What Are The Parts Of The Urinary Tract
People usually have two kidneys, but can live a normal, healthy life with just one. The kidneys are under the ribcage in the back, one on each side. Each adult kidney is about the size of a fist.
Each kidney has an outer layer called the cortex, which contains filtering units. The center part of the kidney, the medulla , has fan-shaped structures called pyramids. These drain urine into cup-shaped tubes called calyxes .
From the calyxes, pee travels out of the kidneys through the ureters to be stored in the bladder . When a person urinates, the pee exits the bladder and goes out of the body through the urethra , another tube-like structure. The male urethra ends at the tip of the penis the female urethra ends just above the vaginal opening.
Kidneys And Urinary Tract
Our bodies produce several kinds of wastes, including sweat, carbon dioxide gas, feces , and urine .
These wastes exit the body in different ways: Sweat is released through pores in the skin. Water vapor and carbon dioxide are exhaled from the lungs. And undigested food materials are formed into feces in the intestines and excreted from the body as solid waste in bowel movements.
Urine, which is produced by the kidneys, contains the by-products of our bodys metabolism salts, toxins, and water that end up in our blood. The kidneys and urinary tract filter and eliminate these waste substances from our blood. Without the kidneys, waste products and other toxins would soon build up in the blood to dangerous levels.
In addition to eliminating wastes, the kidneys and urinary tract also regulate many important body functions. For example, the kidneys monitor and maintain the bodys balance of water, ensuring that our tissues receive enough water to function properly and be healthy.
When youre asked to give a urine sample during a doctors visit, the results reveal how well your two kidneys are working. For example, blood, protein, or white blood cells in the urine may indicate injury, infection, or inflammation of the kidneys, and glucose in the urine may be an indication of diabetes.
How Do My Kidneys Work
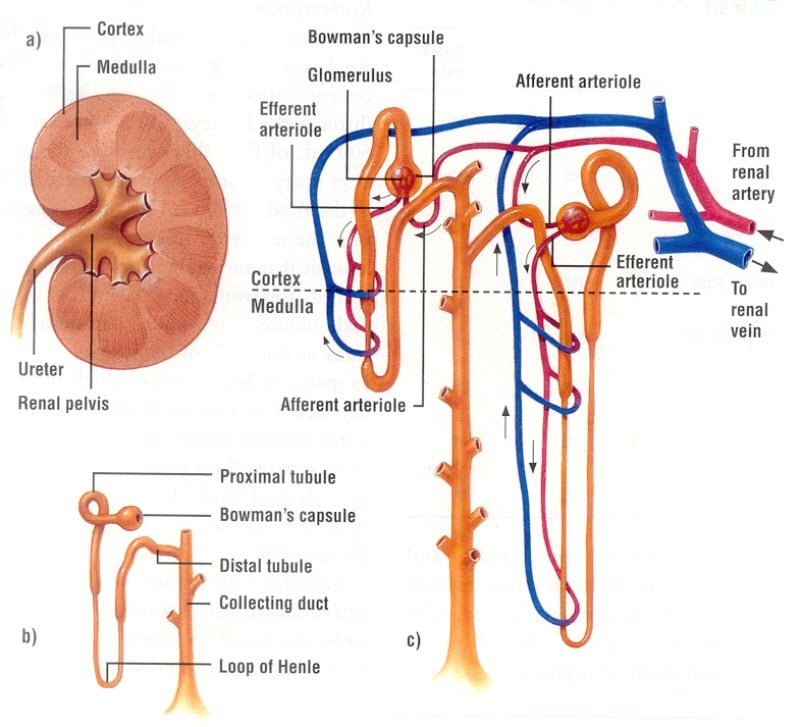
Each of your kidneys is made up of about a million filtering units called nephrons. Each nephron includes a filter, called the glomerulus, and a tubule. The nephrons work through a two-step process: the glomerulus filters your blood, and the tubule returns needed substances to your blood and removes wastes.
