Where Are The Kidneys And How Do They Function
There are two kidneys, each about the size of a fist, located on either side of the spine at the lowest level of the rib cage. Each kidney contains up to a million functioning units called nephrons. A nephron consists of a filtering unit of tiny blood vessels called a glomerulus attached to a tubule. When blood enters the glomerulus, it is filtered and the remaining fluid then passes along the tubule. In the tubule, chemicals and water are either added to or removed from this filtered fluid according to the body’s needs, the final product being the urine we excrete.
The kidneys perform their life-sustaining job of filtering and returning to the bloodstream about 200 quarts of fluid every 24 hours. About two quarts are removed from the body in the form of urine, and about 198 quarts are recovered. The urine we excrete has been stored in the bladder for anywhere from 1 to 8 hours.
What Are Clinical Trials And Are They Right For You
Clinical trials are part of clinical research and at the heart of all medical advances. Clinical trials look at new ways to prevent, detect, or treat disease. Researchers also use clinical trials to look at other aspects of care, such as improving the quality of life for people with chronic illnesses. Find out if clinical trials are right for you.
Measuring How Your Kidneys Work
It is difficult to calculate the exact rate at which your kidneys work. The best measure of kidney function is called the glomerular filtration rate . The GFR can be estimated using a mathematical formula. This formula uses the level of creatinine in your blood to estimate how well your kidneys are filtering waste from your blood. It can indicate if there is any kidney damage.
The higher the filtration rate, the better the kidneys are working. A GFR of 100 mL/min/1.73 m2 is in the normal range. This is about equal to 100 per cent kidney function. Based on this measurement system, a GFR of 50 mL/min/1.73 m2 could be called 50 per cent kidney function and a GFR of 30 mL/min/1.73 m2 could be called 30 per cent kidney function.
If your doctor orders a blood test to learn more about your kidney function, an eGFR result is provided automatically, along with your creatinine results.
Your doctor may also test for other signs and conditions that may indicate you have chronic kidney disease. These may include tests for:
- protein in your urine
- blood in your urine
- high blood pressure
- diabetes.
Don’t Miss: Can Pepsi Cause Kidney Stones
Functional Structure Of The Kidneys
nephrons
1. The tubule begins with a hollow enlargement called Bowman’s capsule, which is where water and solutes initially enter the tubule from the bloodstream. This process is known as filtration. The structure comprised of Bowman’s capsule and associated capillaries is called the renal corpuscle.
2. From Bowman’s capsule the tubular fluid flows towards the proximal tubule, which remains in the outer layer of the kidney. The proximal tubule is the major site of reabsorption of water and solutes in equal proportions from the filtered tubular fluid.
3. Then the tubule dips into the hairpin loop of Henle, which descends toward the center of the kidney and then rises back to the cortex. The loop of Henle is also a major site of reabsorption, but unlike the proximal tubule, proportionately more solute than water is reabsorbed, so the tubular fluid is dilute relative to plasma by the end of this segment.
4. The next segment is the distal tubule, which like the proximal tubule remains in the cortex. Both reabsorption and secretion take place in this segment, which is where sodium and potassium concentrations and the pH of the tubular fluid are adjusted to ensure homeostasis.
1. An afferent arteriole takes blood to the renal corpuscle, where the blood passes through the first capillary bed, a ball-shape tuft known as the glomerulus.
