Timing Of The Complications
The time to clinical manifestation or imaging-based diagnosis of major bleeding was assessed from clinical chart review for every case and ranged from immediately after the procedure to 14 days thereafter . Of note, bleeding complications tended to manifest later in inpatients compared to planned outpatients .
Fig. 3.
Manifestation of major bleeding by time after the procedure. Shown is the number or the percentage of major bleeding episodes in specified time intervals after the procedure, separated by planned outpatient versus inpatient procedures. h, hours w, weeks.
Biomarkers Of Kidney Pathology
LN is so intrinsically heterogeneous it is difficult to adequately convey what is seen on kidney biopsy using only standard classification terminology. LN classes are divided into active, active plus chronic, and chronic, and lesions into global and segmental. Active raises a spectrum of lesions including endocapillary hypercellularity, subendothelial immune complexes, crescents and/or glomerular capillary necrosis. Likewise, chronic connotes glomerulosclerosis, fibrous crescents, interstitial fibrosis, and/or tubular atrophy. Thus a pathologic diagnosis of Class IV-G must be accompanied by a description of what was seen under the microscope. Complicating the heterogeneity of LN is that the lesions evolve over time, classes change, and patients are not uniformly identified at a specific stage. Therefore, biomarkers that non-invasively identify the presence and severity of specific pathologic lesions are likely to be more useful for prognostic and treatment decisions than biomarkers that identify a specific LN class. Such biomarkers would be applicable across LN classes and individual patients. Nonetheless, many investigators have focused on identifying biomarkers to non-invasively diagnose LN class .
How Is A Kidney Biopsy Done
- The procedure of biopsy is started by laying the patient on the bed in a position that is comfortable and suitable for the biopsy
- Then the patient will get an intravenous placed via which the sedative will be given during the procedure if needed
- Identification of the spot from where the needle is to be inserted in the next step. To execute this, certain procedures such as ultrasound is used.
- After identification, that spot is marked and given local anesthesia.
- Once the needle is inserted through that spot, the movement of the needle to go further at the kidney is again assisted by the ultrasound
- A specialized tool at the front of the needle will collect the sample from the kidneys. Meanwhile, the patient will be asked to stay still and not get overwhelmed by the sound of removal of tissue
- As to avoid the pain of the patient, the doctors will only take a tiny portion of kidney tissue at a time. Therefore, a needle might be inserted more than once to gather enough tissue to be studied under a microscope
As the patients who are required to get a kidney biopsy done do not suffer from the same condition, hence the above procedure is not the only method of performing a kidney biopsy.
For some patients, the method of laparoscopy is used and for some, open kidney biopsy is done.
Read Also: Watermelon Renal Diet
Talking With A Health Care Provider
People should talk with their health care provider about medical conditions they have and all prescribed and over-the-counter medications, vitamins, and supplements they take, including
- aspirin or medications that contain aspirin
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications such as ibuprofen and naproxen
- blood thinners
- arthritis medications
People should also tell their health care provider about any allergies they have to medications or foods.
The health care provider should discuss the risks of the procedure, and the person should ask questions or bring up concerns. Two weeks before the biopsy, the health care provider may instruct a person to stop taking certain medications that cause thinning of the blood because this may increase the risk of bleeding after the kidney biopsy. The health care provider may also tell the person not to eat or drink anything for 8 hours before the biopsy.
