The Disadvantages Of Sodium Ascorbate
Sodium ascorbate is an alternate form of vitamin C, and may be used as a vitamin supplement. Sodium ascorbate is a more bioavailable form of the vitamin — your body can absorb, access and use sodium ascorbate with greater efficiency than regular vitamin C. While taking sodium ascorbate may prove beneficial for people suffering from vitamin C deficiency, there are also a number of risks associated with taking sodium ascorbate supplements.
What Are The Symptoms Of High Blood Pressure And Kidney Disease
Most people with high blood pressure do not have symptoms. In rare cases, high blood pressure can cause headaches.
Early CKD also may not have symptoms. As kidney disease gets worse, some people may have swelling, called edema. Edema happens when the kidneys cannot get rid of extra fluid and salt. Edema can occur in the legs, feet, ankles, orless oftenin the hands or face.
Symptoms of advanced kidney disease can include
- loss of appetite, nausea, or vomiting
- drowsiness, feeling tired, or sleep problems
- headaches or trouble concentrating
- chest pain or shortness of breath
Evaluation Of Kidney Function
A blood test can be done to evaluate the function of the kidneys the blood is checked for levels of blood urea nitrogen, or BUN, and creatinine. When kidney function is reduced, BUN and creatinine are increased the ratio of BUN to creatinine may also be useful in determining the cause of kidney dysfunction. The urine may also be analyzed for its composition the urine is more concentrated when kidney function is reduced. Since increased sodium excretion by the kidneys can result in low blood sodium, examination of the urine for sodium concentration may be helpful as well.
Also Check: What Is The Functional Unit Of The Kidneys
Lifestyle Changes Can Help
One of the first things your doctor will recommend is modifying your lifestyle by:
- Eating a low-sodium diet , especially if youre at risk.
- Limiting alcohol.
- Exercising regularly.
- Maintaining a healthy weight.
Even with salt restriction and lifestyle changes, blood pressure may remain elevated, Dr. Laffin notes. Medications, in addition to lifestyle changes, are oftentimes also needed to lower your blood pressure. Examples of medications include:
- Diuretics, or water pills, which increase urination to help discharge excess fluid.
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin II receptor blockers , which help to relax blood vessels.
Besides encouraging you to keep hypertension and diabetes under control, your doctor may test you annually for kidney disease.
Working with your doctor to ensure that salt intake is not raising your blood pressure and impacting your heart and kidneys can have a dramatic impact on your health and longevity.
The Question Of Salt Sensitivity
Salt affects people differently. Some people can consume sodium with no effect on their blood pressure, says Dr. Thomas. But for others who are salt sensitive, even a slight increase in sodium intake wreaks havoc on the kidneys ability to regulate fluid, and increases blood pressure.
Salt sensitivity is most prevalent among people who are middle-aged or elderly, overweight or obese, and African-American. It also tends to become more prevalent as we age.
Don’t Miss: Can You Have 4 Kidneys
Symptoms Associated With Low Sodium
If you have low sodium, you may experience a change in mental status, such as confusion, hallucination and reduced awareness. When blood sodium is very low, it may result in coma or extended unconsciousness. Other symptoms that may be associated with low blood sodium include tiredness, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, headaches, muscle weakness and cramps.
Effects Of Altered Dietary Salt Intake In Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease
AMY CRAWFORD-FAUCHER, MD, FAAFP, Forbes Family Medicine Residency Program, Allegheny Health Network, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania
R. MICHAEL HUIJON, MD, Western Psychiatric Institute and Clinic, St. Margaret Family Medicine Residency Program, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania
Am Fam Physician. 2017 Apr 1 95:423-424.
