Diagnosis: Too Much Calcium In The Urine
Possible treatments:
Thiazide diuretics
These drugs help to decrease urine calcium excretion. They also help to keep calcium in the bones, reducing the risk for osteoporosis. The most common side effect of thiazide diuretics is potassium loss, so in many cases your doctor will prescribe a potassium supplement to go along with the thiazide diuretic.
Lower sodium intake
The human body carefully regulates its sodium levels. When excess sodium is excreted in the urine, calcium is also excreted proportionally. In other words, the more sodium you consume, the more calcium that will be in your urine. Your goal should be to reduce your sodium intake so that you consume less than 2 grams of sodium per day. Watch out for silent sources of salt, such as fast foods, packaged or canned foods, softened water and sports drinks.
Normal calcium diet
People who form stones sometimes think that because there is too much calcium in their urine, they should restrict their calcium intake. There is no research that supports this practice. Your body needs dietary calcium to support the skeleton. You should be encouraged to consume two servings of dairy or other calcium-rich foods to maintain bone stores of calcium.
Increase fluid intake
No matter what your diagnosis, you should drink enough water to produce at least 2 liters of urine per day.
The 4 Stages Of Passing A Kidney Stone
Your kidneys work hard to remove fluid and waste from the body. During this process, kidney stones can sometimes form. Kidney stones are hardened mineral deposits that can form in the urinary tract. They often pass unnoticed or can be extremely painful and require treatment.
This article provides a look at the four main stages of passing a kidney stone.
supersizer / Getty Images
Are There Any Foods Or Drinks That Help Treat Kidney Stones Are There Any Home Remedies
There are three liquids rumored to help with kidney stones:
- Cranberry juice. Although cranberry juice can help prevent urinary tract infections , it doesnt help with kidney stones.
- Apple cider vinegar. Vinegar is acidic and it can sometimes create changes to your urine, which helps with kidney stones. But, this doesnt always help. Talk to your healthcare provider about the use of vinegar.
- Lemon juice. Lemon juice is rich in citrate, which can help prevent kidney stones from forming. Citrates are found in several citrus fruits including lemons, limes, oranges and melons.
- Coffee. Studies show that coffee may decrease your risk of developing kidney stones.
Avoid soda and other drinks with added sugar or fructose corn syrup. They increase your risk.
You May Like: How Do You Get Chronic Kidney Disease
What Is The Medical Term For The Condition Of Stones In The Ureters
Urinary tract stones begin to form in a kidney and may grow larger in a ureter or in the bladder. Depending on where a stone is, it may be called a kidney stone, ureteral stone, or bladder stone. The process of stone formation is called urolithiasis, nephrolithiasis or nephrolithiasis.
Which organ is 8/12 inches long?
The ureters are tubes that carry urine and connect the kidneys to the bladder. The ureters are tubes made of smooth muscle that propel urine from the kidneys to the bladder. In an adult human, the ureters are typically 2030 cm long and about 34 mm in diameter.
What is the medical term for crushing a kidney stone?
AB kidney stone stone in the kidney cystorrhaphy bladder suture cystostomy creating an artificial opening in the lithotripsy surgical crushing of a stone
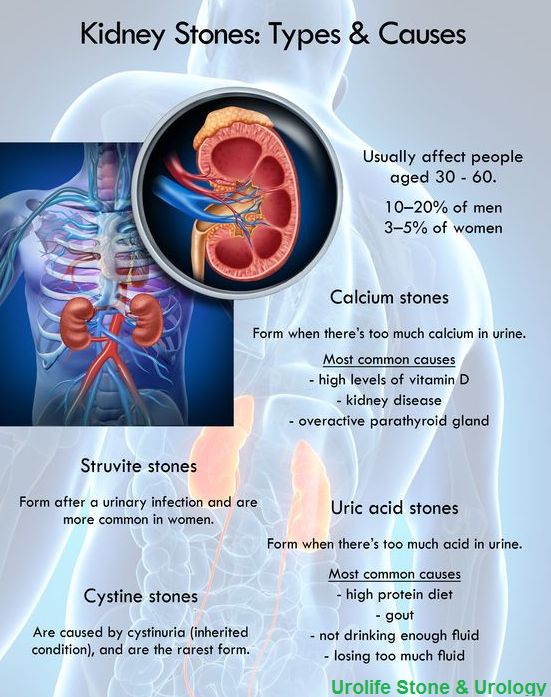
Causes Of Kidney Stones
Kidney stones are most likely to occur in people between the ages of 20 and 50.
