Diagnosis Of Kidney Stones
Many kidney stones are discovered by chance during examinations for other conditions. Urine and blood tests can help with finding out the cause of the stone. Further tests may include:
- x-rays, including an intravenous pyelogram , where dye is injected into the bloodstream before the x-rays are taken.
What Happens To Patients With Kidney Stones
After the passage of a first kidney stone, recurrences are common with rates of approximately 40 % at 5 years, 50 % at 10 years, and 75 % at 20 years. Stone formation is associated with increased rates of chronic kidney disease, hypertension, osteoporosis, and obesity. Although systemic diseases increase risk of kidney stones, the majority are idiopathic.
More than 90% of recurrent stones are preventable with adequate management of metabolic risk factors.
Most idiopathic stone formers have at least one metabolic abnormality that can be addressed as a preventive measure for stone recurrence.
Preventive measures include:
You May Like: What Is The Functional Unit Of The Kidneys
Diagnosis Of A Kidney Stone
A doctor may suggest the following methods of diagnosis, if you suffer from symptoms of Kidney Stones.
-
Blood analysis: Blood tests may suggest that you have an excess of uric acid or calcium. The results of a blood test allow your doctor to look for additional medical issues while also monitoring the condition of your kidneys.
-
Urine analysis: A urine test may reveal the amount of stone-forming minerals or insufficient amounts of stone-preventing chemicals. Your doctor might ask you to perform two urine collections over two consecutive days in preparation for this test.
-
Ultrasound imaging: Diagnosing kidney stones using an ultrasound is a rapid and simple noninvasive examination. Kidney stones in your urinary tract may be visible on an ultrasound. Even microscopic stones may be found using high-speed or dual-energy computed tomography .
-
Stone analysis: To collect stones you pass, you might be requested to urinate through a strainer. The stone composition will be determined via laboratory analysis. This information is used by your doctor to identify the cause of your kidney stones and to develop a plan to stop further stone formation.
You May Like: Does A Kidney Stone Hurt All The Time
Cell Injury And Apoptosis
Exposure to high levels of oxalate or CaOx crystals induces epithelial cellular injury, which is a predisposing factor to subsequent stone formation . CaOx crystal depositions in the kidneys upregulate the expression and synthesis of macromolecules that can promote inflammation . Crystals may be endocytosed by cells or transported to the interstitium. It has been suggested that injured cells develop a nidus which promotes the retention of particles on the renal papillary surface . In individuals with severe primary hyperoxaluria, renal tubular cells are injured and crystals become attached to them . The addition of CaOx crystals onto MadinDarby canine kidney cell lines showed an increase in the release of lysosomal enzymes, prostaglandin E2, and cytosolic enzymes . A study on animal models also revealed that the administration of high concentrations of CaOx crystals or oxalate ions appears to be toxic causing renal tubular cell damage . It has been suggested that oxalate increases the availability of free radicals by inhibiting enzymes responsible for their degradation. For instance, reactive oxygen species can damage the mitochondrial membrane and reduce its transmembrane potential. These events are known features of early process in apoptotic pathways .
Can Kidney Stones Lead To Chronic Kidney Disease
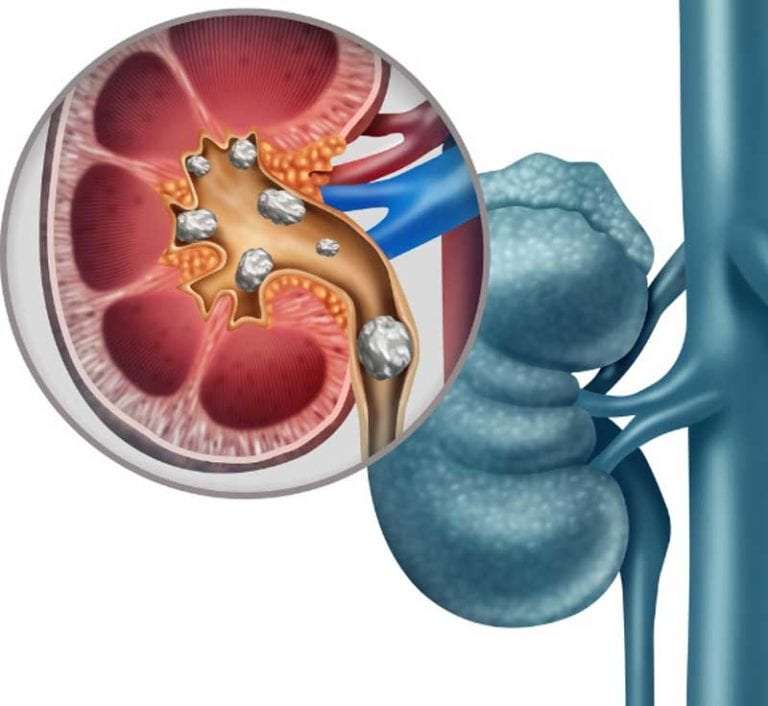
If you or someone you know has had a kidney stone before, you probably heard them describe the excruciating pain. What may start out feeling like a stomachache or some lower back pain can quickly become unbearable as your body tries to pass the stone.