Read Also: Is Almond Milk Bad For Your Kidneys
Capillary Network Within The Nephron
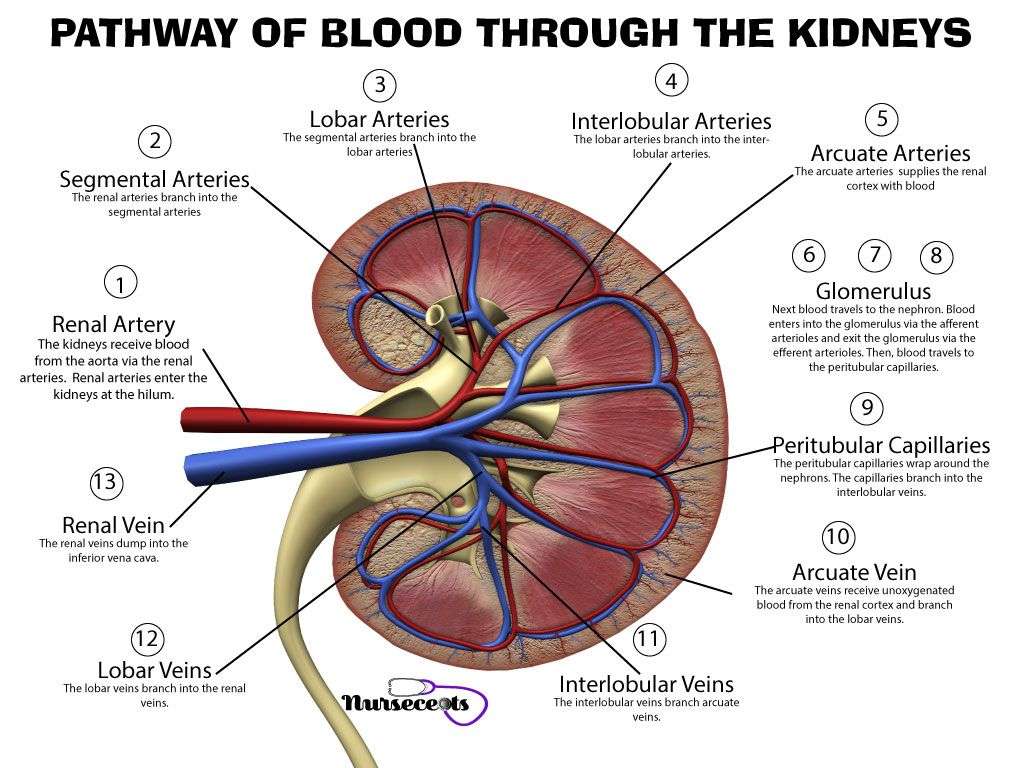
The capillary network that originates from the renal arteries supplies the nephron with blood that needs to be filtered. The branch that enters the glomerulus is called the afferent arteriole. The branch that exits the glomerulus is called the efferent arteriole. Within the glomerulus, the network of capillaries is called the glomerular capillary bed. Once the efferent arteriole exits the glomerulus, it forms the peritubular capillary network, which surrounds and interacts with parts of the renal tubule. In cortical nephrons, the peritubular capillary network surrounds the PCT and DCT. In juxtamedullary nephrons, the peritubular capillary network forms a network around the loop of Henle and is called the vasa recta.
What Causes Problems In The Urinary System
Problems in the urinary system can be caused by aging, illness, or injury. As you get older, changes in the kidneys structure cause them to lose some of their ability to remove wastes from the blood. Also, the muscles in your ureters, bladder, and urethra tend to lose some of their strength. You may have more urinary infections because the bladder muscles do not tighten enough to empty your bladder completely. A decrease in strength of muscles of the sphincters and the pelvis can also cause incontinence, the unwanted leakage of urine. Illness or injury can also prevent the kidneys from filtering the blood completely or block the passage of urine.
Recommended Reading: Can Kidney Stones Cause Gas And Constipation
The Filtration Membrane Keeps Blood Cells And Large Proteins In The Bloodstream
Inside the glomerulus, blood pressure pushes fluid from capillaries into the glomerular capsule through a specialized layer of cells. This layer, the filtration membrane, allows water and small solutes to pass but blocks blood cells and large proteins. Those components remain in the bloodstream. The filtrate flows from the glomerular capsule further into the nephron.
Where Are The Kidneys And How Do They Function
There are two kidneys, each about the size of a fist, located on either side of the spine at the lowest level of the rib cage. Each kidney contains up to a million functioning units called nephrons. A nephron consists of a filtering unit of tiny blood vessels called a glomerulus attached to a tubule. When blood enters the glomerulus, it is filtered and the remaining fluid then passes along the tubule. In the tubule, chemicals and water are either added to or removed from this filtered fluid according to the body’s needs, the final product being the urine we excrete.
