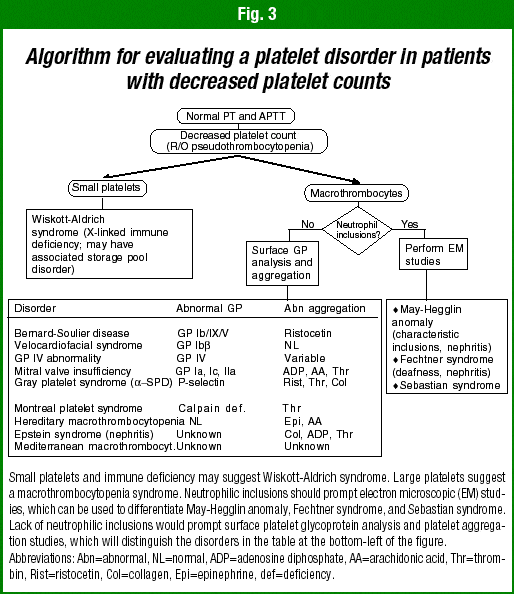
What Is The Prognosis For Children With Congenital Heart Defects
The prognosis depends on the defect. In many cases, children with congenital heart defects go on to live normal lives. In most cases, people with heart defects are at greater risk for developing infection of the heart and valves. They may need to take antibiotics when having certain dental or surgical procedures in order to prevent endocarditis, an infection of the hearts lining.
What Happens If I Have Too Much Erythropoietin
Excess erythropoietin results from chronic exposure to low oxygen levels or from rare tumours that produce high levels of erythropoietin. It causes a condition known as polycythaemia which means high red blood cell count. In many people, polycythaemia does not cause any symptoms. However, there are some general and non-specific symptoms including weakness, fatigue, headache, itching, joint pain and dizziness.
Why The Test Is Performed
Creatinine is a chemical waste product of creatine. Creatine is a chemical made by the body and is used to supply energy mainly to muscles.
This test is done to see how well your kidneys work. Creatinine is removed from the body entirely by the kidneys. If kidney function is not normal, the creatinine level in your blood will increase. This is because less creatinine is excreted through your urine.
Also Check: Can Stress Affect Your Kidneys
Blood Tests For Diagnosing Kidney Disease
Following are a variety of blood tests that help determine whether or not you have kidney disease:
- CBC complete blood count of your red blood cells, white blood cells, and plateletslow CBC level can mean kidney function is reduced.
- Creatinine waste product of muscles that is normally eliminated by the kidneys, may be elevated when kidney function is reduced.
- Creatinine clearance measure of how well creatinine is removed by the kidneys over a 24-hour period of urine collection. When kidney function is reduced, clearance may be low.
- Blood electrolyte tests also known as chemistries. Electrolytes are filtered out of the blood by the kidneys. Abnormal levels may indicate reduced kidney function.
- Hemoglobin A1C measures how well blood sugar is controlled during three months before testing. Elevation indicates blood sugar is not well-controlled and may be causing reduced kidney function.
- Blood urea nitrogen also a waste product that is eliminated by the kidneys. BUN is elevated when kidney function is reduced.
- Glomerular filtration rate the best measure of kidney function and also determines the stage or progression of the disease. The higher the numbers of the GFR, the better the kidneys are working.
What Are The Symptoms Of High Potassium
Many people do not feel symptoms of high potassium. Having too much potassium in your blood can be dangerous. It can even cause a heart attack.
If you do feel symptoms, some of the most common are:
- Feeling tired or weak
- Feeling sick to the stomach
- Muscle pains or cramps
- Trouble breathing, unusual heartbeat, chest pains
If you have trouble breathing or think there could be a problem with your heart, call 911 for emergency help.
Don’t Miss: Does Ectopic Kidney Affect Pregnancy
What Questions Should I Ask My Doctor
Questions to ask include:
- Should I be concerned that my platelet levels are high?
- Will I need follow-up tests to check my platelets?
- What tests will I need to determine whats causing my thrombocytosis?
- What treatments do you recommend?
- What lifestyle changes can I make to manage my condition?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Dont be alarmed if your blood work results show high platelet levels. Your platelets may be elevated for various reasons. Many causes dont require treatment. If your levels remain high and youre experiencing symptoms, your healthcare provider will work to determine the cause. Careful monitoring and medications can usually prevent the most concerning complications associated with thrombocytosis.
