What Is Polycystic Kidney Disease
In this section:
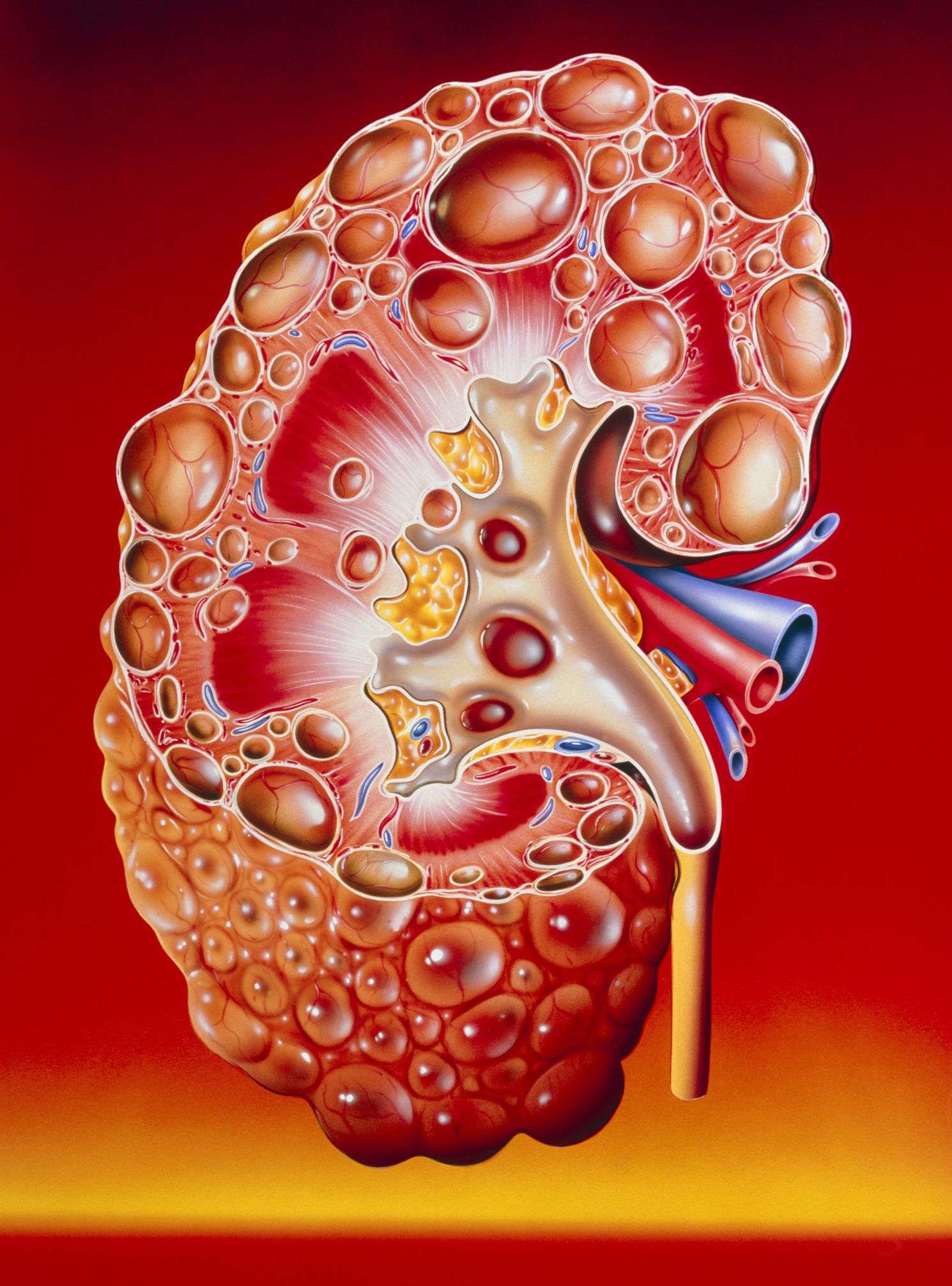
Polycystic kidney disease is a genetic disorder that causes many fluid-filled cysts to grow in your kidneys. Unlike the usually harmless simple kidney cysts that can form in the kidneys later in life, PKD cysts can change the shape of your kidneys, including making them much larger.
