Symptoms Of Kidney Infection
Symptoms of pyelonephritis often begin suddenly with chills, fever, pain in the lower part of the back on either side, nausea, and vomiting.
, including frequent, painful urination. One or both kidneys may be enlarged and painful, and doctors may find tenderness in the small of the back on the affected side. Sometimes the muscles of the abdomen are tightly contracted. Irritation from the infection or the passing of a kidney stone can cause spasms of the ureters. If the ureters go into spasms, people may experience episodes of intense pain . In children, symptoms of a kidney infection Urinary Tract Infection in Children A urinary tract infection is a bacterial infection of the urinary bladder , the kidneys , or both. Urinary tract infections are caused by bacteria. Infants and younger… read more often are slight and more difficult to recognize. In older people, pyelonephritis may not cause any symptoms that seem to indicate a problem in the urinary tract. Instead, older people may have a decrease in mental function , fever, or an infection of the bloodstream .
In chronic pyelonephritis, the pain may be vague, and fever may come and go or not occur at all.
Are There Risk Factors For Pyelonephritis
There are several developmental conditions that increase the risk for pyelonephritis.
- Ectopic ureters describe a condition in which the ureters do not attach to the bladder properly or may attach to reproductive organs instead of the bladder.
- Vesicoureteral reflux describes backflow of urine from the bladder back into the ureters.
- Renal dysplasia describes abnormal development of the kidneys from birth.
There are several medical and procedural conditions that increase the likelihood of urinary tract infection including:
- Diabetes mellitus, causing glucose in the urine, making the urine very attractive to bacteria.
- Cushingâs disease , or overactive adrenal glands, causing increased levels of steroids in the body and decreasing the bodyâs resistance to infection.
- Administration of medications containing steroids.
- Kidney failure.
When Does A Uti Turn Into A Kidney Infection
What happens if a UTI goes untreated? If left untreated, the E. coli or other bacteria that caused your urinary tract infection can move farther up your urinary system.
When they reach your upper urinary system , you may experience a kidney infection, medically known as pyelonephritis.
Most people seek medical help and receive treatment before they get to this point.
Most often, the bacteria involved in a kidney infection are the same that caused the initial bladder or urethral infection. In rare instances, bacteria from your skin or the environment can cause a kidney infection.
Any condition that reduces or obstructs urine flow increases your risk of contracting a kidney infection as it allows bacteria to more easily flow from the bladder, up the ureters, to the kidneys. These conditions include:
- Kidney, bladder, or ureter stones
- Masses in the abdomen or pelvis caused by cancer or other disorders
You May Like: Can Urine Retention Cause Kidney Damage
How Is A Kidney Infection Diagnosed
Your doctor will ask about your symptoms, do a physical exam, and likely run some diagnostic tests. Those include a urinalysis, to check your pee under a microscope for bacteria and white blood cells, which your body makes to fight infection, and a urine culture to help find out what kind of bacteria is causing the infection, the NIDDK says. Your doctor may even take a blood sample to check for bacteria or other organisms in your blood, the Mayo Clinic says.
Other tests that might come up include an ultrasound, a CT scan, or a form of X-ray called a voiding cystourethrogram, which involves injecting a contrast dye to take X-rays of your bladder when its full and while youre peeing, per the Mayo Clinic.
Differences Between Uti And Pyuria Without Uti
To clarify the effect of UTI, we divided the patients by episodes of UTI, which was less frequent than pyuria.> 1UTI episode was associated with an increased risk of ESRD with a HR of 1.90 . The associations of> 1UTI episode with rapid GFR decline and all-cause mortality were also significant. To clarify the effect of pyuria without UTI, we selected 2661 patients without any UTI episodes and without any high grade urine WBC and then divided them by episodes of pyuria .> 2 episodes of pyuria without UTI were associated with an increased risk of ESRD with a HR of 3.53 .> 2 episodes of pyuria without UTI were associated with rapid GFR decline, but not with all-cause mortality. Because the risk of pyuria without UTI for renal outcomes was numerically higher than that with UTI, we further compared the differences between baseline parameters. eGFR and UPCR were associated with pyuria without UTI, but not with UTI in multivariate logistic regression .