Different factors can increase your risk of developing a stone. In the United States, white people are more likely to have kidney stones than Black people.
Sex also plays a role. More men than women develop kidney stones, according to the .
A history of kidney stones can increase your risk. So does a family history of kidney stones.
Other risk factors include:
narcotic medications. The presence of infection requires treatment with antibiotics. Other medications include:
- allopurinol for uric acid stones
- thiazide diuretics to prevent calcium stones from forming
- sodium bicarbonate or sodium citrate to make the urine less acidic
- phosphorus solutions to prevent calcium stones from forming
- ibuprofen for pain
- naproxen sodium for pain
Don’t Miss: Do Kidney Stones Make You Dizzy
Are Home Remedies Effective For Kidney Stones
For some people who have had many kidney stones, home care may be appropriate. When passing a kidney stone, drinking lots of fluid is important. In fact, this is the most important home care measure. Medications may help control the pain . However, if it is the first time one has had symptoms suggestive of a kidney stone, it is important to see a doctor right away.
Health Solutions From Our Sponsors
Genetic Basis Of Kidney Stone Formation
Environmental factors interacting with underlying genetic factors cause rare stone disease . The production of promoters and inhibitors of crystallization depends on proper functioning of the renal epithelial cells. Cellular dysfunction affects the supersaturation of urinary excretion by influencing ions such as calcium, oxalate, and citrate . Some genetic defects which lead to stone formation are shown in Table 3.
Recommended Reading: Do Energy Drinks Give You Kidney Stones
Recommended Reading: How Long Can A Person Survive With Kidney Failure
How Common Are Kidney Stones
Each year, more than half a million people go to emergency rooms for kidney stone problems. It is estimated that one in ten people will have a kidney stone at some time in their lives.
The prevalence of kidney stones in the United States increased from 3.8% in the late 1970s to 8.8% in the late 2000s. The prevalence of kidney stones was 10% during 20132014. The risk of kidney stones is about 11% in men and 9% in women. Other diseases such as high blood pressure, diabetes, and obesity may increase the risk for kidney stones.
Medical Definition Of Renal Stone
- Medical Editor: Melissa Conrad Stöppler, MD
Reviewed on 3/29/2021
Renal stone: A stone in the kidney . Also called a kidney stone.
Renal stones are a common cause of blood in the urine and pain in the abdomen, flank, or groin. Kidney stones occur in 1 in 20 people at some time in their life.
The development of the stones is related to decreased urine volume or increased excretion of stone-forming components such as calcium, oxalate, urate, cystine, xanthine, and phosphate. The stones form in the urine collecting area of the kidney and may range in size from tiny to staghorn stones the size of the renal pelvis itself.
The cystine stones compared in size to a quarter were obtained from the kidney of a young woman by percutaneous nephrolithotripsy , a procedure for crushing and removing the dense stubborn stones characteristic of cystinuria.
The pain with kidney stones is usually of sudden onset, very severe and colicky , not improved by changes in position, radiating from the back, down the flank, and into the groin. Nausea and vomiting are common.
Factors predisposing to kidney stones include recent reduction in fluid intake, increased exercise with dehydration, medications that cause hyperuricemia and a history of gout.
Treatment includes relief of pain, hydration and, if there is concurrent urinary infection, antibiotics.
Recommended Reading: Can Massage Help Kidney Function
Is It Possible To Prevent Kidney Stones
Rather than having to undergo treatment, it is best to avoid kidney stones in the first place when possible. It can be especially helpful to drink more water since low fluid intake and dehydration are major risk factors for kidney stone formation.
Depending on the cause of the kidney stones and an individual’s medical history, changes in the diet or medications are sometimes recommended to decrease the likelihood of developing further kidney stones. If one has passed a stone, it can be particularly helpful to have it analyzed in a laboratory to determine the precise type of stone so specific prevention measures can be considered.