Though painful, a kidney stone typically does not cause damage. However, kidney stones can be a sign of other health issues.
More people are getting kidney stones, which is cause for concern because of the factors that contribute to kidney stones and what can happen if kidney stones keep recurring, said Prince Mohan, M.D., medical director of Transplant Nephrology at Geisinger.
Typically, any waste that builds up in the kidneys is dissolved in the liquid that passes through them. But when there is a high level of minerals or salt and too little liquid, kidney stones begin to form. Usually, kidney stones that stay in the kidney arent noticeable.
The pain is a result of the kidney stone beginning to move from a kidney to the bladder through a tube called the ureter.
Most people dont know they have a kidney stone until they begin to feel severe pain in the side or abdomen, nausea, or if their urine is pink or red, said Dr. Mohan. They may be diagnosed in the emergency department after experiencing severe pain.
Having one kidney stone increases the risk of developing another one, said Dr. Mohan. This also increases the risk of chronic kidney disease and kidney failure.
Don’t Miss: How Long Can Someone Live Without Kidney Function
Kidney Stone Inhibitors And Promoters
Inhibitors are substances which decrease the initiation of supersaturation, nucleation, crystal growth, rate of aggregation, or any other processes required to stone formation . Normally, urine contains chemicals that prevent crystal formation. Inhibitors in urine includes small organic anions such as citrate, small inorganic anions such as pyrophosphates, multivalent metallic cations such as magnesium, or macromolecules such as osteopontin, glycosaminoglycans, glycoproteins, urinary prothrombin fragment-1, and TammHorsfall proteins . These inhibitors do not seem to work equally for everyone therefore, some people form stones. But, if crystals formed remain tiny, usually it travels through the urinary tract and passes out from the body with urine splash without being noticed. Inhibitors may act either directly by interacting with crystal or indirectly by influencing the urinary environment . When inhibitory compounds adsorb onto the surface of the crystal, it inhibits nucleation, crystal growth, aggregation, or crystal-cell adherence.
Common Kidney Stone Signs And Symptoms
Kidney stones can form when you have high amounts of salt and other minerals in your urine which turn into crystals. These crystals grow into a stone, which can range in size from sand-like grains to small pebbles to a gravel-like chunks.1
A variety of factors can lead to kidney stonesfor instance, supplementing with vitamin C increases the risk of kidney stones for men.2 Use of antibiotics may also play a role.3 The biggest factor: Not staying hydrated. Drink more liquids, and you’ll dilute urine, reduce its acidity, and remove excess salt, three tactics that can help prevent stones from forming.4
Kidney stones are known for feeling tremendously painful when they pass. But that’s not the only symptomtake a look at the most common signs of a kidney stone.
You May Like: Do Almonds Cause Kidney Stones
How Are Kidney Stones Treated
Once diagnosed, your healthcare provider will first determine if you even need treatment. Some smaller kidney stones may leave your system when you urinate. This can be very painful. If your provider decides that you do need treatment, your options include medications and surgery.
Medications. Medications may be prescribed to:
- Your healthcare provider may recommend that you take an over-the-counter medication like ibuprofen or, if youre in the emergency room, an IV narcotic.
- Manage nausea/vomiting.
- Relax your ureter so that the stones pass. Commonly prescribed medicines include tamsulosin and nifedipine .
You should ask your healthcare provider before you take ibuprofen. This drug can increase the risk of kidney failure if taken while youre having an acute attack of kidney stones especially in those who have a history of kidney disease and associated illnesses such as diabetes, hypertension and obesity.
