Data Sources And Searches
Two investigators independently searched and identified relevant studies from the following data sources: MEDLINE , EMBASE , and the Cochrane Library database using PubMed and Ovid search engines with the text words of randomised controlled trial, chronic kidney disease, and all spellings of known ACE inhibitors and ARBs. Trials were considered without language restrictions. We also searched relevant reference lists from identified trials and review articles. When detailed information that was needed for the analysis was not available, we wrote to the author to request the data.
Rationale: Recommendations For Initiation And Dose Escalation Of Ace Inhibitors And Arbs In Ckd
Strength of Evidence
ACE inhibitors and ARBs have not been tested in all types of CKD. Where tested, ACE inhibitors and ARBs have generally similar effects on blood pressure, urine protein excretion, and slowing the progression of kidney disease . Large, controlled trials have not been performed in all types of CKD, and there have been no direct comparisons of these two agents in any type of CKD. Their comparative efficacy remains unknown. It was the opinion of the Work Group that guidelines should reflect the strength of evidence for each agent in specific types of CKD. Thus, ACE inhibitors and ARBs were preferred for kidney disease with microalbuminuria due type 1 and type 2 diabetes ACE inhibitors were preferred for kidney disease with macroalbuminuria due to type 1 diabetes and nondiabetic kidney disease with urine total protein-to-creatinine ratio 200 mg/g and ARBs were considered preferred agents for kidney disease with macroalbuminuria due to type 2 diabetes. Both classes are preferred for reducing proteinuria. There does not appear to be a substantial difference among the ACE inhibitors, among the ARBs, or between ACE inhibitors or ARBs in regard to their antiproteinuric effects, although these comparisons are difficult due to differences in potency and administered dose.
Rationale: Review Of Physiology And Pharmacology
Renin-Angiotensin System
Fig 54. Physiology of the renin-angiotensin system and sites of action of ACE inhibitors and angiotensin-receptor blockers.
Renin, a proteolytic enzyme, is stored in the juxtaglomerular cells around the afferent glomerular arterioles. Under normal circumstances, it is released in response to stimuli such as reduced kidney blood flow or increased sympathetic tone. Renin acts on the substrate angiotensinogen to form angiotensin I. Angiotensin I undergoes transformation under the activity of several enzymes, including ACE and chymase, to angiotensin II. Angiotensin II has two major target receptors, AT1 and AT2. The stimulation of AT1 receptors, which appears to occur at a greater degree than stimulation of AT2 receptors, leads to significant efferent arteriolar constriction, which would have the effect of increasing the intraglomerular pressure head and maintaining filtration rate. AT2 receptor stimulation appears to produce antagonistic effects on efferent arterioles.
The main effects of angiotensin II are to constrict precapillary arterioles, leading to increased blood pressure, and to stimulate aldosterone release from the adrenal cortex, which in turn causes enhanced renal sodium retention and expansion of circulating blood volume.
Mechanism of Effects of ACE Inhibitors and ARBs to Slow Progression of CKD
Adverse Effects of ACE Inhibitors and ARBs
Fig 55. Physiology of side-effects of ACE inhibitors.
Also Check: Is Celery Juice Good For Kidneys
How Can Diabetic Nephropathy Be Prevented
The best way to prevent kidney damage is to keep your blood sugar in your target range and your blood pressure under control. You do this by eating healthy foods, staying at a healthy weight, exercising regularly, and taking your medicines as directed.
At the first sign of protein in your urine, you can take high blood pressure medicines to keep kidney damage from getting worse.
Do Ace Inhibitors Or Arbs Help Prevent Kidney Disease In Patients With Diabetes And Normal Bp
J Fam Pract
Gregory S. Trietley, PharmD, BCPS Stephen A. Wilson, MD, MPH Parul Chaudhri, DO Nicole Payette, PharmD, BCPSUPMC St. Margaret, Pittsburgh, Pa
Ashley Higbea, PharmD, BCPSTexas Tech University Health Science Center, Dallas
Joan Nashelsky, MLSFamily Physician Inquiries Network, Iowa City, Iowa
DEPUTY EDITOR
You May Like: Is Pomegranate Juice Good For Kidneys
Ace Inhibitors Or Arbs To Prevent Ckd In Patients With Microalbuminuria
JASON M. CORBO, PharmD, BCPS, South Texas Veterans Health Care System, San Antonio, Texas
TERESA M. DELELLIS, PharmD, BCPS, Manchester University College of Pharmacy, Natural, and Health Sciences, Fort Wayne, Indiana
LUCAS G. HILL, PharmD, BCPS, BCACP, The University of Texas at Austin College of Pharmacy, Austin, Texas
SARAH L. RINDFUSS, PharmD, BCPS, Allegheny Health Network, West Penn Hospital Care Partner Clinic, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania
JOAN NASHELSKY, MLS, University of Iowa Center for Human Rights, Iowa City, Iowa
Am Fam Physician. 2016 Oct 15 94:652-653.
