I Have Heard I Might Have To Reuse My Dialyzer Each Treatment Is This Safe
Before you reuse your dialyzer, your dialysis center cleans it according to careful guidelines. If done properly, reuse is generally safe. Before each treatment, your dialyzer must be tested to make sure it is still working well. If your dialyzer no longer works well, it should be discarded and you should be given a new one. Ask your dialysis care team if they have tested your dialyzer and if it still works well.
If you do not wish to reuse your dialyzer, your center may be willing to provide you with a new dialyzer for each treatment. Ask about the center’s policy on reuse.
How Long Can You Live On Dialysis
If your kidneys have failed, you will need to have dialysis treatments for your whole life unless you are able to get a kidney transplant. Life expectancy on dialysis can vary depending on your other medical conditions and how well you follow your treatment plan. Average life expectancy on dialysis is 5-10 years, however, many patients have lived well on dialysis for 20 or even 30 years. Talk to your healthcare team about how to take care of yourself and stay healthy on dialysis.
Kidney Transplantlifesaving Yet Still Limited
Chris Freise, MD, has 25 years of experience at UCSF Medical Center as an organ transplant surgeon with a particular interest in adult and pediatric liver and kidney transplants. His research looks at drugs to suppress the immune system after transplantation and improved methods to prevent the tissue injury that commonly occurs after blood supply is restored to a transplanted organ.
At what point do you see patients with kidney disease?
Freise: Patients are referred to me by nephrologists, like Lynda Frassetto, when their level of kidney function drops to 20 percent or less. Kidney transplant is one option, and the other option is dialysis.
Keep in mind that most patients end up needing dialysis before they can receive a kidney because of the shortage of available donor kidneys. Almost 100,000 patients are on the kidney transplant wait list today in the U.S, with a wait time of 1.4 to 5.1 years. The wait time in the Bay Area is even longer, up to 10 years in some cases. The reality is that we have just as many patients dying on our wait list as we transplant there is still a marked shortage of organs.
How many kidney transplants are performed each year?
Transplant, like dialysis, is not a permanent solution is it?
Who can receive a kidney transplant, and how long is the wait for a new kidney?
Can you speak to the shortage of donor kidneys?
In your experiences as a transplant surgeon and researcher, what are the solutions, hopes for the future?
You May Like: How Do You Know If Your Kidneys Are Bad
Rates Of Decline Of Renal Function
Table shows estimates for the rates of decline of GFR derived from the best fitting models. It shows that the rate of decline attenuated to a slower rate after a few months of dialysis. Patients with an available GFR measurement at the start of dialysis were stratified on whether their GFR level was equal/above or below the median GFR level at the start of dialysis treatment. Both categories show attenuation to a slower rate of decline after a few months of dialysis.
Course of decline of glomerular filtration rate in 1143 haemodialysis and 718 peritoneal dialysis patients in the period of 1 year before until 1 year after the start of dialysis treatment
| . |
|---|
What Happens During Hemodialysis
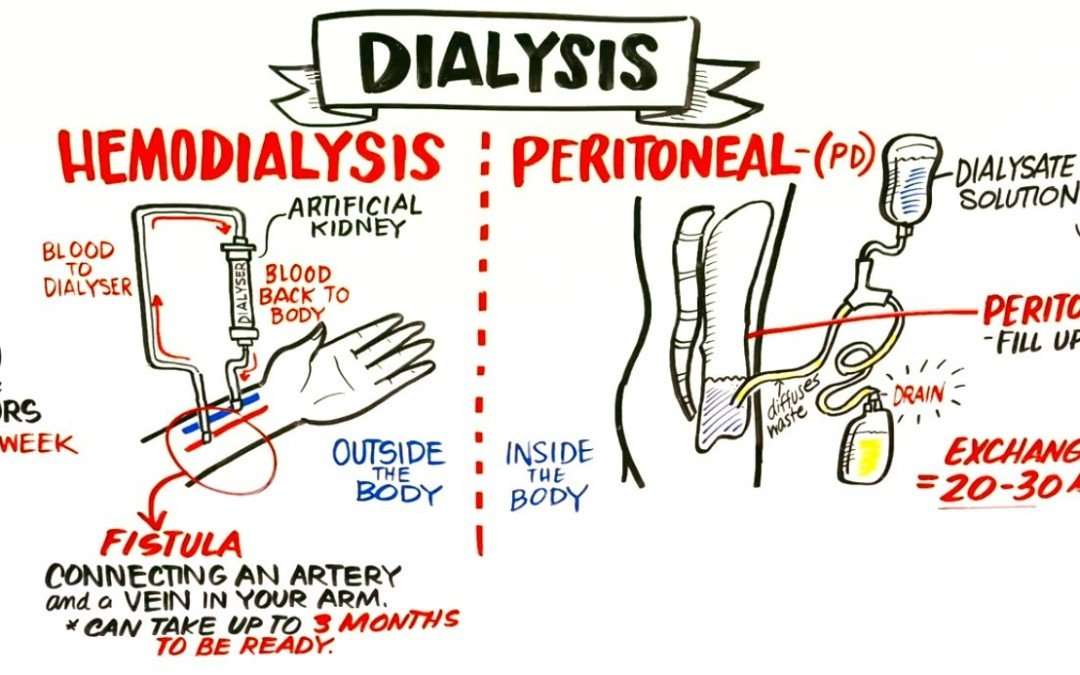
During hemodialysis, your blood goes through a filter, called a dialyzer, outside your body. A dialyzer is sometimes called an artificial kidney.
