Primarily Cardiovascular Disease Leading To Kidney Dysfunction
Mechanisms by which cardiovascular disease can lead to kidney dysfunction include activation of the RAAS and the sympathetic nervous system or glomerular injury secondary to deposition of antigenantibody complexes.
Examples include:
- Systemic hypertension leading to glomerular disease
- Cardiac shock, low cardiac output, and systemic hypotension leading to decreased renal perfusion, azotemia, and acute kidney injury
- Heartworm infection leading to glomerulonephritis
- Caval syndrome leading to AKI
How Are Chronic Kidney Disease And Cardiovascular Disease Related
It is understood that the underlying pathology and manifestation of CVD differ in the presence of CKD. CKD is a known important and independent risk factor for CVD. CKD can lead to many cardiovascular issues such as coronary artery disease, heart attack and congestive heart failure. A common complication in CKD patients, which can lead to cardiovascular problems, is anemia. In a CKD patient with anemia, damaged kidneys are not able to produce adequate amounts of a hormone called erythropoietin, which stimulates bone marrow to produce red blood cells. Since red blood cells carry oxygen to the entire body, a lack of oxygen to the bodies tissues and organs can make a person susceptible to organ failure or a heart attack. Furthermore, high blood pressure, another common complication in patients with CKD, can increase the risk of heart attack and congestive heart failure.
Chronic Kidney Disease And Your Heart
According to the Center for Disease Control , heart disease is the leading cause of death in the United States and stroke is the third leading cause. Both of these conditions are caused by cardiovascular disease. Cardiovascular disease is common in people with chronic kidney disease regardless of age, stage of kidney disease or if theyve had a transplant. In addition, underlying conditions that cause renal disease, such as high blood pressure and diabetes, put people at risk for cardiovascular disease.
What is cardiovascular disease?
The adult human heart is about as big as two clenched fists and weighs about 11 ounces. It pumps oxygen and nutrient-rich blood through the arteries to vital organs, including your brain and tissues. Cardiovascular disease is an umbrella term used to describe conditions that affect the heart and blood vessels .
Cardiovascular disease can affect the function of the heart and the blood vessels, leading to serious health problems. A breakdown or interruption in oxygen supply to your organs will cause damage and possibly death. If you suffer from CVD, life-sustaining organs like your heart and brain are at risk.
Many chronic kidney disease patients suffer from heart disease, which is a type of CVD. Heart disease is a general term to describe any cardiovascular disease that affects the heart and/or the blood vessels in the heart. The following conditions are considered heart disease:
Chronic kidney disease and the risk of cardiovascular disease
Read Also: Acv Kidney
Interactions Between Hf And Dm
DM is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease , cardiovascular mortality, and a more severe disease course. The likelihood of developing CVD is 1.5-fold higher in patients with DM than in patients without DM, and the likelihood of experiencing CV-related events is higher in patients with severe or uncontrolled DM . Furthermore, DM increases the risk of developing HF, with greater risk observed in women with DM than in men with DM . The high prevalence of HF and increased risk of new-onset HF in individuals with DM compared to individuals in general or matched populations support a shared pathogenesis between the 2 conditions.
DM can contribute to the development of both CVD and HF via cellular, molecular, and systemic mechanisms, which have been described extensively elsewhere . In brief, DM is characterized by hyperglycemia and insulin resistance, which trigger a cascade of deleterious effects. In particular, these features can drive inflammation, dyslipidemia, endothelial dysfunction , and autonomic dysfunction . Conversely, HF may be an independent risk factor for DM through mechanisms related to neurohormonal activation and chronic inflammation . Metabolic risks may be further heightened by the use of glucose-lowering medication that can increase the risk of mortality and hospitalization in patients with or without HF .
Effects Of Kidney Transplantation On Cardiac Structure And Function
J Am Coll Cardiol.
- Gottlieb S.S.
- et al.
J Am Coll Cardiol.J Am Coll Cardiol.Transplantation.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol.Clin Nephrol.Postgrad Med J.Med J Aust.Transplant Proc.Echocardiography.
- Espinoza R.
- Gracida C.
Transplant Proc.
- Bocksch W.