Data Extraction And Quality Assessment
We extracted information using standard data extraction forms, which included baseline patient characteristics, intervention, dose of drug, follow-up duration, outcome events, and adverse events. These data were extracted from either studies which were conducted only for CKD35 patients or studies which included subgroup populations with CKD35 at baseline. We used standard criteria to assess the inherent risk of bias of trials, as showed in Table S1. Two investigators independently undertook data extraction and quality assessment using a standardised approach. Any disagreements between the two investigators were resolved by consultation with a third reviewer .
Don’t Miss: Does Red Wine Cause Kidney Stones
When Are Ace Inhibitors Used
ACE inhibitors have many different effects on the body and are used to treat a variety of conditions. They may be used for:
- high blood pressure by relaxing and widening your blood vessels and lowering your blood pressure
- heart failure to help the heart pump blood more easily. This can help to relieve symptoms such as shortness of breath and swelling of feet, legs and abdomen
- diabetic kidney disease to protect your kidneys and help them to function
- chronic kidney disease to slow the progress of kidney disease
- after a heart attack to protect your heart.
ACE inhibitors can work very quickly for high blood pressure . If you have heart failure it may be a few weeks or months before you notice an improvement in your symptoms. Once you have started taking an ACE inhibitor you will generally keep taking it for life unless you have a side effect.The following animation describes how ACE inhibitors work in the body
Role Of Proteinuria: Clinical Data
Clinical studies found a significant correlation between the extent of urinary protein excretion and the rate of GFR decline both in diabetic and nondiabetic chronic nephropathies. A 20-yr observational study in a large white population found that dipstick-positive proteinuria independently predicts risk for ESRD and overall mortality . On the same line, increased urinary albumin excretion predicted increased renal and cardiovascular mortality 8 yr later in a remote Australian Aborigine community .
Studies showed that whenever proteinuria is decreased, progression to ESRD is consistently reduced. The Modification of Diet in Renal Disease study found that a reduction of proteinuria, independent of the reduction in BP, was associated with a decrease in the rate of decline in GFR and that the degree of protection of renal function achieved by lowering BP was dependent on the level of initial proteinuria . The Ramipril Efficacy In Nephropathy study, which recruited patients with nondiabetic chronic nephropathies, also found that a rapid and sustained reduction in proteinuria prevented or limited long-term GFR decline . Patients who had more proteinuria to start with had more benefit from BP-lowering treatment. Finding that the extent of residual proteinuria was also a major determinant of disease progression provided further evidence of the pathogenic role of protein traffic .
Don’t Miss: Is Grape Juice Good For Kidney Disease
How Do Ace Inhibitors Help Renal Failure
CEI inhibitor is commonly used to reduce high blood pressure by renal failure patients. It is the abbreviation of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme inhibitors. Though many kidney failure patients are family with this medicine, seldom of them know how ACE inhibitors help renal failure.
Why ACE inhibitors are used by renal failure patients?
ACE inhibitor is a medication pharmaceutical drug used primarily for the treatment for high blood pressure and weak heart muscle. In cases of renal failure, commonly used ACE inhibitors include
Benazepril, Captopril, Enalapril, Fosinopril, Lisinopril, Perindopril and Quinapril and so on. For renal failure patients, there are several reasons for them to use ACE inhibitors:
1. ACE inhibitors can reduce the workload on the heart. Renal failure is a severe illness condition that cause heart problem easily, so it is necessary to protect heart actively, so as to avoid unnecessary heart problems.
2. ACE inhibitors produce no influence on blood sugar, so for renal failure patients whose kidney problem occur due to Diabetes, ACE inhibitor is the best choice.
3. ACE inhibitors may help to prevent stroke.
How do ACE inhibitors help renal failure?
ACE inhibitors are used to lower blood pressure by renal failure patients. Well then, how do ACE inhibitors work?
Which Medications Are Used To Protect The Kidneys
Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers
Medications that lower blood pressure also help slow kidney disease. Two types of blood pressure medicines, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers , play a special role in protecting the kidneys. Each has been found to slow kidney damage in people with diabetes who have high blood pressure.
