Gross Anatomy Of The Kidney
- Describe the external structure of the kidney, including its location, support structures, and covering
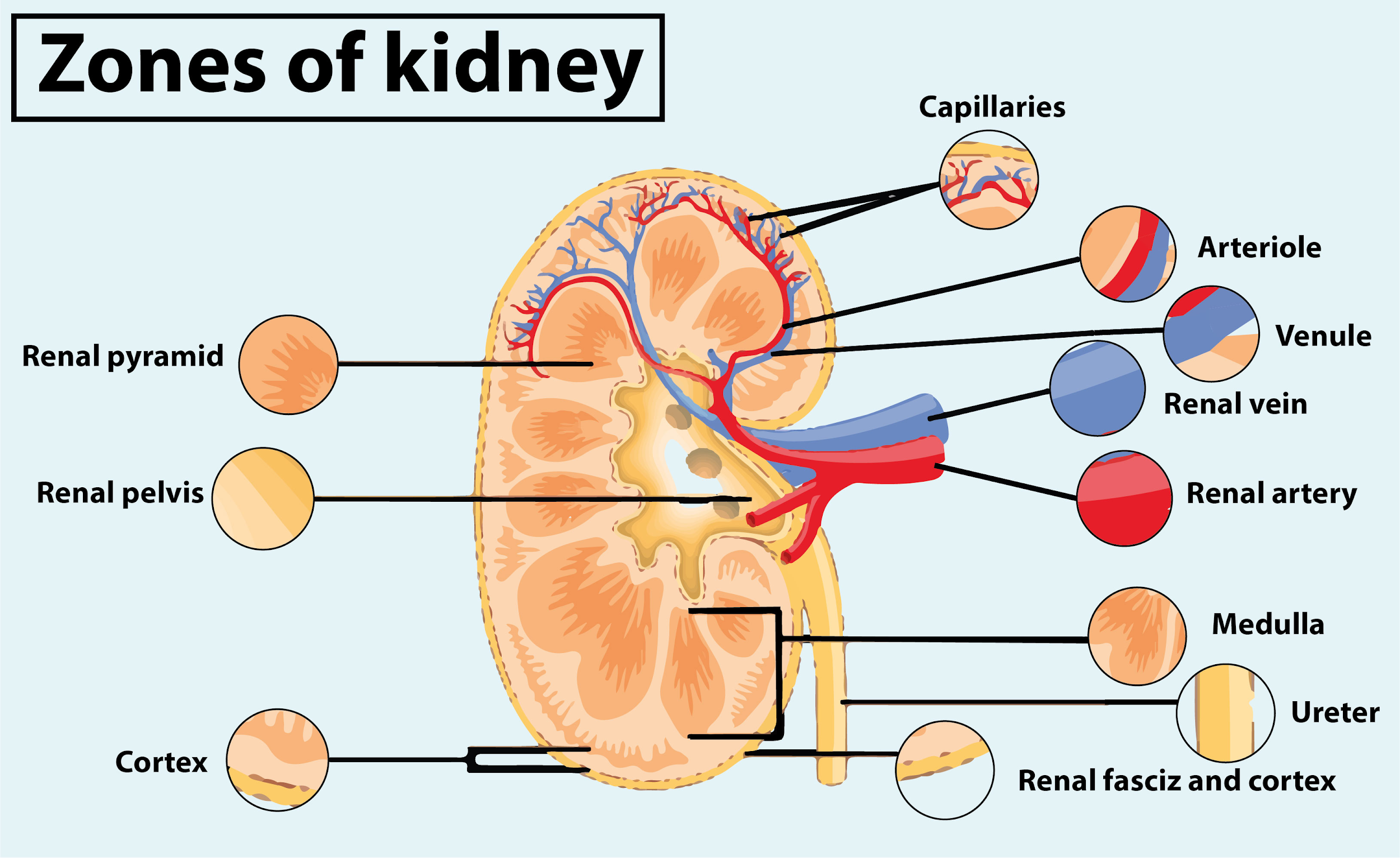
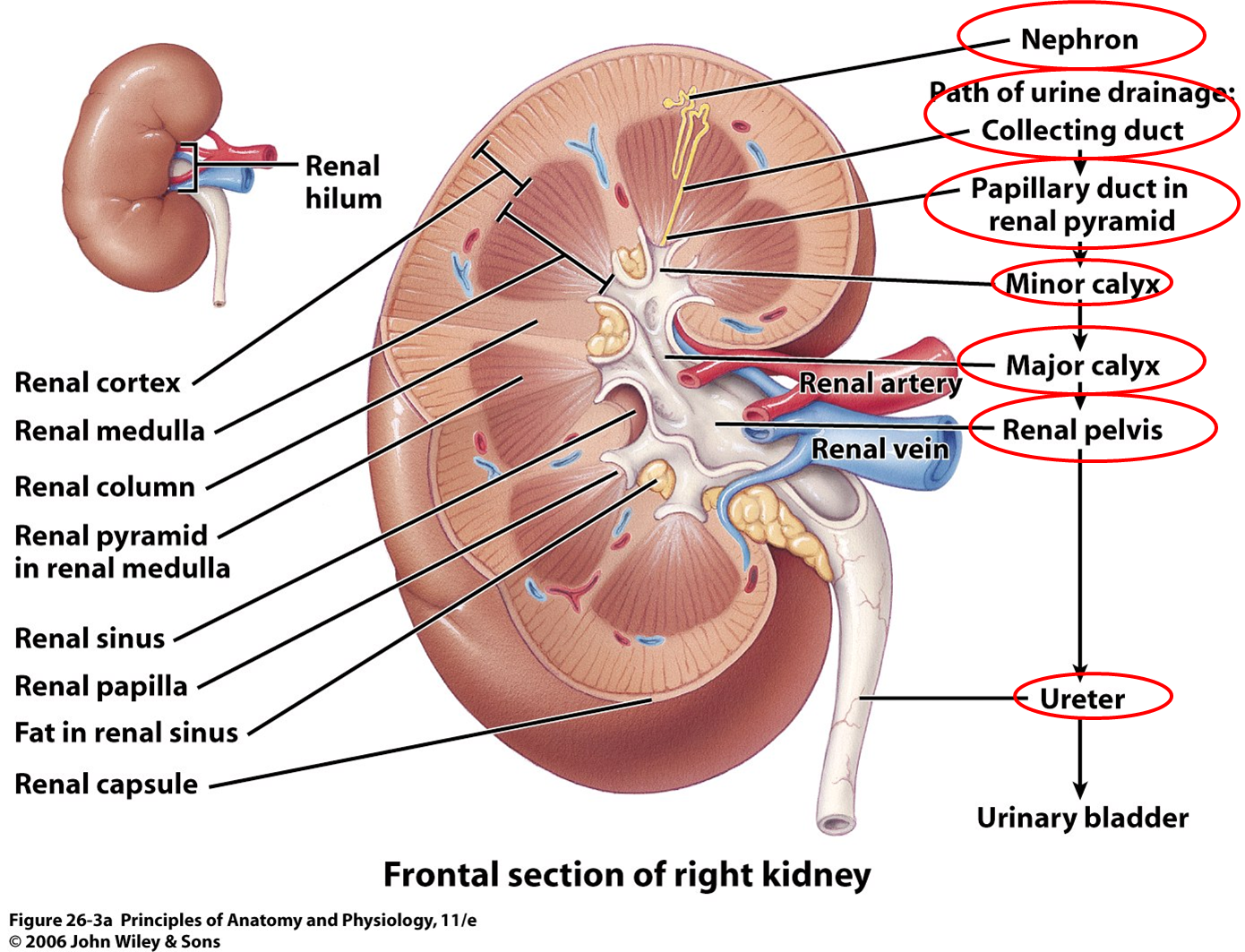
- Identify the major internal divisions and structures of the kidney
- Identify the major blood vessels associated with the kidney and trace the path of blood through the kidney
- Compare and contrast the cortical and juxtamedullary nephrons
- Name structures found in the cortex and medulla
- Describe the physiological characteristics of the cortex and medulla
The kidneys lie on either side of the spine in the retroperitoneal space between the parietal peritoneum and the posterior abdominal wall, well protected by muscle, fat, and ribs. They are roughly the size of your fist, and the male kidney is typically a bit larger than the female kidney. The kidneys are well vascularized, receiving about 25 percent of the cardiac output at rest.
