What Are The Possible Complications Of Urinary Retention
The complications of urinary retention and its treatments may include:
UTIs: the normal flow of urine usually prevents germs from infecting the urine. With urinary retention, bacteria may be able to infect the urine because the urine cannot flow out of the bladder.
Bladder damage: if the bladder becomes stretched too far or for long periods, the muscles may become damaged and unable to work properly.
Chronic kidney disease: for some people, urinary retention causes urine to flow backwards into the kidneys. This backward flow is called reflux and it may damage or scar the kidneys.
Urinary incontinence: this may occur together with chronic urinary retention or after surgery .
Prostate gland surgery may cause urinary incontinence in some men. This problem is often temporary and gets better quite quickly. Most men recover their bladder control in a few weeks or months after surgery.
Searching For The Evidence: Literature Search Strategies For Identification Of Relevant Studies To Answer The Key Questions
We will utilize bibliographic database searching to identify previous systematic reviews, randomized controlled trials, and observational studies published from 1946 to the present for studies enrolling adults based on a diagnosis of CUR. Relevant bibliographic databases for this topic include MEDLINE® and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials . Our preliminary search strategy appears in Appendix A. This search strategy searches on only one concept, CUR, and employs relevant Medical Subject Headings and natural language terms to find studies on the topic. The concept search is supplemented with filters designed to select experimental designs. Bibliographic database searches will be supplemented with backward citation searches of highly relevant systematic reviews. We will update searches while the draft report is under public/peer review.
We will conduct additional grey literature searching to identify relevant completed and ongoing studies. Relevant grey literature resources include trial registries and U.S. Food and Drug Administration databases. We will search ClinicalTrials.gov and the International Controlled Trials Registry Platform . We will also review Scientific Information Packets sent by manufacturers of relevant interventions. Grey literature search results will be used to identify studies, outcomes, and analyses not reported in the published literature to assess publication and reporting bias.
Rhabdomyolysis And Aki With Opioids
In the setting of non-medical opioid use with dehydration, immobility, and with decreased respiratory drive, there is a drop in MAP, renal blood flow, GFR, and hypoxia. In addition, frequently there may be other toxins involved as with polysubstance abuse.
Myocyte hypoxia and immobility result in muscle damage, starting with hypoxia and resultant ATP depletion leading to an increase in unregulated intracellular calcium and a cascade of destruction with further muscle damage, which results in lysosomal digestion of muscle. The muscle breakdown products and other intra-cellular components are released into the serum and these include myoglobin, phosphate, potassium and other markers like creatinine phosphokinase .
You May Like: Can Kidney Infection Cause Diarrhea
Not Sure What To Do Next
If you are still concerned about your urinary retention, why not use healthdirects online Symptom Checker to get advice on when to seek medical attention.
The Symptom Checker guides you to the next appropriate healthcare steps, whether its self care, talking to a health professional, going to a hospital or calling triple zero .
What Are The Symptoms Of Kidney Failure
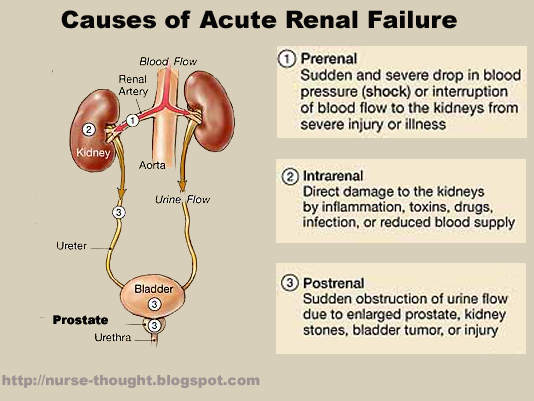
Initially, kidney failure may cause no symptoms. Many symptoms and signs of kidney failure are due to the buildup of waste products and fluid retention in the body. Symptoms and signs can include edema , weakness, shortness of breath, confusion, and lethargy.
You May Like: Whats Kidney
How Can I Spot The Symptoms
Acute urinary retention is extremely painful and causes abdominal bloating.
There may not be any noticeable symptoms with chronic urinary retention, but symptoms can include urinary incontinence and urinary tract infections, an increased urge to wee more frequently, difficulty getting started and producing a weak or interrupted stream of urine when weeing. There may also be mild abdominal discomfort.