2. An efferent arteriole takes blood away from the glomerulus.
How Do The Kidneys And Urinary Tract Work
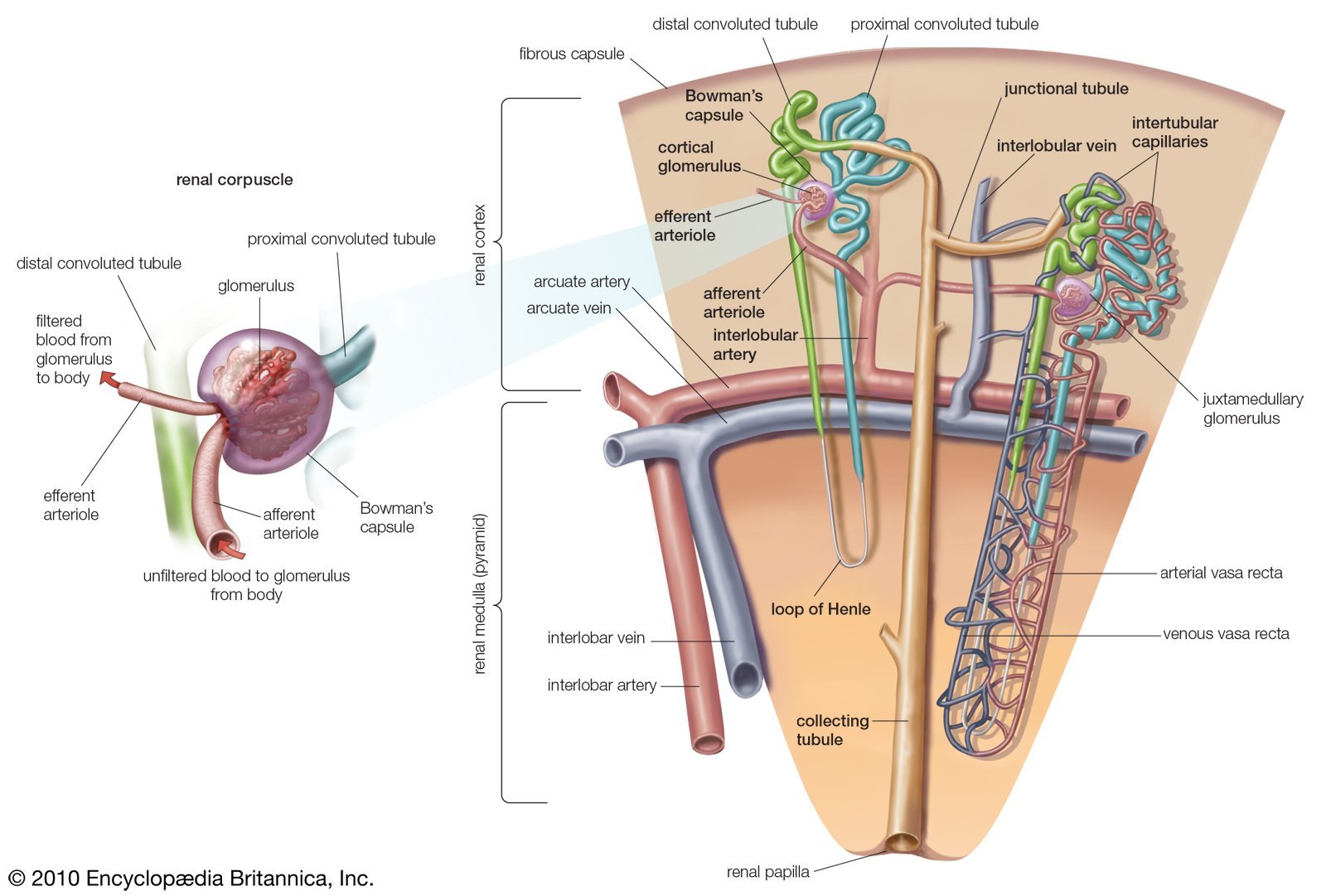
Blood travels to each kidney through the renal artery. The artery enters the kidney at the hilus , the indentation in middle of the kidney that gives it its bean shape. The artery then branches so blood can get to the nephrons 1 million tiny filtering units in each kidney that remove the harmful substances from the blood.
Each of the nephrons contain a filter called the glomerulus . The fluid that is filtered out from the blood then travels down a tiny tube-like structure called a tubule . The tubule adjusts the level of salts, water, and wastes that will leave the body in the urine. Filtered blood leaves the kidney through the renal vein and flows back to the heart.
Pee leaves the kidneys and travels through the ureters to the bladder. The bladder expands as it fills. When the bladder is full, nerve endings in its wall send messages to the brain. When a person needs to pee, the bladder walls tighten and a ring-like muscle that guards the exit from the bladder to the urethra, called the sphincter , relaxes. This lets pee go into the urethra and out of the body.
Read Also: Constipation And Kidney Stones
What Clinical Trials Are Open
Clinical trials that are currently open and are recruiting can be viewed at www.ClinicalTrials.gov.
This content is provided as a service of the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, part of the National Institutes of Health. The NIDDK translates and disseminates research findings to increase knowledge and understanding about health and disease among patients, health professionals, and the public. Content produced by the NIDDK is carefully reviewed by NIDDK scientists and other experts.
How Does Blood Flow Through My Kidneys
Blood flows into your kidney through the renalartery. This large blood vessel branches into smaller and smaller blood vessels until the blood reaches the nephrons. In the nephron, your blood is filtered by the tiny blood vessels of the glomeruli and then flows out of your kidney through the renal vein.