PKD is a form of chronic kidney disease that reduces kidney function and may lead to kidney failure. PKD also can cause other complications, or problems, such as high blood pressure, cysts in the liver, and problems with blood vessels in your brain and heart.
What Is The Treatment For Adpkd
There is no cure for ADPKD, but a new treatment is available that has been shown to slow the progression of ADPKD to kidney failure. For more information, .There may be other ways to treat the symptoms of ADPKD and to make you feel better. Talk to your doctor about the best ways to manage your condition.
What Is Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease is one of the most common forms of polycystic kidney disease. It is present at birth in 1 in 400 to 1 in 1,000 babies, and it affects approximately 400,000 people in the United States. ADPKD occurs in individuals and families worldwide and in all races.
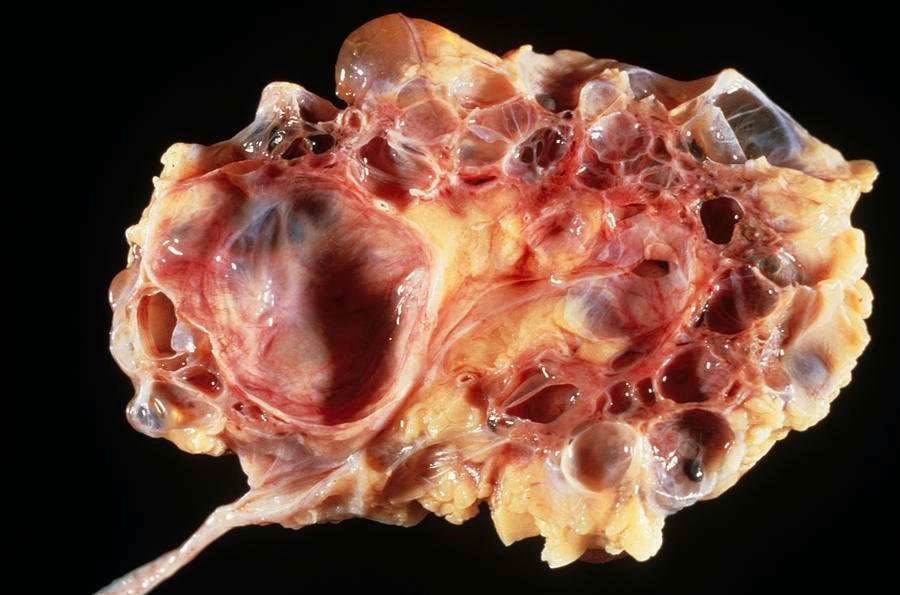
Polycystic kidney disease is a genetic disorder characterized by the growth of numerous cysts in both kidneys. The cysts are filled with fluid. The progressive expansion of PKD cysts slowly replaces much of the normal mass of the kidneys, and can reduce kidney function and lead to kidney failure.
When PKD causes kidneys to fail – which usually happens after many years – the patient requires dialysis or kidney transplantation. About one-half of people with the major type of PKD progress to kidney failure, also called end-stage kidney disease. PKD can also cause cysts in the liver and problems in other organs, such as the heart and blood vessels in the brain.
Also Check: Almond Milk Kidney Disease
Genetic Counselling For Polycystic Kidney Disease
If you or a family member have been diagnosed with PKD, or if PKD runs in your family, it can be helpful to speak to a genetic counsellor. Genetic counsellors are health professionals qualified in both counselling and genetics. As well as providing emotional support, they can help you to understand PKD and what causes it, how it is inherited, and what a diagnosis means for your health, lifestyle, and plans for the future. Genetic counsellors are trained provide information and support that is sensitive to your family circumstances, culture and beliefs.
If PKD runs in your family, a genetic counsellor can explain what genetic testing options are available to you and other family members. You may choose to visit a genetic counsellor if you are planning a family, to find out your risk of passing that condition on to your child, or to arrange for prenatal tests.
is connected with a wide range of support groups throughout Victoria and Australia and can connect you with other individuals and families affected by MCKD.
What Is The Outlook For People With Polycystic Kidney Disease
For most people, PKD slowly gets worse over time. It is estimated that 50 percent of people with PKD will experience kidney failure by age 60. This number increases to 60 percent by age 70. Because the kidneys are such important organs, their failure may start to affect other organs, such as the liver.
