Causes Of Struvite Stones
Struvite stones are almost always caused by urinary tract infections. Certain bacteria produce urease, which breaks down urate and raises the concentration of ammonia in the urine. Ammonia makes up the crystals that form struvite stones. The bacteria that promote stone formation are most often Proteus, but they may also include Ureaplasma urealyticum, as well as Pseudomonas, Klebsiella, Providencia, Serratia, and Staphylococcus species. Women are twice as likely to have struvite stones as men.
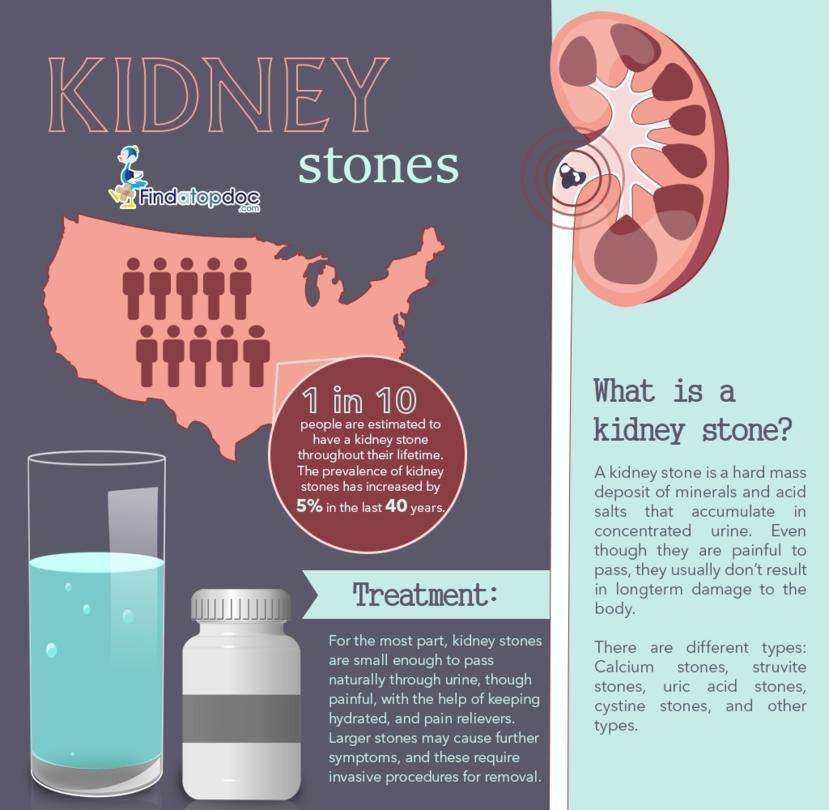
Drugs For Kidney Stones
Drugs for kidney stones are used to treat the acute symptoms like pain caused by the stone and also to prevent new stones from forming. Kidney and other urinary tract stones are a common problem that can affect individuals of all age groups. Urinary tract stones cause pain. Their passage through the ureters causes severe spasmodic pain, which is an attempt by the urinary tract to expel the stone.
Kidney stones also cause symptoms of nausea, vomiting and blood in the urine. They may obstruct the flow of urine through the urinary tract resulting in swelling of the kidney , kidney infection and chronic kidney disease. Early treatment is necessary to relieve symptoms and prevent long-term damage.
Kidney stones vary according to their chemical composition. Calcium oxalate stones are the most common type, followed by calcium phosphate, uric acid, struvite / triple phosphate stones and cystine stones. Some stones can be mixed.
Smaller stones may be expelled spontaneously by the urinary tract and medical treatment helps to relieve symptoms, dissolve the stone and assist in its expulsion. Larger stones require surgical treatment. The introduction of minimally invasive surgeries has almost eliminated the need for open surgeries.
Drugs used to treat kidney stones can be classified based on the role they play in the treatment of kidney stones:
Drugs that relieve the symptoms such as Pain and Vomiting or Nausea Caused by Kidney Stones:
These include:
- Antiemetics
Diagnosis: Low Urine Ph
Possible treatments:
Citrate supplementation
Citrate supplements, such as potassium citrate, will raise the pH of your urine, making stones, such as those composed of uric acid, less likely to form. If your blood potassium level is high, your doctor may prescribe sodium bicarbonate or Bicitra.
Lower protein intake
A diet high in protein will reduce urinary pH. As a general recommendation, limit your daily protein intake to 12 ounces per day of beef, poultry, fish and pork. Twelve ounces is equivalent in size to about three decks of cards. This will be plenty of protein to meet your bodys needs.