How You Have It
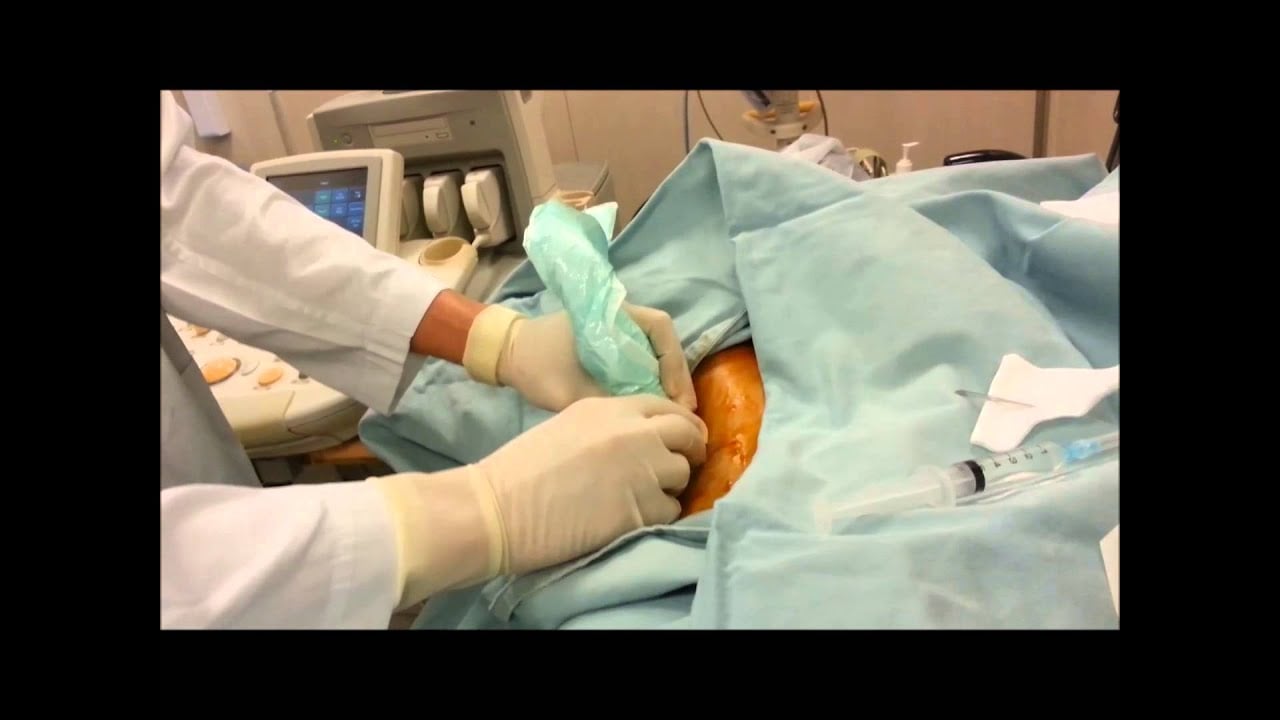
Your doctor uses an ultrasound or CT scanner to help them see exactly where the tumour is.
You lie on your front on a couch or bed to have the biopsy. The doctor cleans the skin over the kidney with antiseptic. They inject local anaesthetic into the area to make it numb. This may sting a little at first.
A hollow needle goes through the skin and muscle into the kidney tissue. They take a small sample. You might feel some pressure at this time.
You need to hold your breath for 5 to 10 seconds while the needle is pushed in and out. This is because the kidneys move slightly when you breathe in and out. Your doctor tells you exactly when to hold your breath.
Recommended Reading: Is Aleve Hard On Your Kidneys
Monoclonal Gammopathies And Paraprotein Diseases
Patients with monoclonal gammopathies may require a kidney biopsy to document end organ damage from the offending paraprotein. Although it has been suggested that patients with monoclonal gammopathies and amyloidosis have a higher risk of complications from bleeding diathesis , there is no evidence that this translates to a higher clinical risk with PRBs. One series found a statistically increased risk of bleeding in patients who had renal amyloidosis , but the definition of bleeding was a hemoglobin decrease > 1 g/dl and did not include need for transfusion or intervention. A second series found no difference in overall or major bleeding complications after PRB in patients with systemic amyloidosis versus controls . Another series found no increased risk of PRB complications for patients with monoclonal gammopathies versus controls .
What Is A Renal Biopsy
A biopsy is the removal of very small pieces of tissue from a body organ, that a pathologist doctor may examine under the microscope to identify various types of disease.