The kidneys perform their life-sustaining job of filtering and returning to the bloodstream about 200 quarts of fluid every 24 hours. About two quarts are removed from the body in the form of urine, and about 198 quarts are recovered. The urine we excrete has been stored in the bladder for anywhere from 1 to 8 hours.
You May Like: Can Kidney Stones Increase Blood Sugar
Kidneys: The Main Osmoregulatory Organ
The kidneys, in mammals, are a pair of bean-shaped structures that are located just below and posterior to the liver in the peritoneal cavity. The adrenal glands sit on top of each kidney and are also called the suprarenal glands. Kidneys filter blood and purify it. All the blood in the human body is filtered many times a day by the kidneys these organs use up almost 25 percent of the oxygen absorbed through the lungs to perform this function. Oxygen allows the kidney cells to efficiently manufacture chemical energy in the form of ATP through aerobic respiration. The filtrate coming out of the kidneys is called urine.
Kidneys filter the blood, producing urine that is stored in the bladder prior to elimination through the urethra.
Structure Of The Nephron
The nephron consists of a Malpighian body and Renal tubules.a. Malpighian Body- It consists of a cup-shaped Bowmans capsule and glomerulus. The glomerulus is a tuft of capillaries. Afferent arteriole enters the Bowmans capsule and leaves it through the efferent arteriole.
Fig: Bowmans Capsule
Bowmans Capsule is a cup-shaped structure that surrounds the glomerulus. Its wall is double-layered and consists of special types of cells called podocytes.These cells have projections, and gaps between these projections form pores. These pores allow the filtration of blood from the glomerulus to the Bowmans capsule.
Fig: Podocyte
b. Renal Tubules- A tubule continues from the Bowmans capsule called renal tubule, which has the following distinct regions:-I. Proximal convoluted tubuleIII. Distal convoluted tubule
Read Also: Is Red Wine Good For Kidney Stones
How Does Urination Occur
To urinate, your brain signals the sphincters to relax. Then it signals the muscular bladder wall to tighten, squeezing urine through the urethra and out of your bladder.
How often you need to urinate depends on how quickly your kidneys produce the urine that fills the bladder and how much urine your bladder can comfortably hold. The muscles of your bladder wall remain relaxed while the bladder fills with urine, and the sphincter muscles remain contracted to keep urine in the bladder. As your bladder fills up, signals sent to your brain tell you to find a toilet soon.
What Do The Kidneys Do
Kidneys have many jobs, from filtering blood and making pee to keeping bones healthy and making a hormone that controls the production of red blood cells.
The kidneys also help regulate blood pressure, the level of salts in the blood, and the acid-base balance of the blood. All these jobs make the kidneys essential to keeping the body working as it should.
Read Also: Is Watermelon Good For The Kidneys
How Does Blood Flow Through My Kidneys
Blood flows into your kidney through the renalartery. This large blood vessel branches into smaller and smaller blood vessels until the blood reaches the nephrons. In the nephron, your blood is filtered by the tiny blood vessels of the glomeruli and then flows out of your kidney through the renal vein.
Your blood circulates through your kidneys many times a day. In a single day, your kidneys filter about 150 quarts of blood. Most of the water and other substances that filter through your glomeruli are returned to your blood by the tubules. Only 1 to 2 quarts become urine.
Processes Of The Kidneys
Filtration
Filtration is the mass movement of water and solutes from plasma to the renal tubule that occurs in the renal corpuscle. About 20% of the plasma volume passing through the glomerulus at any given time is filtered. This means that about180 liters of fluid are filtered by the kidneys every day. Thus, the entire plasma volume is filtered 60 times a day! Filtration is primarily driven by hydraulic pressure in the capillaries of the glomerulus.
Note that the kidneys filter much more fluid than the amount of urine that is actually excreted . This is essential for the kidneys to rapidly remove waste and toxins from the plasma efficiently.
