Enlarged Kidney: Causes Symptoms And Treatment
Written byEmily LunardoPublished onJuly 27, 2017
Enlarged kidneys are relatively uncommon, with only a few select disorders leading to the condition. The kidneys are responsible for filtering the blood from harmful metabolites and ensuring proper volume status that affects our blood pressure. Having an enlarged kidney will likely compromise all of its function.
What Are The Causes Of Hydronephrosis
Two types of problems cause hydronephrosis. One is obstruction, where urine is physically prevented from draining out of the kidney. The obstruction, or blockage, can occur at any point in the urinary system from the kidney down to the urethra. The second is reflux, in which urine flows back up into the kidney.
What Is Urinary Tract Dilation
Urinary tract dilation occurs when part of the unborn babyâs urinary tract swells abnormally with excessive amounts of urine. The swelling is often caused by a blockage or narrowing of the urinary tract, which stops or slows the urine from leaving the babyâs body. Usually, the swelling goes away on its own, either during the pregnancy or after the baby is born. In more severe cases, which are uncommon, the condition can lead to low levels of amniotic fluid .
The urinary tract consists of two kidneys, two ureters, a bladder, and a urethra. Special arteries in the kidneys make the urine, which then drains into a funnel-shaped area near the opening of each kidney known as the renal pelvis. From there the urine travels via the ureters to the bladder, which collects the liquid before it exits the body through the urethra. When urine leaves an unborn baby, it becomes the main part of the amniotic fluid, the protective liquid that surrounds the baby in the womb. The amniotic fluid plays an essential role in the babyâs development, particularly lung development.
In most cases of urinary tract dilation, the abnormal buildup of urine occurs in the renal pelvis. But the urine can get blocked further down the urinary tract as well, causing the ureters, bladder, or urethra to swell. .
Figure â Urinary tract dilation occurs when a normal urinary tract becomes swollen, or dilated, with fluid .
Recommended Reading: Is Watermelon Good For Kidneys
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Hydronephrosis
Most infants with hydronephrosis have no symptoms at all. Older children may also have no symptoms and the condition may disappear without intervention.
If a child has more severe hydronephrosis, they may experience one or more of the following symptoms:
- Abdominal pain with nausea and/or vomiting, especially after large fluid intakes.
- Flank pain .
When Your Child Has Hydronephrosis
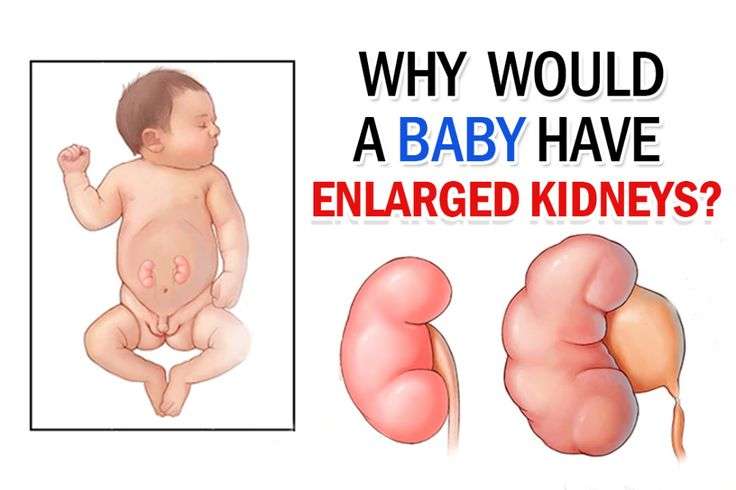
One or more of your childs kidneys is enlarged because of urine backup. This is called hydronephrosis. The problem may have been diagnosed before your child was even born. Often, the condition is not serious. In fact, in many children the problem goes away with time. In some cases, treatment is needed. Your childs healthcare provider can tell you about treatment options. Your child may see a pediatric urologist. This is a doctor who manages problems of the urinary tract in children.