In the case of kidney diseases, there are two general reasons for doing a kidney biopsy. When blood or urine tests indicate that the kidneys are not functioning properly, a biopsy is done of a randomly chosen part of one kidney, assuming that all parts of both kidneys are equally affected. On the other hand, there may be a lump or mass in one kidney which may require a biopsy. The information gained by having a pathologist examine renal tissue is used to name the disease and determine appropriate treatment.
You May Like: Can Apple Cider Vinegar Affect Your Kidneys
Considerations For A Renal Biopsy
Although renal biopsies are effective tools for diagnosing the presence or extent of kidney disease, there are problems associated with their use. One problem is that they produce false-negative results. Another is that they cannot be performed if kidney cancer is suspected, because the biopsies themselves can cause the spread of malignant cells. In the case of a known malignancy, removal of the tumor, or removal of the kidney , is recommended.
The Role Of Nephrologists In Kidney Biopsies
The Accreditation Council on Graduate Medical Education requires that nephrology fellows must be able to competently perform PRBs of both native and transplanted kidneys , and the American Board of Internal Medicine requires that competence in the performance of native and allograft PRBs be verified by the fellowship program director for initial certification in nephrology . Requirements for training and determination of competence are at the discretion of the individual training program and vary widely . In one survey of nephrologists who completed their fellowship training from 2004 to 2008, 15%20% indicated that they did not feel competent performing native and transplant PRBs . Evidence-based standards for assessment and documentation of proficiency among nephrology fellows are needed , and use of simulation training may enhance competency .
Given how integral it is in the diagnosis and treatment of patients with kidney disease, we believe that the PRB should remain an essential component of nephrology training and practice. Rather than giving up performance of a procedure long considered to be a critically important component of the scope of practice of nephrologists, we believe that standards for establishing and documenting that all fellows are competent to perform kidney biopsies independently and without direct supervision at the completion of fellowship are essential and urgently needed.
Also Check: Is Apple Cider Vinegar Good For The Kidneys
Complication Rate In Kidney Biopsies Planned As Outpatient Procedures
One thousand five hundred seven kidney biopsies were scheduled as outpatient procedures. Characteristics of these patients compared to inpatients are shown in Table 5, and complication rates for inpatients versus outpatients and transplant versus native kidney biopsies are listed in Table 6. Major bleeding occurred significantly more often after inpatient versus planned outpatient procedures . Of note, 8 of the 15 major bleeding episodes occurring after planned outpatient biopsies did not require intervention and qualified as major bleeding only due to hospital admission for overnight surveillance. Of the remaining 7 major bleeding events, 3 required catheter placement for gross hematuria, 3 a transfusion, and 1 operative revision of a transplant kidney. Most major bleeding episodes in planned outpatients were detected during the 4-h postbiopsy surveillance period with only 3 manifesting after outpatients had left the hospital . One patient experienced gross hematuria with consecutive tamponade and readmission for urinary retention after 24 h. Another patient developed flank pain 6 days after the procedure due to retroperitoneal hematoma and required a blood transfusion but no other intervention. The third patient felt pain in the iliac fossa shortly after leaving the hospital and was readmitted for operative revision of the transplant kidney.
Table 5.
All complications by inpatient versus outpatient and native versus transplant biopsies
Why Is A Kidney Biopsy Done
A kidney biopsy helps doctors identify the cause of kidney problems so they can treat the condition effectively. It can reveal scarring, inflammation , and protein deposits that cannot be identified with other tests, such as ultrasounds or blood and urine tests.
The test can also enable a doctor to see how well a transplanted kidney is working and monitor the progression of kidney disease.
Your doctor may recommend a kidney biopsy if you have:
- A transplanted kidney.
- Abnormal results from a blood test.
- Glomerular disease or glomerulonephritis.
- Hematuria .
- Kidney disease with no known cause.
- Proteinuria .