Causes Of Water Retention Due To Kidney Disease And Kidney Damage
Whenever a person suffers from a kidney disease, sodium and additional fluid in the circulation may cause the problem of water retention. Furthermore, damage to the nephrons or filtering blood vessels present in the kidney may cause nephritic syndrome, because of which declining albumin/protein present in the blood result in accumulation of fluid and the problem of water retention. Based on the facts mentioned here, water retention mainly occurs in patients with kidney problems because of two major reasons, which include:
Also Check: What Std Messes With Your Kidneys
How Does A Stroke Affectyour Bladder
Since a stroke causes neurological damage to the body, the nerves that control the bladder can also be damaged.
Nerves play a big role in the process of urination. When you urinate, the nerves that control the bladder trigger the bladders detrusor muscle to contract and push urine into the urethra, and the nerves also signal to the urethral sphincters to relax and let urine flow out of the body. When you are not urinating, the nerves signal the detrusor muscle to relax and the sphincter to contract to keep the urine in.
After a stroke, nerves controlling the bladder can be damaged. Because nerves can no longer properly signal to the bladder, this can lead to frequent urination , inability to hold in urine , sudden urge to urinate or inability to urinate .
Grading The Strength Of Evidence For Individual Comparisons And Outcomes
The overall strength of evidence for select clinical outcomes within each comparison will be evaluated based on four required domains: study limitations directness consistency and precision .13 A fifth domain, reporting bias, will be assessed when the strength of evidence is moderate or high based on the first four domains.13 Risk of bias will be rated as low, medium, or high according to study design and conduct. Consistency will be rated as consistent, inconsistent, or unknown/not applicable . Directness will be rated as either direct or indirect. Precision will be rated as precise or imprecise. Other factors that may be considered in assessing strength of evidence include dose-response relationship, the presence of confounders, and strength of association. Based on these factors, the overall evidence for each outcome will be rated as:13
Also Check: Can Seltzer Water Cause Kidney Stones
What Are The Complications Of A Neurogenic Bladder
The following are often linked to a neurogenic bladder:
- Urine leakage often happens when the muscles holding urine in do not get the right message.
- Urine retention happens if the muscles holding urine in do not get the message that it is time to pass urine.
- Damage to the tiny blood vessels in the kidney may happen if the bladder becomes too full and urine backs up into the kidneys. This causes extra pressure and may lead to blood in the urine.
- Infection of the bladder, ureters, or kidneys often results from urine that is held too long before its passed out of the body.
Renal System Dysfunction Caused By Lyme Disease
The renal system is a vital part of the overall functioning of the body. Without the ability to filter the blood, it can lead to the aforementioned symptoms and conditions.
The damage done to the renal system following a Lyme disease infection can:
- Cause the kidney filtration system to cease functioning, or function at a lower level.
- Aid in the formation of lesions on the kidneys.
- Cause the build-up of waste in the bloodstream.
- Lead to the leakage of proteins and red blood cells out of the system.
- Eventually cause kidney disease or kidney failure.
Recommended Reading: Constipation And Kidney Stones
How Is Urinary Retention Treated
For men, urinating in a sitting position may be helpful in reducing urinary retention. Additionally, there are a variety of medical interventions for treating urinary retention in both women and men.
Tamsulosin, finasteride, and dutasteride When a mild case of benign prostatic hyperplasia is causing the urinary retention, some patients may be treated with these medications. Tamsulosin is designed to relax smooth muscles in the bladder neck, and finasteride and dutasteride are prescribed to decrease prostate enlargement.
Prostatic stents or suprapubic cystostomy In acute urinary retention, placement of a prostatic stent or suprapubic cystostomy can relieve the retention.
Catheters Acute urinary retention may be treated by placement of a urinary catheter into the bladder.
Alpha-blockers Alpha-blockers may be used to provide relief of urinary retention following de-catheterization for both men and women.
Transurethral resection In most patients with benign prostate hyperplasia , a procedure known as transurethral resection of the prostate may be performed to relieve bladder obstruction.
Open Prostatectomy This is the surgical removal of the prostate gland done under a general or spinal anesthetic.
If You Suffer From Urinary Retentioncheck Out Compactcath
We produce catheters that are compact, mess-free, non-touch, and pre-lubricated. They are discreetly designed, convenient, and perfect for those who lead an active life.
