How Do You Get Rid Of A Cyst On Your Kidney
Options include:
How Are Renal Cysts Treated
Renal cysts generally do not require treatment unless they are causing symptoms or harming kidney function. Treatment options include:
- Sclerotherapy: Also known as percutaneous alcohol ablation, sclerotherapy involves the insertion of a long needle through the skin and into the cyst under ultrasound guidance. The doctor will drain the cyst and fill it with an alcohol-based solution that causes the tissue to harden and shrink, reducing the chance of recurrence. The procedure is usually performed on an outpatient basis with a local anesthetic.
- Surgery: For larger cysts, a surgeon will make a small incision and access the cyst with a laparoscope. The surgeon will then drain the cyst and burn or cut away its outer layer. Laparoscopic surgery requires general anesthesia.
What Are The Signs That Complex Kidney Cyst Is Cancer
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video.
Read Also: How Long Does Kidney Cancer Take To Spread
How Should Patients With Renal Cell Carcinoma Be Managed
Surgery
Laparoscopic or open approach depends on the nature of the tumor and surgeon preference and expertise:
-
Partial nephrectomy- limited resection of the portion of the kidney where the mass is
-
Simple nephrectomy- removal of the kidney without node or adrenal resection
-
Radical nephrectomy- includes a perifascial resection of the kidney, perirenal fat, regional lymph nodes, and ipsilateral adrenal gland
-
Cytoreductive nephrectomy- removal of the kidney in the setting of advanced stage IV disease where cure is not expected to be achieved
Surgical resection of localized disease remains the treatment of choice for either cure or long-term disease-free survival. Nephrectomy is recommended in patients with stage I-III disease. The degree of resection is dictated by the extent of disease and location of the tumor. Historically, partial resection was done in patients with a solitary kidney or severe CKD where a radical nephrectomy would render a patient functionally anephric. With recent data suggesting that nephrectomy-induced CKD is associated with an increased risk of all-cause and cardiovascular death, nephron-sparing procedures should be considered when at all possible.
Summary of surgical recommendations based on TNM stage of disease
Ablation Therapy
These procedures are performed by urologists and interventional radiologists. They are generally performed under conscious sedation but may require general anesthesia.
Immunotherapy
Living With Kidney Cysts
If you are over 50 years old, there is a good chance you have kidney cysts and dont realize it. You may never realize it because you may never have symptoms. And most kidney cysts do not cause any problems.
If you do have symptoms , see your doctor. He or she can advise you on a treatment or ways to help relieve your symptoms.
Recommended Reading: Celery Juice Kidneys
Read Also: How Do You Diagnose Kidney Stones
History Of Present Illness:
A 73-year-old male presented with one day of hematuria associated with urinary frequency and acute on chronic abdominal cramping. On exam, he had diffuse abdominal tenderness, which he stated was normal for him. He was afebrile with no costovertebral angle tenderness or any other pertinent findings on physical exam. The urinalysis showed large red blood cells and small leukocyte esterase and nitrites. Labs were significant for white blood cell count 24.6/mm3, hemoglobin 11.6 g/dL, blood urea nitrogen 56 mg/dL, creatinine 3.8 mg/dL , glomerular filtration rate 16 mL/min. These findings were consistent with acute on chronic kidney injury with concomitant urinary tract infection specifically concerning for pyelonephritis or an infected renal stone.
Causes Of Complex Renal Cysts: Complex Kidney Cysts Symptoms
A cyst is a fluid filled sac located in any organ of the body. Cysts in kidney are also called renal cysts. As there are two kidneys, the cysts can be unilateral or bilateral . Further cyst can be divided into two categories, simple cyst and complex cyst. Simple cyst is small in size, having oval or round shape.
Complex renal cyst has irregular shape. They can become cancerous. Symptoms of complex renal cyst are hematuria, dull and throbbing pain in the abdomen. Cause of complex renal cyst is congenital renal tubular defect and repeated dialysis, certain kidney diseases etc.