Don’t Miss: Is Honey Good For The Kidneys
Gross And Microscopic Changes
One way in which alcohol directly affects the kidneys is by altering the form and structure of this pair of organs, as demonstrated by various animal studies. For example, in an early study on dogs , investigators observed several striking alterations after chronic alcohol administration. The basement membrane of the glomerulus became abnormally thickened and was characterized by cell proliferation. Further changes included enlarged and altered cells in the kidney tubules. In another study, compared kidney structure and function in alcohol-fed and control rats. The alcohol-fed group experienced kidney swelling and significantly reduced kidney function in addition, under microscopic examination, the kidneys of alcohol-fed rats were found to have cells enlarged with increased amounts of protein, fat, and water, compared with those of the control animals.
The Adverse Events During The Study Period
Mean body weight was significantly increased after 12 months in the treatment group of stage 5 CKD. There was no significant difference in the changes of body weight during study period between the treatment group and control group . In stage 4 CKD, there was no statistically significant difference in the change of body weight during the study between the treatment group and control group. However, in stage 5 CKD, there was a significant difference in the changes of body weight during the study between the treatment group and control group .
There was no significant difference in the changes of systolic and diastolic blood pressure during the study between the treatment group and control group . There was no difference in the number and types of antihypertensive medications during the study between the two groups. All patients in stage 5 CKD was received loop diuretics at the end of the study. Loop diuretic use increased similarly by 75 and 82 % in the control and treatment group, respectively. Three patients in the treatment group and 4 patients in the control group required dialysis during the study period.
Recommended Reading: Aleve Kidney Side Effects
Effects On Fluid And Electrolyte Balance
One of the main functions of the kidneys is to regulate both the volume and the composition of body fluid, including electrically charged particles , such as sodium, potassium, and chloride ions . However, alcohols ability to increase urine volume alters the bodys fluid level and produces disturbances in electrolyte concentrations. These effects vary depending on factors such as the amount and duration of drinking, the presence of other diseases, and the drinkers nutritional status .
Spices To Use Instead Of Salt
- Chili powdertastes great in chili or taco meat flavoring. Also try it in rubs. View a recipe using this spice.
- Smoked paprikaadds a smoky flavor to marinades, gives brown color to breadcrumb casserole toppings and is great for barbecue rubs, or seasoning blends for sautéing or searing proteins. View a recipe using this spice.
- Lemon zestadds a lively taste to breadcrumbs, breaded chicken tenders, fish sticks and kidney-friendly vegetables . Lemon zest is also great in dressings, marinades and when added to dry spices for rubs. View a recipe using this spice.
- Dried oreganoenhances flavor of scampi sauces and combines well with lemon zest. Gives steamed vegetables and tossed salads a fresh, earthy taste and aroma. Add it to fajita seasonings with chili powder, cumin, cayenne and lemon zest. View a recipe using this spice.
- Italian seasoning*a blend of thyme, oregano and basil is great for finishing off sauces such as a stroganoff or gravies. Works well on baked, grilled or sautéed proteins with lemon zest and a little oil. Add it to lemon zest, lemon juice and olive oil to make delicious dressings. View a recipe using this spice. *Check to be sure you are using a salt-free product.
Recommended Reading: Is Mulberry Good For Kidneys
How Common Is Kidney Disease
A recent survey found that chronic kidney disease is more common in people who have another chronic disease, such as diabetes, high blood pressure, Parkinsons disease or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
In people with diabetes, kidney disease is very common. In fact, diabetes is the leading cause of kidney disease in Canada. It is estimated that 50% of people with diabetes will have signs of kidney damage in their lifetime.
