What Is The Kidney: Anatomy Function Conditions And Procedures
- Highest rating: 5
- Summary: The kidneys are bean-shaped organs located near the back of the abdominal cavity. Each person has a pair of kidneys, with each organ measuring about 4 to 5
See Details
- Highest rating: 4
- Summary: In the adult, each kidney is approximately 3 cm thick, 6 cm wide, and 12 cm long. It is roughly bean-shaped with an indentation, called the hilum, on the medial
See Details
Feature: Human Biology In The News
Kidney failure is a complication of common disorders including diabetes mellitus and hypertension. It is estimated that approximately 12.5% of Canadians have some form of kidney disease. If the disease is serious, the patient must either receive a donated kidney or have frequent hemodialysis, a medical procedure in which the blood is artificially filtered through a machine. Transplant generally results in better outcomes than hemodialysis, but demand for organs far outstrips the supply. The average time on the organ donation waitlist for a kidney is four years. There are over 3,000 Canadians on the wait list for a kidney transplant and some will die waiting for a kidney to become available.
For the past decade, Dr. William Fissell, a kidney specialist at Vanderbilt University, has been working to create an implantable part-biological and part-artificial kidney. Using microchips like those used in computers, he has produced an artificial kidney small enough to implant in the patients body in place of the failed kidney. According to Dr. Fissell, the artificial kidney is a bio-hybrid device that can mimic a kidney to remove enough waste products, salt, and water to keep a patient off dialysis.
Functional Structure Of The Kidneys
nephrons
1. The tubule begins with a hollow enlargement called Bowman’s capsule, which is where water and solutes initially enter the tubule from the bloodstream. This process is known as filtration. The structure comprised of Bowman’s capsule and associated capillaries is called the renal corpuscle.
2. From Bowman’s capsule the tubular fluid flows towards the proximal tubule, which remains in the outer layer of the kidney. The proximal tubule is the major site of reabsorption of water and solutes in equal proportions from the filtered tubular fluid.
3. Then the tubule dips into the hairpin loop of Henle, which descends toward the center of the kidney and then rises back to the cortex. The loop of Henle is also a major site of reabsorption, but unlike the proximal tubule, proportionately more solute than water is reabsorbed, so the tubular fluid is dilute relative to plasma by the end of this segment.
4. The next segment is the distal tubule, which like the proximal tubule remains in the cortex. Both reabsorption and secretion take place in this segment, which is where sodium and potassium concentrations and the pH of the tubular fluid are adjusted to ensure homeostasis.
1. An afferent arteriole takes blood to the renal corpuscle, where the blood passes through the first capillary bed, a ball-shape tuft known as the glomerulus.
2. An efferent arteriole takes blood away from the glomerulus.
Also Check: What Medications Cause Kidney Stones
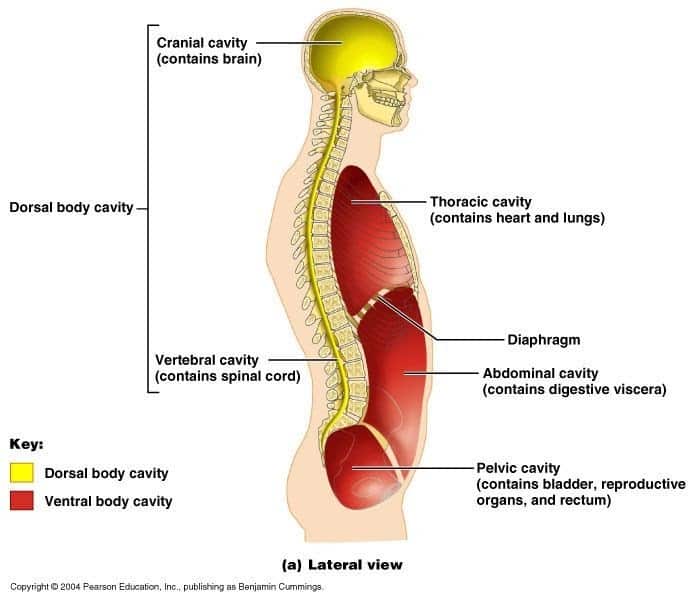
What Cavity Contains The Reproductive And Excretory System
The abdominal-pelvic cavity is a bodily cavity formed by the abdominal cavity and the pelvic cavity. It also houses the urine bladder and reproductive organs. The abdominal cavity is located between the rib cage and the pelvis, which protects it from trauma. The diaphragm separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity.
