What Are The 4 Steps Of Urine Formation
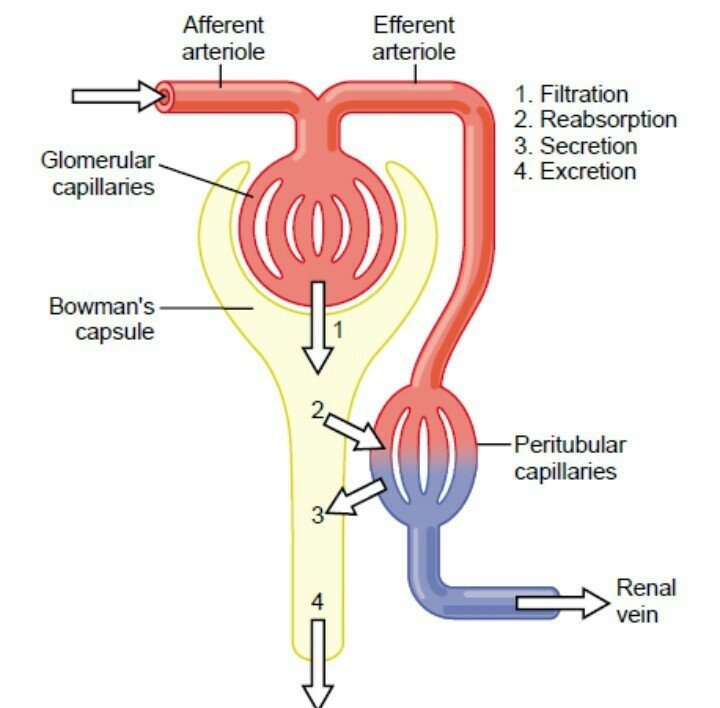
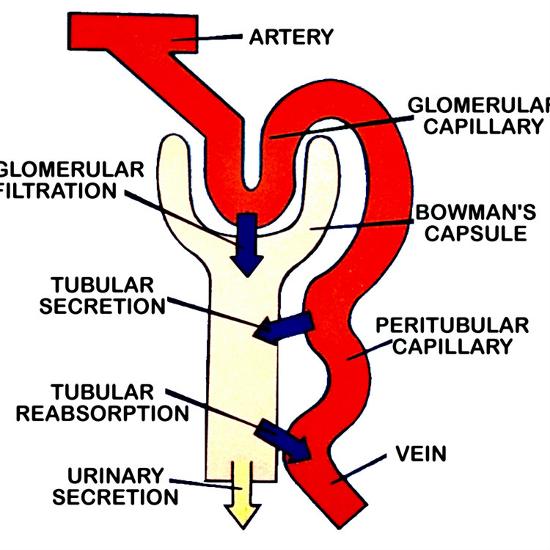
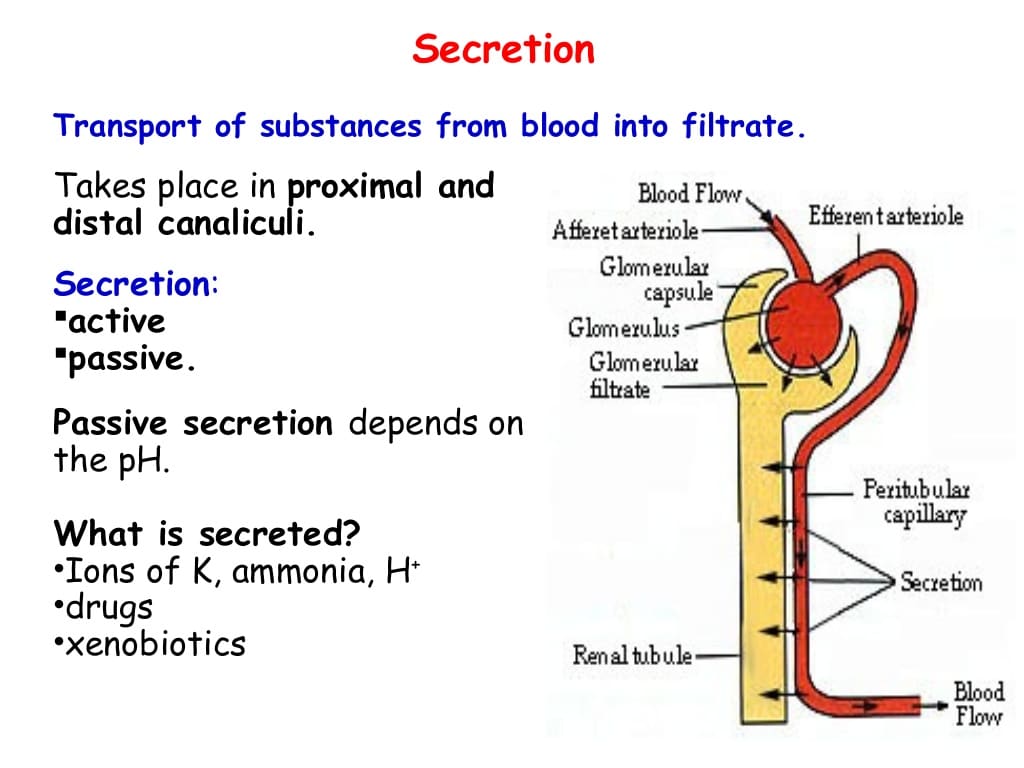
There are four basic processes in the formation of urine starting with plasma. Filtration. Reabsorption. Regulated reabsorption, in which hormones control the rate of transport of sodium and water depending on systemic conditions, takes place in the distal tubule and collecting duct. Secretion. Excretion.
How Can I Keep My Urinary System Healthy
You cant prevent most urinary tract problems. But you can try to keep your urinary system healthy with proper hygiene and a healthy lifestyle. To help your urinary system work the way it should, you can:
- Drink plenty of water: Staying hydrated will flush out your system and can help you prevent kidney stones and UTIs. You can try drinking cranberry juice to ward off a UTI. Compounds in cranberries may stop bacteria from growing.
- Eat a healthy diet: Low sodium, high-calcium foods may prevent kidney stones.
- Wipe the right way: Women should always wipe front to back after using the toilet. Proper wiping reduces the risk of bacteria getting into the vagina and causing a UTI.
- Empty your bladder after sex: If youre a woman, you should use the bathroom after having sex. Peeing promptly can clear out bacteria and reduce your risk of a UTI.
- Practice safe sex: Protect yourself from an STI with a condom. But be careful with spermicides because they can cause bacteria to flourish.
- Do pelvic floor exercises: Also called Kegel exercises, these can reduce your risk of urinary incontinence by strengthening the muscles in your pelvic floor.
Regulation Of Water Reabsorption
There are two main hormones that regulate the rate of excretion of water.