- et al.
Transplant Proc.
- Debska-Slizien A.
- Rutkowski B.
Transplant Proc.Am J Cardiol.Ann Intern Med.
- Gottlieb S.S.
- et al.
J Am Coll Cardiol.
Also Check: Is Apple Cider Vinegar Bad For Kidneys
Are Kidney Disease And Heart Failure Linked
Because March is National Kidney Month, we are exploring how the heart and kidneys are connected. According to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, heart disease is the most common cause of death among people who have kidney disease. But how are kidney disease and heart failure linked? And what can be done to prevent them?
Recommended Reading: Wine And Kidney Stones
Over Time High Blood Pressure Harms Renal Blood Vessels
The nephrons in the kidneys are supplied with a dense network of blood vessels, and high volumes of blood flow through them. Over time, uncontrolled high blood pressure can cause arteries around the kidneys to narrow, weaken or harden. These damaged arteries are not able to deliver enough blood to the kidney tissue.
- Damaged kidney arteries do not filter blood well. Kidneys have small, finger-like nephrons that filter your blood. Each nephron receives its blood supply through tiny hair-like capillaries, the smallest of all blood vessels. When the arteries become damaged, the nephrons do not receive the essential oxygen and nutrients and the kidneys lose their ability to filter blood and regulate the fluid, hormones, acids and salts in the body.
- Damaged kidneys fail to regulate blood pressure. Healthy kidneys produce a hormone called aldosterone to help the body regulate blood pressure. Kidney damage and uncontrolled high blood pressure each contribute to a negative spiral. As more arteries become blocked and stop functioning, the kidneys eventually fail.
You May Like: Watermelon Renal Diet
You May Like: Kidney Pain Std
Research Is Revealing More About Sars
While kidney damage in COVID-19 is still not well understood, more data will reveal how this occurs. Sperati, who also conducts research on kidney disease, says the Johns Hopkins Division of Nephrology is exploring exactly how SARS-CoV-2 and the bodys response to it is affecting kidney health.
He says that patients with COVID-19-related kidney damage should follow up with their doctors to ensure kidney function is returning to normal. Lasting kidney damage might require dialysis or other therapies even after recovery from COVID-19.
Mostly, Sperati stresses the importance of adhering to guidelines around physical distancing and hand-washing, the basics of prevention. For everyone, especially people with underlying chronic disease, avoiding infection with COVID-19 for as long as you can is crucial, he says.