These medications either prevent or block a hormone that tells blood vessels to tighten, which allows the blood vessels to open and thus reduce blood pressure. For most people with diabetes, a blood pressure target of less than 130/80 mm Hg is sufficient for kidney protection. Both ACE inhibitors and ARBs can reduce the risk of developing kidney disease in diabetes, independent of their effect on blood pressure, and they can also protect against the progression of kidney disease.
Is special monitoring required for these medications?
It is important that people with diabetes who are taking an ACE inhibitor or ARB have their serum creatinine and potassium levels checked within one to two weeks of starting the medication, when the dosage is increased, or during times of acute illness.
This is important because your healthcare team needs to check your eGFR . Your eGFR is a number based on your blood test for creatinine.
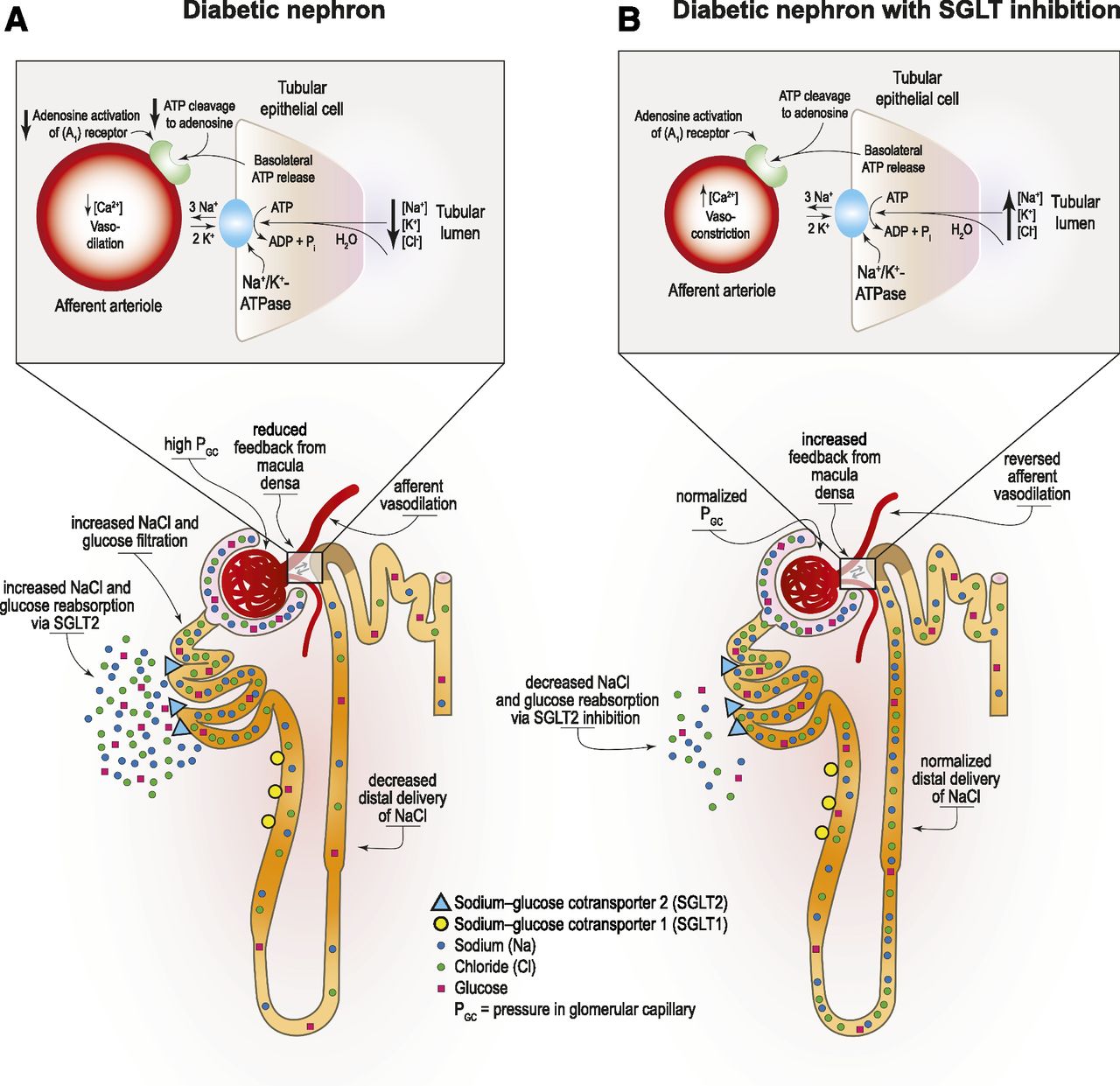
Sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors
What is the effect of SGLT2 inhibitors on kidney health?