Surgery. There are four types of surgeries used to treat kidney stones. The first three are minimally invasive, meaning that the surgeon enters your body through a natural opening , or makes a small incision.
Warning Signs And Symptoms
A kidney stone usually does not cause symptoms until it moves around within the kidney or passes into the ureters. If it becomes lodged in the ureters, it may block the flow of urine causing the kidney to swell and the ureter to spasm. Signs that might likely indicate kidney stones are as follows:
- Severe and sharp pain in the side and back, below the ribs
- Pain that radiates to one side of the back or lower abdomen
- Pain that comes in waves with fluctuating intensity
- Fever and chills, if an infection is present
- Nausea and vomiting
- Intense pain in the abdomen when the stone moves to the ureters
**Nevertheless, some patients may not develop any of these symptoms.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Know If You Have Bad Kidneys
What Are The Symptoms Of Kidney Stones
If you have a small kidney stone, it may travel out of your body through your urine . You may not have any symptoms and may never know that you had a kidney stone.
If you have a larger kidney stone, it may get stuck in your urinary tract and block urine from getting through. You may notice symptoms, including:
- Pain while urinating
- Sharp pain in your back or lower belly area
- Stomachache that does not go away
- Feeling sick to your stomach or throwing up
- A fever and chills
- Urine that smells bad or looks cloudy
You may feel a lot of pain when you pass a kidney stone or if a large kidney stone blocks the flow of your urine.
If you are having any of these symptoms, contact your doctor.
How Long Does It Take A Kidney Stone To Form
You can have kidney stones for years without knowing theyre there. As long as these stones stay in place within your kidney, you wont feel anything. Pain from a kidney stone typically starts when it moves out of your kidney. Sometimes, a stone can form more quickly within a few months.
Talk with your healthcare provider about your risk factors. They might do a 24-hour urine test to check how quickly you develop stones.
Read Also: Can You Cure Stage 4 Kidney Cancer
Risk For Ckd By Stone Type
There is evidence that the risk for CKD varies by stone type, but more studies are needed. Population-based studies often lack the granular detailed data to characterize stone type because many stone formers never have their stones analyzed or urine chemistries evaluated, and, even if so, this information often is not available in the databases available for study. Saucier et al. studied community stone formers in Olmsted County, MN, and identified 53 who developed CKD and were matched with 106 who did not develop CKD. Hypertension, diabetes, six or more urinary tract infections, allopurinol therapy, and struvite stone type were identified as risk factors for CKD. The association with allopurinol could either reflect treatment of hyperuricosuria for stone prevention or treatment of hyperuricemia secondary to CKD. Only half of the participants had stone type determined, and even fewer had urine chemistry data. Number of stone episodes, surgical procedures, and stone passage symptoms were not associated with CKD, although there was limited statistical power in this study .
Pretreatment urinary creatinine clearance in normal control subjects and different types of stone formers: Brushite , calcium oxalate , apatite , struvite , uric acid , and cystine . Reprinted from reference , with permission.
Why Is Fish A Superfood
Fish is a good source of protein without being high in saturated fat Just a 3 oz portion of fish provides an average of 20 grams of protein.
Other reasons why fish is considered a superfood include:
- Fish is loaded with vitamins such as D and B2 .
- Fish is a great source of minerals, calcium, phosphorus, iron, zinc, iodine, magnesium, and potassium.
- Fatty fish, such as salmon, are some of the best sources of omega-3 fatty acids. These omega 3-fatty acids are packed with benefits for your heart, brain, eyes, inflammation, and your overall health.
You May Like: How To Decrease Kidney Stone Pain
Size Of Kidney Stones
Kidney stones are of variable sizes. They range from small sized crystals to large sized stones such as the size of a golf ball. Variations in sizes of kidney stones affect the following things:
The size of kidney stones affect the treatment method required for their removal. Small-sized stones can easily pass through the kidney without any medical assistance but large-sized stones require medical intervention. Certain tests are conducted which help in determining the size of kidney stones, such as KUB, an Ultrasound or an IVP. They help in analyzing which treatment should be effective for the removal of your kidney stones.
It is estimated that one in ten people will have a kidney stone sometime in their lives. The prevalence of kidney stones has increased significantly in the United States from 3.8% in the late 1970s to about 9% in the 2000s. The lifetime risk of developing kidney stones is about 19% in men and 10% in women.
