Stage : Gfr < 15ml/min Kidney Failure
End stage renal disease is the final stage of chronic kidney disease , also known as kidney failure. This occurs when the kidneys function below 10-15 percent and is often a result of years of chronic kidney disease. After being diagnosed with ESRD, it is important to decide what treatment option you will use, such as home dialysis, incenter hemodialysis, transplantation, or palliative care.
Dialysis And Peritoneal Access Dialysis
In end-stage kidney disease, kidney functions can be replaced only by dialysis or by kidney transplantation. The planning for dialysis and transplantation is usually started in stage 4 of chronic kidney disease. Most patients are candidates for both hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis . There are few differences in outcomes between the two procedures. The physician or an educator will discuss the appropriate options with the patient and help them make a decision that will match their personal and medical needs. It is best to choose a modality of dialysis after understanding both procedures and matching them to one’s lifestyle, daily activities, schedule, distance from the dialysis unit, support system, and personal preference.
The doctor will consider multiple factors when recommending the appropriate point to start dialysis, including the patient’s laboratory work and actual or estimated glomerular filtration rate, nutritional status, fluid volume status, the presence of symptoms compatible with advanced kidney failure, and risk of future complications. Dialysis is usually started before individuals are very symptomatic or at risk for life-threatening complications.
Dialysis
There are two types of dialysis 1) hemodialysis and 2) peritoneal dialysis. Before dialysis can be initiated, a dialysis access has to be created.
Dialysis access
Peritoneal access
Can Chronic Kidney Disease Be Prevented
Chronic kidney disease cannot be prevented in most situations. The patient may be able to protect their kidneys from damage, or slow the progression of the disease by controlling their underlying conditions such as diabetes mellitus and high blood pressure.
- Kidney disease is usually advanced by the time symptoms appear. If a patient is at high risk of developing chronic kidney disease, they should see their doctor as recommended for screening tests.
- If a patient has a chronic condition such as diabetes, high blood pressure, or high cholesterol, they should follow the treatment recommendations of their health care practitioner. The patient should see their health care practitioner regularly for monitoring. Aggressive treatment of these diseases is essential.
- The patient should avoid exposure to drugs especially NSAIDs , chemicals, and other toxic substances as much as possible.
You May Like: Grapes For Kidney Stones
How Can Doctors Tell My Stage Of Ckd
To find out your stage of CKD, doctors will do tests, such as:
- eFGR tests , which is a measure of how well your kidneys are working
- Urine tests
Please note: eGFR is an estimate of how well your kidneys are working. The way eGFR is calculated will be changing. Currently the test considers your age, sex and race, among other things. A task force led by the National Kidney Foundation and the American Society of Nephrology is working on recommendations that may remove Black race as a factor in the eGFR calculation. The task force has been seeking the input of kidney disease experts to come up with the best way to make the eGFR test as accurate as possible. The American Kidney Fund advised the task force to remove race from the eGFR so there is no bias in testing kidney function. This would help to make sure that every person will receive health care that is fair and of the highest quality. When the NKF-ASN task force makes its recommendations, AKF will promptly review them and then update our educational materials.
Working With Your Care Team
Good healthcare is always a team effort – especially for people with CKD. You should remain engaged with your primary care clinician. Some questions you can ask your primary care clinician, if you have not discussed them with anyone, are as follows:
-
Do I need a referral to a nephrologist?
-
If I am seeing a nephrologist, how will the both of you remain updated on my condition?
-
What changes or symptoms do I need to watch for and tell you about?
-
Do I need any new treatments? If so, what are my options?
-
When and how should I prepare for any new treatments?
If you have stage 4 CKD, your primary clinician can refer you to a nephrologist, also known as a kidney doctor. A nephrologist is a doctor who has advanced training in treating kidney disease. There are also other members of a nephrology healthcare team, including a nephrology nurse, nephrology advanced practitioner, renal dietitian, and a nephrology social worker. These members of the healthcare team also have specialized training in kidney disease. Some questions you can ask a nephrology clinician include:
-
What is wrong with my kidneys?
-
How severe is my kidney disease?
-
What can I do about it?
-
Should I visit a transplant center for an evaluation?
-
What are my other treatment options?
-
When and how should I prepare for treatment?
-
How will both you and my primary care clinician stay updated on my condition?
