What Causes Polycystic Kidney Disease
People who have PKD were born with it. PKD is almost always inherited from a parent or from both parents. People of all genders, ages, races, ethnicities and nationalities can have PKD. Men and women get PKD equally as often. If you have a blood relative with PKD, you are more likely to have PKD or carry the gene that causes it. If you carry the gene that causes PKD but you do not have the disease, you are called a carrier. This is possible with autosomal recessive PKD.
What Makes Yale Medicines Approach To Treating Polycystic Kidney Disease Unique
The Yale Medicine Chronic Kidney Disease Program offers patients the opportunity to receive care from nephrologists, liver disease experts, aneurysm experts and geneticists who can explain the nuances of inherited disorders to patients and skillfully manage the illness.
Yale Medicine offers opportunities for patients with polycystic kidney disease to take part in clinical trials to better explain the disease and to evaluate new treatment approaches. The experts at Yale Medicine also continue to study the mechanisms underlying the cyst formation.
We hope these studies will lead to the development of therapies, Dr. Somlo says. We focus on research that we can translate into the care of our patients.
Cloning Of The Arpkd Gene
All typical cases of ARPKD are due to mutations of the PKHD1 gene on chromosome 6p21.1-p12. Genetic linkage to chromosome 6 was first demonstrated in 1994 , and subsequent genetic and physical mapping refined the gene locus to a 1-Mb interval . Earlier this year, three groups independently cloned the PKHD1 gene in the critical region on chromosome 6p21.1-p12. Using comparative genomics, Ward et al. mapped a rat model of PICD to a region on rat chromosome 9 that was syntenic with the ARPKD candidate region on human chromosome 6p. Further analysis identified a gene that was mutated in both the Pck rat and in humans with ARPKD. Onuchic et al. cloned the identical gene by assembling a transcription map of the ARPKD region and identifying a novel transcript that was highly expressed in the kidney. Analysis of this gene identified mutations found only in affected individuals and segregating with the disease phenotype in affected families. Xiong et al. have also recently reported the identification of the human ARPKD gene and mapped the mouse orthologue on mouse chromosome 1. Taken together, these results prove that the gene responsible for ARPKD has been identified.
Recommended Reading: Pomegranate Juice For Kidney Stones
Questions For Your Doctor
- What treatment is best for my symptoms?
- How can I know if my baby has PKD?
- I have PKD. Is it certain that my children will have it?
- If my symptoms get worse, when should I call my doctor?
- What kinds of tests do I need to diagnose PKD?
- Will my PKD affect any of my other organs?
- Are there any medications I should take?
- What is the best way to treat my high blood pressure?
- What side effects will I experience from my medications?
- What kinds of complications can I expect?
What Is The Treatment Of Polycystic Kidney Disease
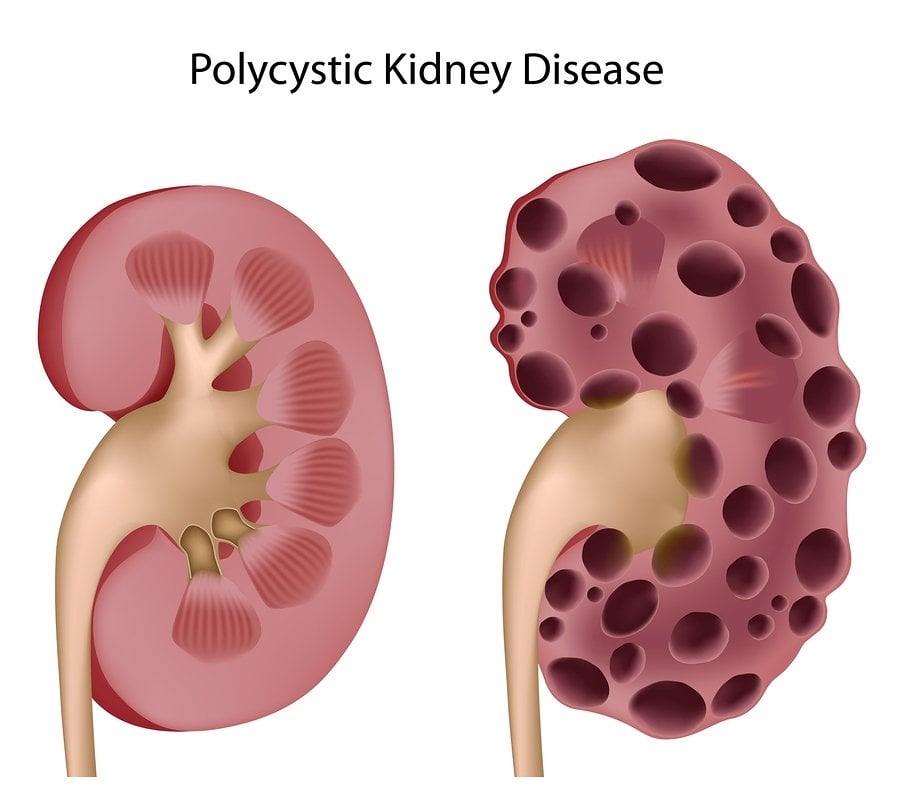
The goal of polycystic kidney disease treatment is to manage symptoms and avoid complications. Controlling high blood pressure is the most important part of treatment for polycystic kidney disease.