At the start of a hemodialysis treatment, a dialysis nurse or technician places two needles into your arm. You may prefer to put in your own needles after youre trained by your health care team. A numbing cream or spray can be used if placing the needles bothers you. Each needle is attached to a soft tube connected to the dialysis machine.
The dialysis machine pumps blood through the filter and returns the blood to your body. During the process, the dialysis machine checks your blood pressure and controls how quickly
- blood flows through the filter
- fluid is removed from your body
Don’t Miss: Orange Juice Renal Diet
How Does Reduction In Renal Mass Affect Renal Function In The Short And Long Term
A reduction of renal mass is followed by a decrease in renal function. Inevitably, the removal of 50% of the renal mass by a RN immediately reduces renal function to about half of its pre-nephrectomy value. However, over a very short time, the remaining contralateral kidney begins to compensate for the loss in renal function. Along with a decrease in the number of functioning nephrons, and with similar intake of food and water, these remaining nephrons increase their function to maintain fluid and electrolyte homeostasis. Over time, chronic hyperfiltration, driven partly by an increase in glomerular pressure, will lead to renal damage or an accelerated deterioration of pre-existing renal damage. These short- and long-term structural and functional adaptations of the remaining renal tissue need to be taken into consideration when predicting renal compensation and outcomes.
How To Preserve Residual Renal Function For Longer
This is an active area of research in nephrology. What we do know so far is that certain interventions can help preserve residual renal function better and longer, and therefore might translate into a longer lifespan and a better quality of life for dialysis patients. Some of these interventions are:
- Good blood pressure control
- Tight blood sugar control if you have diabetes
- Use of certain medications, called ACE inhibitors has been shown to help
- Conversely, avoiding certain medications that are known to be toxic to the kidneys makes sense like NSAIDs , aminoglycosides, Amphotericin B, etc.
- Considering starting kidney failure patients preferentially on peritoneal dialysis .
- There are suggestions from some studies that a gradual incremental increase of hemodialysis might lead to better preservation of residual renal function.
Also Check: Red Wine Kidney Stones
In The United Kingdom
The National Health Service provides dialysis in the United Kingdom. In England, the service is commissioned by NHS England. About 23,000 patients use the service each year.Patient transport services are generally provided without charge, for patients who need to travel to dialysis centres. Cornwall Clinical Commissioning Group proposed to restrict this provision to patients who did not have specific medical or financial reasons in 2018 but changed their minds after a campaign led by Kidney Care UK and decided to fund transport for patients requiring dialysis three times a week for a minimum or six times a month for a minimum of three months.
How Does Hemodialysis Work
Hemodialysis is a procedure where a dialysis machine and a special filter called an artificial kidney, or a dialyzer, are used to clean your blood. To get your blood into the dialyzer, the doctor needs to make an access, or entrance, into your blood vessels. This is done with minor surgery, usually to your arm. For more information on hemodialysis access, .
Also Check: Can Pop Cause Kidney Stones
What Happens Before Hemodialysis
Before you start hemodialysis, youll undergo a minor surgical procedure to make it easier to access the bloodstream. You may have:
- Arteriovenous fistula : A surgeon connects an artery and vein in your arm.
- Arteriovenous graft : If the artery and vein are too short to connect, your surgeon will use a graft to connect the artery and vein.
AV fistulas and grafts enlarge the connected artery and vein, which makes dialysis access easier. They also help blood flow in and out of your body faster.
If dialysis needs to happen quickly, your provider may place a catheter into a vein in your neck, chest or leg for temporary access.