Don’t Miss: Celery Juice And Kidney Disease
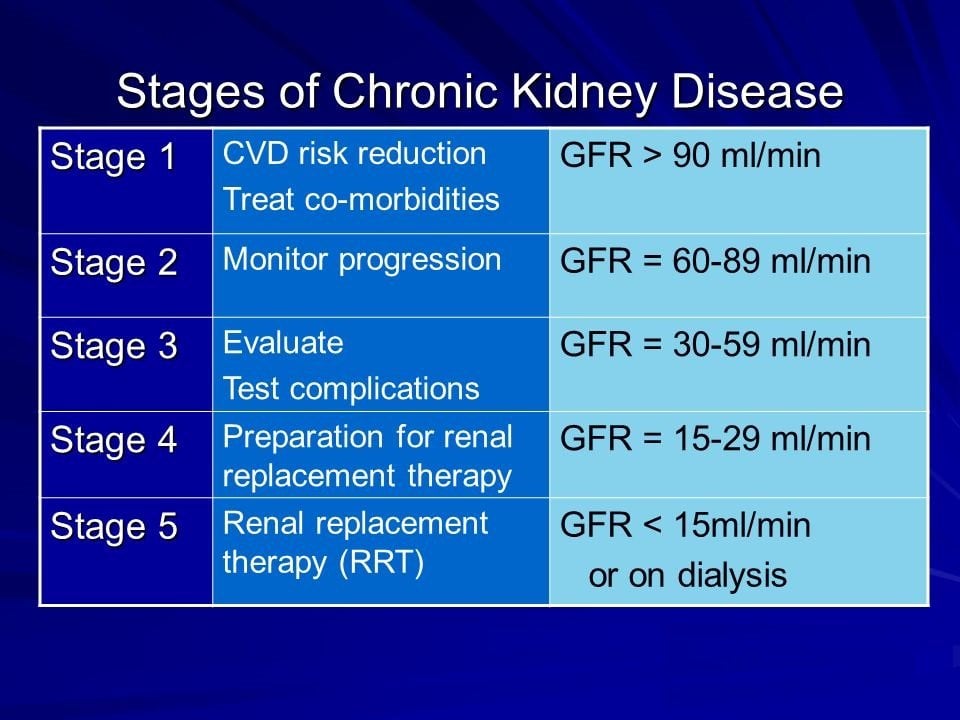
Stages Of Kidney Disease
Each of the five stages of chronic kidney disease is related to the level of kidney function and kidney damage.
There are five stages to kidney disease. You can find out what stage youre in by testing:
- your blood pressure
- the bloods eGFR
- your urines ACR
Depending on your stage of kidney disease, your test result will vary. There will also be different ways to manage your health. While everyones experience of kidney disease is unique, weve prepared some guidelines on what you can expect below.
What Tests And Procedures Diagnose Chronic Kidney Disease
Chronic kidney disease usually causes no symptoms in its early stages. Only lab tests can detect any developing problems. Anyone at increased risk for chronic kidney disease should be routinely tested for development of this disease.
- Urine, blood, and imaging tests are used to detect kidney disease, as well as to follow its progress.
- All of these tests have limitations. They are often used together to develop a picture of the nature and extent of the kidney disease.
- In general, this testing can be performed on an outpatient basis.
Urine tests
Urinalysis: Analysis of the urine affords enormous insight into the function of the kidneys. The first step in urinalysis is doing a dipstick test. The dipstick has reagents that check the urine for the presence of various normal and abnormal constituents including protein. Then, the urine is examined under a microscope to look for red and white blood cells, and the presence of casts and crystals .
Only minimal quantities of albumin are present in urine normally. A positive result on a dipstick test for protein is abnormal. More sensitive than a dipstick test for protein is a laboratory estimation of the urine albumin and creatinine in the urine. The ratio of albumin and creatinine in the urine provides a good estimate of albumin excretion per day.
Blood tests
Other tests
Don’t Miss: Yerba Mate Kidney Stones
Referral To A Nephrologist
Guidelines for referral to a nephrologist vary between countries. Most agree that nephrology referral is required by Stage 4 CKD .