Your blood circulates through your kidneys many times a day. In a single day, your kidneys filter about 150 quarts of blood. Most of the water and other substances that filter through your glomeruli are returned to your blood by the tubules. Only 1 to 2 quarts become urine.
Read Also: Can Soda Pop Cause Kidney Stones
Acquired Solitary Kidney: Unilateral Nephrectomy
Table 1. Cardio-renal implications of living with single kidney
| Proteinuria | |
|---|---|
| + |
Renal impairment is based on elevated serum creatinine, decreased creatinine clearance, or formal glomerular filtration rate measurement. +, 510% ++, 1120% +++, 2130% ++++, 3140% +++++, > 40% patients exhibiting given phenotype N/A, no measurements were performed , no change between control and experimental group.
Blood Flows In And Out Of The Kidneys Through Renal Arteries And Veins
Blood enters the kidneys through renal arteries. These arteries branch into tiny capillaries that interact with urinary structures inside the kidneys . Here the blood is filtered. Waste is removed and vital substances are reabsorbed back into the bloodstream. The filtered blood leaves through the renal veins. All the blood in the body moves in and out of the kidneys hundreds of times each daythats about 200 quarts of liquid to be filtered every 24 hours.
Also Check: Does Red Wine Cause Kidney Stones
Major Molecular Factors Involved In Nephrogenesis
There are several key developmental events and signaling cascades in renal development that have been elucidated, mostly through studies in mice . However, there are likely still genes and genetic factors yet to be identified as well as a lack of understanding of the interactions and coordination of these factors to generate the complex structure of a kidney . In general, the development of the metanephric kidney and lower urinary tract is coordinated by complex interactions among numerous transcription/growth factors and intracellular signaling molecules . These genes can be coexpressed in the MM, stroma, angioblasts, UB, and cloaca . However, cells at the UB tip express many genes that are not expressed by cells in the tubular portions and vice versa . The discussion below will focus on providing a review of important genes and networks that function at crucial stages of renal development and are also associated with CAKUT .
| pattern of tubular and collecting duct | polycystic kidneys | Rossetti and Harris, 2007 |
How Is Chronic Kidney Disease Detected
Early detection and treatment of chronic kidney disease are the keys to keeping kidney disease from progressing to kidney failure. Some simple tests can be done to detect early kidney disease. They are:
It is especially important that people who have an increased risk for chronic kidney disease have these tests. You may have an increased risk for kidney disease if you:
- are older
Also Check: What Std Messes With Your Kidneys
Capillary Network Within The Nephron
The capillary network that originates from the renal arteries supplies the nephron with blood that needs to be filtered. The branch that enters the glomerulus is called the afferent arteriole. The branch that exits the glomerulus is called the efferent arteriole. Within the glomerulus, the network of capillaries is called the glomerular capillary bed. Once the efferent arteriole exits the glomerulus, it forms the peritubular capillary network, which surrounds and interacts with parts of the renal tubule. In cortical nephrons, the peritubular capillary network surrounds the PCT and DCT. In juxtamedullary nephrons, the peritubular capillary network forms a network around the loop of Henle and is called the vasa recta.
Nephrotoxicity Or Renal Toxicity
The nephron, comprised of glomerulus and renal tubule, is the functional unit of the kidney. The three main functions of the kidneys include plasma filtration and maintenance of whole-body electrolyte homeostasis, elimination, and concentration of waste products from both endogenous metabolism and exogenous metabolism, and synthesis and secretion of hormones . Renal blood flow is approximately 25% of resting cardiac output. The glomerular, tubular, and renal interstitial cells frequently encounter significant concentrations of endogenous and exogenous metabolites that can induce changes in kidney function and structure. As such, the kidney is at risk due to exposure to high volumes of blood-borne endogenous and exogenous metabolites including toxicants and toxic metabolites . Nephrotoxicity or renal toxicity can be a result of hemodynamic changes, direct injury to cells and tissue, inflammatory tissue injury, and/or obstruction of renal excretion. Nephrotoxicity is frequently induced by a wide spectrum of therapeutic drugs and environmental pollutants .
