal anemia in the setting of active malignancy should be referred to an oncologist.
What Is The Prognosis For Someone With Anemia Of Chronic Disease
Treating the disease that causes the anemia usually means that the anemia will be resolved. You should always let your provider know if symptoms, like fatigue, return.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 07/23/2018.
References
- Weiss G, MD, Goodnough LT, MD. Anemia of chronic disease. N Engl J Med. 2005 352:1011-23. Accessed 7/24/2018.
- Cullis J. Anaemia of chronic disease. Clin Med . 2013 Apr 13:193-6. Accessed 7/24/2018.
- Fraenkel PG. Understanding anemia of chronic disease. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2015 2015:14-8. Accessed 7/24/2018.
- National Organization of Rare Diseases. Anemia of Chronic Disease. Accessed 7/24/2018.
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Anemia of Inflammation & Chronic Disease. Accessed 7/24/2018.
- Madu AJ, Ughasoro MD. Anaemia of Chronic Disease: An In-Depth Review. Med Princ Pract. 2017 26:1-9. Accessed 7/24/2018.
- American Association of Clinical Chemistry. Hemoglobin. 7/24/2018.
You May Like: Can Kidney Stones Cause High Blood Sugar
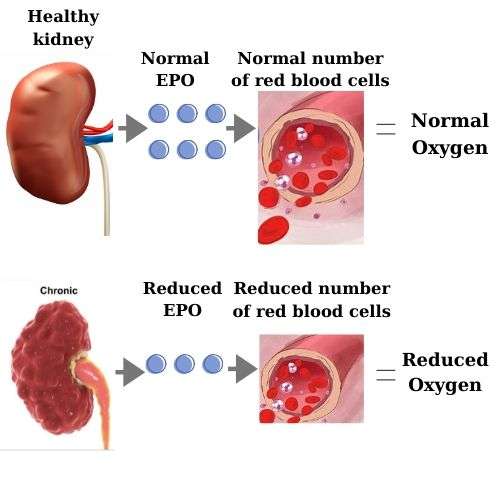
Less Erythropoietin Than Normal
All of the cells in your body live for a certain amount of time and then die. Your body is always working to make new cells to replace the ones that have died. Red blood cells live for about 115 days. Your kidneys help your body make red blood cells.
Healthy kidneys make a hormone called erythropoietin . EPO sends a signal to the body to make more red blood cells. If your kidneys are not working as well as they should, they cant make enough EPO. Without enough EPO, your body doesnt know to make enough red blood cells. This means fewer red blood cells are available for carrying oxygen through your body, leading to anemia.
What Causes Anemia Of Inflammation
Experts think that when you have an infection or disease that causes inflammation, your immune system causes changes in how your body works that may lead to anemia of inflammation.
- Your body may not store and use iron normally.
- Your kidneys may produce less erythropoietin , a hormone that signals your bone marrowthe spongy tissue inside most of your bonesto make red blood cells.
- Your bone marrow may not respond normally to EPO, making fewer red blood cells than needed.
- Your red blood cells may live for a shorter time than normal, causing them to die faster than they can be replaced.
Also Check: Aleve Effect On Kidneys
Anemia Of Chronic Disease
NORD gratefully acknowledges Robert T. Means, Jr., MD, Professor of Internal Medicine and Dean, James H. Quillen College of Medicine, East Tennessee State University for assistance in the preparation of this report.
Synonyms of Anemia of Chronic Disease
- anemia of chronic inflammation
- anemia of inflammation
General Discussion
Anemia of chronic disease, also called the anemia of inflammation, is a condition that can be associated with many different underlying disorders including chronic illnesses such as cancer, certain infections, and autoimmune and inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis or lupus. Anemia is characterized by low levels of circulating red blood cells or hemoglobin, the part of red blood cells that carries oxygen. Anemia of chronic disease is usually a mild or moderate condition. In mild cases, anemia may not be associated with any symptoms or may cause fatigue, paleness of the skin and lightheadedness. The underlying mechanisms that cause anemia of chronic disease are complex and not fully understood.
Signs & Symptoms
Causes
Researchers believe that the immune system, which remains constantly active in individuals with chronic diseases, produces substances that influence the development, storage and transport of iron within the body. Cells in the immune system produce cytokines, specialized proteins that stimulate or inhibit the function of other immune system cells.