Your provider will teach you how to prevent infections in your fistula or graft. This provider will also show you how to do hemodialysis at home if you choose to do so.
Assessing Kidney Function And Renal Risk Factors
The Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative is a classification system used to determine the stage of CKD, which is staged from 1 to 5 based on the estimated GFR stage 5 is end-stage requiring renal replacement therapy. Typically, consequences of CKD, such as anemia, acidosis, hyperkalemia and deranged calcium phosphorus balance, become prominent at a GFR of less than 30 mL/min/1.73m2 . At this threshold, it is typical to have a nephrologist involved in the care of the patient. Proteinuria, initially screened for using a semi-quantitative dipstick approach and refined using an albumin to creatinine ratio in spot urine, is associated with faster progression of CKD. During diagnosis and workup, the patients electrolytes should be examined for secondary consequences of renal disease, such as hyperkalemia. Urinalysis abnormalities can indicate other co-existing renal conditions. A nuclear scan can determine split renal function.
Don’t Miss: Can Wine Cause Kidney Stones
Historical Basis Of Hemodialysis
Acute and chronic kidney failure, which can lead to death if untreated for several days or weeks, is an illness that is as old as humanity itself. In early Rome and later in the Middle Ages, treatments for uremia included the use of hot baths, sweating therapies, bloodletting, and enemas. Current procedures for the treatment of kidney failure include physical processes such as osmosis and diffusion, which are widespread in nature and assist in the transport of water and dissolved substances.
The first scientific descriptions of these procedures dates back to the 19th century and came from the Scottish chemist Thomas Graham, who became known as the Father of Dialysis. At first, osmosis and dialysis became popular as methods used in chemical laboratories that allowed the separation of dissolved substances or the removal of water from solutions through semipermeable membranes.
Far ahead of his time, Graham indicated in his work the potential uses of these procedures in medicine. Today hemodialysis describes an extracorporeal procedure, or procedure outside the body, for filtering uremic substances from the blood of patients suffering from kidney disease.
How Does The Dialyzer Clean My Blood
The dialyzer, or filter, has two parts, one for your blood and one for a washing fluid called dialysate. A thin membrane separates these two parts. Blood cells, protein and other important things remain in your blood because they are too big to pass through the membrane. Smaller waste products in the blood, such as urea, creatinine, potassium and extra fluid pass through the membrane and are washed away.
Don’t Miss: Apple Cider Vinegar For Kidneys
How Long Will Each Hemodialysis Treatment Last
In a dialysis center, hemodialysis is usually done 3 times per week for about 4 hours at a time. People who choose to do hemodialysis at home may do dialysis treatment more frequently, 4-7 times per week for shorter hours each time.
Your doctor will give you a prescription that tells you how much treatment you need. Studies have shown that getting the right amount of dialysis improves your overall health, keeps you out of the hospital and enables you to live longer. Your dialysis care team will monitor your treatment with monthly lab tests to ensure you are getting the right amount of dialysis. One of the measures your dialysis care team may use is called urea reduction ratio . Another measure is called Kt/V . Ask your dialysis care team what measure they use and what your number is. To ensure that you are getting enough dialysis:
- *your Kt/V should be at least 1.2 or
- *your URR should be at least 65 percent.
Dialysis Cant Replace Hormones
Your kidneys are a part of the bodys endocrine system. The endocrine system controls certain body functions by making and releasing hormones into the bloodstream. When your kidneys are damaged, they may create very little hormones or none in any way. Sadly, dialysis cannot fabricate or replace these chemicals. These will need to be replaced in the body with medication.
Among the hormones your kidneys create is calcitriol . Calcitriol allows your body to absorb calcium from the foods you eat. Without it, your body would not be able to get enough calcium, even if youre taking calcium supplements. Calcium has many functions in the body. One of its own main functions is keeping bones strong. A deficiency of calcium can make bones weak and fragile. Calcium is also important in preserving a normal heartbeat and keeping your nerves and muscles working properly. Your doctor may elect to prescribe a vitamin D supplement such as prescribe ZEMPLAR®, in case your kidneys are not creating calcitriol.
You May Like: Does Sparkling Water Cause Kidney Stones
Will I Have Activity Restrictions While Im On Dialysis
Many people on dialysis continue to live active lives, working, raising families and traveling. When you travel, your healthcare provider can help arrange for you to get dialysis at a center at your new location. If youre doing either type of self-dialysis, you can take dialysis solution bags and the portable home dialysis machine with you.