Recommended Reading: Can Mio Cause Kidney Stones
How Is Urinary Tract Dilation Diagnosed
Urinary tract dilation is diagnosed by ultrasound. In most cases, mild dilation of the kidney is seen on the ultrasound routinely done at the 20th week of pregnancy. Because kidney dilation seen at 20 weeks often completely resolves later in pregnancy, your doctor or midwife will send you for a follow-up ultrasound at 32-36 weeks to reassess the kidneys, bladder, and urinary tract. If dilation of the kidneys or of other areas of the urinary tract is still present at 32-36 weeks, your baby will be diagnosed with urinary tract dilation.
Is Hydronephrosis A Sign Of A Problem
If a fetus or newborn is found to have hydronephrosis, health care professionals will begin to examine how urine drains from the kidneys. The more severe hydronephrosis is, the more likely it is to be a sign of a blockage in the urinary tract or reflux of urine from the bladder to the kidney, which may need treatment. Early diagnosis and treatment of the blockage or reflux may help prevent complications or prevent complications from getting worse.
Normally, the fetuss urine becomes part of the amniotic fluid that surrounds the fetus in the womb. In a fetus with severe hydronephrosis, too much urine may stay in the urinary tract, leading to low levels of amniotic fluid in the womb. Low levels of amniotic fluid can harm the fetuss developing lungs.
After an infant is born, hydronephrosis may lead to complications such as urinary tract infections, kidney stones, and chronic kidney disease.
You May Like: How Much Money Is A Kidney Worth
What Is Hydronephrosis In Children Or Infants
Overview. Antenatal hydronephrosis, the most common urological problem found during prenatal ultrasound screening, refers to the fluid-filled enlargement of the kidney as a result of obstruction in its output of urine. It is usually detected in the fetus in the first trimester of pregnancy, though it can also be discovered later in the pregnancy or after birth.
It is most commonly caused by narrowing of the ureter close to the kidney blockage in the kidney or bladder or vesicouretal reflux, in which a faulty valve between the bladder and the ureter causes the urine to back up into the kidney when the bladder fills or empties. In more rare cases, antenatal hydronephrosis can result from a duplication anomaly or a multicystic dysplastic kidney.
Diagnosis and Management. The initial approach to most cases of antenatal hydronephrosis is to perform regular ultrasound testing to carefully monitor kidney growth and function during the pregnancy, infancy and childhood. Usually, this is all that is necessary. Obstetrical care is generally unchanged, although low-dose antibiotics are sometimes given to prevent infection. After birth, the condition will usually resolve itself with no damage to the kidney in some instances, the kidney that appears enlarged in the ultrasound is found to function normally after delivery.
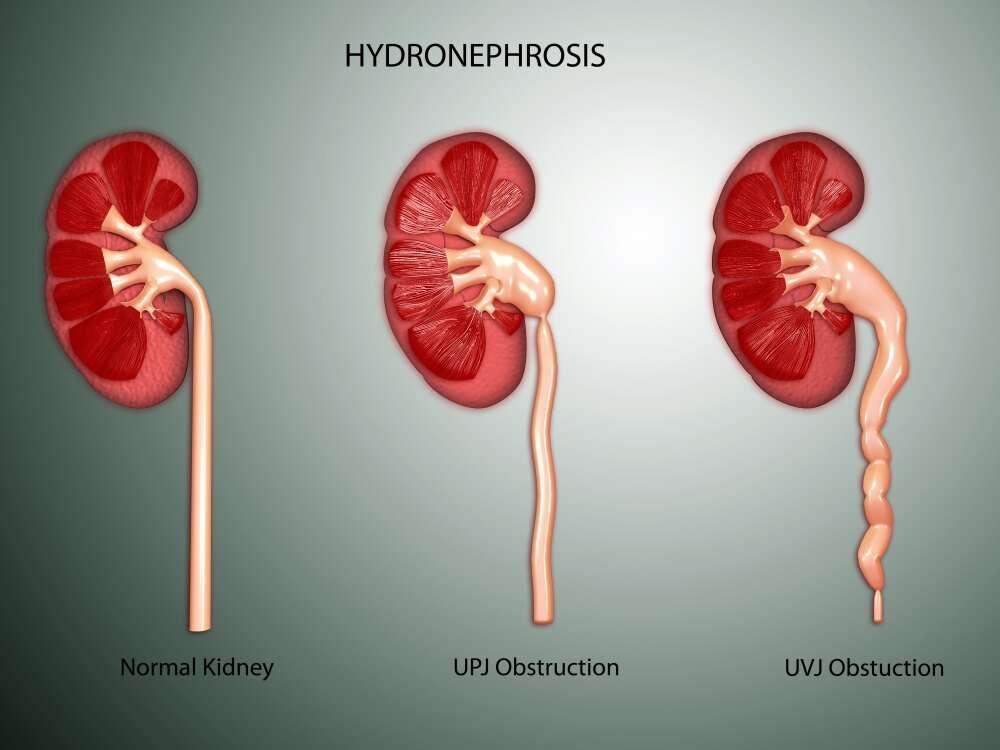
How Is Hydronephrosis Detected During Pregnancy
Ultrasound can detect the fetal kidneys and bladder by 14 or 15 weeks gestation, though 20 weeks of pregnancy is the ideal time to detect hydronephrosis as the fetus is larger and the kidneys are producing urine. When a UPJ obstruction is identified, the kidneys are closely examined for other findings more common with UPJ, such as cysts or an abnormal shape .