Affected Populations
Related Disorders
Diagnosis
Standard Therapies
Report Index
Individualizing Hb Target According To The Patient Profile
The target Hb concentration during ESA therapy is still controversial. Studies early after the appearance of rhuEPO demonstrated its efficacy in reducing the need for blood transfusions, the symptoms related to anemia and an improved quality of life . Various landmark trials have dwelt on the convenience of a complete correction of anemia. Indeed, in the CHOIR trial the use of a target Hb level of 13,5 g/dl was associated with increased risk of suffering a composite of death, myocardial infarction, hospitalization for congestive heart failure and stroke, and no incremental improvement in the quality of life. CREATE trial did not observe an increase of the risk of cardiovascular events, but showed an increase in the necessity of dialysis among the group that targeted Hb in normal range The TREAT trial compared the use of darbepoetin alfa targeting Hb level of 13 g/dl vs. a rescue therapy when Hb level dropped below 9 g/dl in patients with diabetes, NDD-CKD and moderate anemia. The use of darbepoetin alfa did not reduce the risk of either of the two primary composite outcomes , and was associated with an increased risk of stroke . Yet, it is still unclear whether this increased risk is due to the higher ESA doses and the possible non-erythropoietic effects, whether it is due to the underlying systemic inflammation in patients with ESA-hyporresponsiveness, rather than due to the high Hb level itself .
Recommended Reading: Can Aleve Cause Kidney Damage
What Causes Anemia In Ckd
Anemia in people with CKD often has more than one cause.
When your kidneys are damaged, they produce less erythropoietin , a hormone that signals your bone marrowthe spongy tissue inside most of your bonesto make red blood cells. With less EPO, your body makes fewer red blood cells, and less oxygen is delivered to your organs and tissues.
In addition to your body making fewer red blood cells, the red blood cells of people with anemia and CKD tend to live in the bloodstream for a shorter time than normal, causing the blood cells to die faster than they can be replaced.
People with anemia and CKD may have low levels of nutrients, such as iron, vitamin B12, and folate, that are needed to make healthy red blood cells.
Other causes of anemia related to CKD include
- blood loss, particularly if you are treated with dialysis for kidney failure
- infection
- examine your body, including checking for changes in skin color, rashes, or bruising
Iron Supplementation For Anemia In Ckd
Guidelines acknowledge that the optimal strategy to manage iron metabolism remains unclear, and advocate for balancing the potential benefits and risks of iron supplementation . Table 1 summarizes the principles and targets of the management of iron supplements of the KDIGO ERBP NICE guidelines. In recent years some good quality pre-clinical studies, clinical trials and epidemiological studies have shed some light on the therapeutic approach regarding iron deficiency in CKD and will surely change clinical practice.
Intravenous iron has shown benefits both in DD-CKD and more recently in NDD-CKD, as it has proved to be more efficacious in rising ferritin and Hb levels, while reducing ESA and transfusion requirements. Specifically, in hemodialysis patients, oral preparations seem to be useless, maybe except for the phosphate binder ferric citrate . In addition, gastrointestinal intolerance and constipation reduce tolerance and compliance of oral iron formulations .
However, some concerns raised about IV iron formulation such as enhanced oxidative stress, endothelial dysfunction or the potential role in favoring infection. Further, IV iron administration has been associated with an increased risk of hypotension, headaches or hypersensitivity reactions. Labile iron, which is the iron that is freed into the circulation after administration and non-bound to transferrin, is an important cause of such adverse reactions.
Don’t Miss: Red Wine And Kidney Stones
Iron Targets: How Much Iron Is Too Much Iron
Iron overload is a condition of elevated body iron content associated with signs of organ dysfunction that is presumably caused by excess iron. Some studies have demonstrated an increase in the liver iron content in hemodialysis patients, and an association between hepatic iron overload and hepatic steatosis has been recently described . However, its clinical relevance is still not known, and no deposits have been observed in other territories, such as cardiac or pancreatic . A metaanalysis of clinical trials and observational studies in the setting of hemodialysis suggests that patients that received higher doses of IV iron did not show a higher risk of mortality, infections or cardiovascular events . Nonetheless, the strength of the findings is limited by the small number of patients and of events in the clinical trials, and by the statistical heterogeneity in the observational studies included.
There has long been a concern whether iron supplements increased the risk of infections. A sub-analysis of PIVOTAL study did not show differences in infection episodes, hospitalization or death for infection between the proactive high dose regimen and reactive low dose-iron groups of patients .
What You Need To Know About Anemia And Kidney Disease
Anemia and Kidney DiseaseAnemia can make you feel weak, tired, and short of breath. You may also have headaches and trouble sleeping. You may also experience a loss of appetite and a more rapid heart rate.
Anemia comes from the Greek work that means without blood. Anemia is common in people with chronic kidney disease When kidneys are healthy, they make a hormone called erythropoietin, or EPO. This hormone helps the bone marrow to produce the amount of red blood cells that the body needs to carry oxygen to vital organs. When the kidneys are damaged, they often do not make enough EPO. As a result, the bone marrow makes too few red blood cells.
Anemia often develops in the early stages of kidney disease and gets worse as kidney disease progresses.