Hormones Of The Adrenal Glands
The role of the adrenal glands in your body is to release certain hormones directly into the bloodstream. Many of these hormones have to do with how the body responds to stress, and some are vital to existence. Both parts of the adrenal glands the adrenal cortex and the adrenal medulla perform distinct and separate functions.
Each zone of the adrenal cortex secretes a specific hormone. The key hormones produced by the adrenal cortex include:
When Should I Call My Doctor If I Think I Might Have A Problem With My Urinary Tract
If youre having trouble or pain when urinating, you should visit your doctor. It may be a sign of an infection or another condition. Call your doctor if you have:
- Burning sensation, pain or difficulty urinating.
- Pain in your pelvic area, lower back, genital area, or flank .
- Trouble holding your urine or problems with leaking urine.
- A feeling that something is bulging out of your vagina.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Your urinary system plays a critical role in keeping you alive. It filters your blood and removes waste and excess water through urine. Your urinary system includes your kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra. Conditions like urinary tract infections, sexually transmitted diseases, kidney diseases, and urinary tract obstruction can affect the health of your urinary system. If you have one of these conditions, talk to your healthcare provider about steps you can take to ensure your health.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 12/05/2019.
References
Also Check: What Does Flomax Do For Kidney Stones
Blood Oxygenation Level Dependent Mri
Blood flow to the renal cortex normally supplies oxygen far in excess of its metabolic needs. In contrast, blood flow to the renal medulla is low and it is poorly oxygenated due to considerable diffusion of oxygen from the arterial to the venous side, and the high oxygen demand required to generate an osmotic gradient to actively reabsorb sodium. Thus, the renal medulla functions in a hypoxic state . Renal BOLD imaging can be used to assess the heterogeneity of oxygenation in the kidney , particularly the medulla.
BOLD imaging is most widely associated with its application to functional MRI of the brain , but provides a non-invasive method to assess oxygenation of an organ. BOLD uses the dependence of the magnetic properties of haemoglobin on oxygenation state, deoxygenated blood being paramagnetic leading to shortening of the T2* relaxation time compared to diamagnetic oxygenated blood . The rate of spin dephasing, R2* = 1/T2*, therefore provides an index of tissue oxygenation.
A multiple gradient-recalled echo sequence is most widely used to assess renal BOLD . Using this sequence, a number of echoes are collected during each breathhold, with the maximum TE being equal to the T2* of the medulla . The scan is acquired over a number of breathholds to collect the entire of k-space. R2* can then be obtained from the line fit of the natural log of signal versus TE, and an R2* map formed , .
Rachel E. Cianciolo, F. Charles Mohr, in, 2016
How To Diagnose Diabetic Nephropathy
-
Urine Test:
This test detects the presence of blood and the protein albumin in the urine. The kidneys do not filter albumin out of the blood. Therefore, the presence of protein in the urine indicates poor kidney function.
To detect the albumin: creatinine ratio. Creatinine is a waste product that is filtered by the kidneys, and albumin is a protein that is reabsorbed by the kidneys. In renal dysfunction, this ratio is increased as albumin is excreted through urine. Thus, a urine sample will show increased albumin to creatinine ratio.
-
Blood Test: Glomerular filtration rate is calculated based on the creatinine clearance from the blood. The faster the clearance, the healthier the kidneys are.