Also Check: Can You Die Stage 3 Kidney Disease
What Causes Simple Kidney Cysts
Kidney cysts occur when the tube of a nephron begins to get bigger and fill with fluid. Researchers dont know what causes this to occur, but they do know that simple cysts arent inherited. It is believed that injury or microscopic blockages in the tubules may lead to the development of some simple kidney cysts.
Recommended Reading: Is Grape Juice Good For Kidney Stones
What Are Kidney Cysts
A cyst is a closed pouch or sac filled with air or liquid. Kidneys are bean-shaped organs located in the lower back that help to control the amount of salt and water in the body. They also remove waste products by filtering the blood and making urine.
Inside the kidneys are small working parts called nephrons. Each nephron is made up of a filter and a tube. As blood flows through the kidneys to be filtered, the nephrons remove extra water and waste products, which leave the body as urine.
Simple kidney cysts are usually small round sacs that have a thin wall and are filled with a watery fluid. As people get older, cysts can form on the surface or in the nephrons of the kidneys. They can range in size from a small pea to as large as a grapefruit. Cysts can also grow over time.
Read Also: What Is Acute Renal Kidney Failure
What Causes Cysts On The Liver And Kidneys
A cyst is a sac like structure that resembles like a membranous tissue containing fluid like substances inside which can grow anywhere in the body or skin. A cyst is a bump on the skin or a lump under the skin, but in some cases like kidneys and liver, it is located internally. Polycystic kidney disease causes the cyst to form in the kidneys that can adversely affect kidney functions. On the other side, a cyst in the liver leads to the fluid-filled sacs throughout the organ. What Causes Cysts on the Liver and Kidneys?
There are many causes that can cause a cyst in the liver and kidneys. In the liver, most of the people inherit the condition but it can also occur without any genetic link. Women are more prone to this condition than man. Polycystic liver disease is most common in polycystic kidney disease. There are mainly three types of PKD:
- Autosomal dominant PKD is common in adults and mainly happens to patients whose parents with PKD condition. What Causes Cysts on the Liver and Kidneys?
- Autosomal recessive PKD is less common and mainly occur when both the parents have a gene for the disease.
- Acquired cystic kidney disease is not inherited and occurs in middle or old age. It is common in people who already have one or the other kidney problem especially the one that has kidney failure or is on dialysis. What Causes Cysts on the Liver and Kidneys?
The symptoms of this condition are only visible in advanced stages. Some of the common visible signs are:
Latest Posts
Complex Kidney Cyst Complications
Complex kidney cyst has its complications. Its important not to allow starting of inflammatory processes. They often occur in the fluid filling the cyst cavity.
In addition, there may be a hemorrhagic kidney cyst. This occurs when there is bleeding inside the cyst. Blood partially or completely fills the cavities of a complex kidney cyst.
Echinococcosis cyst is extremely unpleasant thing caused by hydatid tape worm. This disease is called hydatidosis.
As a rule, mature worm lives in the small intestine of a dog. Man is a random intermediate master. The most common localization site is the liver. Renal hydatidosis is about 2% of human echinococcal cysts.
Renal cancers account for about 7-10% of cystic lesions detected by ultrasound. Although the percentage is small, the risk of cancer is worth carrying out some additional diagnostic procedures to make accurate diagnose.
Don’t Miss: Can Heart Disease Cause Kidney Disease
Causes Of Complex Kidney Cysts
A complex kidney cyst can develop as a secondary manifestation of a simple cyst. Such relapse occurs as a result of complications such as infection or bleeding, and also as a result of the proliferative process .
As is the case with simple kidney cyst formation, different types of complex kidney cyst can give similar pictures on medical ultrasound diagnosis. Therefore, it is not possible to make an accurate diagnosis without additional examinations.