Also Check: Can Advil Cause Blood In Urine
Low Nephron Numbers And Impact Of Second Hit
There are a number of animal studies that have investigated the impact of additional stressors that induce hypertension, such as angiotensin II , NG-nitro-l-arginine methyl ester , deoxycorticosterone acetate , and salt-loading, in the context of reduced nephron numbers . In general, these studies demonstrate that renal injury and/or cardiovascular dysfunction is more severe than nephrectomy alone. ANG II used in combination with nephrectomy hastened glomerulosclerosis, proteinuria, and/or kidney function decline compared with sham animals . Interestingly, Tsukamoto et al. showed ANG II infusion in uninephrectomized mice plus salt loading has a significant impact apart from renal injury as mice demonstrate hypertensive heart disease that leads to a heart failure phenotype.
Age itself can also be viewed as secondary stressor. A long-term study by Rodríguez-Gómez et al. demonstrated that both male and female uninephrectomized rats exhibited proteinuria and increased blood pressure after 18 mo, compared with sham animals. Male uninephrectomized rats tended to have earlier and more severe lesions than female uninephrectomized rats. In total, there is strong experimental evidence to support the idea that uninephrectomy/nephron deficiency alone can cause a predisposition to progressive kidney injury, but when combined with a secondary stressor this predisposition can be significantly accelerated.
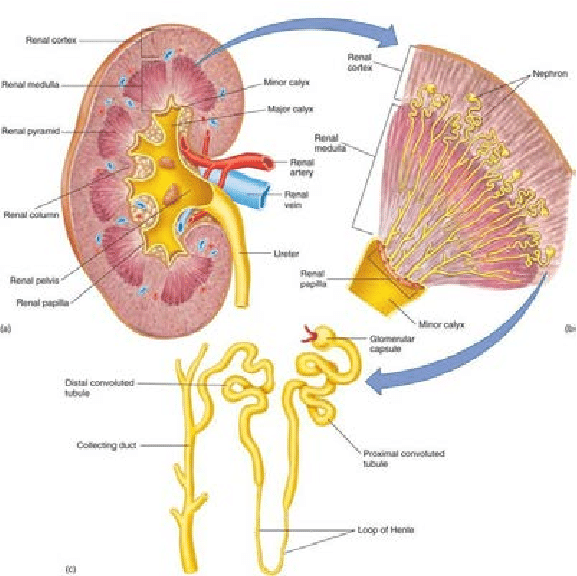
How Many Nephrons Are In The Kidney
Nephronkidneynephronskidney
. Similarly, where are nephrons in the kidney?
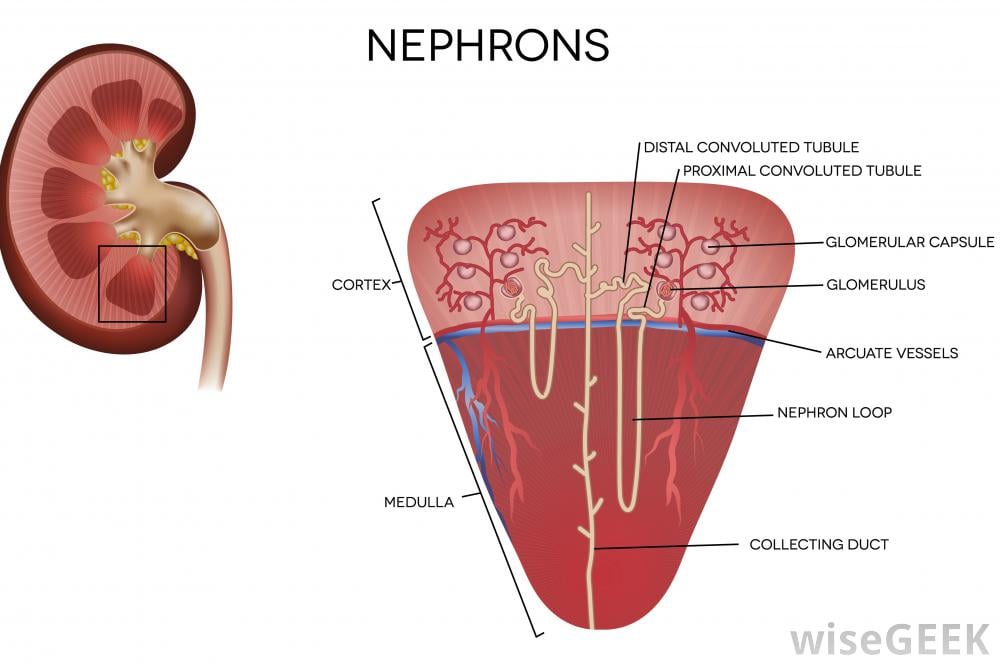
The nephron is the functional unit of the kidney. The glomerulus and convoluted tubules of the nephron are located in the cortex of the kidney, while the collecting ducts are located in the pyramids of the kidney’s medulla.