Right now, we dont have a treatment or vaccine for this disease. The longer a person can go without getting infected, the better chance they have of benefiting from a future therapy.
Coronavirus
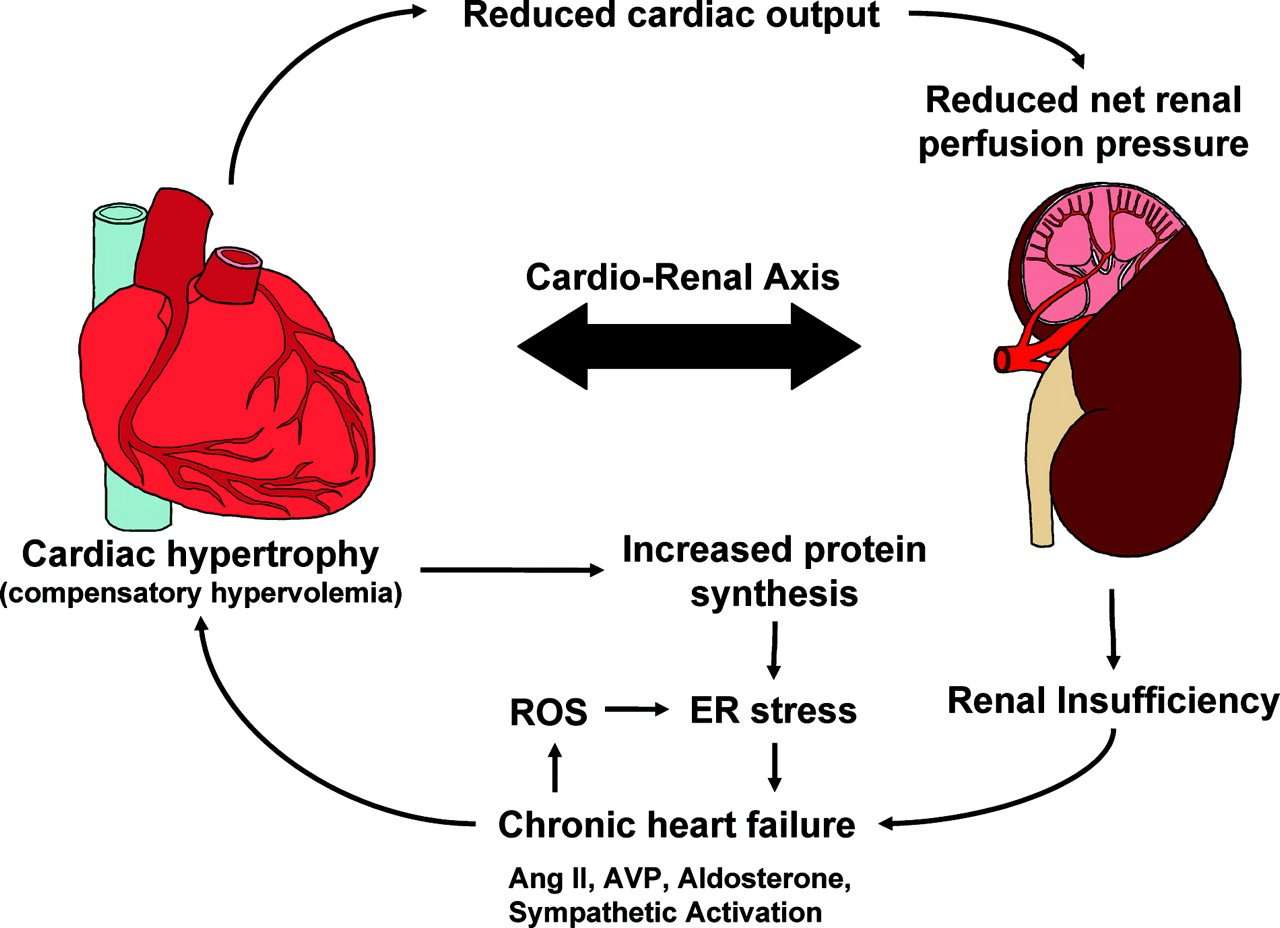
Physiologic Link Between Heart And Kidneys
Both the heart and the kidneys play a role in volume regulation and can directly or indirectly influence endocrine responses that affect fluid balance. The kidneys are one of the bodys primary volume monitors. Glomerular filtration rate is a surrogate indicator of extracellular volume status. If an animal is dehydrated or acutely volume depleted, renal perfusion will drop and GFR will decrease. This response triggers the release of renin from the juxtaglomerular apparatus in the kidney, the starting point for the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system .
Don’t Miss: Does Diet Coke Cause Kidney Stones
And The Worse The Kidney Problems The Greater The Odds Of The Heart Condition Researchers Say
THURSDAY, Aug. 10, 2017 — People with failing kidneys are at increased risk of developing a life-threatening abnormal heart rhythm, a new report suggests.
Chronic kidney disease can as much as double a patient’s risk of atrial fibrillation, a quivering or irregular heartbeat that can lead to stroke or heart failure, said lead researcher Dr. Nisha Bansal. She is an associate professor of nephrology at the University of Washington’s Kidney Research Institute, in Seattle.
The risk of atrial fibrillation increases as kidney function declines, Bansal said.
“We saw the worse your kidney function, the greater your risk of developing atrial fibrillation. Even mild changes in kidney function were strongly linked to atrial fibrillation,” Bansal noted.
The study included data gathered from three separate research projects focused on heart health in the United States. The three projects created a combined pool of almost 17,000 patients with follow-up periods averaging between 8.5 years and 12.5 years. None of the participants had atrial fibrillation when first recruited.
Each project checked participants’ kidney function when they first joined the study, using one or two different lab tests. One was a blood test that evaluated how well the kidneys were removing toxins from the bloodstream. The other was a urine test that assessed whether the kidneys were properly filtering out a specific protein.