People who have a tendency to form calcium oxalate kidney stones may be advised to limit their consumption of foods high in oxalates, such as spinach, rhubarb, Swiss chard, beets, wheat germ, and peanuts. Also drinking lemon juice or lemonade may be helpful in preventing kidney stones.
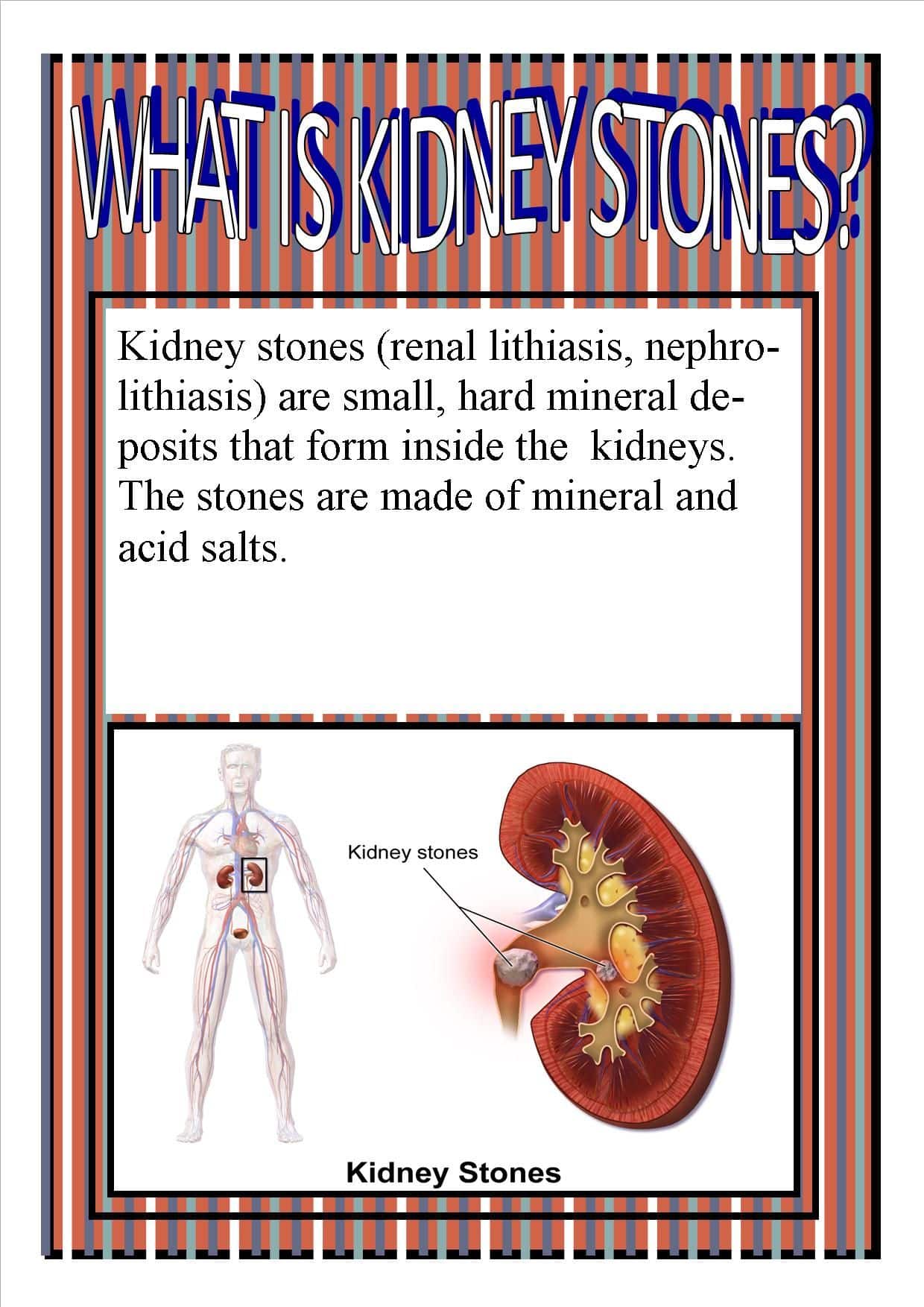
What Is A Kidney Stone
A kidney stone is a hard object that is made from chemicals in the urine. There are four types of kidney stones: calcium oxalate, uric acid, struvite, and cystine. A kidney stone may be treated with shockwave lithotripsy, uteroscopy, percutaneous nephrolithomy or nephrolithotripsy. Common symptoms include severe pain in lower back, blood in your urine, nausea, vomiting, fever and chills, or urine that smells bad or looks cloudy.