Proper medical care can help you manage PKD symptoms for years. If you dont have other medical problems, you may be a good candidate for a kidney transplant.
Also, you may consider speaking with a genetic counselor if you have a family history of PKD and are planning to have children.
Also Check: Kidneys And Apple Cider Vinegar
Is Acquired Cystic Kidney Disease A Type Of Pkd
Acquired cystic kidney disease is not a type of PKD. While ACKD does cause cysts to form inside the kidneys like PKD does, people with PKD are born with it and people with ACKD are not. Instead, ACKD is caused by chronic kidney disease or kidney failure/ESRD. ACKD is more common in people who have had kidney disease for a long time. ACKD happens most often in people who are on dialysis, but the cysts are not caused by dialysis treatments. The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases has more information about ACKD.
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Pkd
The signs and symptoms of ADPKD, such as pain, high blood pressure, and kidney failure, are also PKD complications. In many cases, ADPKD does not cause signs or symptoms until your kidney cysts are a half inch or larger in size.
Early signs of ARPKD in the womb are larger-than-normal kidneys and a smaller-than-average size baby, a condition called growth failure. The early signs of ARPKD are also complications. However, some people with ARPKD do not develop signs or symptoms until later in childhood or even adulthood.
Also Check: Can I Take Flomax Twice A Day For Kidney Stones
Mutations In Other Ciliary Genes May Mimic Arpkd
In rare instances, especially in the prenatal setting and during early childhood, polycystic kidney disease may be mimicked by mutations in genes that typically cause other, usually more complex ciliopathies such as BardetBiedl, Joubert, and Meckel syndrome .
BardetBiedl syndrome is usually characterized by obesity, hypogonadism, retinal degeneration, polydactyly, mental retardation, and renal malformations. Various additional features such as hearing loss, diabetes mellitus, and other metabolic defects have also been described. Renal disease is a major cause of morbidity and mortality in BBS and can be heterogeneous in phenotype, but often presents with features of ARPKD or ADPKD with enlarged, hyperechogenic kidneys, and loss of corticomedullary differentiation. Currently, more than 20 BBS genes have been identified and ALMS1, the causative gene for Alstrom syndrome which has significant phenotypic overlap with BBS.
What Is The Treatment For Polycystic Kidney Disease
The most common treatments for PKD include:
- Blood pressure management: Your provider helps you control your blood pressure with medicine, diet and exercise. Keeping your blood pressure within a safe range reduces your risk of heart disease and stroke.
- Breathing support: Infants with underdeveloped lungs and breathing problems may need mechanical ventilation.
- Dialysis: If you have kidney failure, you may need dialysis . Hemodialysis uses a machine to filter blood outside the body. Peritoneal dialysis uses the lining of your belly and a special fluid to filter blood.
- Growth therapy: Underweight or underdeveloped infants may need help growing. A healthcare provider may recommend nutritional therapy or human growth hormone.
- Kidney transplant: You may need a kidney transplant if ADPKD progresses to end-stage renal failure. A transplant is surgery to replace a failing kidney with a donor kidney.
- Pain management: Medicine can control pain caused by infections, kidney stones or burst cysts. Your healthcare provider should approve any pain medicines you take. Some medicines can make kidney damage worse.
Recommended Reading: Is Apple Cider Vinegar Bad For Kidneys
Symptoms Of Polycystic Kidney Disease
The most common symptom is high blood pressure. About 60% of people who have PKD also have high blood pressure, which can be treated with medicine. Other symptoms include:
- Pain in the back and side.
- Blood in the urine.
- Frequent kidney infections.
Not all patients will have all of these symptoms. For many people, PKD is mild and causes only minor problems. For others, PKD is more severe and can cause kidney failure. About 50% of patients who have PKD have kidney failure by age 60. Dialysis and kidney transplants are both effective treatments for kidney failure.
People who have PKD may also have cysts in the liver, but these cysts seldom cause problems. Other organs that may be affected include the heart, brain, intestines, pancreas, ovaries, and spleen. PKD can cause problems with heart valves in some people. When PKD affects the brain, it can cause an aneurysm .