-
Imaging Tests: X-rays and ultrasound to check kidney structure and size. CT and magnetic resonance imaging to determine blood circulation within the kidneys.
-
Kidney Biopsy: A thin needle is used to take a piece of the kidney tissue, and then an examination is done under a microscope.
Read Also: Apple Cider Vinegar For Kidney
How Do My Kidneys Work
Each of your kidneys is made up of about a million filtering units called nephrons. Each nephron includes a filter, called the glomerulus, and a tubule. The nephrons work through a two-step process: the glomerulus filters your blood, and the tubule returns needed substances to your blood and removes wastes.
Importance Of The Kidney In Blood Pressure Control
To appreciate the importance of renal medullary blood flow in the control of arterial blood pressure, one must first accept the important role of the kidney in the regulation of arterial blood pressure. The theoretical importance of the kidney in the control of arterial pressure and the concept that alterations in renal function lead to adjustments in arterial blood pressure was first introduced by Guyton and colleagues and has been reviewed extensively . Although arterial blood pressure is controlled by many regulatory systems, it is proposed that the kidney, through its ability to regulate extracellular fluid volume, is the dominant long-term controller of arterial pressure.
Similar data have been obtained from clinical studies. It was first demonstrated that mean arterial pressure was significantly higher in patients who received a renal transplant from a donor with a family history of hypertension than in patients whose donor family had a normotensive history . Second, patients who received a transplant from a hypertensive donor had higher blood pressures compared with patients who received kidneys from normotensive donors . Finally, transplantation of a kidney from a normotensive donor produced a sustained normalization of arterial pressure in hypertensive patients who had demonstrated long-standing essential hypertension . These clinical data emphasize the importance of the kidney in the development and maintenance of hypertension in humans and experimental animals.
Don’t Miss: Is Watermelon Good For Your Kidneys
What Are Common Tests To Check The Health Of The Renal Cortex
Healthcare providers use several tests to measure kidney function and diagnose kidney problems. Your provider may recommend:
- Imaging tests : These tests can show kidney abnormalities or obstructions . For instance, these can show the thickness of the renal cortex. Thinning of the cortex may mean that the kidney has been injured.
- Blood tests: These can show how well your glomeruli filter your blood.
- Kidney biopsy: In this test, your provider removes a small amount of kidney tissue to examine under a microscope.
- Ureteroscopy: This is a test where your provider passes a tube through your urethra into your bladder and ureters to look for abnormalities.
- Urinalysis: This measures specific substances, such as protein or blood, in urine to detect any abnormality that may indicate a disease condition or infection.
- Kidney function tests : These tests show how well the kidneys are working. One of the blood tests is called creatinine which can estimate kidney function and assess how efficiently your kidneys are clearing wastes from your blood.
What Is The Functional Filtering Unit Of The Kidneys
Nephrons are the basic structural and functional units of the kidney. They consist of a network of tubules and canals specialized in filtration.
The kidney is responsible for maintaining fluid balance within the body. The basic structural and functional units of the kidneys are the nephrons. Each nephron is made of intricately interwoven capillaries and drainage canals to filter wastes, macromolecules, and ions from the blood to urine. The approximately 1 million nephrons in each human kidney form 10-20 cone-shaped tissue units called renal pyramids that span both the inner and outer portions of the kidney, the renal medulla and renal cortex.
There are two main parts of a nephron: the renal corpuscle and renal tubule.
You May Like: Almond Milk Kidney Disease
Diagnosis Of Cortical Necrosis Of The Kidneys
-
Routine blood and urine tests
-
Imaging test
-
Sometimes kidney biopsy
. Kidney biopsy Kidney biopsy Site-specific biopsies and cell sampling are also used in the evaluation of people with suspected kidney and urinary tract disorders. A kidney biopsy… read more can give doctors the most accurate diagnostic information, but a biopsy involves removing tissue and can cause complications and may be unnecessary if the diagnosis is evident. Thus, a biopsy is not done in most people.