It may also be useful at an earlier stage when urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio is more than 30 mg/mmol, when blood pressure is difficult to control, or when hematuria or other findings suggest either a primarily glomerular disorder or secondary disease amenable to specific treatment. Other benefits of early nephrology referral include proper education regarding options for kidney replacement therapy as well as pre-emptive transplantation, and timely workup and placement of an arteriovenous fistula in those people with chronic kidney disease opting for future hemodialysis.
Stages Of Chronic Kidney Disease
www.kidneyfund.orgKidney DiseaseChronic Kidney Disease Stages of Chronic Kidney DiseaseMedical Advisory Committee
Chronic kidney disease is divided into five stages. The stages are based on the eGFR test result and how well your kidneys work to filter waste and extra fluid out of your blood. As the stages go up, kidney disease gets worse and your kidneys do not work as well. At each stage, it is important to take steps to slow down the damage to your kidneys.
Also Check: Can You Get A Kidney Infection From Drinking Alcohol
Preventing Or Slowing Down The Progression Of Chronic Kidney Disease
There are ways to stop chronic kidney disease becoming any worse or to slow down any progression. You should have checks every now and then by your GP or practice nurse to monitor your kidney function – the eGFR test. They will also give you treatment and advice on how to prevent or slow down the progression of CKD. This usually includes:
- Blood pressure control. The most important treatment to prevent or delay the progression of chronic kidney disease, whatever the underlying cause, is to keep your blood pressure well controlled. Most people with CKD will require medication to control their blood pressure. Depending on the amount of albumin in your urine, your doctor may recommend a target blood pressure level to aim for of below 140/90 mm Hg or 130/80 mm Hg, and even lower in some circumstances. For children and young people with CKD and high levels of albumin in the urine, blood pressure should be kept less than average for their height.
- Review of your medication. Certain medicines can affect the kidneys as a side-effect which can make CKD worse. For example, if you have CKD you should not take anti-inflammatory medicines unless advised to by a doctor. You may also need to adjust the dose of certain medicines that you may take if your CKD gets worse.
- Diet. if you have more advanced CKD then you will need to follow a special diet. See the separate leaflet called Diet in Chronic Kidney Disease.
What Is The Treatment And Management Of Chronic Kidney Disease
There is no cure for chronic kidney disease. The four goals of therapy are to:
Strategies for slowing progression and treating conditions underlying chronic kidney disease include the following:
- Control of blood glucose: Maintaining good control of diabetes is critical. People with diabetes who do not control their blood glucose have a much higher risk of all complications of diabetes, including chronic kidney disease.
- Control of high blood pressure: This also slows progression of chronic kidney disease. It is recommended to keep blood pressure below 130/80 mm Hg if one has kidney disease. It is often useful to monitor blood pressure at home. Blood pressure medications known as angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers have special benefit in protecting the kidneys.
- Diet: Diet control is essential to slowing progression of chronic kidney disease and should be done in close consultation with a health care practitioner and a dietitian. For some general guidelines, see the Chronic Kidney Disease Self-Care at Home section of this article.
The complications of chronic kidney disease may require medical treatment.
- Lightheadedness
- Allergic reactions
Diuretics also may cause a decline in kidney function especially if fluid is removed rapidly from the body.
Read Also: Teas Good For Kidneys
Can You Change Treatments For Kidney Failure
If you start on one type of treatment for kidney failure but feel you would like to try something else, you can speak to your healthcare professional about changing. For most people, it is often possible to change treatments. For example, if you choose hemodialysis, it doesn’t mean you can’t switch to peritoneal dialysis at a later date. Even if you choose to have a kidney transplant, you may need a period of dialysis until you can be transplanted with a new kidney. It is not uncommon for people who have had kidney failure for many years to have had more than one type of treatment in that time.
Reducing The Risk Of Developing Cardiovascular Diseases
People with chronic kidney disease have an increased risk of developing CVDs, such as heart disease, stroke, and peripheral arterial disease. People with CKD are actually twenty times more likely to die from cardiovascular-related problems than from kidney failure. This is why reducing any other cardiovascular risk factors is so important. See the separate leaflet called Cardiovascular Disease .
This typically includes:
Don’t Miss: Is Apple Cider Vinegar Bad For Kidney Disease
Medication To Protect Your Kidneys
- ACE inhibitors and ARBs. If you have high levels of protein in your urine then you may be advised to take medication even if your blood pressure is normal. Two related types of medication have been shown to be beneficial for many people with CKD. This is because they can prevent further worsening of the function of your kidneys. These medicines are called:
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and
- Angiotensin receptor blockers , such as losartan, valsartan, candesartan, telmisartan).