CompactCath® is designed at Stanford d.school. It is FDA-cleared in 2014, holds six patents, covered by CNN Money, won two grants and two iF product design awards .
You May Like: Can You Have 4 Kidneys
Symptoms Of Water Retention Because Of Kidney Disease
Water retention because of kidney disease may involve the following major symptoms-
- Person suffering from water retention may have symptoms of puffiness or swelling of tissues, which remain present directly beneath the skin, particularly in the arms or legs of a person
- Shiny or stretched skin is a symptoms of water retention
- Skin to retain pits or dimples after pressed for a period of many seconds
- Increase in the size of ones abdomen is also a sign of water retention because of kidney disease.
When Should I See A Health Care Professional
See a health care professional right away if you are unable to urinate or have severe pain in your abdomen. Acute urinary retention can be life threatening.
If you have any of the other symptoms of urinary retention, such as trouble urinating, frequent urination, or leaking urine, talk with your health care professional about your symptoms and possible treatments. Chronic urinary retention can cause serious health problems.
Recommended Reading: High Blood Pressure Kidney Pain
Clinical Events And Treatment Of Aki Due To Opioids
Clinically, opioids can result in AKI from changes in GFR, dehydration, rhabdomyolysis and urinary retention. The presentation of opioid overdose may be with hypopnea or apnea, miosis, and stupor. The combination of decreased respiratory drive, hypoxia, a drop in renal blood flow and GFR results in renal tubular damage. Dehydration with signs of volume depletion and hypotension may be noted. Confusion or a change of mental status could be seen.
The drop in renal blood flow would activate renal sympathetics, furthering the effect of renal ischemia and tubular damage. Overall cardiac output and mean arterial pressure decreases are noted. Physical examination should include a careful evaluation for muscle tenderness the only finding in a comatose patient may be muscle edema that could reflect the start of muscle necrosis. Abdominal examination may reveal a palpable distended bladder from urinary retention.
Once this stage is reached, with decreased kidney function, metabolism of opioids may further change depending on the specific drug. With morphine, for example, there is an increase in the mean peak concentration and the area under the concentration-time curve for both active and principle metabolites which could further worsen respiratory depression.
In the setting of methodone use, an electrocardiogram should be done early to determine if there is QT interval prolongation that could lead to arrhythmias.
Enlarged Prostate Complications: Urinary Retention Hematuria Bladder Stones And Urinary Tract Infections
Written byEmily LunardoPublished onSeptember 15, 2016
Benign prostatic hyperplasia is a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate. There are two prostate growth periods: one during early puberty and another around the age of 25. As it grows, the gland can press and pinch the urethra, and the bladder walls thicken. Over time, the bladder can become weaker and lose its ability to empty fully. If the urethra continues to narrow and the bladder still cant empty, complications associated with benign prostatic hyperplasia can arise.
Benign prostatic hyperplasia does not increase a mans risk of developing prostate cancer. Prostate cancer begins in the outer peripheral zone and grows outward to invade surrounding tissue. In BPH, the growth moves inward towards the prostates core, causing the urethra to become tighter and making it difficult to urinate.
The growth dynamics of BPH determines the symptoms. BPH can have annoying symptoms, such as the inability to urinate or releasing a small amount only.
Hormonal changes that occur through aging contribute to the BPH onset. Genetics, too, can be a possible cause for BPH. The prostate continues to grow from the age of 25, but when the prostate grows too much, it can cause complications in older men.
Recommended Reading: Is Grape Juice Good For Kidneys
First Some Fast Facts
There are two types of strokes, ischemic stroke, and hemorrhagic stroke.
The ischemic stroke is the more common one, and it occurs when a blood clot blocks a blood vessel in the brain, causing brain cells to quickly die from the lack of blood circulation and oxygen, which in turn causes the body to lose some neurological functions. The ischemic stroke can also occur when plaque builds up inside an artery, causing it to narrow and eventually become blocked.
If you have suffered a mini ischemic stroke , you are at risk of suffering a more serious one.
Hemorrhagic stroke is the second type, and it happens when the blood vessel bursts or leaks.
In the United States, stroke is the fifth leading cause of adult death and disability, and nearly 800,000 people experience strokes each year.