Table 5 Association between UTI or pyuria without UTI and clinical outcomes.
Recommended Reading: Can Heart Failure Cause Kidney Problems
Use Your Health Insurance Just Like You Normally Would To See Your Doctor
During your UTI treatment, you can take steps to ensure that you get the maximum effect out of your antibiotics while promoting your own comfort.
- Use a heating pad on your abdomen to soothe any pain and discomfort and relieve pressure.
- Drink plenty of water to help flush out the bacteria in your urinary tract.
- Avoid any food and drink that may irritate your urinary system. This includes coffee, alcohol, and sugary sodas that contain citrus juice or caffeine.
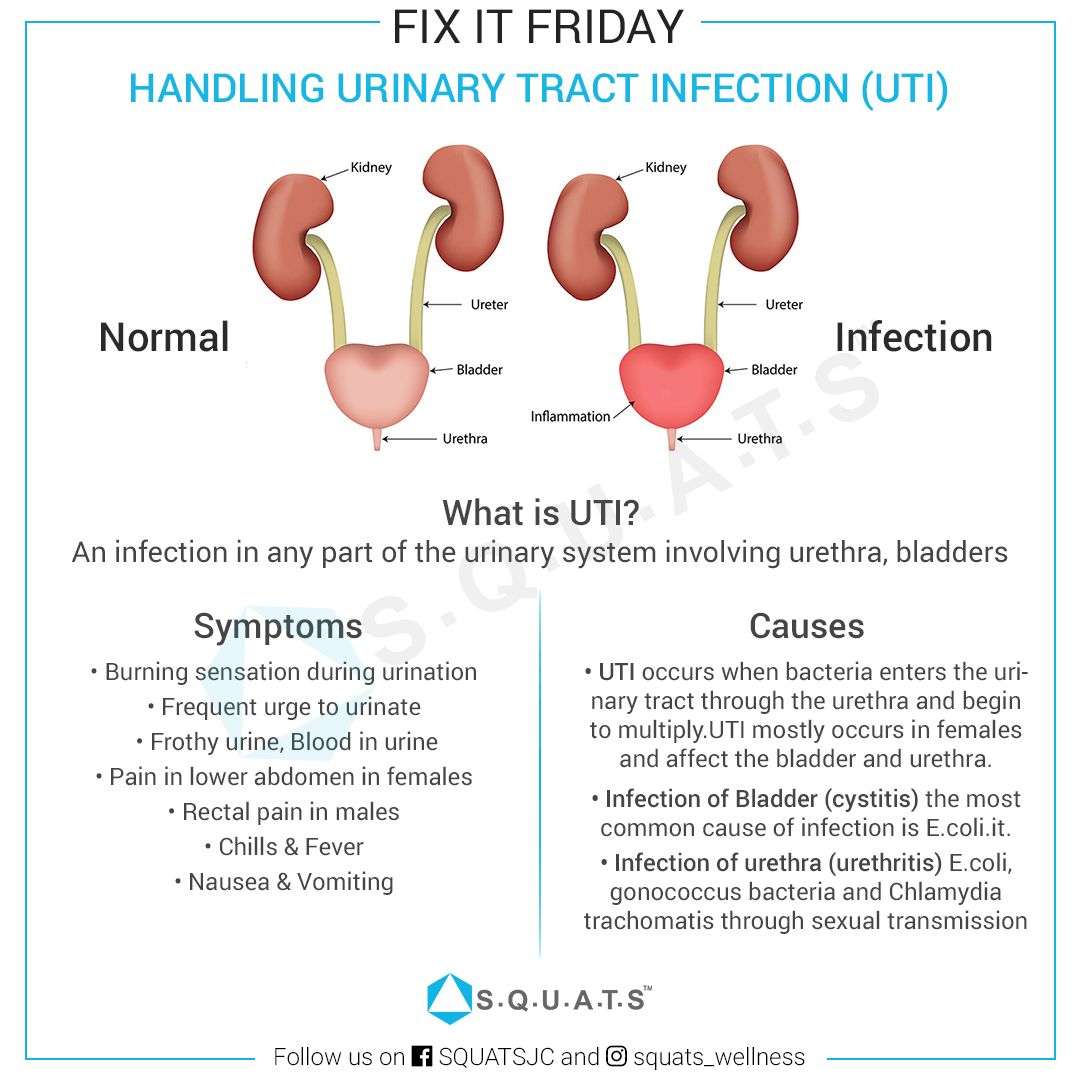
What Is A Urinary Tract Infection
UTIs are common infections that happen when bacteria, often from the skin or rectum, enter the urethra, and infect the urinary tract. The infections can affect several parts of the urinary tract, but the most common type is a bladder infection .