How Is Pkd Treated
At present, there is no cure for PKD. However, a lot of research is being done. Recent studies suggest that drinking plain water throughout the day and avoiding caffeine in beverages can slow the growth of cysts. Research is also helping us understand the genetic basis of PKD.
Studies also suggest that some treatments may slow the rate of kidney disease in PKD, but further research is needed before these treatments can be used in patients. In the meantime, many supportive treatments can be done to control symptoms, help slow the growth of cysts, and help prevent or slow down the loss of kidney function in people with PKD. These include:
- careful control of blood pressure
- prompt treatment with antibiotics of a bladder or kidney infection
- lots of fluid when blood in the urine is first noted
- medication to control pain
- a healthy lifestyle with regard to smoking cessation, exercise, weight control and reduced salt intake
- drinking lots of plain water throughout the day
- avoiding caffeine in all beverages
In April 2018, the FDA approved a new drug called tolvaptan for the treatment of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease . The drug can be used to help slow kidney function decline in adults at risk for this type of PKD. You can speak with a healthcare professional for more information about this treatment and if its right for you.
Also Check: Can Apple Cider Vinegar Hurt Your Kidneys
Are There Any Risk Factors Or Groups For Polycystic Kidney Disease
Polycystic kidney disease is, for the most part, an inherited disorder. People whose parents have polycystic kidney disease are at risk of developing either ADPKD or ARPKD.
People who have had different types of kidney disease and used dialysis as a form of treatment are at risk of developing acquired polycystic kidney disease.
Research Into Polycystic Kidney Disease
PKD is an active area of research both for scientists, like Dr Jill Norman, who study the genetics and disease at the microscopic and molecular level and for doctors who conduct clinical trials. We have learnt much about blood pressure control and the use of drugs to reduce kidney and liver cysts. Future research studies are focussed on understanding how cysts form in the first place and stopping or slowing down the disease at a very early stage.
Read Also: Can Kidney Stones Increase Blood Sugar
Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease
About 90% of polycystic kidney disease cases are ADPKD, and this form affects anywhere from 1 in every 400 to 1 in 1,000 people worldwide, says NIDDK. It’s passed to you from either your mom or dad by something called dominant inheritance. That means you need only one copy of the abnormal gene to cause the disease. Every child of a parent with that gene has a 50% chance of getting ADPKD, says the NKF.
Symptoms Of Kidney Disease In Children
Polycystic Kidney Disease Symptoms In Adults Aug 26, 2021 · The most common primary cause of nephrotic syndrome in adults is a disease called focal segmental glomerulosclerosis . The only way to know for sure whether you have FSGS is to get a kidney biopsy . ADPKD is often diagnosed in adulthood. It used to be called adult polycystic kidney disease. The
The young girl was recently diagnosed with a condition called dense deposit disease, a very rare kidney disease that attacks.
There can be kidney or gastrointestinal troubles that persist for years. There can be staggering hospital bills that for some.
A salmonella outbreak sickened more than 60 people at a funeral reception in Texas. Two years later, some of them are still.
It can be caused by infection, an autoimmune disease , or an unknown reason. The first symptoms of nephritis usually are high levels of protein and blood in the urine. Urinary tract infections . Symptoms of Kidney Problems. The signs and symptoms of urinary tract or kidney problems vary and include: fever
Common Mistakes in Reducing Kidney Stones Esenler Medipol University Hospital, Department of Urology Op. Dr. Nuh Aldemir.
This 77-Year-Old Multiple Myeloma Survivor Serves as a Beacon of Hope for Others Fighting the Incurable Disease Gerry Auths cancer journey began before he was even diagnosed with multiple myeloma. It began in 2012 when he was diagnosed.
Read Also: Grapes And Kidney Stones
How Is Pkd Diagnosed
Ultrasound is the most reliable, inexpensive and non-invasive way to diagnose PKD. If someone at risk for PKD is older than 40 years and has a normal ultrasound of the kidneys, he or she probably does not have PKD. Occasionally, a CT scan and MRI may detect smaller cysts that cannot be found by an ultrasound. MRI is used to measure and monitor volume and growth of kidneys and cysts.