The first hormone is aldosterone which acts on the collecting duct and causes the body to retain more water. Blood pressure increases when the body retains more water. This system is triggered when there is low blood pressure or low sodium ion concentration in the blood. Aldosterone is part of the renin-angiotensin aldosterone system .
The second hormone is antidiuretic hormone which causes increase water reabsorption at the collecting duct by increasing the water permeability of the collecting ducts. Water then moves back into the blood by osmosis. More ADH is secreted when the body needs to retain more water and this will lead to a concentrated urine.
You May Like: What Laxative Is Safe For Kidneys
Where Are The Kidneys And How Do They Function
There are two kidneys, each about the size of a fist, located on either side of the spine at the lowest level of the rib cage. Each kidney contains up to a million functioning units called nephrons. A nephron consists of a filtering unit of tiny blood vessels called a glomerulus attached to a tubule. When blood enters the glomerulus, it is filtered and the remaining fluid then passes along the tubule. In the tubule, chemicals and water are either added to or removed from this filtered fluid according to the body’s needs, the final product being the urine we excrete.
The kidneys perform their life-sustaining job of filtering and returning to the bloodstream about 200 quarts of fluid every 24 hours. About two quarts are removed from the body in the form of urine, and about 198 quarts are recovered. The urine we excrete has been stored in the bladder for anywhere from 1 to 8 hours.
Clues From Urine Color
Urine can provide a lot of information about what is going on in the body, including kidney failure. It can be all sorts of colors, from pale yellow to amber, and even pink, orange or green. For healthy urine, the color ranges from pale yellow to amber-colored, depending on the bodys hydration level. Pale yellow urine means high hydration while dark amber means more concentrated urine, indicating dehydration.