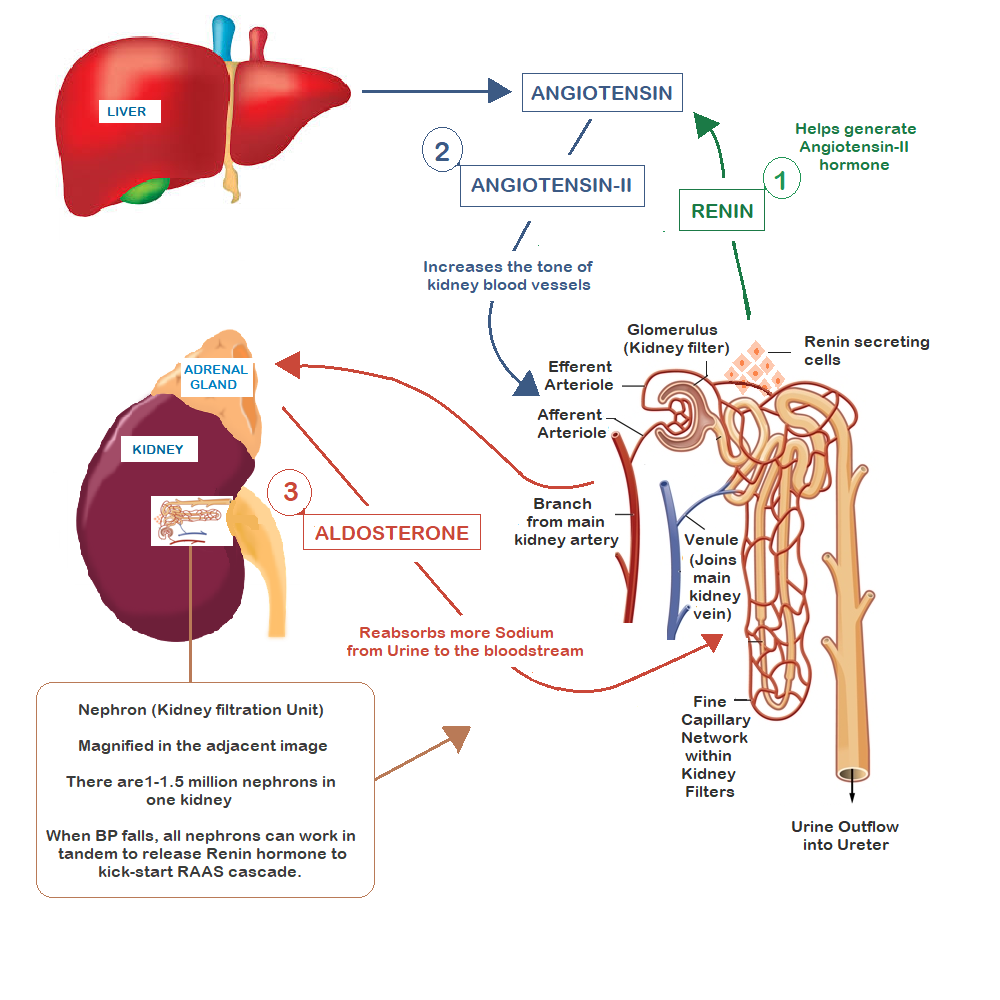
Alternative Mechanism Of Sodium Toxicity
Recent experimental findings suggest that skin could work as a reservoir of sodium, escaping from renal control . In particular, high salt intake might cause sodium accumulation in the skin, which is detected by cells of the Monocytes Phagocytes System located in the skin interstitium, which act as osmoreceptors by expression of the tonicity enhancer-binding protein . This transcription factor leads to Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor production that increases sodium clearance by the lymphatic network . Moreover, high sodium levels in the CKD condition would promote the expression of pro-inflammatory factors, such as Interleukin-6, VEGF, and Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 , via Ton-EBP pathway, leading to local inflammation and vascular proliferation in peritoneal, heart, and vascular tissue .
summarizes the potential mechanisms underlying the increase of BP levels and dependent CV risk associated with high salt intake in CKD.
Potential pathogenic mechanisms of hypertension in CKD due to high salt intake. Abbreviations: CKD: Chronic Kidney Disease AT-II: Angiotensin-II CNS Central Nervous System CV: cardiovascular.
You May Like: What Can Cause A Swollen Kidney
Altered Dietary Salt Intake For Adults With Chronic Kidney Disease
What is the issue?
People with chronic kidney disease have a reduced kidney function that persists over time. People with CKD are at increased risk of heart disease and worsening kidney function which can lead to the need for dialysis or kidney transplantation to survive. High salt intake is linked to risk factors for both heart disease and worsening kidney function, including high blood pressure, excess protein in the urine and fluid overload. Therefore reducing salt intake may help reduce risk of heart disease and preserve kidney function. We aimed to assess the benefits and harms of reducing salt intake for people with CKD.
