Early History: Graham And Abel
The principle behind the process was discovered by Scottish chemist Thomas Graham in about 1861. Graham found that the rate at which some substances, such as inorganic salts, pass through a semipermeable membrane is up to 50 times as great as the rate at which other substances, such as proteins, do so. Scientists now know that such rate differences depend on the fact that the openings in semipermeable membranes are very nearly the size of atoms, ions, and small molecules. That makes possible the passage of such small particles while greatly restricting the passage of large particles.
In a typical dialysis experiment, a bag made of a semipermeable membrane is filled with a solution to be dialyzed. The bag is then suspended in a stream of running water. Small particles in solution within the bag gradually diffuse across the semipermeable membrane and are carried away by the running water. Larger molecules are essentially retained within the bag. By this process, a highly efficient separation of substances can be achieved.
The kidney is a dialyzing organ. By the process described above, it filters waste products such as urea out of the blood and forces them into the urine,
through which they are excreted from the body. Proteins and other important large molecules are retained in the blood.
Questions On Artificial Kidney Dialysis
- Why is a salt solution, rather than pure water, used as the external solution for artificial kidney dialysis?
- Are the pores formed by the cellulose fibers best suited for allowing the passage of polar or nonpolar molecules? Briefly, explain your answer in terms of the functional groups of the cellulose polymer.
Questions On Diffusion And Concentration Gradients
- Look at Figure 6, and the movie showing the diffusion of particles between two solutions, separated by a membrane.
At what point is the rate of change in the concentrations of the two solutions greatest? Briefly, explain why the rate of concentration change is greatest at this point.
- A solution of 0.10 M NaCl is separated from another solution of 0.10 M NaCl by a membrane that is permeable to Na+ and Cl- ions.
Does diffusion occur across the membrane? Briefly, explain your answer. Does the concentration of Na+ or Cl- change in neither, either, or both of the two solutions? Briefly, explain your answer.
Also Check: Ginger Tea Dissolves Kidney Stones
Hemofiltration And Hemoperfusion: Other Ways Of Filtering The Blood
|
Occasionally, techniques other than dialysis are used to filter the blood. Hemofiltration is often done as a continuous procedure in people who are seriously ill and in an intensive care unit. This procedure allows doctors to filter large amounts of blood. Hemoperfusion is most often used in treating poisoning. The person’s blood flows over a filter that contains charcoal or some other material that absorbs the poison. |
Will I Be Uncomfortable On Hemodialysis
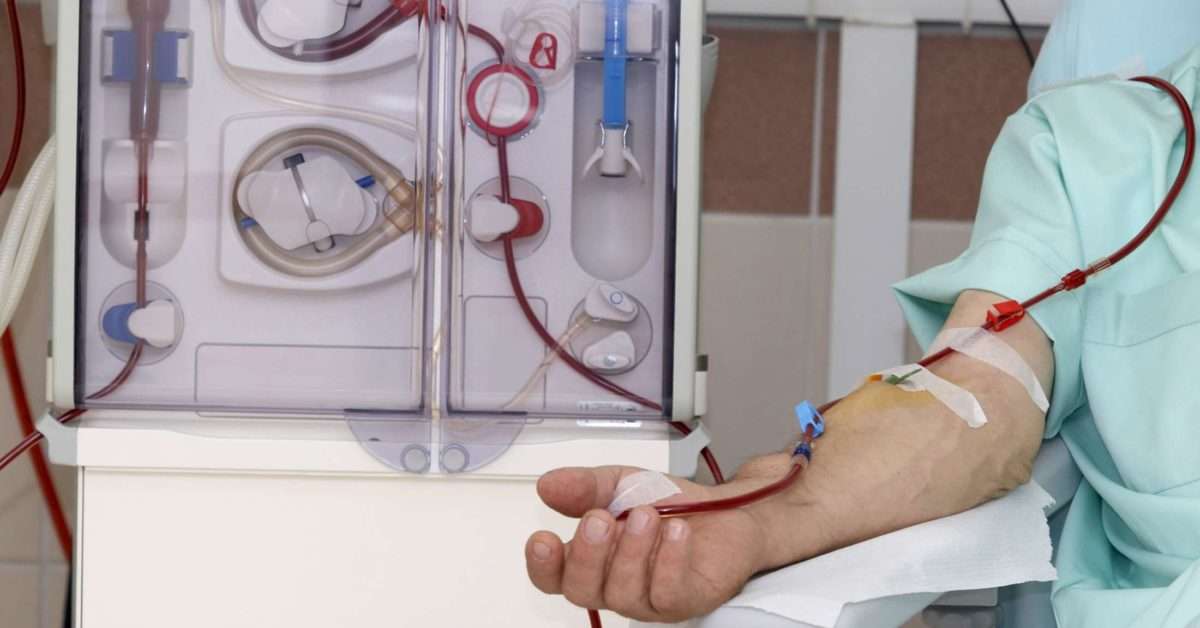
When you begin hemodialysis, the needles put in your fistula or graft may be uncomfortable. Most patients get used to this in time. Your dialysis care team will make sure you are as comfortable as possible during your treatment. Symptoms like cramps, headaches, nausea or dizziness are not common, but if you do have any of them, ask your dialysis care team if any of the following steps could help you:
- *Slow down your fluid removal, which could increase your dialysis time.