Urine has various wastes dissolved in it. When there is too much waste in too little liquid, crystals begin to form. The crystals attract other elements and join together to form a solid that will get larger unless it is passed out of the body with the urine. Usually, these chemicals are eliminated in the urine by the body’s master chemist: the kidney. In most people, having enough liquid washes them out or other chemicals in urine stop a stone from forming. The stone-forming chemicals are calcium, oxalate, urate, cystine, xanthine, and phosphate.
After it is formed, the stone may stay in the kidney or travel down the urinary tract into the ureter. Sometimes, tiny stones move out of the body in the urine without causing too much pain. But stones that don’t move may cause a back-up of urine in the kidney, ureter, the bladder, or the urethra. This is what causes the pain.
Also Check: When Does A Kidney Stone Hurt The Worst
What Are The Different Types Of Kidney Stones
Crystals make stones and their names mean types of kidney stones. Here are the names of the crystals that make up the stones: CAOX, Calcium Oxalate PAC, Calcium Phosphate UA, uric acid Cystine Struvite.
Why are kidney stones called Silent Stones?
These are called silent stones. Kidney stones cause problems when they interfere with the normal flow of urine. They can block the flow in the tube that carries urine from the kidney to the bladder. The kidney is not used to being subjected to any pressure.
What are the symptoms of a small kidney stone?
Kidney stones vary in size. Small stones are less likely to get stuck in the kidneys or other parts of the urinary tract. Mild to moderate symptoms can occur when passing a small stone, although many people can pass stones without feeling pain.
How Should My Kidney Stone Be Treated
Historically, the treatment of kidney stones required major surgery and was associated with long hospitalization and recovery periods. However, in recent years an improved understanding of kidney stone disease, along with advances in surgical technology, has led to the development of minimally invasive and even noninvasive treatments for people with kidney stones.
At Johns Hopkins, we believe that the treatment of a patients stones requires an approach that is unique to that individual. We offer a complete range of state-of-the-art treatment options, including ESWL , ureteroscopy and PERC, and we will discuss with you the advantages and disadvantages of each therapy as they apply to your situation. Our goal is to provide each patient with a clear understanding of the nature of their stone burden as well as the most appropriate course of treatment.
Recommended Reading: How To Blast Kidney Stones
What Are The Symptoms Of Nephrolithiasis
Symptoms of Nephrolithiasis may include:
- Pain of sudden onset that radiates from the back, down the flank, and into the groin
- Pain does not improve with body position
- Pain is very severe and colicky but intermittent
- Nausea and vomiting
- Blood in the urine
The pain is primarily caused by dilation, stretching, and spasm of the blood vessels inside the urinary tract because of the obstruction.
Racial Differences In Incidence
Urinary tract calculi are far more common in Asians and Caucasians than in Native Americans, Africans, African Americans, and some natives of the Mediterranean region. Caucasian males are affected 3-4 times more often than African American males, though African Americans have a higher incidence of infected ureteral calculi than Caucasians. With uric acid stones, however, non-Caucasian have a higher frequency of stone formation than Caucasians. Some groups, such as the Hmong, have frequencies up to 50%.{ref80)
Although some differences may be attributable to geography and diet, heredity also appears to be a factor. This is suggested by the finding that, in regions with both Caucasian and non-Caucasian populations, stone disease is much more common in Caucasians.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Role Of The Kidney
Dietary Calcium And Kidney Stones
Only lower your calcium intake below that of a normal diet if instructed by your doctor. Decreased calcium intake is only necessary in some cases where absorption of calcium from the bowel is high.
A low-calcium diet has not been shown to be useful in preventing the recurrence of kidney stones and may worsen the problem of weak bones. People with calcium-containing stones may be at greater risk of developing weak bones and osteoporosis. Discuss this risk with your doctor.