Also Know, what is the main function of nephron? A nephron is the basic structural and functional unit of the kidney. Its chief function is to regulate water and soluble substances by filtering the blood, reabsorbing what is needed and excreting the rest as urine.
Also to know is, what are nephrons in the kidney?
Each of your kidneys is made up of about a million filtering units called nephrons. Each nephron includes a filter, called the glomerulus, and a tubule. The nephrons work through a two-step process: the glomerulus filters your blood, and the tubule returns needed substances to your blood and removes wastes.
What is the unit of kidney?
nephron
Also Check: Carbonation And Kidney Stones
Kidneys And Water Balance
A nephron is the functional unit of the kidneys. Each kidney contains approximately one million such units. A nephron is composed of a glomerulus and a renal tubule . The renal tubule is subdivided further into the proximal convoluted tubule, the loop of Henle, the distal convoluted tubule, and the collecting duct.
Figure 3. Nephron and juxtaglomerular apparatus.
The glomeruli filter about 180 l of fluid each day. Up to 9099% of the filtered water is reabsorbed by the renal tubules. It is reabsorbed passively in the proximal convoluted tubules and the descending limbs of the loops of Henle, with down osmotic gradients created by the active transport of sodium and chloride out of the lumina. Water is not permeable in the ascending limb of the loop of Henle and the distal convoluted tubule. The final urine volume is determined by the action of AVP on the collecting ducts.
S. Akilesh, in, 2014
The Kidneys Are Retroperitoneal Organs In The Abdomen
The kidneys are located behind the peritoneum, and so are called retroperitoneal organs. They sit in the back of the abdomen between the levels of the T12 and L03 vertebrae. The right kidney is slightly lower than the left kidney to accommodate the liver. Both kidneys are bean-shaped and about the size of an adult fist.
Also Check: How Much Money Is A Kidney Worth
Where Is Bowmans Capsule Found
The Bowmans capsule is found in the outer part of the kidney, the cortex. Essentially, the capsule is a sealed, expanded sac at the end of the tubule, the rest of which elongates into a twisted and looped tubule in which urine is formed. Figure 9.2. Structural overview of a nephron, the functional unit of the kidney.
How Do My Kidneys Work
Each of your kidneys is made up of about a million filtering units called nephrons. Each nephron includes a filter, called the glomerulus, and a tubule. The nephrons work through a two-step process: the glomerulus filters your blood, and the tubule returns needed substances to your blood and removes wastes.
Recommended Reading: Grapes For Kidney Stones
Why Are The Kidneys So Important
Most people know that a major function of the kidneys is to remove waste products and excess fluid from the body. These waste products and excess fluid are removed through the urine. The production of urine involves highly complex steps of excretion and re-absorption. This process is necessary to maintain a stable balance of body chemicals.
The critical regulation of the body’s salt, potassium and acid content is performed by the kidneys. The kidneys also produce hormones that affect the function of other organs. For example, a hormone produced by the kidneys stimulates red blood cell production. Other hormones produced by the kidneys help regulate blood pressure and control calcium metabolism.
The kidneys are powerful chemical factories that perform the following functions:
- remove waste products from the body
- remove drugs from the body
- balance the body’s fluids
- release hormones that regulate blood pressure
- produce an active form of vitamin D that promotes strong, healthy bones
- control the production of red blood cells
Below you will find more information about the kidneys and the vital role they play in keeping your body functioning.
Other Important Factors Involved In Nephrogenesis
Hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 is involved in renal capsule formation as defects in Hnf1 lead to kidneys fused at inferior lobes and located lower than usual . Mutations in Hnf1 are detected in 33% of children with nonsyndromic multicystic dysplastic kidney or renal hypodysplasia . Polycystic kidney disease is also a congenital kidney disorder, caused by cysts that arise from tubules. Pkd1 and Pkd2 represent an example of patterning defect . The increased tubular cell proliferation together with decreased integration of cells into the plane of tubular epithelium or loss of oriented cell division may account for cyst formation . The developing mammalian metanephros expresses all components of the reninangiotensin system . In humans, their expression in the embryonic kidney is as early as the fifth week of gestation when metanephric organogenesis is initiated . Mutations in the genes encoding for AGT , REN , ACE , or AGTR1 lead to autosomal recessive renal tubular dysgenesis .
Don’t Miss: Can Seltzer Water Cause Kidney Stones