Normal And Abnormal Cell Types Encountered
The normal histological anatomies of the canine and feline renal cortices are shown in Fig. 22.1. The renal parenchyma consists of glomeruli, tubules, interstitium, and blood vessels. Renal tubules make up the bulk of the parenchyma. Findings in normal renal aspirates are listed in Table 22.2. Renal tubular epithelial cells are the predominant cell type seen in fine-needle aspirates from normal kidneys. They are rather large, round-to-polygonal cells that occur singly and in clusters . They have a round, eccentrically placed nucleus and moderately abundant pale basophilic cytoplasm, which, in cats, often contains several distinct, clear vacuoles from the presence of lipid droplets . Clear cytoplasmic vacuoles may also be present in dogs with diabetes mellitus, long-term exposure to corticosteroids, or lysosomal storage disease . Cells of the distal convoluted tubules and ascending limb of the loop of Henle may contain dark intracytoplasmic granules .6
Kevin M. O’Shaughnessy, in, 2012
Don’t Miss: Is Watermelon Bad For Your Kidneys
How The Kidneys Work
Blood is filtered at high pressure to remove glucose, water, salts and urea.
All the glucose, and some water and salts, are reabsorbed back into the blood. Note that urea is not reabsorbed.
Dr Alice Roberts dissects a pigs kidney and explains the structure and function of the kidney and urinary system
Cortical Necrosis Of The Kidneys
, MD, Loma Linda University School of Medicine
-
Usually the cause is a major, catastrophic disorder that decreases blood pressure.
-
Symptoms may include dark urine, decreased urine volume, fever, and pain in the side of the body.
-
Sometimes an imaging test or tissue analysis is done to confirm the diagnosis.
Renal cortical necrosis can occur at any age. About 10% of the cases occur in infants and children.
Read Also: Flomax Dosage For Kidney Stones
Renal Medullary Vasoconstriction In Normotensive Rats
Fig. 4.Chronic influence of renal medullary interstitial infusion of the nitric oxide synthase inhibitor l-NAME on renal medullary blood flow , daily sodium balance , and mean arterial blood pressure in conscious Sprague-Dawley rats. Vertical dashed lines indicate the l-NAME infusion period. * Significant difference from control .