What did we do?
We searched the evidence up to October 2020 to find randomised controlled trials comparing two or more levels of salt intake in adults with CKD, including those in the earlier stages of CKD, those treated with dialysis, and those who had received a kidney transplant.
What did we find?
We found 21 studies that included 1197 adults with CKD . Study participants included adults who were in the early stages of CKD , adults who were on dialysis , and adult kidney transplant recipients . The average study duration was seven weeks, ranging from one to 36 weeks. We did not find any studies that measured the effect on the incidence of death, heart disease, or need for dialysis or kidney transplantation. Instead, we found studies that measured risk factors for these outcomes.
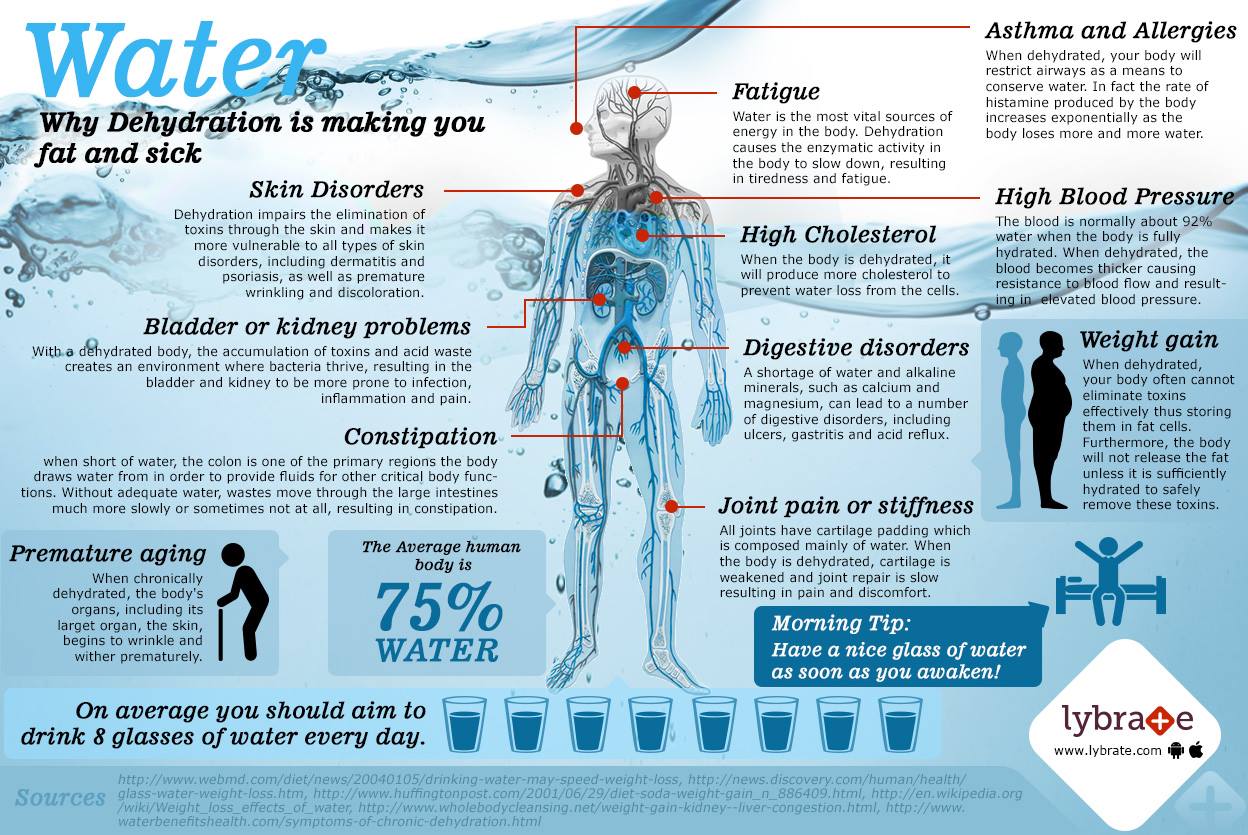
A Case Of Too High Sodium Level Or Hypernatremia
A blood level of sodium higher than 145 meq/L is referred to as “hypernatremia”. The most common cause of hypernatremia is an elevation in sodium created because of a deficit of water. Hence, disease states associated with dehydration, or increase water loss from the body can cause hypernatremia. The average person typically starts to get a strong sensation of thirst when sodium levels begin to go up in the blood. As long as they have access to water, the sodium level should come down. The problem, however, arises if people do not have access to water, or if they lose too much water from the kidneys or the gut, or if they cannot sense thirst . Since most hypernatremia states involve dehydration, treatment strategies include administration of water-rich IV fluids or oral intake of water.