Increase fluid intake
No matter what your diagnosis, you should drink enough water to produce at least 2 liters of urine per day.
Also Check: How Bad Is A Kidney Infection
Treatment For Kidney Stones
Most kidney stones can be treated without surgery. Ninety per cent of stones pass by themselves within three to six weeks. In this situation, the only treatment required is pain relief. However, pain can be so severe that hospital admission and very strong pain-relieving medication may be needed. Always seek immediate medical attention if you are suffering strong pain.
Small stones in the kidney do not usually cause problems, so there is often no need to remove them. A doctor specialising in the treatment of kidney stones is the best person to advise you on treatment.
If a stone doesnt pass and blocks urine flow or causes bleeding or an infection, then it may need to be removed. New surgical techniques have reduced hospital stay time to as little as 48 hours. Treatments include:
How Can Vegetables Cause Kidney Stones

Oxalic acid, commonly known as oxalates are compounds that naturally occur in plants and humans. These plant-based oxalates are consumed through a normal daily diet as well as produced as waste by the body. Oxalates are not a required nutrient for people, and too much can lead to kidney stones. The body has the ability to naturally expel oxalic acid without issue except in individuals who might have a genetic predisposition that does not allow the body from processing the acid, resulting in kidney stones.Oxalates can increase the risk of kidney stones in some people as they tend to bind with calcium in the kidneys when they leave the body. When urine contains higher levels of calcium and oxalate than it can dilute, those calcium and oxalate crystals bind together and form into hard masses called kidney stones. The only way to get rid of them from the body is to pass the stones through urination.
Read Also: Where Do You Hurt With A Kidney Infection
Gout And Kidney Stones Related
Many people think of gout as an archaic and uncommon affliction, but it.
difficult to control, gout with a history of kidney stones, or attacks that.
The University of Chicago: Why Do Kidney Stones Cause Pain? Urology Care Foundation: Kidney Stones: What You Should Know,What Causes Kidney Stones? National Kidney Foundation: Kidney Stones,.
gout makes uric acid build up in the blood and form crystals in the joints and the kidneys. the kidney stones can become large and very painful.
Causes of kidney stones. There are literally several reasons why kidney stones appear. Calcium or oxalate mixed with phosphorus is the first and the main cause. But, uric acid can cause kidney stones as well. We all know that all gout sufferers have a high level of this acid, therefore the higher risk of appearing kidney stones.
People with refractory gout can also have problems with the kidneys.
People with refractory gout are at higher risk for kidney stones and chronic kidney disease (when.
A physical exam will check for signs and symptoms related to gout.
Short-term probiotic therapy regimen may improve symptoms of gout, kidney disease New research suggests that an individualized probiotic therapy regimen may improve symptoms of gout, gout-related kidney disease and other signs of metabolic syndrome. The study will be presented.
Uric acid stones are one of four major types of kidney stones, which are hard masses.
Gout is a disorder in which uric acid builds up in the.
What Are Kidney Stones And Why Are They A Problem
Kidney stones are solid, pebble-like bits of material that can form in one or both of your kidneys.4 They can range in size from as small as a grain of sand to as large as a pea.4 Most small kidney stones can pass through your urinary tract without causing any problems.4 Larger kidney stones, however, can get stuck and block the flow of urine, causing intense pain and sometimes bleeding.4 If ignored, they can even cause kidney infection and loss of kidney function.4
You May Like: How Long Is Surgery For A Kidney Transplant
How Are Kidney Stones Diagnosed
Your healthcare provider will discuss your medical history and possibly order some tests. These tests include:
- Imaging tests: An X-ray, CT scan and ultrasound will help your healthcare provider see the size, shape, location and number of your kidney stones. These tests help your provider decide what treatment you need.
- Blood test: A blood test will reveal how well your kidneys are functioning, check for infection and look for biochemical problems that may lead to kidney stones.
- Urine test: This test also looks for signs of infection and examines the levels of the substances that form kidney stones.
What Is A Kidney Stone
A kidney stone is a hard object that is made from chemicals in the urine. There are four types of kidney stones: calcium oxalate, uric acid, struvite, and cystine. A kidney stone may be treated with shockwave lithotripsy, uteroscopy, percutaneous nephrolithomy or nephrolithotripsy. Common symptoms include severe pain in lower back, blood in your urine, nausea, vomiting, fever and chills, or urine that smells bad or looks cloudy.