Reabsorption
Reabsorption is the movement of water and solutes from the tubule back into the plasma. Reabsorption of water and specific solutes occurs to varying degrees over the entire length of the renal tubule. Bulk reabsorption, which is not under hormonal control, occurs largely in the proximal tubule. Over 70% the filtrate is reabsorbed here. In addition, many important solutes are actively transported out of the proximal tubule such that their concentrations are normally extremely low in the remaining fluid. Further bulk reabsorption of sodium occurs in the loop of Henle.
Regulated reabsorption, in which hormones control the rate of transport of sodium and water depending on systemic conditions, takes place in the distal tubule and collecting duct.
Secretion
Excretion
Also Check: Is Watermelon Kidney Friendly
How Is Chronic Kidney Disease Detected
Early detection and treatment of chronic kidney disease are the keys to keeping kidney disease from progressing to kidney failure. Some simple tests can be done to detect early kidney disease. They are:
It is especially important that people who have an increased risk for chronic kidney disease have these tests. You may have an increased risk for kidney disease if you:
- are older
Mechanism Of Concentration Of The Filtrate
Kidneys not only excrete harmful substances out from the body but also maintain the amount of water and salt in the body. The filtrate from the Bowmans capsule enters the PCT, which is almost isotonic to the blood plasma. But here in PCT, as \ of the filtrate is reabsorbed, it gets hypertonic to the blood plasma in the descending loop of Henle. Then in the ascending loop of Henle, the filtrate gets hypotonic to the blood plasma. Then again, in DCT, due to the action of aldosterone and ADH, the filtrate becomes isotonic as sodium ions and water are reabsorbed by them, respectively. In the collecting duct, further reabsorption of water takes place which makes filtrate more hypertonic. Now this filtrate is called urine.
Recommended Reading: Can Diet Soda Cause Kidney Stones
Renal Pelvis And Ureter
Numerous collecting ducts merge into the renal pelvis, which then becomes the ureter. The ureter is a muscular tube, composed of an inner longitudinal layer and an outer circular layer. The lumen of the ureter is covered by transitional epithelium . Recall from the Laboratory on Epithelia that the transitional epithelium is unique to the conducting passages of the urinary system. Its ability to stretch allows the dilation of the conducting passages when necessary. The ureter connects the kidney and the urinary bladder.
What Are The Kidneys And Urinary Tract
The urinary tract is one of the systems that our bodies use to get rid of waste products. The kidneys are the part of the urinary tract that makes urine . Urine has salts, toxins, and water that need to be filtered out of the blood. After the kidneys make urine, it leaves the body using the rest of the urinary tract as a pathway.
Read Also: Orange Juice Renal Diet
How The Urinary System Works Step By Step
When you urinate, the brain signals the bladder muscles to tighten, squeezing urine out of the bladder. At the same time, the brain signals the sphincter muscles to relax. As these muscles relax, urine exits the bladder through the urethra. When all the signals occur in the correct order, normal urination occurs.
When Should I Call My Doctor If I Think I Might Have A Problem With My Urinary Tract
If youre having trouble or pain when urinating, you should visit your doctor. It may be a sign of an infection or another condition. Call your doctor if you have:
- Blood in your urine.
- Burning sensation, pain or difficulty urinating.
- Pain in your pelvic area, lower back, genital area, or flank .
- Trouble holding your urine or problems with leaking urine.
- A feeling that something is bulging out of your vagina.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Your urinary system plays a critical role in keeping you alive. It filters your blood and removes waste and excess water through urine. Your urinary system includes your kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra. Conditions like urinary tract infections, sexually transmitted diseases, kidney diseases, and urinary tract obstruction can affect the health of your urinary system. If you have one of these conditions, talk to your healthcare provider about steps you can take to ensure your health.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 12/05/2019.
References
Don’t Miss: Ginger Is Good For Kidney
What Vessel Connects To Kidney
The renal arteries branch off of the abdominal aorta and supply the kidneys with blood. The arterial supply of the kidneys varies from person to person, and there may be one or more renal arteries to supply each kidney. The renal veins are the veins that drain the kidneys and connect them to the inferior vena cava.