Here as some of the common causes of high sodium level in the blood:
Also Check: Whats A Kidney
Current Salt Intake & Dietary Advice
Almost everyone in the UK eats too much salt. The daily recommended amount in the UK is no more than 6 grams a day the current average salt intake is around 8g salt a day although many people are eating more than this.
People with or considered at risk of kidney disease or renal failure should ensure that they keep their salt intake below the recommended maximum of 6g. This can be achieved by simple changes, such as consuming less processed foods and checking product labels before purchase.
The Cycle Of Damage: How Your Heart Is Affected
Over time, excessive salt intake can lead to high blood pressure , which stiffens and narrows the blood vessels. Blood and oxygen flow to key organs decreases. So the heart tries harder to pump blood throughout the body, which further increases blood pressure.
Elevated blood pressure, particularly over a long period of time, puts an incredible strain on the heart, says cardiologist Luke Laffin, MD. It can enlarge the hearts left pumping chamber and weaken the heart muscle .
Unchecked hypertension can also damage the artery walls, which begin to collect fat, leading to heart disease and potentially heart attack or stroke.
The best way to prevent a heart attack is to stop the arteries from becoming damaged, Dr. Laffin says.
Recommended Reading: Seltzer Water And Kidney Stones
Causes Of Low Phosphate Levels In Alcoholics
The following causes may underlie low phosphate levels in severe alcoholics:
-
Phosphorus deficiency in the diet
-
Increased blood pH due to prolonged rapid breathing
-
Insulin administration
-
Administration of nutrients beyond normal requirements
-
Excessive excretion in urine
-
Magnesium deficiency.
SOURCE: Adapted from Epstein, M. Alcohol and the kidney. In: Lieber, C.S., ed. Medical and Nutritional Complications of Alcoholism: Mechanisms and Management. New York: Plenum Medical Book Company, 1992. p. 498.
Another potential cause of hypophosphatemia in alcoholic patients is hyperventilation, which can occur during alcohol withdrawal. Prolonged rapid, shallow breathing results in excessive loss of carbon dioxide and decreased blood acidity , which in turn activates an enzyme that enhances glucose breakdown. In glucose breakdown, phosphate becomes incorporated into various metabolic compounds, ultimately lowering blood levels of phosphate. As the rate of glucose breakdown increases, profound hypophosphatemia potentially can result.
What Causes Hyponatremia
A low sodium level in your blood may be caused by too much water or fluid in the body. This “watering down” effect makes the amount of sodium seem low. Low blood sodium can also be due to losing sodium from the body or losing both sodium and fluid from the body.
Hyponatremia can be the result of illnesses and medications. Some causes that may be related to kidney disease include:
- Kidney failure – the kidneys cannot get rid of extra fluid from the body
- Congestive heart failure – excess fluid builds up in the body
- Diuretics – makes the body get rid of more sodium in the urine
- Antidepressants and pain medication – may cause more sweating or urinating than normal
- Severe vomiting or diarrhea – the body loses a lot of fluid and sodium
- Excessive thirst – causes too much fluid intake
Read Also: Std That Affects Kidneys
Uses Of Docusate Sodium
Docusate is an electrolyte produced by the human body. It is found in small amounts in all foods. When the bodys ability to make the correct amount of Docusate is lowered, it results in electrolyte imbalances which result in a variety of illnesses. The major medical use of docusate is as an anticoagulant.