- SGLT2 inhibitors. A group of medicines called the SGLT2 inhibitors were originally used to keep blood sugar under control in type 2 diabetes. However, more recent studies show that some of them can significantly reduce decline in kidney function. These may be recommended whether you have type 2 diabetes or not. The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence has issued new guidance recommending that they should be offered to, or considered for, most people with type 2 diabetes and CKD.
How Is Chronic Kidney Disease Diagnosed
Kidney function is assessed using a combination of:
- A blood test called the estimated glomerular filtration rate and
- A measure of the amount of protein in the urine .
Increased protein in the urine and decreased eGFR are both associated with an increased risk of progressive chronic kidney disease.
You May Like: Is Almond Milk Good For Your Kidneys
Treatments For Kidney Failure
The two treatments for kidney failure are kidney transplantation and dialysis. Two different types of dialysis can be done – hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis.
To learn more about each type of treatment, see “Choosing a Treatment for Kidney Failure” in the A-to-Z Guide.
How Common Is Chronic Kidney Disease
About 1 in 10 people have some degree of chronic kidney disease. It can develop at any age and various conditions can lead to CKD. It becomes more common with increasing age and is more common in women.
Although about half of people aged 75 or more have some degree of chronic kidney disease, most of these people do not actually have diseases of their kidneys they have normal ageing of their kidneys.
Most cases of CKD are mild or moderate .
Read Also: Kidney Stone And Constipation
Control Other Health Problems
You may have other disorders, such as diabetes and high blood pressure, which can damage your kidneys. One of the goals of your treatment is to make sure these are well-controlled. Ask your healthcare professional what you can do to keep these conditions under control – and do it! Some of the things your healthcare professional may ask you to do:
- Take medications called angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers as part of your therapy. Studies have shown that these medications help to protect your kidney function. You may also need other blood pressure medications to control your blood pressure.
- Lose weight if you are overweight
- Cut down on salt in your diet to control blood pressure
- If you have diabetes, monitor your blood sugar, follow your diet and take your medications as prescribed
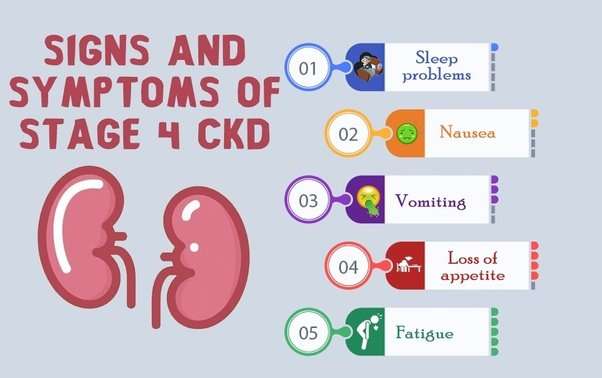
Stage 4 Of Chronic Kidney Disease
A person with stage 4 chronic kidney disease has advanced kidney damage with a severe decrease in the glomerular filtration rate to 15-30 ml/min. It is likely someone with stage 4 CKD will need dialysis or a kidney transplant in the near future.
As kidney function declines, waste products build up in the blood causing a condition known as uremia. In stage 4, a person is likely to develop complications of kidney disease such as high blood pressure, anemia , bone disease, heart disease and other cardiovascular diseases.
At stage 4, its necessary to see a nephrologist . The nephrologist examines the patient and orders lab tests to gather information to recommend treatment.
People in stage 4 CKD will usually visit their doctor at least every three months. Blood tests for creatinine, hemoglobin, potassium, calcium and phosphorus levels will be done to see how well the kidneys are working. The doctor will also monitor other conditions such as high blood pressure and diabetes. In addition to helping the patient keep their kidneys working as long as possible, the nephrologist will also help prepare the patient for dialysis or a kidney transplant.
A person in stage 4 may also be referred to a dietitian. Because diet is such an important part of treatment, the dietitian will review a persons lab work results and recommend a meal plan individualized for their needs. Eating a proper diet can help preserve kidney function and overall health.
Treatments for Kidney Failure
Also Check: Is Almond Milk Good For Kidney Disease