More information
Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology
Filter Assisted Sample Preparation And Itraq Labeling
Protein lysates of HF and Controls were processed by filter assisted sample preparation essentially as FASP method as described each in two technical replicates according the following scheme: 114-HF , 115-Control , 116-HF , 117 Control . The iTRAQ labelling was integrated into the FASP workflow as described . In total three iTRAQ analyses were performed according the same scheme.
Don’t Miss: Apple Cider Vinegar Kidney
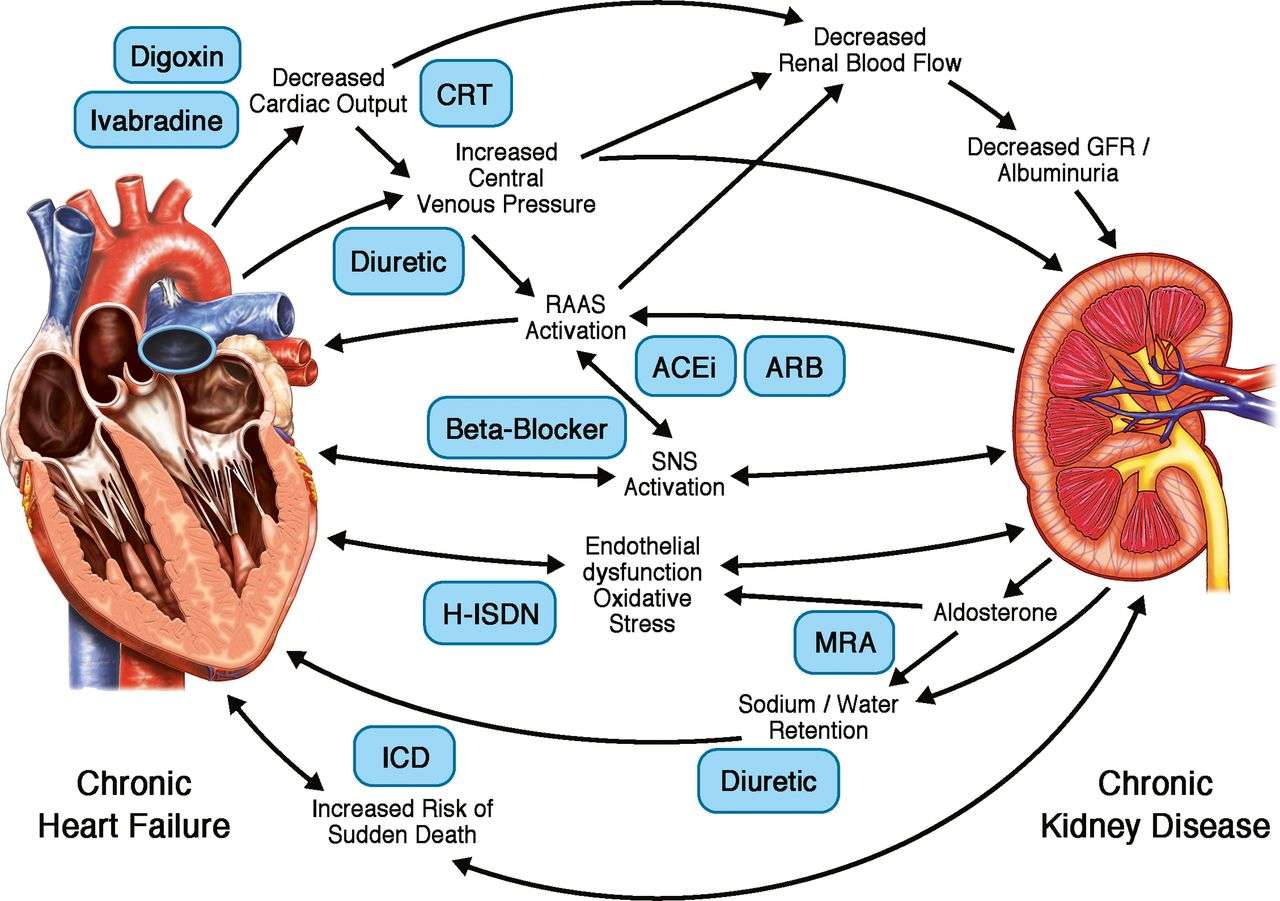
How Do Doctors Treat Heart Disease
If you have heart disease and CKD, your doctor may prescribe medicines to treat your heart disease.