Complications Of Kidney Stones
Kidney stones can range in size from a grain of sand to that of a pearl or even larger. They can be smooth or jagged, and are usually yellow or brown. A large stone may get stuck in the urinary system. This can block the flow of urine and may cause strong pain.
Kidney stones can cause permanent kidney damage. Stones also increase the risk of urinary and kidney infection, which can result in germs spreading into the bloodstream.
Don’t Miss: Does It Hurt To Pee Out A Kidney Stone
How Do You Prevent Kidney Stones
- Drinking enough non-sugary fluid will help to keep your urine less concentrated with waste products. It is recommended to drink 2-3 liters of fluid per day . Urine should appear very light yellow to clear if you are well hydrated.
- Diets low in sodium and protein by eating less processed, fast food, and restaurant meals
- Restricting foods rich in oxalates
- Eating more fruits and vegetables which make the urine less acidic.
- Maintaining a healthy weight
Please consult your healthcare provider before making any dietary changes.
Genetic Causes of Kidney Stones
It is estimated that 40% of patients with kidney stones are caused by inherited genetics. Listed below are a few rare genetic causes of kidney stones.
One of the major genetic causes of kidney stones is due to Primary Hyperoxaluria disease.
Cell Injury And Apoptosis
Exposure to high levels of oxalate or CaOx crystals induces epithelial cellular injury, which is a predisposing factor to subsequent stone formation . CaOx crystal depositions in the kidneys upregulate the expression and synthesis of macromolecules that can promote inflammation . Crystals may be endocytosed by cells or transported to the interstitium. It has been suggested that injured cells develop a nidus which promotes the retention of particles on the renal papillary surface . In individuals with severe primary hyperoxaluria, renal tubular cells are injured and crystals become attached to them . The addition of CaOx crystals onto MadinDarby canine kidney cell lines showed an increase in the release of lysosomal enzymes, prostaglandin E2, and cytosolic enzymes . A study on animal models also revealed that the administration of high concentrations of CaOx crystals or oxalate ions appears to be toxic causing renal tubular cell damage . It has been suggested that oxalate increases the availability of free radicals by inhibiting enzymes responsible for their degradation. For instance, reactive oxygen species can damage the mitochondrial membrane and reduce its transmembrane potential. These events are known features of early process in apoptotic pathways .
Don’t Miss: Which Condition Is A Genetic Kidney Disorder
Medication For Kidney Stones
For most people with recurrent calcium stones, a combination of drinking enough fluids, avoiding urinary infections, and specific treatment with medications will significantly reduce or stop new stone formation.
Certain medications such as thiazide diuretics or indapamide reduce calcium excretion and decrease the chance of another calcium stone. Potassium citrate or citric juices are used to supplement thiazide treatment and are used by themselves for some conditions where the urine is too acidic.
For people who have a high level of uric acid in their urine, or who make uric acid stones, the medication allopurinol will usually stop the formation of new stones.
You May Like: Can Stage 2 Chronic Kidney Disease Be Reversed
Why You Get Stones
Part of preventing stones is finding out why you get them. Your health care provider will perform tests to find out what is causing this. After finding out why you get stones, your health care provider will give you tips to help stop them from coming back.
Some of the tests he or she may do are listed below.
Medical and Dietary History
Your health care provider will ask questions about your personal and family medical history. He or she may ask if:
- Have you had more than one stone before?
- Has anyone in your family had stones?
- Do you have a medical condition that may increase your chance of having stones, like frequent diarrhea, gout or diabetes?
Knowing your eating habits is also helpful. You may be eating foods that are known to raise the risk of stones. You may also be eating too few foods that protect against stones or not drinking enough fluids.
Understanding your medical, family and dietary history helps your health care provider find out how likely you are to form more stones.
Blood and Urine Tests
Imaging Tests
When a health care provider sees you for the first time and you have had stones before, he or she may want to see recent X-rays or order a new X-ray. They will do this to see if there are any stones in your urinary tract. Imaging tests may be repeated over time to check for stone growth. You may also need this test if you are having pain, hematuria or recurrent infections.
Stone Analysis
Also Check: When Kidneys Are Not Functioning Properly