Read Also: Is Ibuprofen Metabolized In The Kidneys Or Liver
Preparation For A Renal Biopsy
Typically, you dont need to do much to prepare for a renal biopsy.
Be sure to tell your doctor about any prescription drugs, over-the-counter medications, and herbal supplements youre taking. You should discuss with them whether you should stop taking them before and during the test, or if you should change the dosage.
Your doctor may provide special instructions if youre taking medications that could affect the results of the renal biopsy. These medications include:
- anticoagulants
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, including aspirin or ibuprofen
- any medications that affect blood clotting
- herbal or dietary supplements
Tell your doctor if youre pregnant or think you might be pregnant. Also, before your renal biopsy, youll have a blood test and provide a urine sample. This ensures that you dont have any preexisting infections.
You need to fast from food and drink for at least eight hours prior to your kidney biopsy.
If youre given a sedative to take at home before the biopsy, you wont be able to drive yourself to the procedure and need to arrange for transportation.
Operator Experience And Complication Rate
Most kidney biopsies were performed by nephrology fellows as operators under supervision of an experienced staff physician who held the ultrasound probe . During the observation period, 57 physicians performed kidney biopsies as operators. The average number of biopsies performed per operator was 39 , and the operators had a median experience of 23 prior biopsies. Operator experience did not differ significantly between procedures with major bleeding versus without complication, and the rate of major bleeding events was not different between biopsies performed by operators who had performed < 5 prior procedures versus more experienced operators . Operator experience was also not significantly associated with the complication rate in the multifactorial analysis .
You May Like: Does Wine Cause Kidney Stones
A Kidney Biopsy Should Routinely Be Obtained To Confirm The Diagnosis Of Ln Before Treatment Is Started
This traditional approach is used when SLE patients develop clinical evidence that is consistent with renal involvement by lupus and that cannot be explained by other conditions. These clinical findings include hematuria, pyuria, red and white blood cell casts, declining kidney function, and/or proteinuria 6. Dysmorphic red blood cells, specifically acanthocytes , indicate glomerular hematuria and are often seen in the urine sediment of LN patients with active nephritis. Red blood cell casts also indicate glomerular hematuria, but are found less commonly. Urine white blood cells and white blood cell casts, in the absence of kidney or urinary tract infection, are consistent with kidney inflammation due to LN. A kidney biopsy is generally not indicated for hematuria or pyuria alone, however patients who develop active urine sediment do require close follow-up for signs of worsening kidney injury such as proteinuria and an increase in serum creatinine.
Urine findings of glomerular hematuria in lupus nephritis. A. Acanthocytes are a type of dysmorphic red blood cell that is specific for glomerular hematuria. The arrow indicates a bleb that distorts the normal biconcave disc appearance of the red blood cell. B. Red blood cell casts also indicate glomerular bleeding.
How The Test Will Feel
Numbing medicine is used, so the pain during the procedure is often slight. The numbing medicine may burn or sting when first injected.
After the procedure, the area may feel tender or sore for a few days.
You may see bright, red blood in the urine during the first 24 hours after the test. If the bleeding lasts longer, tell your provider.
Also Check: Functional Unit Of The Kidney
Safety Of The Procedure
Kidney biopsies are invasive procedures and not without risk. The decision to proceed requires oversight from the nephrology team and a shared decision with the patient. Biopsies should only be performed when the results will guide treatment, assist with diagnosis that will alter treatment or inform prognosis. Meticulous preparation of the patient is key and important contraindications to biopsy are outlined in Table . Ultrasound is important prior to biopsy to ensure that the kidneys can be visualised, to rule out anatomical abnormalities and to provide further information to determine the riskbenefit balance of the procedure. For instance, small kidneys and poor corticomedullary differentiation indicate chronicity of the renal disease and potential for limited reversibility, and there may be challenges in differentiating the kidneys from surrounding retroperitoneal structures. Patients may be concerned about the effect of removing kidney tissue on kidney function. Reassuringly, one study estimated that, in stable transplant patients, the GFR loss due to biopsy is 0.77 mL/min.