- *Increase the amount of sodium in your dialysate.
- *Check your high blood pressure medications.
- *Adjust your dry weight, or target weight.
- *Cool the dialysate a little.
- *Use a special medication to help prevent low blood pressure during dialysis.
You can help yourself by following your diet and fluid allowances. The need to remove too much fluid during dialysis is one of the things that may make you feel uncomfortable during your treatment.
Don’t Miss: Is Aleve Bad For Your Kidneys
Students Who Viewed This Also Studied
Brookdale Community College CHEM 136
Solutions, colloids, and suspensions
Brookdale Community College CHEM 136
Lab G-1.rtf
University of California, Berkeley CHEM 11190
148550979-Chem-136-Lab-G-1.pdf
Brookdale Community College CHEM 136
D. Gianvecchio Lab G-1
Stony Brook University CHE 477
lec18 .pdf
In The United Kingdom
The National Health Service provides dialysis in the United Kingdom. In England, the service is commissioned by NHS England. About 23,000 patients use the service each year.Patient transport services are generally provided without charge, for patients who need to travel to dialysis centres. Cornwall Clinical Commissioning Group proposed to restrict this provision to patients who did not have specific medical or financial reasons in 2018 but changed their minds after a campaign led by Kidney Care UK and decided to fund transport for patients requiring dialysis three times a week for a minimum or six times a month for a minimum of three months.
Read Also: Constipation And Kidney Stones
How Does Hemodialysis Work
Hemodialysis is a procedure where a dialysis machine and a special filter called an artificial kidney, or a dialyzer, are used to clean your blood. To get your blood into the dialyzer, the doctor needs to make an access, or entrance, into your blood vessels. This is done with minor surgery, usually to your arm. For more information on hemodialysis access, .
Can Dialysis Cure My Kidney Disease
In some cases of sudden or acute kidney failure, dialysis may only be needed for a short time until the kidneys get better. However, when chronic kidney disease progresses to kidney failure over time, your kidneys do not get better and you will need dialysis for the rest of your life unless you are able to receive a kidney transplant.
Read Also: Grapes Kidney Stones
Membranes And Concentration Gradients In Thekidneys
How do the kidneys actually filter the blood to remove the necessary particles in the proper amounts? The specialized semi-permeable membranes of the nephron, protein channels, and protein pumps act in conjunction with concentration gradients to perform the dialysis functions of the kidney.
Lipid-soluble substances can easily pass through the phospholipid membrane, and so these substances tend to be readily reabsorbed into the blood. This can be a problem because many drugs and toxins, such as the pesticide DDT, are lipid-soluble. Hence, removal of these toxins is very difficult.
Most of the components of the blood, however, are polar or charged and require protein channels to cross the membrane. The channels in the nephrons are specialized to allow only the passage of particular types of particles, based on size, shape, and charge interactions with the amino acids lining the channel interior. The kidneys control the concentration of different species in two ways: by regulating the number of channels in the membrane and the number of channels that are open. In the end, most waste products undergo only partial reabsorption, so large amounts of the substance remain in the tubule and are thus removed from the body in the urine. In contrast, useful plasma components, such as water, nutrients, and inorganic ions, are completely reabsorbed.
Urea Reabsorption a Concentration Gradient)
Sodium Reabsorption
Water Reabsorption
Membranes And Concentration Gradients In The Kidneys
How do the kidneys actually filter the blood to remove the necessary particles in the proper amounts? The specialized semi-permeable membranes of the nephron, protein channels, and protein pumps act in conjunction with concentration gradients to perform the dialysis functions of the kidney.