Platelets And Liver Disease
Platelets play an important role in liver disease. Recent evidence suggests that in the injured liver, platelets are present and interact with sinusoidal endothelial cells, influencing the recruitment and activation of other cells., Hepatic sinusoids are lined by a unique endothelium, which is fenestrated, exposed to minimal shear stress, and may display scavengerlike functions. Several studies have suggested that platelets may be sequestered within the liver sinusoids and may play a role to assist in leukocyte recruitment during inflammation., In several types of hepatic injury, neutrophils play a key role in the pathogenesis of liver injury. Current research suggests that circulating platelet-neutrophil aggregates may play a role in driving organ damage in patients with cirrhosis., Interestingly, the role of platelets in liver disease appears to be time-specific in that induction of thrombocytopenia in some models of chronic liver disease can worsen liver function by causing hepatic fibrosis, and in other forms of liver disease, antiplatelet therapy may mitigate liver injury., With this information in mind, we can examine the more classical, hemostatic role of platelets in liver disease.
Also Check: How To Remove Kidney Stones
What Abnormal Results Mean
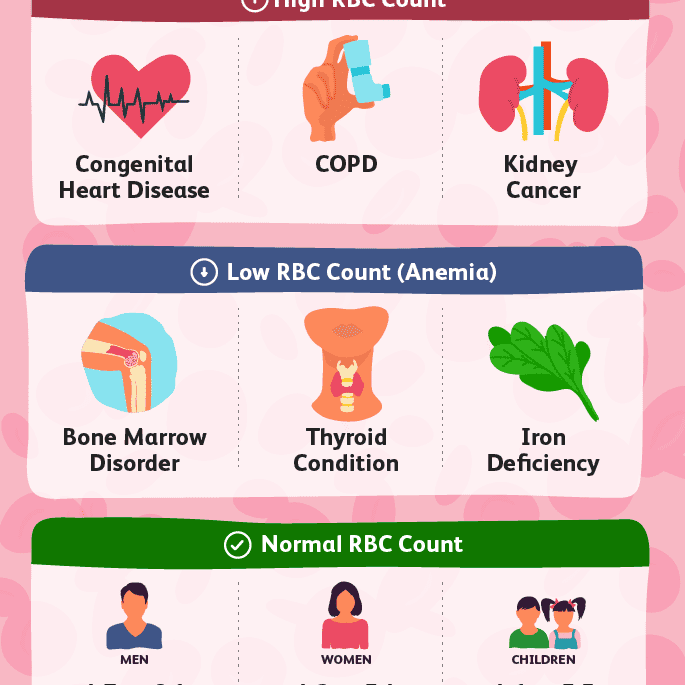
High RBC, hemoglobin, or hematocrit may be due to:
- A lack of enough water and fluids, such as from severe diarrhea, excessive sweating, or water pills used to treat high blood pressure
- Kidney disease with high erythropoietin production
- Low oxygen level in the blood for a long time, most often due to heart or lung disease
- Polycythemia vera
Low RBC, hemoglobin, or hematocrit is a sign of anemia, which can result from:
- Breakdown of red blood cells ( hemolysis
- Certain long-term medical conditions, such as chronic kidney disease, ulcerative colitis, or rheumatoid arthritis
A high platelet count may be due to:
- Problems with the bone marrow
A low platelet count may be due to:
- Disorders where platelets are destroyed
- Chemotherapy medicines used to treat cancer
Medical History And Physical Examination
Evaluation of an individual with suspected ET should start with a detailed medical history and a physical examination by a hematologist-oncologist
The medical history should include information about the patients:
- Cardiovascular risk factors, such as high blood pressure and diabetes
- Past illnesses and injuries
- Current and past medical treatments
- History of thrombus or hemorrhagic events
- Family medical history
- Current symptoms
After the medical history, the doctor will conduct a physical examination. During the physical examination, the doctor may:
- Listen to the patient’s heart and lungs
- Examine the patient’s body for signs of disease
- Check different organs of the body
Don’t Miss: Is A Kidney Infection Contagious
Mayo Clinic Q And A: What Causes A High Platelet Count
DEAR MAYO CLINIC: I am 33 years old and recently had an annual physical and routine blood work. I’m active with two children and feel fantastic, but my platelet count came back as 651. My health care professional said it could indicate a blood cancer and referred me to a hematologist. What can cause my platelets to be so high? I’m nervous, as my only prior medical problem was iron deficiency anemia.
ANSWER: Being told you might have cancer can be scary, but, thankfully, most people with an elevated platelet count do not have cancer. Understanding what platelets are can help you understand the situation.
Your bone marrow makes white blood cells, red blood cells and platelets. White blood cells help fight infection, red blood cells help carry oxygen to parts of the body, and platelets help keep you from bleeding too much. When a blood vessel is injured, like after a cut, platelets are activated and stick together to plug the hole and stop the bleeding.