Recommended Reading: Does Carbonation Cause Kidney Stones
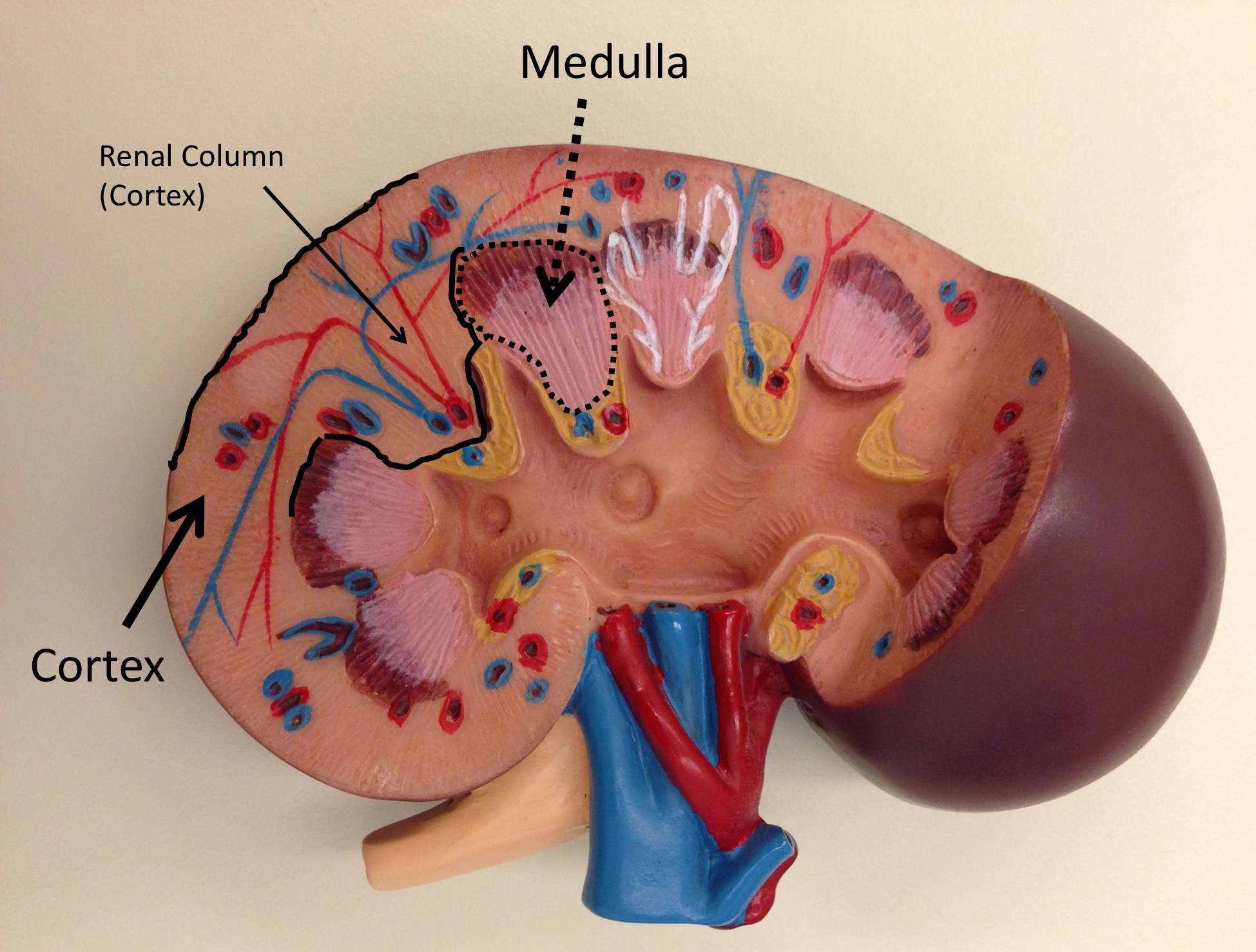
What Is The Difference Between The Renal Cortex And The Renal Medulla
The kidney is made up of solid tissue called parenchyma which consists of cortex and the medulla. The renal cortex is the outside section of the kidney, while the medulla is the inside section.
The renal cortex has a more grainy texture, while the medulla is smoother.
Both sections contain tubules , but the cortex has the glomeruli and convoluted tubules and blood vessels which gives it a grainy appearance. The tubules of the medulla are straighter and are called the collecting tubules . The medulla also contains the loops of Henle, or the U-shaped parts of the collecting tubules.
Also Check: Kidney Apple Cider Vinegar
Capillary Network Within The Nephron
The capillary network that originates from the renal arteries supplies the nephron with blood that needs to be filtered. The branch that enters the glomerulus is called the afferent arteriole. The branch that exits the glomerulus is called the efferent arteriole. Within the glomerulus, the network of capillaries is called the glomerular capillary bed. Once the efferent arteriole exits the glomerulus, it forms the peritubular capillary network, which surrounds and interacts with parts of the renal tubule. In cortical nephrons, the peritubular capillary network surrounds the PCT and DCT. In juxtamedullary nephrons, the peritubular capillary network forms a network around the loop of Henle and is called the vasa recta.
What Is The Cerebral Cortex
The cerebral cortex is the outermost layer of the brain that is associated with our highest mental capabilities. The cerebral cortex is primarily constructed of grey matter , with between 14 and 16 billion neurons being found here.
Although the cerebral cortex is only a few millimeters in thickness, it consists of approximately half the weight of the total brain mass.The cerebral cortex has a wrinkled appearance, consisting of bulges, also known as gyri, and deep furrows, known as sulci.