The pigment called urobilin causes the yellow color in urine. The kidney filters out this byproduct from the bloodstream and removes it from the body in urine. The more fluids you drink, the lighter the color of this pigment in urine. The less you drink, the stronger the color. For example, during pregnancy there is 50% increase in blood volume, so urine tends to be clearer and more diluted during pregnancy.
Read Also: What Causes Kidney Problems In Humans
Treatment Of Kidney Failure
Kidney failure can be a debilitating and life threatening condition with symptoms such as lethargy, weakness, generalized swelling, shortness of breath, congestive heart failure and fatal heart rhythm disturbances. If your kidney is failing, treatment of the underlying disease may be the first step in correcting the problem.
Many causes of kidney failure are treatable and visiting a urologist will ensure the underlying condition is diagnosed and treated to restore normal function. The urologist may also plan for control of blood pressure, diabetes or other underlying conditions as a way of preventing chronic kidney disease. But in some situations, kidney failure is progressive and irreversible. When that happens, the only treatment options are dialysis or transplant, each with benefits and drawbacks.
Whatever treatment your urologist recommends, you will need to make some changes in your life, including how you eat and plan your activities. With the help of your urologist, family and friends, you can continue to lead a full and active life. For more information on symptoms, diagnosis, treatment and management of kidney failure, visit the St Pete Urology website.
Kidneys: The Main Osmoregulatory Organ
The kidneys, illustrated in Figure 22.4, are a pair of bean-shaped structures that are located just below and posterior to the liver in the peritoneal cavity. The adrenal glands sit on top of each kidney and are also called the suprarenal glands. Kidneys filter blood and purify it. All the blood in the human body is filtered many times a day by the kidneys these organs use up almost 25 percent of the oxygen absorbed through the lungs to perform this function. Oxygen allows the kidney cells to efficiently manufacture chemical energy in the form of ATP through aerobic respiration. The filtrate coming out of the kidneys is called urine.
Don’t Miss: Can Soda Pop Cause Kidney Stones
How Do You Keep Your Kidneys And Urinary System Healthy
How can I keep my urinary system healthy? Drink plenty of water: Staying hydrated will flush out your system and can help you prevent kidney stones and UTIs. Eat a healthy diet: Low sodium, high-calcium foods may prevent kidney stones. Wipe the right way: Women should always wipe front to back after using the toilet.
Components Of The Urinary System
The urinary system consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra. The kidneys form the urine and account for the other functions attributed to the urinary system. The ureters carry the urine away from kidneys to the urinary bladder, which is a temporary reservoir for the urine. The urethra is a tubular structure that carries the urine from the urinary bladder to the outside.
Read Also: Can Soda Pop Cause Kidney Stones
What Are Clinical Trials And Are They Right For You
Watch a video of NIDDK Director Dr. Griffin P. Rodgers explaining the importance of participating in clinical trials.
This content is provided as a service of the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, part of the National Institutes of Health. The NIDDK translates and disseminates research findings to increase knowledge and understanding about health and disease among patients, health professionals, and the public. Content produced by the NIDDK is carefully reviewed by NIDDK scientists and other experts.
The NIDDK would like to thank:Ariana L. Smith, M.D., FPMRS,University of Pennsylvania Health System
How Does Blood Flow Through My Kidneys
Blood flows into your kidney through the renalartery. This large blood vessel branches into smaller and smaller blood vessels until the blood reaches the nephrons. In the nephron, your blood is filtered by the tiny blood vessels of the glomeruli and then flows out of your kidney through the renal vein.
Your blood circulates through your kidneys many times a day. In a single day, your kidneys filter about 150 quarts of blood. Most of the water and other substances that filter through your glomeruli are returned to your blood by the tubules. Only 1 to 2 quarts become urine.
You May Like: Is Club Soda Good For Kidney Stones
What The Color Of Your Urine Means
The color of your pee can offer clues into your health, but kidney disease typically doesn’t show any visible symptoms, so the only way to know if you have it is to get tested. Even if your urine looks okay, kidney damage may be hiding in the form of protein. Get checked to know for sure!