Kidney infection is another type of UTI. Theyre less common, but more serious than bladder infections.
Also Check: How To Save Kidneys Naturally
How Common Are Urinary Tract Infections
Urinary tract infections are very common, occurring in 1 out of 5 women sometime in their lifetime. Though UTIs are common in women, they can also happen to men, older adults and children. One to 2% of children develop urinary tract infections. Each year, 8 million to 10 million visits to doctors are for urinary tract infections.
How To Prevent Utis In Seniors
Older adults can help prevent UTIs by drinking plenty of fluids to flush the bacteria from their systems, Forciea says. She recommends older adults drink four to six 8-ounce glasses of water a day. Forciea further notes that drinking cranberry juice or taking cranberry tablets also can make urine less inviting for bacteria.
Use these strategies to help prevent UTIs in elderly women:
- Urinating promptly after the urge arises
- Wiping front to back
- Emptying the bladder shortly after sex
- Taking showers instead of baths
If your loved one has frequent UTIs or other challenges that require help with daily tasks, consider talking to one of our Senior Living Advisors about home care or senior living options that can improve their quality of life.
Recommended Reading: Is Honey Good For Kidney
Read Also: Can Too Many Eggs Cause Kidney Stones
How Are Kidney Infections Diagnosed
Two common laboratory tests are performed to diagnose kidney infections . A urine sample is examined under a microscope to determine if white and/or red blood cells are present. The urine is also sent to the lab to see if bacteria grow in a urine culture. If a person is very sick, blood cultures may also be sent. The strain of bacteria that are cultured will determine the type of therapy used in your treatment.
Pyelonephritis can often be treated without X-ray studies, unless your doctor suspects there may be an addition problem. CT scans produce images of structures and organs and these scans are usually done without contrast . A renal ultrasound may sometimes suffice for evaluation.
When Should I Go To The Doctor For A Uti
Any time youre suffering from symptoms that are similar to those of a urinary tract infection, you should visit a doctor to receive a proper diagnosis.
These symptoms include pain or burning when you urinate, blood in your urine, an urgent feeling to urinate, frequent urination in small amount, fever or chills, back pain, pain over the bladder or cloudy or dark urine.
If youve been diagnosed with a UTI and are currently being treated with an antibiotic, there is a good chance you wont need to return to your doctor.
However, if do not feel your symptoms going away after youve completed your antibiotics, its a good idea to go back to the doctor.
At CareNow®, were staffed with experienced healthcare providers who are trained in family practice, emergency medicine or internal medicine.
Rest at home instead of a doctors waiting room by using the CareNow® Web Check-In® before your visit too.
With more than 100 locations throughout the United States, its never been easier to receive the quality medical care you deserve when and where its convenient for you
Disclaimer: Patients health can vary. Always consult with a medical professional before taking medication, making health-related decisions or deciding if medical advice is right for you.
You May Like: How To Know If You Have Bad Kidneys
Don’t Miss: What Is The Best Hospital For Kidney Cancer
Drink Plenty Of Liquids
Drinking plenty of liquids, particularly water, will help to wash bacteria from your bladder and urinary tract.