The average human being has a total number of cells equal to about 100 billion . Of these, 50% are immune cells, 25% are digestive tract cells, 15% are brain cells, and so on. Human beings are composed of many different types of cells that work together to allow us to live.
The abdominal cavity is one of the largest in the body. It connects with other larger cavities including the thoracic cavity and the pelvic cavity . The abdomen is divided into two parts: the thorax and the pelvis. The thorax includes the lungs and the heart the pelvis includes the urinary system and the reproductive system.
Cells need oxygen to function properly. They take oxygen from the blood and use it as fuel for working molecules called enzymes.
Diseases Of The Sinuses
The most common disorder affecting the paranasal sinuses is infection, a condition that is known as sinusitis .
Polyps, consisting of swollen nasal lining, may grow from both the maxillary and ethmoidal sinuses and cause nasal obstruction. They occur most commonly as a result of nasal allergy and require surgical removal.
Cancers affecting the paranasal sinuses are rare, especially in the sphenoidal and frontal area. They occur most commonly among the Bantu of South Africa, where they are related to the long-term use of a homemade snuff that is carcinogenic. Recently, however, it has been shown that certain woodworkers in the furniture industry have a greatly increased incidence of nasal sinus cancer.
Don’t Miss: How Much Kidney Function Does Dialysis Replace
What Is Contained In The Peritoneal Cavity
The peritoneal cavity houses the visceral organs, which include the liver, stomach, small and large intestines, and other smaller organs. The uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries all extend into the peritoneal cavity in women. The peritoneal cavity covers an area of about 5-10% of the total surface area of the body, depending on the size of the person. It contains a relatively constant amount of fluid called peritoneal fluid that helps lubricate and cushion the internal organs.
There are two main layers to the peritoneal cavity: the serous layer and the muscular layer. Under the serous layer are several important structures such as the liver, intestines, and stomach. Small blood vessels and nerves run between the two layers. The peritoneal cavity communicates with the rest of the abdominal cavity through three sets of openings: the thoracic duct leaves the lymphatic system at the neck and enters the peritoneal cavity through a vein the hepatic portal triad consists of three branches of the portal vein that enter the peritoneal cavity lastly, the inferior vena cava returns blood from the pelvic region to the heart through the peritoneal cavity.
The peritoneal cavity includes both parietal and visceral surfaces. The parietal surface faces toward the outside of the body and lines the inner wall of the chest and abdomen.
Read A Brief Summary Of This Topic
thoracic cavity, also called chest cavity, the second largest hollow space of the body. It is enclosed by the ribs, the vertebral column, and the sternum, or breastbone, and is separated from the abdominal cavity by a muscular and membranous partition, the diaphragm. It contains the lungs, the middle and lower airwaysthe tracheobronchial treethe heart, the vessels transporting blood between the heart and the lungs, the great arteries bringing blood from the heart out into general circulation, and the major veins into which the blood is collected for transport back to the heart. The heart is covered by a fibrous membrane sac called the pericardium that blends with the trunks of the vessels running to and from the heart. The thoracic cavity also contains the esophagus, the channel through which food is passed from the throat to the stomach.
Diseases affecting the pleura and pleural cavity, other than primary tumours, are brought by the blood vessels or may spread from contiguous structures. The pleural cavity may be contaminated by the rupture of either the visceral pleura or the parietal pleura.
Rupture of the thoracic duct, the main channel for lymph, gives rise to chylothorax, characterized by escape of lymph into the pleural space.
Recommended Reading: Where Is You Kidney Located
Physiologic Considerations In Microscopic Anatomy
The renal tubular system is uniquely structured in order to maximize its physiologic function. One of its primary functions is to concentrate urine accordingly to the bodyâs hydro-osmotic state . A hyperosmotic state results in the excretion of hyperosmotic urine, and the reverse is true for when the body is in a hypo-osmotic state. The kidney is able to carry out this function by 2 mechanisms: the action of antidiuretic hormone on the medullary collecting ducts and the phenomenon termed countercurrent multiplication.
Countercurrent multiplication is responsible for keeping the medullary interstitial osmotic concentration higher than the renal tubular osmotic concentration. When the iso-osmotic fluid from the proximal tubule enters the descending limb, the osmotic concentration gradient forces water to move out of the descending limb. By the time the tubular fluid reaches the bottom of the loop of Henle, it has a higher osmotic concentration than the interstitial medullary fluid in the ascending limb. Hyperosmolar tubular fluid entering the ascending limb causes NaCl to be reabsorbed back into the medullary interstitium passively. Once the tubular fluid reaches the thick ascending limb, more ions are reabsorbed into the medullary interstitium actively.