Clear/Pale yellowGood! This means you are well hydrated and have been drinking plenty of water and fluids!
Dark yellowYou might be dehydrated. Drink more water.
Pink to reddishMay be caused by some foods or it may be blood in your urine. Have your doctor test your urine to be sure.
BlueCertain food dyes can turn your urine blue when your body doesn’t absorb them during digestion.
Foamy or fizzy
How The Urinary System Works Step By Step
When you urinate, the brain signals the bladder muscles to tighten, squeezing urine out of the bladder. At the same time, the brain signals the sphincter muscles to relax. As these muscles relax, urine exits the bladder through the urethra. When all the signals occur in the correct order, normal urination occurs.
Read Also: Is Pomegranate Juice Good For Your Kidneys
How Does Urine Form In The Human Being
The Formation of urine Is a complex process that begins in the nephrons and consists of three parts: filtration, reabsorption and tubular secretion.
Urine is a yellow liquid that every human being expels several times a day. This liquid is made up of water and other substances that the body discards, such as urea, uric acid, creatinine, among other compounds.
Throughout history, urine has been considered and used in different ways, depending on the age and culture. In Ancient Rome, this liquid was used to wash the clothes, and was distributed to all the inhabitants of that place.
In China, it was used to make all kinds of cosmetics. Also, it was used as a toothpaste, as an insecticide, for pregnancy tests and how to remove stains. However, the concept that was given to urine in the Middle Ages is the current use: to diagnose various diseases, depending on the color of it.
For example, when urine is red, it may be due to the presence of blood. On the other hand, a brown urine is indicative of a vesicointestinal fistula and thanks to that, a connection between the bladder and the intestine
It is for this utility that urination, that is, the act of urinating, is important in our daily lives. By preventing the expulsion of urine or resist the urge to go to the bathroom our body is affected, contracting different diseases. An example of these are interstitial cystitis, kidney stones, pyelonephritis or vesico-urethral reflux.
Kidney And Urinary System Parts And Their Functions
-
Two kidneys. This pair of purplish-brown organs is located below the ribs toward the middle of the back. Their function is to:
-
Remove waste products and drugs from the body
-
Balance the body’s fluids
-
Release hormones to regulate blood pressure
-
Control production of red blood cells
The kidneys remove urea from the blood through tiny filtering units called nephrons. Each nephron consists of a ball formed of small blood capillaries, called a glomerulus, and a small tube called a renal tubule. Urea, together with water and other waste substances, forms the urine as it passes through the nephrons and down the renal tubules of the kidney.
Two sphincter muscles. These circular muscles help keep urine from leaking by closing tightly like a rubber band around the opening of the bladder.
Nerves in the bladder. The nerves alert a person when it is time to urinate, or empty the bladder.
Urethra. This tube allows urine to pass outside the body. The brain signals the bladder muscles to tighten, which squeezes urine out of the bladder. At the same time, the brain signals the sphincter muscles to relax to let urine exit the bladder through the urethra. When all the signals occur in the correct order, normal urination occurs.
Also Check: What Is The Functional Unit Of The Kidneys
What Are The Parts Of The Urinary System
The kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra make up the urinary system. They all work together to filter, store and remove liquid waste from your body. Heres what each organ does:
- Kidneys: These organs work constantly. They filter your blood and make urine, which your body eliminates. You have two kidneys, one on either side of the back of your abdomen, just below your rib cage. Each kidney is about as big as your fist.
- Ureters: These two thin tubes inside your pelvis carry urine from your kidneys to your bladder.
- Bladder: Your bladder holds urine until youre ready to empty it . Its hollow, made of muscle, and shaped like a balloon. Your bladder expands as it fills up. Most bladders can hold up to 2 cups of urine.
- Urethra: This tube carries urine from your bladder out of your body. It ends in an opening to the outside of your body in the penis or in front of the vagina .