Medicines to treat heart disease include:
- Diuretics : Medicines that lower blood pressure, remove extra fluid and help your kidneys get rid of water and salt.
- Ace inhibitors: Heart medicines that widen your blood vessels, lower blood pressure and improve blood flow.
- Beta blockers: Medicines that lower blood pressure by blocking the hormone adrenaline, which helps your heart beat more slowly and with less force.
Some of these medicines may cause problems with your kidneys. Talk to your doctor about which medicines could work best for you.
Your doctor will also encourage you to make healthy life changes, such as to be active and eat kidney-friendly foods. They can help you find a dietitian to create a healthy eating plan.
Recognizing Renal Disease In Dogs And Cats With Cardiovascular Disease
In dogs and cats, a routine cardiovascular workup and systemic health examination will probably identify most concurrent renal compromise, although some abnormalities may be subtle. For example, a dog may have International Renal Interest Society stage 1 or 2 CKD 7 but still have a serum creatinine concentration within the reference range . The only evidence of intrinsic renal disease may be poorly concentrated urine . Note that cats and dogs receiving diuretic therapy for heart failure will have a low urine specific gravity thus, urine specific gravity is best evaluated before diuretic therapy is initiated.
For patients with known renal compromise , the need for cardiovascular diagnostics and imaging should be carefully considered. For dogs and cats with all forms of kidney disease, measurement of systemic blood pressure is always indicated to identify hypertension that can cause end-organ damage.
Dogs
Sometimes, a useful biomarker for early CKD in dogs is serum symmetric dimethylarginine . This marker correlates well with measurements of GFR and usually increases before serum creatinine levels suggest renal compromise.8 Alternatively, a dog with well-concentrated urine but substantial proteinuria may have renal disease that might be missed without further testing . For dogs with proteinuria, heartworm testing is appropriate.
Cats
Read Also: Flomax For Kidney Stones In Woman
Chronic Kidney Disease Often Leads To Cad
There are two reasons people with chronic kidney disease have a high risk of developing CAD.
For one thing, population studies have shown that people with chronic kidney disease tend to have a high incidence of typical risk factors for CAD. These include smoking, diabetes, high cholesterol, hypertension, sedentary lifestyle, and older age.
But even without such associated risk factors, chronic kidney disease itself greatly increases the risk of CAD. Kidney disease increases this risk by several mechanisms. For instance, the toxins that accumulate in the blood because of abnormal kidney function increase the risk for CAD. Other blood and metabolic abnormalities associated with chronic kidney disease also increase the risk. These include abnormal calcium metabolism, anemia, a chronic inflammatory state , poor nutrition, and elevated blood protein levels.
Taken together, these risk factors appear to produce generalized endothelial dysfunction, a condition associated with CAD and other cardiovascular conditions including hypertension, diastolic dysfunction, and cardiac syndrome x.
As a result, not only is CAD prevalent in people with chronic kidney disease, but also the CAD associated with kidney disease appears to be more severe, and to respond more poorly to treatment.
How Is Heart Disease Treated
If the tests show that you might have heart disease, you will be sent to see a specialist heart team. Although the damage to your heart may not be able to be repaired, there are a variety of treatments that can help to manage your symptoms.
Lifestyle changes
Stopping smoking, reducing how much alcohol you drink, eating a healthy diet and doing regular exercise can help both your heart and kidneys. These changes can help with your symptoms and reduce the risk of your heart disease getting worse.
Medicines
You may be prescribed several different medicines including:
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors to help relax and open your blood vessels and reduce your blood pressure
- Angiotensin receptor blockers to help relax blood vessels and bring down your blood pressure
- Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists to help you pass more urine, lower your blood pressure and reduce some of the fluid around your heart
- Diuretics to help you pass more urine and reduce ankle swelling and breathlessness
- Beta blockers which regulate the heartbeat and helps to ensure that the heart rate is not too fast. This helps reduce the work of the heart.