Function Of A Nephron
The simplified diagram of a nephron in Figure 16.4.6 shows an overview of how the nephron functions. Blood enters the nephron through an arteriole called the afferent arteriole. Next, some of the blood passes through the capillaries of the glomerulus. Any blood that doesnt pass through the glomerulus as well as blood after it passes through the glomerular capillaries continues on through an arteriole called the efferent arteriole. The efferent arteriole follows the renal tubule of the nephron, where it continues playing a role in nephron functioning.
Don’t Miss: Can Drinking Too Many Sodas Cause Kidney Stones
Kidney Pain Location And Sensation
Most people tend to associate pain in the area between the ribs and hips as either digestive problems or muscular back pain. However, kidney pain isnt always felt in the same place as the kidneys location.
Dr. Charles Patrick Davis on MedicineNet explains that renal or flank pain can be felt anywhere between the lowest rib and the buttocks. The pain may also radiate to the groin or abdominal area. Depending on the underlying cause of the kidney pain, you may feel the pain in just the left or right side of your back. However, sometimes kidney pain affects both sides of the back.3
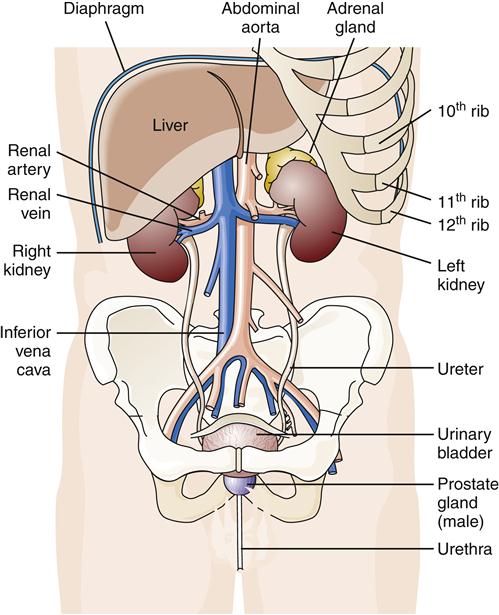
Where Are The Kidneys And Liver Located News
- www.news-medical.net
- Highest rating: 3
- Summary: Therefore, they are actually outside the peritoneal cavity. The kidneys are situated below the diaphragm, one on either side of the spine.
See Details
- Highest rating: 4
- Summary: The abdominopelvic cavity is a body cavity that consists of the abdominal cavity and the pelvic cavity. The upper portion is the abdominal cavity, and it
See Details
- Highest rating: 4
- Summary: In humans, the kidneys are located high in the abdominal cavity The human kidney is a bean-shaped structure with a convex The superior pole of the right
See Details
You May Like: How Does Chemo Affect Your Kidneys
Functions Of The Paranasal Sinuses
Comprehensive studies on the comparative anatomy and physiology of the nose and paranasal sinuses have been made in humans and in lower animals. The presence of the sphenoidal and frontal sinuses in carnivores such as the dog, hyena, and tiger is related to an increased area of olfaction and consequent improvement in the sense of smell. Ethmoidal air cells are found only in higher apes and humans and are probably the result of restriction of the olfactory area.
The maxillary sinuses are largest in humans, in the higher apes, and in capuchin and howler monkeys they are absent in baboons, lorises, and tapirs. It has been suggested that these sinuses play a part in phonation, that they aid in conservation of heat from the nasal fossae, and that they serve to lighten the skull, but evidence for these theories is lacking.
What Hormones Are Produced By The Kidney
The kidney has multiple endocrine roles it secretes various hormones and humoral factors: the hormones of the renin- angiotensin system , erythropoietin , and 1,25 dihydroxy vitamin D3. It also produces enzymes, such as kallikreins, which produce hormones in other, distant sites.
Where is the coelomic cavity located in the body?
What Is Coelomic Cavity? In most animals, Coelom is the main body cavity located in the body to envelop and contain the internal organs, digestive tract etc. It is a hollow, fluid-filled cavity serving as a skeleton.