Drinking cranberry juice or taking cranberry extracts may also help prevent urinary tract infections . However, you should avoid cranberry juice or extracts if you’re taking warfarin, a medicine used to prevent blood clots. Cranberry juice can make the effects of warfarin more potent, so there’s a risk of excessive bleeding.
Risks Of Uti And Comorbidities
Apart from the impaired immune defence associated with CKD, the risk for developing UTI also depends on the underlying kidney disease. High-risk groups are patients suffering from diabetic nephropathy, nephrotic syndrome, and hypoproteinaemia, patients with analgesic nephropathy, autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease, Randall plaques , and renal stone formers. Among them, one may also find those with congenital errors of the metabolism: cystinosis, oxalosis, chloride channel mutations, Fabrys disease, Dents disease, Bartter syndromes , renal tubular acidosis, idiopathic hypercalciuria, hypocitraturia, familiar hypomagnesiaemia, nephrolithiasis, genetic defects of the calcium-sensing receptor, etc. Obstructive nephropathy associated with an increased risk for UTI may arise from papillary necrosis and/or exfoliation of tissue debris into the tubular lumen, most commonly in ischaemia as well as diabetic and analgesic nephropathy. A variety of primary kidney diseases , membranous GN, focal sclerosing glomerulopathy) are treated with immunosuppressive agents. Early diagnosis of UTI may be missed easily in those patients with no or only minor clinical symptoms. In a similar manner, CKD patients suffering from systemic vasculitis, autoimmune disease, and renal allograft dysfunction should be closely monitored for UTI. Typical signs of an infection are often completely missing in these cases.
Read Also: Can Smoking Weed Cause Urinary Problems
You May Like: Can Kidney Patient Drink Coffee
What Is A Kidney Infection Symptoms Causes Diagnosis Treatment And Prevention
A kidney infection, also known as pyelonephritis, occurs when harmful bacteria reach your kidneys as part of a urinary tract infection .
Most UTIs dont involve the kidneys. They affect only your lower urinary tract, meaning your urethra and bladder. But sometimes an infection that begins there moves into your upper urinary tract, affecting one or both kidneys.
Its also possible to get a kidney infection following surgery, if bacteria enter your body during the procedure and travel through your bloodstream to your kidneys. In this case, your lower urinary tract may not be affected.
If you have symptoms of a UTI or bladder infection such as pain with urination, smelly urine, low back pain, or discolored urine its important to seek medical treatment to prevent the infection from spreading to your kidneys.
Kidney infections can be quite painful and require prompt evaluation and treatment. If your infection isnt treated soon enough, it may permanently damage your kidneys or spread to your bloodstream, possibly leading to and the impairment of other vital organs.
Treatment For Utis Vs Kidney Infection Treatment
UTIs, including kidney infections, can be treated with a course of antibiotics. The type of antibiotic can depend on the type of bacteria thats causing your infection as well as how severe your infection is.
The doctor will often start you on an antibiotic that works against a wide variety of UTI-causing bacteria. If a urine culture is performed, the doctor may switch your antibiotic to one thats most effective at treating the specific bacterium thats causing your infection.
Simple UTIs can be treated with short 3- to 5-day courses of antibiotics. Treatment for kidney infections generally lasts 7 to 14 days, depending on which class of antibiotic is prescribed.
You may begin to feel better after only a few days on antibiotics. However, you should still make sure that you complete your entire treatment course as prescribed. If you do not take all of your antibiotics, the stronger bacteria may not be killed, causing your infection to persist and flare up again.
If youre pregnant, your doctor may also request a repeat urine sample following a kidney infection, even if your symptoms have resolved. This allows them to check to see whether your infection has completely cleared.
If there are still bacteria present in the sample, you may need another course of antibiotics. Persistence of bacteria can potentially harm an unborn baby.
People with severe kidney infections may need to be hospitalized. In this case, you may receive antibiotics and fluids intravenously.