However, the timely detection of a complex kidney cyst with using ultrasound is already important in the successful treatment. Features indicating the presence of cystic formation during ultrasound diagnostics:
thickening and irregular contour of the cyst wall
presence of partitions
the presence of seals or solid elements in the tissues present in the plural
distinct vascularization .
Diagnosis Of Cystic Kidney Disease
The tests recommended by your doctor depend on which cystic kidney disease is suspected. Generally, diagnostic tests may include:
- physical examination to detect high blood pressure or enlarged kidneys
- urine tests to look for blood or protein in the urine
- blood tests to assess kidney function
- renal ultrasound a simple test that uses sound waves to detect cysts in the kidneys. It is good at identifying even quite small cysts
- computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging scans these can detect very small cysts. They may be required if the results from the ultrasound are inconclusive or if more information is needed
- genetic testing generally used for family studies and not a routine test.
Read Also: Is Apple Cider Vinegar Good For The Kidneys
Don’t Miss: When Is A Kidney Infection An Emergency
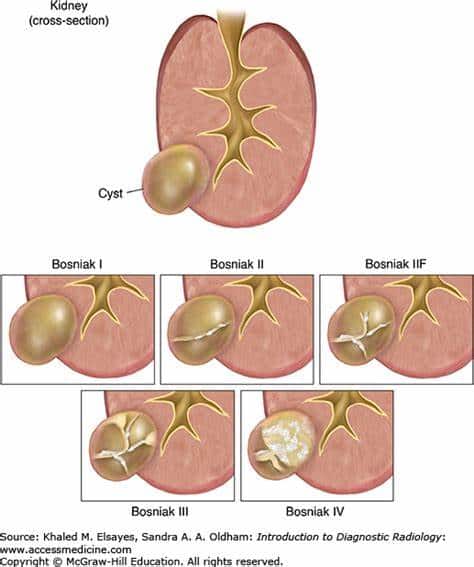
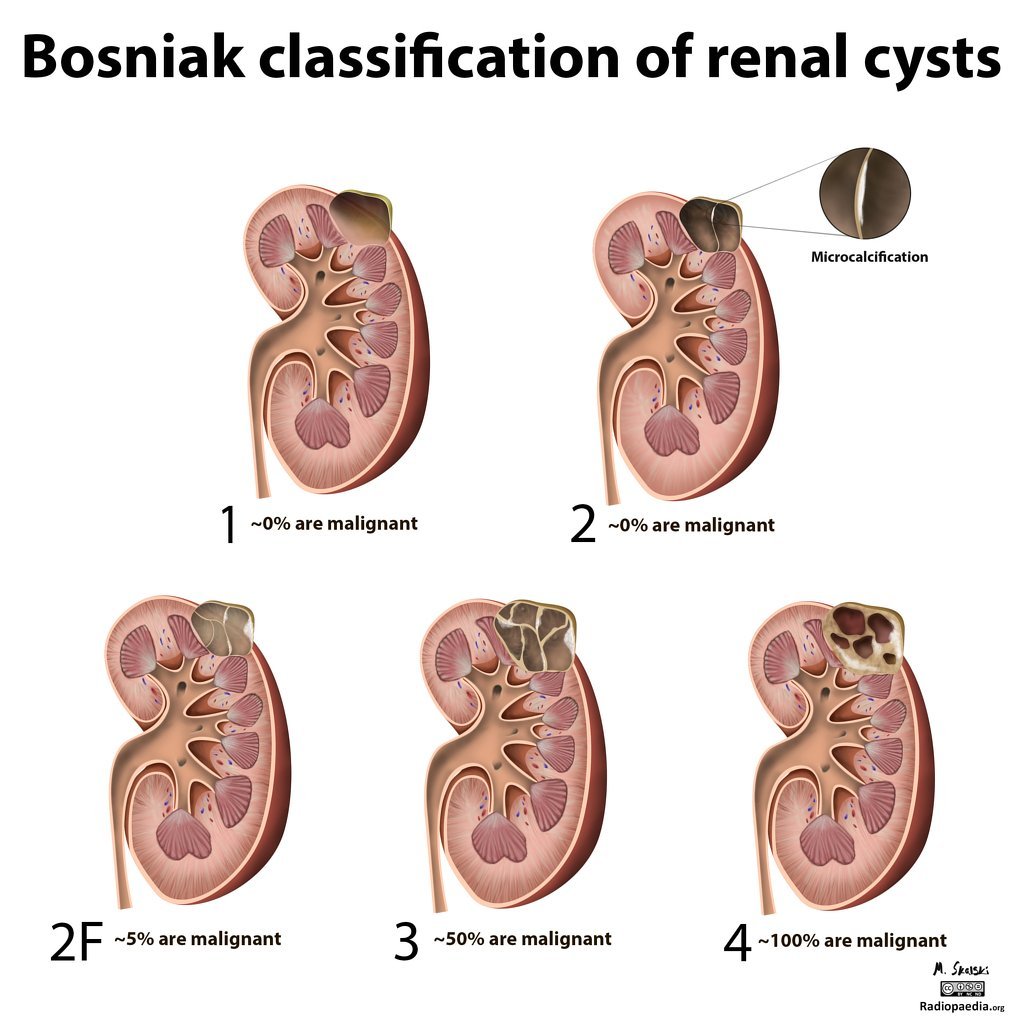
Bosniak Classification System For Renal Cysts
The most widely used system to classify cystic renal lesions was introduced by Bosniak in 1984 and revised in 1997 . This system was originally developed on CT findings, but it can be also used at MRI .
Renal cysts are divided into five categories on the basis of imaging appearance . Each Bosniak category reflects the likelihood of cystic RCC that ranges from I to IV . Category I, II, and, IIF cysts are nonsurgical, while categories III and IV are surgical.
Table 1 The five categories of renal cysts, divided on the basis of imaging appearanceFig. 2