Where Is Kidney Located In Our Body
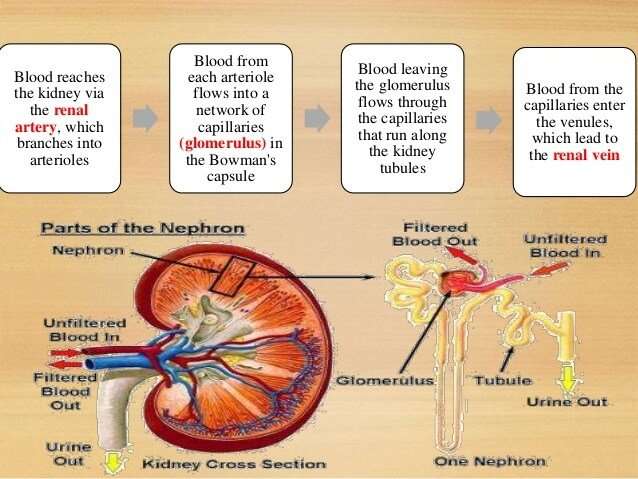
There are two kidneys, each about the size of a fist, located on either side of the spine at the lowest level of the rib cage. Each kidney contains up to a million functioning units called nephrons. A nephron consists of a filtering unit of tiny blood vessels called a glomerulus attached to a tubule.
Read Also: Kidney Stones And Constipation
How Does The Urinary System Clean My Blood
Your kidneys are an essential part of filtering your blood. Heres how the urinary system works:
Kidney Function And Physiology
Kidneys filter blood in a three-step process. First, the nephrons filter blood that runs through the capillary network in the glomerulus. Almost all solutes, except for proteins, are filtered out into the glomerulus by a process called glomerular filtration. Second, the filtrate is collected in the renal tubules. Most of the solutes get reabsorbed in the PCT by a process called tubular reabsorption. In the loop of Henle, the filtrate continues to exchange solutes and water with the renal medulla and the peritubular capillary network. Water is also reabsorbed during this step. Then, additional solutes and wastes are secreted into the kidney tubules during tubular secretion, which is, in essence, the opposite process to tubular reabsorption. The collecting ducts collect filtrate coming from the nephrons and fuse in the medullary papillae. From here, the papillae deliver the filtrate, now called urine, into the minor calyces that eventually connect to the ureters through the renal pelvis.
Also Check: What Laxatives Are Safe For Kidney Disease
The Concentration Of Urine
The secretion of ADH by the hypothalamus and its release from the posterior pituitary is part of a feedback mechanism responsive to the tonicity of plasma. This interrelation between plasma osmotic pressure and ADH output is mediated by specific and sensitive receptors at the base of the brain. These receptors are particularly sensitive to sodium and chloride ions. At normal blood tonicity there is a steady receptor discharge and a steady secretion of ADH. If the plasma becomes hypertonic , either from the ingestion of crystalloids such as common salt, or from shortage of water, receptor discharge increases, triggering increased ADH output, and more water leaves the collecting ducts to be absorbed into the blood. If the osmotic pressure of plasma becomes low, the reverse is the case. Thus water ingestion dilutes body fluids and reduces or stops ADH secretion the urine becomes hypotonic, and the extra water is excreted in the urine.
Diseases Of The Urinary System
Different specialists treat urinary system ailments. Nephrologists treat kidney diseases, while urologists treat problems with the urinary tract, including the kidneys, adrenal glands, ureters, bladder and urethra, according to the American Urological Association . Urologists also treat the male reproductive organs, while gynecologists often treat urinary diseases or disorders in females, including yeast infections. Nephrologists and urologists often work with endocrinologists or oncologists, depending on the disease.
Urinary tract infections occur when bacteria enter the urinary tract they can affect the urethra, bladder or even the kidneys. While UTIs are more common in women, they can occur in men. UTIs are typically treated with antibiotics, according to Dr. Oscar Aguirre, a urogynecologist in Denver. In the United States, about 8.1 million people have a urinary tract infection each year, according to the American Urological Association.
Incontinence is another common disease of the urinary system. “The most common bladder problems I see in my practice in women are frequent urges to urinate and leakage of urine,” said S. Adam Ramin, urologic surgeon and founder of Urology Cancer Specialists in Los Angeles. “The most common bladder problems in men are frequent urination at nights and incomplete bladder emptying. This is usually due to an enlarged prostate causing obstruction of bladder emptying.”
Additional reporting by Alina Bradford, Live Science contributor.
Recommended Reading: Is Renal Insufficiency The Same As Renal Failure