Recommended Reading: Where Does Kidney Pain Hurt
Baseline Parameters Associated With Pyuria
In the multivariate logistic regression analysis, older age, females, DM, CV disease, higher CRP, and higher HbA1c had a higher odds ratio for pyuria . In contrast, higher hemoglobin, albumin, cholesterol and eGFR had a lower OR for pyuria. Glomerulonephropathy and proteinuria were not associated with pyuria, whereas tubulointerstitial nephropathy was associated with pyuria.
Table 3 Association between pyuria and parameters by multivariate logistic regression.
Duration Of Antimicrobial Therapy
There are no valid published data from randomized trials determining the optimal duration of treatment of UTI in patients with CKD and in dialysis patients. It is customary to treat even uncomplicated cystitis for at least 7 days and to continue for 21 days or more, depending on clinical severity , . However, the response to even longer courses of antibiotics in higher dosage may only be transitory. Even if the urinary concentration of the antibiotic is adequate, the underlying infection may not be eradicated, thus leading to a relapse after the end of antimicrobial treatment.
Recurrent UTI presumably occur due to bacterial regrowth from colonies of non-planktonic bacteria residing in a protected biofilm environment. Persistent microbial niches may develop and colonize deeply within damaged renal parenchymal or urothelial tissue. Furthermore, antibiotic therapy may select highly resistant intracellular, ecologically stable bacterial communities living temporarily as commensals, so-called small colony variants .
Importantly, recent studies have confirmed again that any infection irrespective of severity is an independent risk factor for increased adverse events in the CKD population .
Also Check: How Can Your Kidneys Get Damaged
What Are The Signs Of Pyelonephritis
Many dogs have no clinical signs when they have pyelonephritis, although they may have signs of lower urinary tract disease. The signs of lower urinary tract infection include:
- increased drinking and increased urination
- difficult/painful urination
- frequent urination of small volumes of urine
- inappropriate urination
- slow, uncomfortable urination
Additional signs of upper urinary tract infection include fever and pain when the kidneys are palpated during the physical examination. Also, one or both kidneys may be abnormal in size.
The Link Between Uti And Dementia In Older Adults
Your elderly loved one with dementia may suddenly start displaying more severe behavioral symptoms of this disease and you may wonder why. There could be a simple reason behind it all. They could have a urinary tract infection, or UTI. This is a very common phenomenon in elderly dementia patients. Even if your loved one hasnt officially been diagnosed with dementia, you may notice that dementia-like symptoms, such as confusion, come on fairly quickly. Often, this can be traced to the development of a UTI. Whether your loved one is being cared for in a nursing home, in home care, or in hospice, you may wonder why this link exists. Lets explain why.
According to Alzheimers.net, if a senior patient already has dementia, a urinary tract infection may cause behavior changes instead of the physical symptoms that may plague a younger person. Whereas most otherwise healthy people display physical symptoms like burning when urinating, elderly patients may not complain of such pain. However, they may start to behave erratically, which is usually what tips off health care providers. If not detected early, infection can lead to serious health problems.
You May Like: What Does A Small Kidney Mean
How Are Urinary Abnormalities Diagnosed
It’s important for a doctor to rule out any underlying problems in the urinary system when a child gets UTIs repeatedly. Kids with recurrent infections should see a pediatric urologist to see what is causing the infections.
Some problems can be found before birth. Hydronephrosis that develops before birth can be seen in an ultrasound as early as 16 weeks. In rare cases, doctors may consider neonatal surgery if hydronephrosis affects both kidneys and is a risk to the fetus. Most of the time, though, doctors wait until after birth to treat the condition, because almost half of all cases seen prenatally disappear by the time a baby is born.
Doctors will closely watch the blood pressure of a newborn thought to have hydronephrosis or another urinary system abnormality, because some kidney problems can cause high blood pressure. Another ultrasound may be done to get a closer look at the bladder and kidneys. If the condition appears to be affecting both kidneys, doctors usually will order blood tests to check kidney function.