You May Like: Is Wine Good For Kidneys
What System Is The Kidney Part Of
| Thyroid gland Parathyroid gland Adrenal glands Pituitary gland Pancreas Stomach Pineal gland Ovaries Testes | |
| Urinary | Kidneys Ureters Bladder Urethra |
Likewise, how does the kidney work with other systems? The excretory system is a close partner with both the circulatory and endocrine system. The circulatory system connection is obvious. Blood that circulates through the body passes through one of the two kidneys. Urea, uric acid, and water are removed from the blood and most of the water is put back into the system.
Also to know is, is the kidney part of the digestive system?
Wikijunior:Human Body/Digestive System/Kidneys. Kidneys are pairs of organs located in the back of the abdominal cavity. Each kidney is important to keep your body balanced and well suited.
What organs are part of two systems?
Answer and Explanation:
Recommended Reading: How Do The Kidneys Compensate For Acid Base Imbalances
Organ Systems Working Together
Organ systems often work together to do complicated tasks. For example, after a large meal is eaten, several organ systems work together to help the digestive system obtain more blood to perform its functions. The digestive system enlists the aid of the cardiovascular system and the nervous system. Blood vessels of the digestive system widen to transport more blood. Nerve impulses are sent to the brain, notifying it of the increased digestive activity. The digestive system even directly stimulates the heart through nerve impulses and chemicals released into the bloodstream. The heart responds by pumping more blood. The brain responds by perceiving less hunger, more fullness, and less interest in vigorous physical activity, which preserves more blood to be used by the digestive system instead of by skeletal muscles.
Communication between organs and organ systems is vital. Communication allows the body to adjust the function of each organ according to the needs of the whole body. In the example above, the heart needs to know when the digestive organs need more blood so that it can pump more. When the heart knows that the body is resting, it can pump less. The kidneys must know when the body has too much fluid, so that they can produce more urine, and when the body is dehydrated, so that they can conserve water.
Donât Miss: What Eases Kidney Stone Pain
Recommended Reading: What To Eat With Kidney Disease
What Organs Does The Peritoneum Cover
There are two layers to the peritoneum: the superficial parietal layer and the deep visceral layer. The kidneys, urinary bladder, uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries, pleura, pericardium, lungs, and intestines are also within the peritoneal cavity.
The peritoneum covers all organs contained within the abdominal cavity. It provides a protective lining for these organs which would otherwise be exposed to the external environment. Additionally, it acts as a reservoir for excess fluid from the body which can be released upon demand or trapped if the body experiences dehydration. The peritoneum is also responsible for nourishing those organs contained within the abdominal cavity via blood vessels that run between its layers.
Specifically, the peritoneum covers the outer surface of the abdomen except for the area directly over the spine and pelvis. This area is referred to as the pelvic peritoneum. The pelvic peritoneum is a single membrane which extends around the circumference of the pelvis like a bag. This membrane contains several small openings called sinuses that allow urine and other fluids to escape from the cavity and lymphatic vessels to flow through them.
About Article Author
What Is The Difference Between Dorsal And Ventral
The main difference between dorsal and ventral is the area of the to which they refer. In general, ventral refers to the front of the , and dorsal refers to the back. These terms are also known as anterior and posterior, respectively.
However, for certain parts of the , the uses of ventral and dorsal differ from the standard definition. For instance, the dorsal part of the is the area that is closest to the abdomen when erect. Similarly, for the feet, the dorsal side is the top of the foot, or the area facing upwards when standing upright.
Join millions of students and clinicians who learn by Osmosis!
Recommended Reading: Can You Get A Kidney Infection From Alcohol
Human Body Cavities Biology Libretexts
- Highest rating: 4
- Summary: A body cavity is any space or compartment, or potential space, in an animal body. cavity, enclosed by the ribcage and pelvis and contains the kidneys,
See Details
- Highest rating: 4
- Summary: The abdominopelvic cavity is a body cavity that consists of the abdominal cavity and the gallbladder, kidneys, small intestine, and most of the large intestine.
See Details
When To See A Doctor For Kidney Pain
Kidney pain that you feel in your middle back or that radiates to your abdomen or groin is usually an indicator of a serious health condition.
According to Dr. Charles Patrick Davis, you should visit your doctor promptly if you suspect kidney pain. Some of the warning signs of kidney disease or problems are:
- Sharp flank pain that comes on suddenly
- A dull, constant one-sided pain in your back or side
- Blood in your urine
Also Check: Does Cystic Fibrosis Affect The Kidneys