Urine has various wastes dissolved in it. When there is too much waste in too little liquid, crystals begin to form. The crystals attract other elements and join together to form a solid that will get larger unless it is passed out of the body with the urine. Usually, these chemicals are eliminated in the urine by the body’s master chemist: the kidney. In most people, having enough liquid washes them out or other chemicals in urine stop a stone from forming. The stone-forming chemicals are calcium, oxalate, urate, cystine, xanthine, and phosphate.
After it is formed, the stone may stay in the kidney or travel down the urinary tract into the ureter. Sometimes, tiny stones move out of the body in the urine without causing too much pain. But stones that don’t move may cause a back-up of urine in the kidney, ureter, the bladder, or the urethra. This is what causes the pain.
Read Also: Can Constipation Cause Kidney Pain
Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy
Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy is a technique that uses sound waves to break up simple stones in the kidney or upper urinary tract. ESWL is not used for cystine stones. The procedure generally does not work for stones larger than 2 centimeters in diameter. ESWL can often be done on an outpatient basis with limited anesthesia such as IV sedation and topical agents.
There are several variations of ESWL. The following is a typical procedure:
- The person is positioned in a water bath.
- The procedure uses ultrasound to generate shock waves that travel through the skin and body tissues until they hit the dense stones.
- The shock waves crush the stones into tiny sand-like pieces that usually pass easily through the urinary tract.
The shattered stone fragments may cause discomfort as they pass through the urinary tract. If so, the doctor may insert a small tube called a stent through the bladder into the ureter to help the fragments pass. This practice, however, does not usually speed up passage of the stones and is not used routinely.
Extracorporeal SWL is a procedure used to shatter simple stones in the kidney or upper urinary tract. Ultrasonic waves are passed through the body until they strike the dense stones. Pulses of sonic waves pulverize the stones, which then pass more easily through the ureter and out of the body in the urine.
This method cannot be performed for patients who are pregnant, have bleeding risks, or have an untreated urinary tract infection.
If The Kidney Stone Is Not Causing Any Symptoms Should I Still Be Treated
There are some instances when it is OK to leave a kidney stone untreated. If the stone is small and not causing any pain, there is a good chance that it will pass on its own after it falls into the ureter. Such stones may be followed with “watchful waiting.” This means that the stone is not actively treated, but instead your doctor keeps a check on the stone to be sure that it is not growing or changing. This can be done with periodic X-rays.
You May Like: What Antibiotics To Take For A Kidney Infection
Which Is The Best Medicine For Kidney Stones
There is no best medicine for kidney stones. Small kidney stones will pass out of the body without medical intervention. Medicines can help relieve the pain or speed up the process of passing kidney stones. Some stones will be treated with drugs specific to that type of kidney stone. Large stones, however, will need to be broken up into small pieces through shock waves or laser lithotripsy or be surgically removed.
Who Should Avoid Vegetables That Can Cause Kidney Stones
Every person is different and individual needs, choices, and dietary requirements will vary. Similarly, not everyone who wants to prevent kidney stones has to avoid some vegetables. A predisposition to kidney stones may require decreasing the number of certain vegetables consumed daily or opt for other vegetables with similar health benefits. People with risk factors such as obesity, digestive diseases, and those who eat high-sodium diets may be more susceptible to kidney stones. An earlier history of kidney stones or high-risk conditions are the factors to consider whether or not to remove some vegetables from the diet entirely.
Because kidney stones vary according to the minerals they contain, the choice of vegetables to eat or to avoid will also vary. Limiting the intake of vegetables with high oxalate content may be beneficial for people who form calcium oxalate stones which is the more common type of kidney stone. Stones can also form from uric acid, which is a byproduct of protein metabolism. In such cases of second-leading uric acid stones, a diet plan that has mostly vegetables, fruits, and plant-based proteins is recommended. There are no specific vegetables that can cause uric acid stones.
Don’t Miss: How You Get A Kidney Infection
How Are Children Treated For Kidney Stones
Most childrens kidney stones can be treated with the shock wave lithotripsy , a completely non-invasive procedure. Your child is placed under anesthesia and sound waves of specific frequencies are focused on the stones to shatter them into fragments small enough to be easily passed during urination.
Calcium Supplements: Should You Take Them
When you were a child, your mom may have encouraged you to drink milk tobuild strong bones. But as an adult, youre much more likely to take acalcium supplement than down four glasses of milk a day to protect yourbone health. However you do it, getting enough calcium is a good idea,since women are far more likely than men to developosteoporosis a condition of weak and fragile bones that makes you prone to fractures:Of the 10 million Americans with osteoporosis, 80 percent are women.