Read Also: Does Red Wine Cause Kidney Stones
Correlation Between Degree Of Albuminuria And Cardiovascular Disease
It is likely that leakage of albumin in the urine reflects not only renal damage but widespread vascular damage, and, as such, higher susceptibility to atherosclerosis and CV disease. The exact mechanism for the relation between albumin leakage from the kidney and vascular damage at other places is still not clear. However, recent data show that the vasculature contains a barrier function to albumin leakage, a so-called glycocalyx layer containing large amounts of negatively charged molecules which repel the negatively charged serum albumin. This layer is present in all capillary beds. The decrease in function of this layer will result in more albumin leakage in the kidneys as well as in other places in the body. This may well form a mechanism by which general vascular dysfunction leads to general atherosclerosis and CV events.
Data of 8206 patients with hypertension and LVH from the Losartan Intervention For Endpoint reduction in hypertension study showed similar results. The risk of the composite endpoint over the median follow-up of 4.8 years rose continuously as the baseline albuminuria increased. Similar to findings from a previous study, the data showed that there was no specific threshold for increased CV risk even within the normoalbuminuria range, the incidence of CV events increased with urinary albumin levels. Again, other CV risk factors did not explain the predictive power of albuminuria for CV outcome.
Ace Inhibitors And The Diabetic Kidney
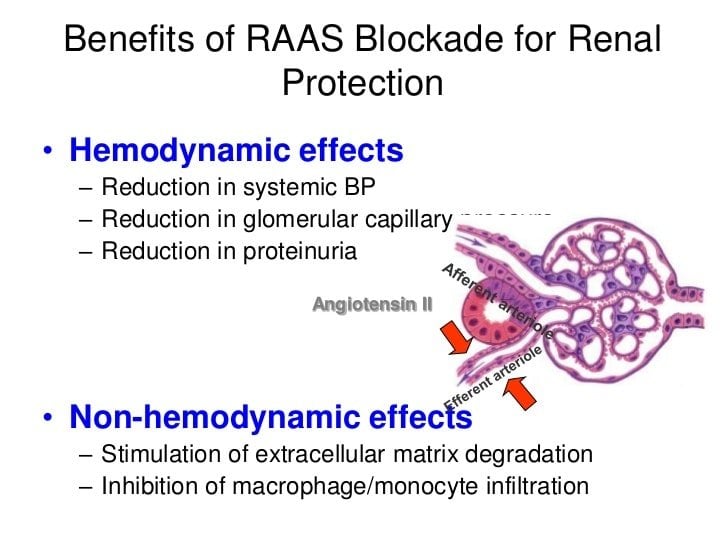
There are a lot of blood-pressure medicines to choose from. For the diabetic patient, not all choices are good ones.
Some blood-pressure medications have the side effect of raising blood sugar levels, and others mask the symptoms of low blood sugar, putting patients at risk of hypoglycemia. For these reasons and more, doctors prefer ACE inhibitors for their diabetic patients.
ACE Inhibitors
ACE inhibitors are a class of drugs that are used to treat high blood pressure. They act to negate the effect of an enzyme in the body which produces angiotensin II.
Angiotensin II causes the muscles surrounding blood vessels to contract, narrowing the arteries, increasing blood pressure and forcing the heart to work harder. ACE inhibitors cause blood vessels to dilate and relax, counteracting the impact of the constricting muscle tension.
Kidney Disease
Diabetic patients are at increased risk for diabetic neuropathy because high blood sugar causes inflammation that damages the epithelial cells lining blood vessels, causing them to become hardened and inflexible and raising blood pressure. Elevated blood pressure can cause damage to the millions of tiny blood vessels that serve as filters in the kidneys. The cumulative effect of this damage is impairment of the filtering mechanisms of the kidney, which is a significant issue for diabetics.
Benefits Beyond Blood Pressure
Side Effects, Etc
Don’t Miss: Does Red Wine Cause Kidney Stones
Recommendations For The Use Of Ace Inhibitors And Arbs In Pregnancy
Definitions
Most ACE inhibitors and ARBs are classified as category C during the first trimester, and category D during the second and third trimesters. There are fewer data available for the ARB class, but the Work Group members have considered them to be similar in effect to ACE inhibitors.