You will need regular blood tests while taking these medicines.
If you have severe heart disease your doctor may discuss further treatment options. These may include:
Coronary angiograms
Device implants
Surgery
Although heart disease is usually treated with medicines, in severe cases surgery may be needed. Possible operations include:
Also Check: Does Soda Pop Cause Kidney Stones
How Can I Prevent Heart Disease
The best way to prevent heart disease is to work with your doctor to find and treat the problems that can lead to heart disease, such as diabetes, high blood pressure and anemia.
You can also help prevent heart disease by making healthy life choices, including to:
- Eat kidney-friendly foods that are low in salt and fats
- Take your medicines exactly how your doctor told you
- Be active most days of the week to help lower blood pressure and improve blood flow, such as walking, biking or swimming
- Quit smoking, if you smoke
- Lower stress by learning ways to relax such as calm breathing, yoga or meditation
Ask your doctor about other ways to lower your chance for heart disease if you have CKD.
What Is Chronic Kidney Disease
Chronic kidney disease mainly comprises persistent reduction of kidneys blood-filtering ability, expressed as glomerular filtration rate below 60 ml/min/1.73 m2 for more than 3 months. It is also diagnosed if certain markers of kidney damage are identified in blood or urine tests, or imaging studies.
Recommended Reading: Is Apple Cider Vinegar Good For Your Kidneys
How Can I Prevent Kidney Disease And Heart Disease
You cannot always prevent kidney disease and heart disease. However, you can lower your chance of having kidney disease and heart disease by taking the following steps:
- See your health care provider as directed.
- Keep your blood pressure below 140/90. Follow your providers advice on how to stay at or below your target.
- Control your blood glucose if you have diabetes.
- Have your blood and urine checked as your provider instructs.
- Try to keep your cholesterol numbers in a healthy range. Talk with your provider about your cholesterol goals.
- Control your weight. If you are overweight, talk with your provider about how you can lose weight.
- Be physically active 30 minutes a day most days of the week.
- Take all medicines as prescribed.
- Eat healthysee Eating, Diet, and Nutrition.
Recognizing Cardiovascular And Renal Disease
Cardiac and renal disease develop differently in dogs and cats, thereby limiting our ability to generalize among species. In dogs, common cardiac conditions include: degenerative mitral valve disease and dilated cardiomyopathy in cats, they are hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and systemic hypertension. In dogs, common renal conditions include: glomerular disease, pyelonephritis, and acute tubular injury in cats, they include idiopathic tubulo-interstitial disease.2
Recommended Reading: Can Kidney Transplant Patients Eat Ginger
How Long For Sternum To Heal After Open Heart Surgery
The recovery process of an open heart surgery takes some time. Typically the sternum is slit open in an open heart surgery which takes around 6 weeks to heal. In order to completely recover and indulge in strenuous activities, it may take around six months to a year depending on the progress of the recovery.
Fibroblast Growth Factor 23
Fibroblast growth factor-23 is a hormone produced by osteoblasts and osteocytes, which inhibits phosphate reabsorption in the kidneys and suppresses circulating calcitriol, effectively lowering plasma phosphate levels in physiological conditions . In CKD, FGF-23 is no longer able to reduce phosphate levels due to loss of renal Klotho-FGF receptor 1 complex, resulting in both high phosphate and high FGF-23 levels . Elevated levels of FGF-23 are associated with an increased cardiovascular risk in patients with CKD , and with left ventricular hypertrophy in a cohort of CKD patients . These findings were confirmed in rats, where FGF-23 could directly induce left ventricular hypertrophy while ejection fraction was preserved . Furthermore, FGF-23 is associated with new-onset HFpEF in a large cohort study of people, who were free of cardiovascular disease at baseline . Interestingly, in a cohort of HFpEF patients, FGF-23 was not associated with increased mortality, while this was the case for a cohort of HFrEF patients , suggesting that FGF-23 may be linked to disease onset rather than progression in HFpEF.
Recommended Reading: Can Aleve Cause Kidney Damage