Imaging features of cystic renal lesions according to Bosniak classification. a Bosniak category I cyst: thin wall. b Bosniak category II cyst: thin wall few, thin septa. c Bosniak category II-F cyst: minimally thickened wall several, minimally thickened septa. d Bosniak category III cyst: irregularly thickened wall several, irregularly thickened septa. e Bosniak category IV cyst: enhancing nodularity irregularly thickened wall several, irregularly thickened septa
In equivocal cases, another option is to use subtraction MRI to assess the presence or absence of enhancement .
Category I renal cysts
Fig. 3
Bosniak category I renal cyst. Axial non-enhanced and contrast-enhanced CT images shows a cyst with a thin and non-enhancing wall
Category II renal cysts
Also Check: Is Cranberry Juice Good For Your Liver And Kidneys
What Are The Symptoms Of Cystic Kidney Disease
The various cystic kidney diseases have different symptoms. Some of the most common among them include:
- Difficulty urinating, or not producing much urine.
- Enlarged kidneys or kidney masses.
- Blood and urine tests can also give your healthcare provider important information about how well your kidneys are working and filtering your blood.
Read Also: Does Flagyl Treat Kidney Infection
Re: Kidney Complex Cyst
I am not a doctor or any sort of medical practitioner. I had not heard of this problem before, however, I have done some checking. One web site states that complex kidney cysts have a low risk for being or becoming a kidney cancer, but should always be evaluated by a Urologist to be certain. I think that theres every hope that you will be ok and well all keep our fingers crossed for you.
I imagine that most people on this forum have been through the agonising wait for tests and then the even more agonising wait for results. Please be reassured that here is a safe place to express your fears and seek reassurance.