Strength of Evidence
ACE inhibitors and ARBs have adverse effects on the fetus during the second and third trimesters of pregnancy. There appears to be little risk of fetal abnormalities from exposure to ACE inhibitors and ARBs during the first trimester, but they should be discontinued immediately after pregnancy is noted. However, during the second and third trimester, ACE inhibitors and ARBs can cause kidney and lung toxicity and skull hypoplasia. Thus, ACE inhibitors are absolutely avoided during the second and third trimesters. There is limited information about the effect of ARBs in the second and third trimesters. To avoid the risk of fetal abnormalities, the Work Group recommends not using ACE inhibitors or ARBs during pregnancy. ACE inhibitors and ARBs appear in breast milk, but there appears to be no adverse effects on development in the neonate or infant. Recommendations for use in women of child-bearing potential are given in Table 143.
Study Design And Sample
We selected individuals who had initiated monotherapy with an ACEI or ARB from July 1, 2002 through December 31, 2013 and who had also been diagnosed with diabetic nephropathy or with both diabetes and proteinuria at the same visit within 180 days before the first observed ACEI or ARB prescription. Patients were considered as having diabetes if they met one of the following criteria :
1. At least one inpatient diagnosis of diabetes
2. Two or more outpatient diagnoses of diabetes
3. One outpatient diagnosis of diabetes and at least one outpatient prescription of antidiabetic medication at the same visit
We then identified patients who had not received a prescription of ACEIs or ARBs for at least 180 days before the first observed prescription during July 1, 2002 to December 31, 2013 , in order to select the new users of these drugs. To identify stable users, patients were required to have a second prescription of the same ACEI or ARB medication within 100 days following the first observed ACEI or ARB prescription. The second prescription date of the ACEI or ARB then served as the index date.
Also Check: Does Red Wine Cause Kidney Stones
Who Cannot Take Ace Inhibitors
ACE inhibitors are not recommended if you:
- are pregnant or planning a pregnancy they should be avoided at all stages of pregnancy
- are breastfeeding
- have allergic reactions with swelling of your lips, eyes or tongue
- have low sodium, high potassium or low blood pressure
- have certain types of kidney disease such as renal artery stenosis.
Do Arbs Affect Kidneys
ARBskidneyskidneykidney
With respect to progression of the renal disease, ACE inhibitors and ARBs can cause a decline in renal function and a rise in serum potassium that typically occur one to two weeks after the onset of therapy.
Beside above, how do ace and ARBs protect kidneys? ACE inhibitors and ARBs have been shown effective in preventing or at least slowing the process of renal disease in patients with diabetes by interfering with the renin-angiotensin system. ACE inhibitors and ARBs lower intraglomerular pressure by decreasing efferent arteriolar pressure.
In respect to this, are ARBs nephrotoxic?
ACEIs and ARBs inhibit efferent renal arteriolar vasoconstriction that lowers glomerular filtration pressure. The administration of an NSAID plus diuretic or ACEI or ARB may reduce the hypotensive effect of the antihypertensive agent but does not commonly lead to acute renal failure.
Do ARBs increase creatinine?
Increased Creatinine after Starting ACEIs/ARBs May Increase Cardiorenal Risk. Rates of all adverse cardiorenal outcomes were significantly higher for the patients with a 30% or greater increase in creatinine, compared to those with increases of less than 30%.
Don’t Miss: Is Watermelon Good For Your Kidneys
What Conditions Are Ace Inhibitors Used To Treat
Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors are used to treat a number of different conditions:
- High blood pressure – ACE inhibitors usually work well to lower blood pressure.
- Heart failure – ACE inhibitors reduce the strain on the heart by decreasing the amount of fluid pumped around the body. They also help the heart by relaxing blood vessels. This reduces the amount of force needed to eject blood from the heart.
- Diabetic kidney disease – these medicines can help to maintain good kidney function.
- Chronic kidney disease – ACE inhibitors may help to slow the progress of kidney disease.
- After a heart attack .
Each of these medicines also has various different brand names. Some ACE inhibitor medicines are also part of a combined tablet with a calcium-channel blocker medicine or ‘water tablet’ medicine.
Important Information About Sick Day Management
Several classes of medications that are used commonly in people with diabetes can either reduce kidney function during periods of illness or build up to a toxic level as kidney flow is reduced during times of sickness. These medications must be stopped temporarily until the person is well. For more information about managing diabetes when you are ill, including a printable sick day plan, .
It is important that people with diabetes have their blood and urine tested annually for early signs of kidney disease. If there are signs of kidney disease, medications and lifestyle changes can help delay further damage to the kidneys. The earlier kidney disease in diabetes is detected, the better, as it will reduce the chance of progression to advanced kidney disease and the need for dialysis or transplant.
You May Like: Does Red Wine Cause Kidney Stones