Lipid-soluble substances can easily pass through the phospholipid membrane, and so these substances tend to be readily reabsorbed into the blood. This can be a problem because many drugs and toxins, such as the pesticide DDT, are lipid-soluble. Hence, removal of these toxins is very difficult.
Most of the components of the blood, however, are polar or charged and require protein channels to cross the membrane. The channels in the nephrons are specialized to allow only the passage of particular types of particles, based on size, shape, and charge interactions with the amino acids lining the channel interior. The kidneys control the concentration of different species in two ways: by regulating the number of channels in the membrane and the number of channels that are open. In the end, most waste products undergo only partial reabsorption, so large amounts of the substance remain in the tubule and are thus removed from the body in the urine. In contrast, useful plasma components, such as water, nutrients, and inorganic ions, are completely reabsorbed.
Urea Reabsorption a Concentration Gradient)
Sodium Reabsorption
Water Reabsorption
Don’t Miss: Watermelon For Kidneys
The Consequences Of Kidney Damage Or Disease
The kidney is responsible for the removal of waste products from the blood. Damage from accidents or disease can lead to a build-up of poisonous wastes in the body. Humans can survive with one kidney, but for people who suffer from total kidney failure this would be fatal if not treated. Treatment is available for kidney failure and can be by organ transplant or by using kidney dialysis.
In this procedure, patients are connected to a dialysis machine which acts as an artificial kidney to remove most of the urea and restore/maintain the water and ion balance of the blood.
Patients with kidney failure can be kept alive by using kidney dialysis until a transplant becomes available, but they have several disadvantages:
- they are expensive
- the patient must have his or her blood connected to the machine for several hours every week
- patients must follow a very rigid diet to avoid complications
- they only work for a limited time for a patient
Questions On Membrane Channels

- A certain channel has been isolated from a cell membrane, that allows cyanide ions, but not nitrate ions, to cross a phospholipid-bilayer membrane.
Briefly, explain how the structure of the channel might allow the channel to discriminate between these two anions. HINT: You may find it helpful to consult the three-dimensional CPK representations in the on-line table of polyatomic ions. Which, if any, of the following ions would you expect to be able to pass through this channel: bicarbonate , hydroxide , or permanganate ? Briefly, explain your reasoning. HINT: You may find it helpful to consult the three-dimensional CPK representations in the on-line table of polyatomic ions.
- Neglecting size considerations, tell whether you expect methane to pass through the K+ channel depicted in Figure 4. Briefly, explain your reasoning.
Don’t Miss: Orange Juice Renal Diet
When To Start Dialysis
Kidney failure is the last stage of long-term kidney disease. This is when your kidneys can no longer support your body’s needs. Your doctor will discuss dialysis with you before you need it. Usually, you will go on dialysis when you have only 10% to 15% of your kidney function left.
You also may need dialysis if your kidneys suddenly stop working due to acute renal failure.
More Information About Dialysis
The following is an English-language resource that may be useful. Please note that THE MANUAL is not responsible for the content of this resource.
-
Suggested Foods for Dialysis Patients: The American Association of Kidney Patients provides this comprehensive list of acceptable foods, grouped by category, for patients on dialysis.
You May Like: Can Diet Soda Cause Kidney Stones
Can Dialysis Patients Travel
Yes. Dialysis centers are located in every part of the United States and in many foreign countries.
Before you travel, you must make an appointment for dialysis treatments at another center. The staff at your center may be able to help you arrange this appointment. For more information on traveling on dialysis .
Johns Hopkins Team Develops Method To Make Dialysis Fluid For Patients With Covid
Posted May 14, 2020 |
On April 9, clinicians from two New York-based hospitals contacted Derek Fine, clinical director of nephrology at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine. They said they were running out of dialysis fluid and asked if we could spare some from our supply, says Chirag Parikh, director of the Division of Nephrology at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine. As the severity of COVID-19 increases and patients are on ventilators for a long time, their needs for dialysis treatment to preserve the function of their kidneys also increases.
In less than two weeks, Fine and Parikh assembled a team of nephrologists, nurses and technicians from the Division of Nephrology and students from the Johns Hopkins Department of Biomedical Engineering to develop a method to make dialysis fluid for the type of dialysis used in intensive care: continuous veno-venous hemodialysis .