Sodium Docosaate is one of its chemical names. It is a salt produced by the kidneys. The kidney produces it for the same reason that the liver makes bicarbonate. It also plays a role in regulating blood pH. Docusate is part of the nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs family:
NSAIDs are used to treat the symptoms of arthritis, chronic inflammation of the joints and in some patients to decrease the effects of rheumatoid arthritis and psoriasis. There is also a risk of side effects with NSAIDs, so doctors typically use other medicines such as aspirin or ibuprofen to treat these issues. The biggest concern is the increased risk of stomach ulcers when using NSAIDs.
The FDA does not regulate the amount of docusate that is added to the diet, but studies have shown that low doses to help reduce symptoms of some conditions, especially arthritis and psoriasis. However, doctors have long suspected that docusate can cause some serious side effects, including an increased risk of heart attacks. In some people, it has also been shown to interfere with the absorption of calcium in the intestines and even increase the risk of ulcer formation.
Signs Of Deficiency And Toxicity
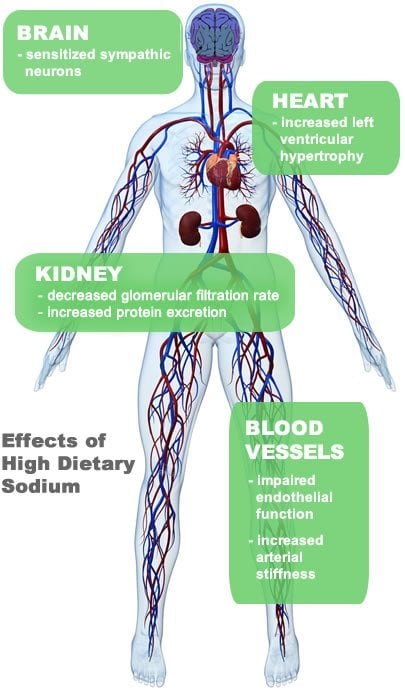
Deficiency
A deficiency of sodium in the U.S. is rare because it is so commonly added to a wide variety of foods and occurs naturally in some foods. Hyponatremia is the term used to describe abnormally low amounts of sodium in the blood. This occurs mainly in older adults, particularly those living in long-term care facilities or hospitals who take medications or have health conditions that deplete the body of sodium, leading to hyponatremia. Excess vomiting, diarrhea, and sweating can also cause hyponatremia if salt is lost in these fluids that are expelled from the body. Sometimes too much fluid abnormally collecting in the body can lead to hyponatremia, which might stem from diseases such as heart failure or liver cirrhosis. In rare cases, simply drinking too much fluid can lead to hyponatremia if the kidneys cant excrete the excess water. Symptoms of hyponatremia can include: nausea, vomiting, headaches, altered mental state/confusion, lethargy, seizures, coma.
Toxicity
The interplay of sodium and potassium
A study in the Archives of Internal Medicine found that:
Also Check: What Artery Delivers Blood To The Kidney
Effect Of Oral Bicarbonate Supplementation On Nutritional Indices
There were no significant differences in albumin, preablumin, transferrin, BMI, and MAMC between baseline and 12 months in both treatment and control groups . However, there was a significant decrease in TLC and OPNI between baseline and 12 months in the control group of stage 5 CKD.
There was no significant difference in the changes of albumin, prealbumin, transferrin, TLC, OPNI during the study period between the treatment group and control group. The decline of TLC in the treatment group was lower than in the control group during the study period, which was not statistically significant . In stage 5 CKD, there was a significant difference in the changes of TLC and OPNI during the study between the treatment group and control group . However, in stage 4 CKD, there was no statistically significant difference in the change of TLC and OPNI during the study between the treatment group and control group .