You May Like: Grapes For Kidney Stones
You May Like: Flomax For Kidney Stones In Woman
Testing And Diagnosis Of Hydronephrosis
Renal bladder ultrasound
This procedure uses sound waves to outline the kidneys and bladder. It will enable us to see the degree of hydronephrosis.
Images from the ultrasound are used to evaluate the size and appearance of the collecting system , and the appearance of the renal parenchyma, ureter and bladder.
Voiding cystourethrogram
In a voiding cystourethrogram , a catheter is placed through your childs urethra into the bladder. The tube will be used to slowly fill the bladder with a contrast solution and pictures will be taken.
While the bladder is being filled, a special machine is used to take pictures. If special ultrasound contrast is used, these pictures can be taken with an ultrasound machine . The radiologist looks to see if any of the solution is going back up into the kidneys. This study confirms the diagnosis of VUR.
Additional pictures are taken while your child is urinating. The radiologist will look at the urethra while urine is passing to be sure there is no blockage noted .
MAG III renal scan
MRI/MRU
MRI is a radiation-free diagnostic procedure that uses a combination of a large magnet, radiofrequencies and a computer to produce detailed images of the body.
What Causes Fetal Hydronephrosis
Fetal hydronephrosis is caused by an obstruction to what should be a free flow of urine out of the kidney. An example of this is kinking of the ureter. It may also be caused by an abnormal backwashing of urine from the bladder back into the kidney. An example of this is vesicoureteral reflux or “reflux.”
Also Check: Renal Diet Watermelon
Diagnosis Of Prenatal Hydronephrosis
Prenatal hydronephrosis is most often discovered by an ultrasound, performed either as a normal maternal imaging evaluation of the fetus or in evaluating a pregnant woman for another medical condition. The ultrasound of the fetus may show fluid buildup in one or both kidneys or ureter tube a ureterocele or an enlarged bladder.
Ultrasound alone does not provide a detailed enough image of prenatal hydronephrosis, and further tests are often required for a proper evaluation. These tests include:
My Ob Says My Baby Has Swollen Kidneys: What Is Prenatal Hydronephrosis
The 20-week anatomy ultrasound for pregnant moms is one full of anticipation and anxiety, as it sets the stage for the rest of the pregnancy. Prenatal Hydronephrosis is the most common anatomic abnormality found in pregnancy during one of those ultrasounds. Its found in one percent of all male fetuses and 0.5 percent of female fetuses. Typically, it is not associated with other organ system abnormalities and often the diagnosis does not affect timing or method in which a baby is delivered.
Prenatal intervention is almost never required, and amniotic fluid is usually normal. Depending upon the abnormality, ultrasound imaging may be needed throughout pregnancy and after a baby is born. In most cases, this diagnosis does not affect when, where, or how a baby is delivered. However, surgery is required in a small percentage of children during infancy and childhood.
Don’t Miss: Seltzer Water Kidney Stones
What Happens After My Evaluation Is Complete
After we have gathered all the anatomic and diagnostic information about your baby, our maternal-fetal specialist will meet with you to discuss the results and share our recommendations. We will connect you to a nurse specialist care coordinator who will assist with setting up future consultations and follow-up care for the baby after birth. One of those consultations will be with a pediatric urologist, who will meet with you either during the pregnancy or soon after the baby is born. We will also communicate with your primary obstetrician or midwife so that he or she can continue to provide your routine prenatal care.