Don’t Miss: Teas Good For Kidneys
When Is It Done
Hemodialysis usually takes about 4 hours and has to be done three times a week. Most people go to a special clinic called a dialysis center to get their treatments. Some people get treatments at a hospital. Occasionally, dialysis centers train families to do the treatments at home, but this isn’t common.
After being hooked up to dialysis machines, patients lie down or sit in a chair. While the treatment is going on, they might use the time to read, watch TV, play videogames, or nap.
Page 2
When To Call Your Doctor
- Bleeding from your vascular access site
- Signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, soreness, pain, warmth, or pus around the site
- A fever over 100.5°F
- The arm where your catheter is placed swells and the hand on that side feels cold
- Your hand gets cold, numb, or weak
Also, call your doctor if any of the following symptoms are severe or last more than 2 days:
- Itching
- Drowsiness, confusion, or problems concentrating
Also Check: Does Pellegrino Cause Kidney Stones
Instructions And Guidelines For Making Dialysis Fluid
On April 20, the team shared its method with experts at the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, which provided guidelines for using the method. These guidelines recommend using the dialysate within 12 hours of making it, and testing the dialysate intermittently to ensure it remains bacteria free.
Parikh shared the method with the clinicians in New York, who reported they were able to produce and collect dialysate for CVVHD using the technique. For other hospitals with a shortage of dialysate, instructions to convert a conventional dialysis machine and the files for printing the connector are available in a or on Twitter from @KidneydrChirag.
Alone, none of us could have done this so quickly, says Fine. Fortunately, we were able to assemble a successful team on very short notice.
Are There Any Risks

Some people feel the needles as they go into the vascular access. After that, dialysis treatments are painless.
Hemodialysis does have some risks, including:
- Infection. Germs can get into the body at the site of a vascular access and cause an infection.
- Low blood pressure. Some people’s blood pressure drops during treatment. When this happens, the person might have trouble breathing, have a headache, and feel sick .
- Itching. Hemodialysis can cause a person’s skin to feel itchy, especially during or right after a treatment.
- Sleep problems. Some people getting dialysis can have trouble sleeping or develop sleep apnea .
Read Also: Reducose Weight Loss
How Dialysis Works
Unfiltered blood that is high in urea is taken from a blood vessel in the arm, mixed with blood thinners or an anti-coagulant to prevent clotting, and pumped into the dialysis machine. Inside the machine the blood and dialysis fluid are separated by a partially permeable membrane the blood flows in the opposite direction to dialysis fluid, allowing exchange to occur between the two where a concentration gradient exists.
Dialysis fluid contains:
- concentration similar to a normal level in the blood
- a concentration of ions similar to that found in normal blood plasma
- no urea
As the dialysis fluid has no urea in it, there is a large concentration gradient – meaning that urea moves across the partially permeable membrane, from the blood to the dialysis fluid, by diffusion. This is very important as it is essential that urea is removed from the patients’ blood.
As the dialysis fluid contains a glucose concentration equal to a normal blood sugar level, this prevents the net movement of glucose across the membrane as no concentration gradient exists. This is very important as the patients’ need to retain glucose for respiration.
And, as the dialysis fluid contains an ion concentration similar to the ideal blood plasma concentration, movement of ions across the membrane only occurs where there is an imbalance.
How Does It Work
Hemodialysis uses a machine to pull blood out of the body, filter it, and pump the clean blood back into the body again. The actual filtering happens in a part of the machine called a dialyzer, or artificial kidney.
The dialyzer has two parts. One part is for blood. The other is filled with a cleaning solution called dialysate.
The two parts of the dialyzer are separated by a thin membrane. Blood cells and other important parts of the blood are too big to pass through the membrane. But waste products and extra fluids go through it easily.
The dialysate pulls waste and extra fluids out of the blood, through the membrane, and carries them away. The filtered blood is then pumped back to the body.
Blood flows from the body into the machine and back again through tubes. These tubes are attached to needles in the person’s skin. The needles go into a large vein or artery through a vascular access. Doctors need to create this vascular access before dialysis can begin.
Creating a vascular access involves minor surgery. Most patients are awake during the procedure, but get local to stop feeling in the area. Surgeons usually create the vascular access a few weeks before hemodialysis starts. That way, the vascular access has time to heal.
There are three different kinds of vascular access, but they all do the same job:
You May Like: Is Aleve Hard On Your Kidneys