These conditions can make you more at risk of stroke: diabetes, heart disease, obesity, and high cholesterol level.
Surgery For Women With Cystocele Or Rectocele
Women may need surgery to lift a fallen bladder or rectum. The most common procedure for cystocele and rectocele repair is for the surgeon to make an incision in the wall of the vagina to find the defect or hole in the membrane-a wall of tissue called fascia-that normally separates the vagina from the other pelvic organs. The surgeon places sutures in the fascia to close up the defect, then closes the incision in the vaginal wall with more stitches, removing any excess tissue. These suturing steps tighten the layers of tissue that separate the organs, creating more support for the pelvic organs.
You May Like: Is Mulberry Good For Kidneys
Common Causes Of Urinary Retention
Examples of some of the most common causes of non-obstructive urinary retention are:
A pelvic fracture is a break that affects the structure of the pelvis, which can include the hip bones, sacrum, or coccyx, and be extremely painful. If complications occur, it may lead to internal bleeding or an injury to the bladder.
Certain medications, such as antihistamines, and antispasmodic drugs which aid digestion, can cause urinary retention. They decrease bladder muscle contraction, preventing the bladder from being completely emptied.
Antidepressant meds have anticholinergic properties at therapeutic doses that contribute to urinary problems.
The side effects of anesthetics after surgery can impair muscle or nerve function of the bladder. The pain-relieving drugs often have a disruptive impact on the neural messaging to the part of the brain, which controls the nerves and the muscles in the urinary process.
Accidents that injure the brain or the spinal cord can also impact negatively on the neurological process of the urinary system.
Fortunately, no matter what type of urinary retention you may have, there is treatment available.
Symptoms Causes & Treatments

Urinary retention can happen at any age, though it most commonly occurs in males aged 50+, and often due to an enlarged prostate . However, urinary retention can also occur in females, typically due to a condition known as cystocele which is when the bladder sags or moves out of its normal position.
A condition known as rectocele can also cause urinary retention in both sexes when the bladder is pulled out of position by the colon. In addition to age-based conditions, people of all ages, male or female, can have nerve disease or damage that can interfere with the bladder function.
Urinary retention is the inability to empty urine from the bladder and can be characterized as acute or chronic. Acute urinary retention usually occurs suddenly and temporarily. Individuals suffering from acute urinary retention are unable to empty their bladder at all they can feel the urge to urinate, but cant go at all.
This can be potentially life-threatening as pressure is built up in the bladder and may lead to a rupture. This causes a great deal of discomfort or pain in the lower abdomen. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to seek emergency medical attention immediately to release the buildup of urine.
You May Like: Is Honey Good For The Kidneys
What Are The Symptoms Of Urine Retention
Chronic urine retention, or urinary retention, usually begins with mild symptoms that progressively worsen with time. In chronic urinary retention, you are usually able to urinate, but with some degree of difficulty. Symptoms of chronic urinary retention include:
-
Constant, mild bladder discomfort, which you can feel just above the pubic bone or lower abdomen
-
Difficulty in starting to urinate
-
Dribbling when not urinating
Neurogenic Bladder Treatment And Home Remedies
Your care will depend on whatâs causing your symptoms and how serious they are. Thereâs no cure for neurogenic bladder, but you can manage your symptoms and get control.
If you have OAB, you may need to:
- Train your bladder. You can do this by squeezing your pelvic floor muscles during the day or when you need to pee .
- Hold it, if you can. Delayed voiding is when you wait a few minutes to urinate after you feel the urge. The goal is to extend this time to a few hours.
- Pee on a schedule. You might avoid accidents if you urinate at certain times of the day.
- Take medicine. Some medications can relax bladder muscles and stop spasms.
- Keep a healthy weight. Extra body mass can add pressure to your bladder.
- Change your diet. Things like caffeine, alcohol, spicy foods, dairy, artificial sweeteners, chocolate, and citrus fruit can irritate your system.
- Use electrical stimulation. A device under your skin sends electricity to the nerve that controls your bladder. These painless pulses help stop overactive signals that tell your brain to pee.
- Get Botox. Your doctor can inject this neurotoxin into your bladder to temporarily stop it from contracting too much. If you have problems emptying your bladder or have urinary tract infections often, this treatment isn’t an option.
If you have UAB, you may need to:
You May Like: Wine For Kidney Stones