Relative and absolute contraindications for kidney biopsy
A Kidney Biopsy Is Not Routinely Needed Before Starting Therapy For Ln
This non-traditional approach is mainly a response to the overwhelming acceptance of mycophenolate mofetil as first line therapy for all of the serious forms of LN 9, theoretically eliminating the need to differentiate between classes before starting therapy. Furthermore, it has been difficult to demonstrate that the pathologic findings at diagnostic kidney biopsy prognosticate how the kidney will do in the long-term or how it will respond to therapy in the short-term 10, 11. It has been shown however that a kidney biopsy done after completion of induction therapy does provide prognostic information on renal outcomes 10, 11. It may therefore be advantageous to hold off biopsy until induction treatment is finished.
Also Check: Flomax Dosage For Kidney Stones
What Do The Results Of A Kidney Biopsy Mean
A kidney biopsy can reveal medical conditions that may impair kidney function, such as an immunologic disease . It can also help a doctor evaluate how well a donated kidney is working after a transplant.
The test results can help your doctor determine the most effective treatment for the kidney disease. People usually receive the results of a kidney biopsy within three to five days.
What Happens During The Biopsy
Your biopsy will be performed by a specialist. It may take place at your bedside, or you may to to a different part of the hospital for it.
During a biopsy on your own kidneys you will usually lie on your front as your kidneys are easiest to get to via
the back. The doctor will clean the area with antiseptic then use an ultrasound machine to help insert the needle in the right place. They will inject local anaesthetic – this may sting for a second or two before going numb. They will then make a small cut in your lower back and insert the special needle to take the sample. The kidneys move as you breathe so the doctor will ask you to hold your breath for a few seconds whilst the sample is taken. You may hear a clicking sound as the sample is taken
A biopsy of a kidney transplant is done the same way, but you will generally lie on your back and the doctor will do the biopsy close to the scar from your transplant operation.
The doctor may need to take two or three samples of kidney in order to ensure that there is enough for analysis. Once they are finished they will put a watertight dressing over the cut to keep it clean whilst it heals.
A biopsy usually take around half an hour in total.
Don’t Miss: Watermelon Is Good For Kidney
Is There A Reason Why A Transplant Kidney Biopsy Might Be Delayed
If it is suspected that a person has an infection prior to the procedure, the transplant renal biopsy may be delayed until the infection is treated. If the patient is taking strong anti-coagulation drugs for other reasons, , they would need to be stopped for several days prior to and immediately after the biopsy. The risk vs. the benefits of stopping anti-coagulation will have to be weighed by your transplant doctor.
Biopsy For Kidney Cancer Communicating Changes In Practice
One question that is routinely posted in our kidney cancer patient communities is: should I have a biopsy of my kidney tumor? The resounding chorus from others is almost always an emphatic: NO! its too dangerous youll spread the cancer.
For more than two decades, the use of biopsy in managing renal cell carcinoma has been shifting dramatically. Advances in cytological techniques as well as increases in the number of unnecessary surgeries have expanded the role of renal mass biopsy. The myth that renal mass biopsy is dangerous has also largely been dispelled by multiple studies.
Despite the fact that biopsy rates are increasing, that the procedure is known to be safe, and that it can result in a reduction in unnecessary surgeries, the shared view in patient communities remains resoundingly negative.
Why do we think that biopsy is so dangerous?
In short? Because we were told that by doctors. If you or a loved one was diagnosed with kidney cancer in the last few decades, you might have been told that renal biopsies are never done and/or are not safe.
The reality is that biopsy is done in kidney cancer its just not always done. If a patient has a large tumor, imaging is generally sufficient to make a recommendation for surgery. It is not that it is dangerous to do a biopsy of the kidney, rather, it is just not necessary and there is no reason to put a patient through an additional invasive procedure.
What is tumor seeding?
Bottom line:
Also Check: Can Kidney Transplant Patients Eat Ginger