Kidney Function And Physiology
Kidneys filter blood in a three-step process. First, the nephrons filter blood that runs through the capillary network in the glomerulus. Almost all solutes, except for proteins, are filtered out into the glomerulus by a process called glomerular filtration. Second, the filtrate is collected in the renal tubules. Most of the solutes get reabsorbed in the PCT by a process called tubular reabsorption. In the loop of Henle, the filtrate continues to exchange solutes and water with the renal medulla and the peritubular capillary network. Water is also reabsorbed during this step. Then, additional solutes and wastes are secreted into the kidney tubules during tubular secretion, which is, in essence, the opposite process to tubular reabsorption. The collecting ducts collect filtrate coming from the nephrons and fuse in the medullary papillae. From here, the papillae deliver the filtrate, now called urine, into the minor calyces that eventually connect to the ureters through the renal pelvis. This entire process is illustrated in Figure 22.7.
Also Check: Is Aleve Ok For Kidneys
What Color Is Urine When Kidneys Are Failing
- Posted on
- In Blog, Kidney Disease, Kidney Stones
Kidney failure is a condition in which one or both kidneys can no longer work on their own. It may be due to an acute injury to the kidneys or a chronic disease that gradually causes them to stop functioning. When kidneys are healthy, they clean the blood by removing excess fluid, minerals and wastes. But when they are failing, harmful wastes build up in the body and excess fluid is retained, changing the appearance, amount and number of times urine is passed.
How Does Urination Occur
To urinate, your brain signals the sphincters to relax. Then it signals the muscular bladder wall to tighten, squeezing urine through the urethra and out of your bladder.
How often you need to urinate depends on how quickly your kidneys produce the urine that fills the bladder and how much urine your bladder can comfortably hold. The muscles of your bladder wall remain relaxed while the bladder fills with urine, and the sphincter muscles remain contracted to keep urine in the bladder. As your bladder fills up, signals sent to your brain tell you to find a toilet soon.
Read Also: Can You Have 4 Kidneys
Diseases Of The Urinary System
Different specialists treat urinary system ailments. Nephrologists treat kidney diseases, while urologists treat problems with the urinary tract, including the kidneys, adrenal glands, ureters, bladder and urethra, according to the American Urological Association . Urologists also treat the male reproductive organs, while gynecologists often treat urinary diseases or disorders in females, including yeast infections. Nephrologists and urologists often work with endocrinologists or oncologists, depending on the disease.
Urinary tract infections occur when bacteria enter the urinary tract they can affect the urethra, bladder or even the kidneys. While UTIs are more common in women, they can occur in men. UTIs are typically treated with antibiotics, according to Dr. Oscar Aguirre, a urogynecologist in Denver. In the United States, about 8.1 million people have a urinary tract infection each year, according to the American Urological Association.
Incontinence is another common disease of the urinary system. “The most common bladder problems I see in my practice in women are frequent urges to urinate and leakage of urine,” said S. Adam Ramin, urologic surgeon and founder of Urology Cancer Specialists in Los Angeles. “The most common bladder problems in men are frequent urination at nights and incomplete bladder emptying. This is usually due to an enlarged prostate causing obstruction of bladder emptying.”
Additional reporting by Alina Bradford, Live Science contributor.
Aging Changes In The Kidneys And Bladder
The kidneys filter the blood and help remove wastes and extra fluid from the body. The kidneys also help control the body’s chemical balance.
The kidneys are part of the urinary system, which includes the ureters, bladder, and urethra.
Muscle changes and changes in the reproductive system can affect bladder control.
AGING CHANGES AND THEIR EFFECTS ON THE KIDNEYS AND BLADDER
As you age, your kidneys and bladder change. This can affect their function.
Changes in the kidneys that occur with age:
- Amount of kidney tissue decreases and kidney function diminishes.
- Number of filtering units decreases. Nephrons filter waste material from the blood.
- Blood vessels supplying the kidneys can become hardened. This causes the kidneys to filter blood more slowly.
Changes in the bladder:
- The bladder wall changes. The elastic tissue becomes stiffer and the bladder becomes less stretchy. The bladder cannot hold as much urine as before.
- The bladder muscles weaken.
- The urethra can become partially or totally blocked. In women, this can be due to weakened muscles that cause the bladder or vagina to fall out of position . In men, the urethra can become blocked by an enlarged prostate gland.
In a healthy aging person, kidney function declines very slowly. Illness, medicines, and other conditions can significantly degrade kidney function.
COMMON PROBLEMS
Aging increases the risk of kidney and bladder problems such as:
Also Check: Is Watermelon Good For Your Kidneys