Measuring The Renal Pelvis
Measurement of the antero-posterior diameter of the renal pelvis as visualised in the transverse plane on ultra sound scan is the most studied parameter for assessing ANH in utero.
ANH is defined as a renal pelvis APD greater than 4 mm on fetal USS in the second trimester and greater than 7 mm in the third trimester. If ANH in the second trimester has resolved by the third trimester, that is, renal pelvis APD less than 7 mm in the third trimester, then the fetus does not have ANH.
There are no distinguishing features to differentiate which children will progress to obstruction on follow up however, a renal pelvis APD of greater than 15 mm represents severe hydronephrosis with a high likelihood of progression, whereas less than 5 mm is a threshold for considering the pelvis as normal.
A recent prospective cohort found that no baby with a renal pelvis APD of less than 6 mm progressed to treatment for ANH. This included all babies with pyelectasis and hydronephrosis.
To assess progression of ANH in utero, the most important step is to assess at two time points, preferably in the second and third trimesters.
|
Degree of ANH |
|---|
Don’t Miss: Can Diet Soda Cause Kidney Stones
Is It Normal To Have A Dilated Left Fetal Kidney
So I went for my 18-20wk ultrasound and my unborn son had a slightly dilated left fetal kidney. Im worried that I have either done something wrong or it could be genetic as my side of the family have a history of being renal patients. Is this something I should be worried about or is it completely normal?
What Is Hydronephrosis
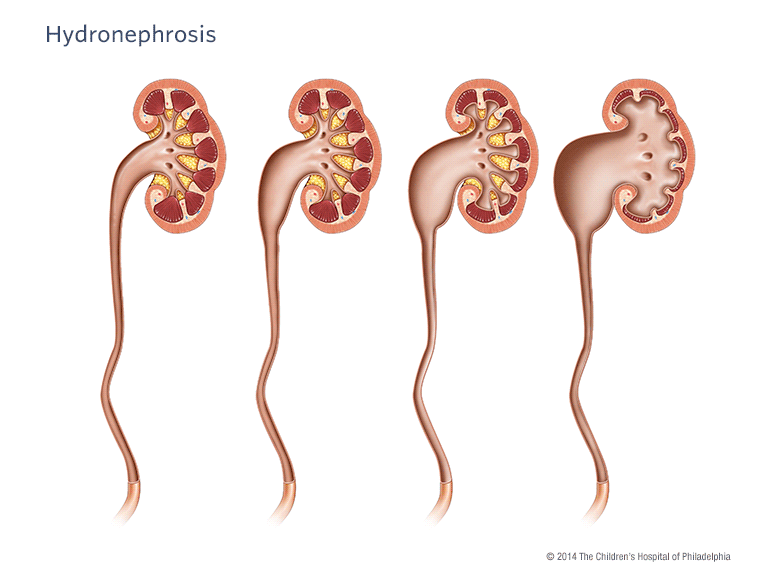
Hydronephrosis, also known as urinary tract dilation, is when the area of the kidney where urine is collected is enlarged, or dilated. It can range from mild to severe, depending on the cause of the dilation. Often children who have hydronephrosis have it from the time of birth.
Hydronephrosis or urinary tract dilation refers to dilation of the pelvis and calyces of the kidney where urine is collected. Pictured left to right: Normal appearance of the renal pelvis, followed by increasing severity of hydronephrosis.
Prenatal hydronephrosis is one of the most common fetal anomalies diagnosed before birth.
Due to the increased use of prenatal ultrasound, hydronephrosis is now found in 1 out of 100 pregnancies. Hydronephrosis can be detected on ultrasound as early as the first trimester of pregnancy and is typically seen on the anatomy ultrasound around 20 weeks gestation. In most cases, prenatally diagnosed hydronephrosis is followed throughout the remainder of the pregnancy with repeated ultrasounds.
The repeated ultrasounds will monitor amniotic fluid levels, the amount of dilation, if the dilation is in one kidney or both, if the ureters are dilated, and if there is normal filling and emptying of the bladder.