In some situations, genetic testing might also be done. This involves a blood test that checks for abnormal genes that cause the disease. Genetic testing is not recommended for everyone. The test is costly, and it also fails to detect PKD in about 15% of people who have it. However, genetic testing can be useful when a person:
- has an uncertain diagnosis based on imaging tests
- has a family history of PKD and wants to donate a kidney
- is younger than 30-years old with a family history of PKD and a negative ultrasound, and is planning to start a family
Are There Different Types Of Polycystic Kidney Disease
There are two types of polycystic kidney disease:
- Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease : ADPKD is the most common form of PKD. Its usually diagnosed in adulthood, between the ages of 30 and 50. ADPKD is usually diagnosed in adulthood, between the ages of 30 and 50, but it may occur in early childhood or adolescence.
- Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease : ARPKD is a rare form of PKD, also called infantile PKD. It causes abnormal kidney development in the womb or soon after birth.
Recommended Reading: Is Ginger Good For The Kidneys
Take Blood Pressure Medicines
If lifestyle and diet changes dont help control your blood pressure, a health care provider may prescribe one or more blood pressure medicines. Two types of blood pressure medicines, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers , may slow kidney disease and delay kidney failure. The names of these medicines end in pril or sartan.
What Makes Yale Medicines Approach To Treating Polycystic Kidney Disease Unique
The Yale Medicine Chronic Kidney Disease Program offers patients the opportunity to receive care from nephrologists, liver disease experts, aneurysm experts and geneticists who can explain the nuances of inherited disorders to patients and skillfully manage the illness.
Yale Medicine offers opportunities for patients with polycystic kidney disease to take part in clinical trials to better explain the disease and to evaluate new treatment approaches. The experts at Yale Medicine also continue to study the mechanisms underlying the cyst formation.
We hope these studies will lead to the development of therapies, Dr. Somlo says. We focus on research that we can translate into the care of our patients.
Recommended Reading: Is Apple Cider Vinegar Good For The Kidneys
What Protein Causes Polycystic Kidney Disease
GFR values of 60 to 90 are characteristic of Stage 2 chronic kidney disease. (Stage 1 has normal GFR, but abnormal protein in the urine.
Chronic kidney disease as a cause of cardiovascular.
Polycystic kidney disease causes numerous cysts to grow in the kidneys. These cysts are filled with fluid. If too many cysts grow or if they get too big, the kidneys can become damaged. PKD cysts can slowly replace much of the kidneys, reducing kidney function and leading to kidney failure.
Kidney disease, or renal disease, technically referred to as nephropathy, is damage to or disease of a kidney. Nephritis is an inflammatory kidney disease and has several types according to the location of the inflammation. Inflammation can be diagnosed by blood tests. Nephrosis is non-inflammatory kidney disease. Nephritis and nephrosis can give rise to.
Healthy Protein For Kidney Disease AV-001 is a novel investigational medicine that targets the Tie2 receptor, a transmembrane protein. disease pathophysiology in patients with COVID-19, including respiratory distress, Try a unique kidney diet recipe for
Research interests The major research goals of my laboratory have been to define the molecular basis of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease.
UK Renal GeCIP investigating genetic causes of.
The etiology is unclear, but may result from different mechanisms, including developmental and acquired causes.
and polycystic diseases, including autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease.
What Causes Autosomal Dominant Pkd
ADPKD is caused by a problem with a specific gene. It is almost always inherited from a parent who also has ADPKD. To inherit the disease, a child needs to have just one parent with ADPKD. On average, if both parents have ADPKD, there is a 75% chance that their child will also be born with PKD.
The genetic problem that causes ADPKD can sometimes happen on its own, meaning that a child may be born with ADPKD, even though neither parent has it. This happens in only 1 out of every 10 cases of ADPKD.
Don’t Miss: Is Watermelon Bad For Your Kidneys
What Causes Autosomal Recessive Pkd
Like ADPKD, autosomal recessive PKD is an inherited disease. In this case, however, a child may be born with the disease only if both parents are carriers of the gene that causes it. A carrier is someone who has the gene, but does not have the disease. When both parents are carriers of the gene that causes ARPKD, their child has a 1 in 4 chance of being born with ARPKD. The child has a 1 in 2 chance of being a carrier of the gene that causes ARPKD and a 1 in 4 chance of neither having the disease nor being a carrier of the gene. The disease usually does not affect every generation of a family.