A normal platelet count typically ranges from 150450 cells per nanoliter of blood. Like you, most patients with a high platelet count do not have any symptoms, and the high count is found unexpectedly on routine blood work.
The referral to a hematologist can help you discern the cause of your high platelet numbers.
There are two possible causes:
Based on your past anemia diagnosis, you most likely would have reactive or secondary thrombocytosis, which is where other conditions cause a high platelet count.
When Should I Get A Platelet Count Test
Your doctor may recommend you take a platelet count test during a check-up as part of a broader screening panel such as a complete blood count. They might also recommend platelet count testing if you have symptoms associated with abnormal platelet levels. Low or high platelet counts may or may not cause signs and symptoms. Its important to speak with your doctor any time you notice health changes that concern you.
Symptoms of low platelet levels
Bleeding is the main sign and symptom of a low platelet count. Early signs of a low platelet count can occur in any part of the body and may include :
- Purple, reddish, or brown bruising, occurring easily and often
- Small red and purple dots on the skin
- Abnormally prolonged bleeding, including from minor cuts
- Bleeding from the nose or mouth
- Atypically heavy vaginal bleeding, especially during menstruation
- Excessive bleeding during dental work, including flossing or surgery
- Blood in the urine or stool, or bleeding from the rectum
Symptoms of high platelet levels
Signs of high platelet levels are primarily related to blot clots and bleeding. They may include:
- Weakness or dizziness
- Tingling of the hands and feet
- Pain, swelling, warmth, and/or tenderness in one or both of the lower extremities
In some instances, extremely high platelet counts may result in signs and symptoms that mirror low platelet counts. Signs and symptoms of high platelet levels include:
Monitoring platelet levels
Don’t Miss: What Do They Give You For Kidney Infection
How Is Thrombocytosis Diagnosed
As thrombocytosis doesnt typically cause symptoms, the first sign is often a high platelet count that shows up during routine blood work .
Thrombocytosis involves having more than 450,000 platelets per microliter of blood. If you have elevated levels, your healthcare provider will likely order a follow-up blood test a few weeks later to see if your levels remain high. Levels that are momentarily high but then return to normal arent usually concerning. Levels that remain elevated may signal an underlying condition.
Identifying the underlying condition thats raising your levels helps healthcare providers diagnose and manage reactive thrombocytosis. If your provider cant find a secondary cause, theyll run tests to see if you have essential thrombocythemia.
Tests may include:
- Peripheral blood smear: Shows if the platelets in your blood look abnormal.
- DNA/genetic tests: Detect gene mutations common in ET, like JAK2.
- Bone marrow biopsy: Checks for abnormal cells in your bone marrow.
How Does Blood Clot
When a blood vessel is injured, the damaged cells in the vessel wall send out chemical signals. These signals cause clots that slow or stop bleeding.
A blood clot forms through several steps.
Your blood vessel narrows. First, chemical signals cause the injured vessels to narrow to prevent more blood from leaking out.
Platelets come to the site of injury. When you have a severe injury that is bleeding, chemical signals travel through your blood to the spleen, where many platelets are stored. The signals tell your spleen to release the platelets into your blood. Back at the injury site, the vessel walls become sticky and capture the platelets as they float past.
A platelet plug forms. The platelets change shape and become stickier. This allows them to attach to the vessel wall and clump together into a plug.
The clot forms. The platelets and other proteins in the blood called clotting factors form a blood clot. The clot contracts to pull the two sides of the damaged vessel closer together, so it is easier to repair.
If you have a high platelet count, blood clots may form often in your blood vessels. These clots can block blood flow through your body and prevent your organs from getting enough blood. If you have a low platelet count, your blood may not clot normally. You may have trouble stopping bleeding. This can make you lose a lot of blood even from a small injury.
Bleeding disorders and blood clotting disorders also can affect how blood clots form in your body.
You May Like: Does Beer Hurt Your Kidneys
Effect Of Platelets In Uraemic Patients
In light of the various platelet aberrancies discussed above in uraemic patients, it would follow that platelets are crucial players in the prognosis of patients with CKD. Both thrombocytosis and thrombocytopenia are commonly seen in patients with end-stage renal disease , and the role of antiplatelet agents in these patients is, at best, controversial.
What Is The Outlook For Someone With Thrombocytosis
Reactive thrombocytosis gets better when the underlying problem resolves. Although your platelet count is elevated for a short time , secondary thrombocytosis doesnt typically lead to abnormal blood clotting.
Essential thrombocythemia , or primary thrombocytosis, can cause serious bleeding or clotting complications. Taking medicine that keeps your platelet levels normal can help prevent this. After many years of having the disease, however, bone marrow fibrosis can develop. A small percentage of people with essential thrombocythemia develop leukemia.