HemoglobinHemoglobin is the protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen from the lungs to the cells of the body.The test for Hgb is usually part of a blood test called a Complete Blood Count or CBC. Hgb volume in the blood is measured in grams per deciliter . Ranges for healthy individuals who do not have CKD can vary by age and gender, for an adult male the range is 14-18 gm/dL, an adult woman 12-16 gm/dL.
The Food and Drug Administration has recommended that a person with chronic kidney disease who has a low Hgb, most likely has anemia caused by decreased EPO production. Hgb levels can also be affected by the amount of iron in the body.
What Is Kidney Disease?
Don’t Miss: Does Flomax Hurt Your Kidneys
Can Anemia Of Chronic Disease Be Prevented
It may not be possible to prevent the anemia of chronic disease, but you might be able to help yourself by making some changes to your diet. You should make sure to get enough iron, folate, and vitamin B-12 . Some foods you could choose include chicken or turkey, beans, spinach, fortified breakfast cereals, and enriched bread.
Anemia And Chronic Kidney Disease
What is anemia?Anemia happens when your red blood cells are in short supply. Red blood cells carry oxygen from your lungs to all parts of your body, giving you the energy you need for your daily activities.
What are the symptoms of anemia?Anemia can cause you to:
- Look pale
- Have little energy for your daily activities
- Have a poor appetite
- Feel dizzy or have headaches
- Have a rapid heartbeat
- Feel depressed or “down in the dumps”
Why do people with kidney disease get anemia?Your kidneys make an important hormone called erythropoietin . Hormones are chemical messengers that travel to tissues and organs to help you stay healthy. EPO tells your body to make red blood cells. When you have kidney disease, your kidneys cannot make enough EPO. Low EPO levels cause your red blood cell count to drop and anemia to develop.
Most people with kidney disease will develop anemia. Anemia can happen early in the course of kidney disease and grow worse as kidneys fail and can no longer make EPO. Anemia is especially common if you:
- Have diabetes
- Have moderate or severe loss of kidney function
- Have kidney failure
- Are female
How do you treat anemia?Your treatment will depend on the exact cause of your anemia.If your anemia is due to kidney disease, your healthcare provider will treat you with:
For more information please view our full PDF brochures or request a free copy by calling or email.
You May Like: Is Ginger Good For Kidney Patients
Outcomes Of Iron Deficiency Anemia In Ckd
Anemia in CKD has been shown to be associated with an increased risk of morbidity and mortality . In a large observational study, 27,998 patients with CKD were followed up for approximately 5.5 years . The authors reported a higher baseline prevalence of anemia in patients who died than in those who survived . Furthermore, the increase in the prevalence of anemia over the observation period was greatest in those who died despite a shorter period of observation.
The high rates of heart disease and anemia in those who died suggest that anemia accelerates the progression of heart disease and increases the risk of death. However, anemia may be a marker for severity of CKD rather than a causative factor .
A retrospective cohort study among patients with incident CKD who had hemoglobin measurements, in a large health maintenance organization administrative data set, evaluated 5,885 patients . Anemia was found to be a predictor of excess mortality, excess cardiovascular hospitalizations, and excess end-stage renal disease . For those with the most severe anemia , there was an increased rate of mortality , cardiovascular hospitalizations , and ESRD when compared to those who were not anemic.
Definition And Risk Factors For Anemia In Ckd
According to the WHO criteria published in 1997, the Hemoglobin and Hematorcrit cutoffs for defining anemia are < 13 g/dL and 39%, respectively, in men and < 12 and 36%, respectively, in non pregnant women . Newer research differentiates anemia cutoffs based on both race and age in addition to sex. Table 1 lists proposed lower limits of normal for hemoglobin concentration based on Scripps-Kaiser data for the 5th percentiles and the NHANES data published in 2006 .
| White Men |
Lower Limits of normal Hemoglobin concentration
Based on reference 3 Beutler et al.
Multiple risk factors increase the risk of developing anemia. Among multiple factors, individuals with CVD, DM and CKD, HTN and of African American race are at significantly high risk than the general population .
Read Also: What Tea Is Good For Kidneys
How Will I Know If I Have Anemia
Talk to your doctor if you think you may have anemia. The only way to know if you have anemia is to have a blood test. When you have kidney disease, your doctor will want you to have blood tests often. These tests are used to check not only your kidney function, but also for signs of any other problems, such as the number of red blood cells and how much iron you have in your body.
The test for anemia is a simple blood test to check for the amount of hemoglobin in your blood. Hemoglobin is a part of your red blood cells. Figuring out the amount of hemoglobin you have in your blood can tell your doctor how many red blood cells you have.
Your doctor may also ask you if youve noticed any symptoms, such as changes in skin color or feeling unusually tired.