Childrens Hospital of Philadelphia developed a detailed clinical pathway for providers dedicated to the evaluation, monitoring and management of perinatal urinary tract dilation/hydronephrosis.
Also Check: Pop And Kidney Stones
How Is Arpkd Treated
Treatment is aimed at each childs symptoms and should be managed by a specialist centre with expertise in ARPKD. Different treatments carry different potential risks, and doctors should always explain clearly to you the benefits and possible drawbacks of each option. Specialists will also monitor your childs health carefully. You may need to travel to specialist units for some appointments, for example for dialysis.
Unfortunately, there are no proven treatments that can slow the progression of ARPKD. Its possible that controlling blood pressure carefully might help to delay damage to the kidneys, but experts are not yet sure. This has been shown for patients with chronic kidney disease in general, but not for children with ARPKD in particular.
Will My Baby Require Long
The findings from your babyâs ultrasound taken after birth will determine whether or not follow-up care with a pediatric urologist is needed. Such care, which may include surgery, can decrease the risk of kidney problems for your baby later in life. The pediatric urologist will recommend an individualized management plan for your baby based on your babyâs specific ultrasound findings.
Recommended Reading: Wine For Kidney Stones
How Does Fetal Hydronephrosis Affect My Baby
Hydronephrosis can range from mild to severe. In most cases, the condition is mild and typically has little or no effect on the fetus or newborn baby. More serious cases may require surgery after birth to repair an obstruction or reflux.
In severe cases, hydronephrosis can cause serious complications, including:
- Too little amniotic fluid, a condition known as oligohydramnios. Fetal urine is the main component of amniotic fluid. If hydronephrosis limits the flow of fetal urine enough to reduce the amniotic fluid below a safe level, it can lead to serious pregnancy complications including underdeveloped lungs and breathing difficulties at birth and deformities of the face and extremities .
- Kidney damage and loss of kidney function. The backup of urine puts pressure on the fetal kidneys. This can cause progressive, permanent damage and the risk of kidney failure or rupture.
Hydronephrosis is sometimes graded on a scale of zero to four, zero being no hydronephrosis present and four being the most severe form of the condition.
How Is It Diagnosed
Presently a vast majority of children are diagnosed with hydronephrosis on fetal scans. At present, the 20 weeks scan can be useful for detecting hydronephrosis and this frequently means there may be further ultrasound scans required in pregnancy. This can occur at approximately 1 2% of all pregnancies. However, hydronephrosis symptoms can also be detected after the baby is born. This usually happens when ultrasound scans are performed to check on the kidneys due to recurring urinary tract infections or other issues.
Also Check: Is Apple Cider Vinegar Bad For Kidneys
How We Care For Hydronephrosis
At Boston Childrens Hospital, we are here to help. Our physicians and nurses are trained in pediatric urology and have extensive experience with hydronephrosis. We are honored to be recognized by U.S. News & World Report as #1 in the nation, and have the largest pediatric urology service in the world.
What Can Be Done
If they find an enlarged kidney in your baby, there are things that can be done to monitor or treat the condition. These include:
During Pregnancy
The doctor will do ultrasounds frequently during your pregnancy to check for the following:
- Kidney development
- How much amniotic fluid you have
Treatments
- If the enlarged kidney in fetus is mild to moderate and does not threaten the pregnancy or your babys life, no treatment is needed.
- In moderate cases where amniotic fluid is low, they can infuse more fluids via amniocentesis through a catheter.
- If the condition is severe and threatens the life of your baby, doctors may opt to send you to a specialized hospital for surgery.
After Baby Is Born
Testing
Newborns, babies, and kids born with hydronephrosis may be sent to a pediatric urologist to be monitored. Tests include:
- Kidney ultrasounds to check the size of the kidneys.
- Voiding cystourethrogram to make sure urine is passing freely.
- Kidney scans can check for blockages and kidney functions.
Treatment:
You will most likely have to take your baby for another ultrasound in the near future. A mild case of hydronephrosis may stay mild and not need any attention. Most cases just need good follow-up care and no treatment if watched closely.
Don’t Miss: Is Aleve Bad For Kidneys