Best wishes
Cystic Renal Cell Carcinoma
Cystic RCC is relatively rare and comprises approximately 315 % of all cases of RCCs. It is found more commonly in younger age and in females compared with solid RCC . The cystic appearance can be related to their inherent architecture or secondary to cystic degeneration and extensive necrosis . Clear cell type RCC is the most common subtype, followed by papillary and chromophobe RCC. Clear cell type RCC can show a dominant cystic component or can arise in a simple cyst . Multilocular cystic RCC of low malignant potential is a rare variant of clear cell type RCC with no reported recurrence or metastasis. This tumor is composed exclusively by cysts with low-grade tumor cell and shows a variable imaging appearance, which ranges from category IIF to category IV renal cysts . Papillary RCC can appear as a cyst with hemorrhagic or necrotic content and a thick pseudocapsule . Cystic renal RCCs have a more favorable prognosis of all subtypes of RCC: they have a low Fuhrman grade, grow slowly, and rarely metastasize or recur .
Also Check: How To Treat Pulpy Kidney In Goats
Diagnosed With Kidney Cancer
We understand the anxiety that a diagnosis of kidney cancer can bring to the patient and their family. The most important thingone can do is to learn about this disease and enlist the help of an experienced team of physicians.
About 1/3 of kidney cancers are diagnosed after the disease has spread to other organs.
The first step is to obtain a “staging” evaluation to determine the extent of cancer. This typically entails obtaining imaging of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis and comprehensive blood work. Bone scans and evaluations of the brain are obtained depending on symptoms and the results of the initial studies.
PET scans are rarely obtained due to their lack of sensitivity for detecting kidney cancer.
Ask The Doctor: What Should I Do About A Kidney Cyst
Q.During a pelvic ultrasound to evaluate uterine fibroids, a radiologist found a cyst in one of my kidneys. Should I be concerned about kidney cancer?
A. Kidney cysts are fluid-filled sacs in the kidney that rarely cause symptoms and are usually harmless. They are quite common, and the likelihood of having one or more of them increases as we age. Cysts may be “simple” or “complex.” Simple cysts are thin, round sacs with clear fluid, and they are not cancerous. Complex cysts may have thick walls, several lobes, and flecks of calcium or solid components. They are also usually benign, but need further evaluation to be sure they do not contain cancer. Most often a CT scan or MRI will help a urologist or renal expert recommend a strategy of watchful waiting, biopsy, or removal of the cyst. Occasionally, a benign cyst grows large enough to affect the function of the kidney or cause pain. A cyst may also become infected or bleed, causing fever, pain, or blood in the urine . In that case, the cyst may need to be removed or drained.
To continue reading this article, you must log in.
- Research health conditions
- Prepare for a doctor’s visit or test
- Find the best treatments and procedures for you
- Explore options for better nutrition and exercise
Read Also: How Long Do Kidney Stones Take To Develop
Understanding The T Word
The term tumor refers to an area in an organ that is not typically supposed to be there. A tumor may also be referred to as a mass, lesion, neoplasm or cyst. All of these terms mean the same thing, but none of them indicate whether or not a tumor is cancer. Often, tumors are found accidentally when an individual is undergoing x-rays for other reasons. Sometimes, they are found when investigating why a patient is experiencing side pain or blood in the urine.
Kidney cysts are closed pockets of tissue, filled with fluid, that develop in the kidneys. Multiple cysts can develop, or a single cyst. Kidney cysts can develop more or less spontaneously with no underlying cause, or they may develop as a result of a condition such as polycystic kidney disease or multicystic kidney dysplasia. The development of so-called âsimpleâ kidney cysts becomes more common in older people: up to 30% of those aged 70 and over have one or more cysts.
Complex kidney cysts are so-called because of their irregular shape. Another difference between simple and complex cysts is that complex kidney cysts often have âenhancedâ tissue, meaning that within the cyst, there is tissue that has access to a blood supply.
What Causes Kidney Cysts
If your kidney cysts are caused by PKD, then they are inherited. This means you have them because they run in your family. For most people, though, this is not the case. Doctors arent sure why kidney cysts form for them. It could be that the kidney surface weakens over time. This could explain why kidney cysts are most common in people who are age 50 and older.
You May Like: Can Kidney Stones Move Back Up