People who use peritoneal dialysis may need to limit exercise or certain physical activities when the abdomen fills with dialysis solution. Otherwise, exercise is typically OK for people on dialysis. You should ask your provider about participating in specific activities or sports.
What Is Peritoneal Dialysis
With peritoneal dialysis, tiny blood vessels inside the abdominal lining filter blood through the aid of a dialysis solution. This solution is a type of cleansing liquid that contains water, salt and other additives.
Peritoneal dialysis takes place at home. There are two ways to do this treatment:
- Automated peritoneal dialysis uses a machine called a cycler.
- Continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis takes place manually.
Read Also: Ginger Good For Kidneys
How Do I Prepare For Dialysis
Before your first dialysis treatment, your doctor will surgically implant a tube or device to gain access to your bloodstream. This is typically a quick operation. You should be able to return home the same day.
Its best to wear comfortable clothing during your dialysis treatments. Also follow your doctors instructions. These may include fasting for a certain amount of time before the treatment.
Both hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis can be performed at home. Peritoneal dialysis can be performed alone, while hemodialysis requires a partner. The partner can be a friend or family member, or you can opt to hire a dialysis nurse.
With either type of treatment, youll receive thorough training from a medical professional beforehand.
Will I Need A Special Diet And Medications
Most people on haemodialysis need to adjust their diet. The major change in diet is usually a reduction in foods high in potassium, phosphate and sodium . But a kidney dietitian will work with you to create a plan which is tailor-made to your needs and lifestyle.
One of the major restrictions that you may find difficult is your fluid intake, but reducing your salt intake may help you feel less thirsty. In the early stages of haemodialysis you may still pass some urine but, as time progresses the volume will decrease. In between dialysis sessions fluid tends to accumulate and if severe, shortness of breath can occur.
Urine measurements will be made from time to time to assess your fluid allowance, and how much dialysis you need. When and if changes are required, your dietician or kidney nurse will discuss these with you.
Also Check: Aleve Kidney Side Effects
Experts Shine Light On Kidney Disease Share Hopes For The Future
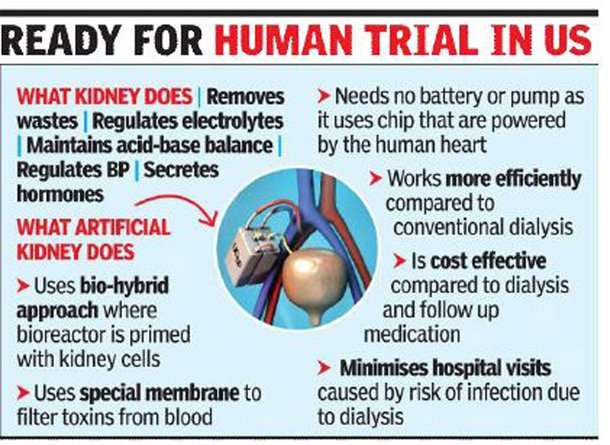
In July 2019, the Executive Order on Advancing American Kidney Health outlined national goals for improving kidney care, helping the overburdened kidney transplant system meet patient needs, and providing treatment options, including the development of a bioartificial kidney.
We asked a team of UC San Francisco kidney experts including a nephrologist, a transplant surgeon, a transplant pharmacist and a bioengineer to shine a light on the problem of kidney disease and share their hopes for the future.
The First Chronic Hemodialysis Patient
This development allowed the long-term treatment of patients with chronic kidney failure. In the spring of 1960, Scribner implanted a shunt in American Clyde Shields, in Seattle. Shields became the first chronic hemodialysis patient, and the dialysis treatments allowed him to live an additional eleven years before dying of cardiac disease. These successes provided a fertile basis for the worlds first-ever chronic hemodialysis program, which was established in Seattle in the following years.
At that time, Scribner and his team refrained from seeking patent protection for many of their inventions and innovations to ensure swift distribution of their life-saving techniques for dialysis patients. The development of improved methods for accessing blood vessels meant that patients with chronic kidney disease could be offered effective treatment for the first time.
However, in the early 1970s, a dialysis treatment lasted around twelve hours and was very expensive, due to the high outlay for materials and the treatment itself. As a result, not all kidney patients could access this life-saving therapy. In the United States, for example, committees decided on how the small number of treatment slots should be allocated a matter of life-or-death decision-making.
Don’t Miss: Does Diet Coke Cause Kidney Stones
Treatments For Kidney Failure
The two treatments for kidney failure are kidney transplantation and dialysis. Two different types of dialysis can be done – hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis.
To learn more about each type of treatment, see “Choosing a Treatment for Kidney Failure” in the A-to-Z Guide.