The many folds and wrinkles of the cerebral cortex allow for a wider surface area for an increased number of neurons to live there, permitting large amounts of information to be processed.
The cortex is also divided into two hemispheres, the right and left, which is separated by a large sulcus called the medial longitudinal fissure.
The two hemispheres are connected via bundles of nerve fibers called the corpus callosum, to allow both hemispheres of the cerebral cortex to communicate with each other and for further connections to be made.
A vast array of functions are controlled by the cerebral cortex through the use of the lobes, which are divided based on the location of gyri and sulci. These lobes are called the frontal lobes, temporal lobes, parietal lobes, and occipital lobes.
Recommended Reading: Aleve Kidney Problems
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Medullary Sponge Kidney
Many people with medullary sponge kidney have no symptoms. The first sign that a person has medullary sponge kidney is usually a UTI or a kidney stone. UTIs and kidney stones share many of the same signs and symptoms:
- burning or painful urination
- fever and chills
- vomiting
People who experience these symptoms should see or call a health care provider as soon as possible.
Nephrons: The Basic Functional Units Of Blood Filtration And Urine Production
Each kidney contains over 1 million tiny structures called nephrons. The nephrons are located partly in the cortex and partly inside the renal pyramids, where the nephron tubules make up most of the pyramid mass. Nephrons perform the primary function of the kidneys: regulating the concentration of water and other substances in the body. They filter the blood, reabsorb what the body needs, and excrete the rest as urine.
Read Also: Is Apple Cider Vinegar Bad For Your Kidneys
What Are The Common Conditions And Disorders That Affect The Renal Cortex
Many different disorders can affect the kidneys, including:
- Chronic kidney disease:Chronic kidney disease may lessen your kidney function. Diabetes or high blood pressure usually causes CKD.
- Kidney cancer: Renal cell carcinoma is the most common type of kidney cancer.
- Kidney failure : Kidney failure may be acute or chronic . End-stage renal disease is a complete loss of kidney function. It requires dialysis .
- Kidney infection : A kidney infection can occur if bacteria enter your kidneys by traveling up your ureters. These infections cause sudden symptoms. Healthcare providers treat them with antibiotics.
- Kidney stones:Kidney stones cause crystals to form in your urine and may block urine flow. Sometimes these stones pass on their own. In other cases, healthcare providers can offer treatment to break them up or remove them.
- Kidney cysts: Fluid-filled sacs called kidney cysts grow on your kidneys. These cysts can cause kidney damage. Healthcare providers can remove them if medically indicated.
- Polycystic kidney disease: Polycystic kidney disease , a genetic condition, causes cysts to form on the kidneys. PKD may lead to high blood pressure and kidney failure. People with PKD need regular medical monitoring.
There are so many other disorders that can affect or be related to your kidneys, and many of them are serious. Some of these conditions include:
What Is The Functional Unit Of The Kidney
The functional units of the kidney refer to the glomeruli, which are the filtering units that filter the blood. The term functional pertains to how well the kidney maintains and functions. When a person has kidney disease, the function of the kidney may be impaired and it may not be able to filter the blood properly. The functional units will determine the health or death of a human kidney
The kidneys filter blood from the blood in the body and they also store other chemicals as well as waste products from the body. The filtering units in the kidney to form a barrier to block the blood from flowing into the urinary system. When these filters become damaged, there is an increased risk of the blood being exposed to toxins, which can result in damage to the kidneys themselves. When the kidneys are damaged, they cannot filter the blood properly and that can lead to problems.
To understand what is the functional unit of the kidney, one must understand the structure of the kidney. This organ is found in the lower portion of the urinary tract and it has two branches, the tubule and the ureter. The tubule has the job of storing the stones that form in the kidneys, along with bacteria and other substances. The ureter carries urine away from the body and allows it to pass through the kidney. Without these organs, the kidney cannot function properly.
Also Check: Can Kidney Stones Increase Blood Sugar