You May Like: Can Kidney Stones Affect Your Psa Count
Microstructure Of Kidney Stones
Kidney stones are solid masses, ranging in size from a grain of sand to a pearl a stone does not have to cause symptoms. Depending on their composition, stones are either yellow or brown in colour and smooth or jagged in appearance. They are composed of crystals and a ubiquitous organic matrix , which not only coats the crystals but is also present inside the crystals and the inter-crystalline spaces. The matrix of calcific stones contains many macromolecules, including osteopontin , interinhibitor and urinary prothrombin fragment 1 all of which are normally present in the urine, albeit in small quantities. The matrix also contains various forms of lipids, which have been shown to induce crystal nucleation. The association between the crystals and the matrix seems to start early upon crystal nucleation and continues throughout the formative and growth phases of the developing stone. Although some urinary molecules, such as UPTF1, are considered crystallization inhibitors, others such as osteopontin can act as both inhibitors and promoters of crystallization. These molecules seem to be produced as a protective response against mineralization. However, both CaOx and CaP crystals have been shown to induce the production of macromolecules that inhibit and/or modulate crystallization,.
Calcium oxalate kidney stones examined using scanning electron microscopyScanning electron microscopy and transmission electron microscopy of kidney stones
Calculi types
Also Check: What Does Passing A Kidney Stone Mean
What Are The Risk Factors Associated With Kidney Stones
Although anyone can develop a kidney stone, there are some factors that can increase your risk. Some risk factors cant be changed, while others can be controlled or modified.
You may be at a higher risk of developing kidney stones if:
- youve had kidney stones before
- somebody in your family has had kidney stones
- you dont drink enough fluids
- your diet is high in protein, salt , and/or sugar
- you have overweight or obesity
- you have diabetes
- you take calcium-based antacids or diuretics
- youve had gastric bypass surgery or other gastrointestinal surgery
- youre of reproductive age and have had one or more pregnancies
- you eat a diet thats high in red meat or high in oxalates
- you have a condition that causes high levels of cystine, uric acid, calcium, or oxalate in your urine
What Causes Kidney Stones
Anyone can get a kidney stone, but some people are more likely than others to get them. Men get kidney stones more often than women. Kidney stones are also more common in non-Hispanic white people than in people of other ethnicities. You may also be more likely to get a kidney stone if you:
- Have had kidney stones before
- Have someone in your family with kidney stones
- Do not drink enough water
- Eat a lot of protein, sodium , or sugar
- Have a health problem that causes your urine to contain high levels of cystine, oxalate, uric acid or calcium
- Have a health problem that causes swelling or damage in your digestive system or your joints
- Take certain medicines, such as diuretics or calcium-based antacids
Read Also: How You Know You Have Kidney Disease
What Are Kidney Stones
Usually, your kidneys remove waste from your blood to make urine . When there is too much waste in your blood and your body is not producing enough urine, crystals begin to form in your kidneys. These crystals attract other wastes and chemicals to form a solid object that will get larger unless it is passed out of your body in your urine.
Kidney stones can be as small as a grain of sand or as large as a golf ball.
Hemodialysis And Daily Home Or Nocturnal Hemodialysis/peritoneal Dialysis
People on dialysis have increased protein needs. Include fish two times per week as a great lean protein option and a way to help boost intake of omega-3 fatty acids. The potassium and phosphorus content of fish varies . Choose fresh fish when possible because it is lower in sodium. Canned fish can be high in sodium. Always talk to your kidney dietitian to find out how you can include fish in your diet.
Also Check: What Causes Cyst On Liver And Kidneys
Mechanisms Of Renal Stone Formation
The pathogenesis of kidney stone or biomineralization is a complex biochemical process which remains incompletely understood . Renal stone formation is a biological process that involves physicochemical changes and supersaturation of urine. Supersaturated solution refers to a solution that contains more of dissolved material than could be dissolved by the solvent under normal circumstances . As a result of supersaturation, solutes precipitate in urine leads to nucleation and then crystal concretions are formed. That is, crystallization occurs when the concentration of two ions exceeds their saturation point in the solution . The transformation of a liquid to a solid phase is influenced by pH and specific concentrations of excess substances. The level of urinary saturation with respect to the stone-forming constituents like calcium, phosphorus, uric acid, oxalate, cystine, and low urine volume are risk factors for crystallization . Thus, crystallization process depends on the thermodynamics and kinetics of a supersaturated solution . Therefore, lithiasis can be prevented by avoiding supersaturation.