Recommended Reading: Does Allopurinol Affect The Kidneys
Study Participants And Study Design
We conducted a retrospective cohort study in patients with CKD5D who commenced dialysis from 2012 to 2017 at the Nephrology Department of West China Hospital. Patients were included if they were receiving HD or PD for more than 3 months. Patients were excluded if they had cirrhosis or lacked core data .
Because of the large sample size, the anonymity of the patients studied, and the nonintrusive nature of the research, the requirement for
Platelet Function In Uraemia
The most common abnormality is prolongation of bleeding time, with multiple platelet abnormalities contributing to defective aggregation and a delay in time to formation of the primary haemostatic plug. Among the platelet abnormalities seen in uraemia are listed abnormal granule content and release, abnormal arachidonic metabolism, abnormal cyclo-oxygenase activity, abnormal handling of cAMP, intracellular calcium, serotonin and abnormal binding of GP IIb-IIIa. Furthermore,uraemic platelets have attenuated response to thrombin, with reduced secretion of ATP and other granule contents, and have diminished ATP release to arachidonic acid, producing an aspirin-like effect as evidenced by platelet aggregation studies. Also interestingly, the abnormalities seen in intracellular calcium may be linked with ambient parathyroid hormone concentration, and thus hyperparathyroidism may further affect platelet reactivity.
It has also been shown that, in addition to these baseline abnormalities, platelet reactivity and aggregation are altered throughout the course of a dialysis session, with similar increases in reactivity as seen in patients with coronary artery disease.
You May Like: Can Magnesium Cause Kidney Problems
Why Does Anemia Occur In Patients With Ckd
Chronic kidney disease refers to lasting damage of the kidneys in which the patient progressively loses kidney function. In advanced stages, CKD can lead to total kidney failure without the assistance of dialysis to filter the blood or in some cases a kidney transplant. Anemia occurs when damaged kidneys are unable to produce a hormone called erythropoietin , which helps your bone marrow produce red blood cells. In the absence of adequate levels of EPO, the body becomes anemic and cannot supply your body with enough oxygen.
Upset Stomach Nausea Vomiting
Why this happens:
A severe build-up of wastes in the blood can also cause nausea and vomiting. Loss of appetite can lead to weight loss.
What patients said:
I had a lot of itching, and I was nauseated, throwing up all the time. I couldnt keep anything down in my stomach.
When I got the nausea, I couldnt eat and I had a hard time taking my blood pressure pills.
Read Also: Is Grape Juice Good For Your Kidneys
Kidney Disease And White Blood Cell Count
Anaemia is common in kidney disease, but many other conditions can also cause.
White blood cells which help to fight infection.
A full blood count is a laboratory blood test to measure the amount of.
Low red blood cell counts. Anemia, or decreased red blood cell numbers, occurs during kidney disease because it hampers the kidneys ability to produce erythropoietin, which triggers the bone marrow to make more red blood cells. Elevated blood pressure.
Leukocytes are white blood cells that help your body fight germs. When you have more of these than usual in your urine, its often a sign of a problem somewhere in your urinary tract.
Hi, The high WBC count could be a part of the inflammatory reactions accompanying the presence and passage of the stone. However, other conditions that can cause high WBC count include infections. This is determined based on the type of white cell that is increased.
Learn if you might be at higher risk for lupus kidney disease, as regular.
are other elements that show up in urine such as red blood cells or white blood cells.
American Association of Kidney Patients: Understanding Iron and Chronic Kidney Disease. 3.
red blood cells, white blood.
The complete blood count or.
GWAS summary statistics of the CKDGen (Chronic Kidney Disease.
Testing the Observational Association Between Blood Cell Counts and.
Congratulations on receiving your kidney transplant . Taking care of.
In some cases, because of side effects, patients must take an.
Interaction With Other Circulating Cells
As part of their role in inflammation, platelets aggregate with leucocytes via their P-selectin receptor interacting with its natural ligand P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1 on monocytes and neutrophils. P-selectin is translocated to the surface of activated platelets where it contributes to platelet-assisted enhancement of thrombosis at sites of endothelial injury.
These aggregates form an anchoring source for inflammatory cells on activated platelets and contribute to ongoing injury at the sites of atheromatous plaques. Levels of plateletmonocyte aggregates have been found to be significantly higher in dialysis patients. In patients with normal renal function, PM aggregates have been associated with cardiovascular disease. Data from our unit would suggest that this also applies in uraemic patients, with a significant increase in cardiovascular morbidity and mortality seen in those patients with higher levels of circulating PM aggregates.
Don’t Miss: Do Non Obstructing Kidney Stones Hurt