But before you unwrap that chocolate-flavored calcium chew or swallow acalcium pill, you should know that taking calcium supplements may not behelping your bones at all. Even worse? The supplements may lead to majorhealth problems
Don’t Miss: What Not To Drink With Kidney Stones
The Next Step: Medications For Kidney Stones
In some patients, the addition of a daily medicine may be recommended to decrease the risk of future stones. In clinical trials, these medications have been shown to significantly reduce the number of stones re-developed in patients with a known history of stones.
While many patients are reluctant to take medications and prefer to focus on dietary modification, medications can be a good option, especially in individuals who frequently develop new stones.
Common preventative medications
Three common medications are used in the prevention of stones.
Potassium Citrate
Useful for: Low urinary citrate , renal tubular acidosis, uric acid stones, calcium oxalate stones, cystine stones.
How does it work: Potassium citrate has two beneficial effects in stone formers. It increases urinary citrate, which acts a direct inhibitor of stone formation of calcium oxalate stones. It also increases urine pH, making urine more alkaline which reduces uric acid stone formation.
How well does it work: In four randomized studies with a total of 227 patients on citrate medications or placebo, treatment reduced the recurrence of stones from 65% to 46.5% after at least one year of treatment. In two randomized studies with a total of 104 patients who were treated with citrate medication after stone surgery, the recurrence rate of stones was 72.5% in those on placebo and 34% in those on medication.
Thiazides
Useful for: High urinary calcium , calcium stones.
Allopurinol
Penicillamine
How Should My Kidney Stone Be Treated
Historically, the treatment of kidney stones required major surgery and was associated with long hospitalization and recovery periods. However, in recent years an improved understanding of kidney stone disease, along with advances in surgical technology, has led to the development of minimally invasive and even noninvasive treatments for people with kidney stones.
At Johns Hopkins, we believe that the treatment of a patients stones requires an approach that is unique to that individual. We offer a complete range of state-of-the-art treatment options, including ESWL , ureteroscopy and PERC, and we will discuss with you the advantages and disadvantages of each therapy as they apply to your situation. Our goal is to provide each patient with a clear understanding of the nature of their stone burden as well as the most appropriate course of treatment.
Read Also: Can Stress Cause Kidney Pain
The Danger Of Developing Kidney Stones If You Suffer From Gout
Kidney stones are not only painful like gout but can be developed due to high uric acid in the blood. If you suffer from gout, you are at an increased risk of developing kidney stones in the future if you dont watch your diet and treat your gout properly. Especially after the age of 40 and even more after the age of 70. If you are a man, you are more likely to develop kidney stones. One in 20 people with or without gout will develop kidney stones in their lifetime.
Once you have already developed kidney stones you are prone to develop it again becoming a recurring illness to deal with. Kidney stones are basically crystalline minerals that form in the urinary tract causing severe pain in either the stomach or groin area and usually causes blood in the urine. If you experience less urination or if there is a large amount of stone-forming substances in the urine, then kidney stones tend to appear. Youll get a burning sensation when peeing and like a gout attack this will be a kidney stone attack!
A mix of oxalate and phosphate or calcium can produce kidney stones as well as uric acid and God knows us gout sufferers have plenty of that in our blood. Among the different types of kidney stones, uric acid stones are the hardest to diagnose since they are not spotted that easily through an x-ray and since your doctor might stall in diagnosing you, this can lead to an enlargement of the kidney stone. Thats why gout has much in common with kidney stones.
Further Study Is Needed To Determine Whether Treatment Of Small Stones Alone Is Justified As Technology Improves And The Costs Of An Intervention Diminish
- Follow us:
Small stones that dont seem to be creating issues are frequently left behind when kidney stones are surgically removed from patients. Leaving these asymptomatic stones behind, however, dramatically raises the likelihood of a patient experiencing a relapse in the five years that follow, according to a recent randomised controlled research.
The findings of the research were published in the journal New England Journal of Medicine.
Generally, stones under 6mm in diameter that are not a procedures primary target are not removed but monitored because secondary stones have high rates of successful passage if they move into the ureter, said lead author Dr Mathew Sorensen, a urologist at the University of Washington School of Medicine.
Before this study, the clinical views were pretty mixed on whether some of these stones should be treated, he said. Most clinicians would decide, based on the size of the stone, whether it hit the bar for treatment, and if it did not, you would often ignore the little stones.
Removal of the secondary stones reduced the relapse rate by 82 per cent, the researchers found, leading the authors to recommend that smaller stones should not be left behind.
Some patients in the study visited the emergency department multiple times and then required surgery, the report noted.
Read the Latest News and Breaking News here
About the Author
Don’t Miss: How Do You Know If You Are Having Kidney Issues