Some treatment of polycystic kidney disease options may include:
- pain medication, except Ibuprofen, which is not recommended as it may worsen kidney disease
- blood pressure medication
- diuretics to help remove excess fluid from the body
- surgery to drain cysts and help relieve discomfort
With advanced PKD that polycystic kidney disease causes renal failure, dialysis and kidney transplant may be necessary. One or both of the kidneys may need to be removed.
Read Also: Celery Juice Kidney
Genetics And Pathogenesis Of Polycystic Kidney Disease
Eberhard Ritz
Polycystic kidney disease , a common genetic cause of chronic renal failure in children and adults, is characterized by the accumulation of fluid-filled cysts in the kidney and other organs. The renal cysts originate from the epithelia of the nephrons and renal collecting system and are lined by a single layer of cells that have higher rates of cellular proliferation and are less differentiated than normal tubular cells . Abnormalities in gene expression, cell polarity, fluid secretion, apoptosis, and extracellular matrix have also been described in PKD, but the mechanism of cyst formation remains incompletely understood . In recent months, there have been several advances in our understanding of the genetics and pathogenesis of PKD. Genes responsible for autosomal recessive PKD in humans and mice have been cloned, the PKD2 gene product has been identified as an intracellular calcium release channel, the PKD1 gene product has been found to regulate the cell cycle, and a neglected cellular organelle, the primary cilium, has emerged as a potential key player in polycystic disease. In this review, we will discuss how the cloning of the human PKD genes and the characterization of animal models have provided new insights into the pathogenesis of PKD. It is hoped that a more thorough understanding of the genetics and pathogenesis of PKD will lead to improvements in diagnosis and treatment.
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Pkd
The signs and symptoms of ADPKD, such as pain, high blood pressure, and kidney failure, are also PKD complications. In many cases, ADPKD does not cause signs or symptoms until your kidney cysts are a half inch or larger in size.
Early signs of ARPKD in the womb are larger-than-normal kidneys and a smaller-than-average size baby, a condition called growth failure. The early signs of ARPKD are also complications. However, some people with ARPKD do not develop signs or symptoms until later in childhood or even adulthood.
Read Also: Kidney Pain Medical Term
What Tests Are Needed To Diagnose Pkd
Initial imaging tests will reveal the condition of the kidneys and the presence of cysts. At this point, the patient will most likely be referred to a nephrologist. The presence of multiple cysts and their bilateral distribution is a strong early indicator of PKD. This may be supported also by cysts in other organs such as the liver. The following tests may be required in order to make a clear diagnosis:
- Physical examination.
Symptoms Of Autosomal Recessive Pkd
A child with this form of the disease exhibits symptoms very early in life, even before birth. A child has a 25 percent risk of developing this disease if both parents carry the disease gene. A child must inherit two defective copies of the gene. Often, children with this disorder go on to develop kidney failure before reaching adulthood. In the most severe cases, newborns can die hours after birth because of respiratory failure. In milder cases, symptoms develop later in childhood and in early adulthood. Liver scarring is common in these cases.
Symptoms include:
Read Also: Reducose Weight Loss
Should Women With Pkd Get Pregnant
Most of the women with PKD have successful and uneventful pregnancies. However, some women with PKD have an increased risk for serious complications for themselves and their babies. This includes women with PKD who also have:
- high blood pressure
Women who have PKD with high blood pressure develop pre-eclampsia in 40 percent of pregnancies. This is a life-threatening disorder for both the mother and baby, and it can develop suddenly and without warning. Therefore, all women with PKD, particularly those who also have high blood pressure, should be followed closely during their pregnancy by their doctor.
What Causes Autosomal Dominant Pkd
ADPKD is caused by a problem with a specific gene. It is almost always inherited from a parent who also has ADPKD. To inherit the disease, a child needs to have just one parent with ADPKD. On average, if both parents have ADPKD, there is a 75% chance that their child will also be born with PKD.
The genetic problem that causes ADPKD can sometimes happen on its own, meaning that a child may be born with ADPKD, even though neither parent has it. This happens in only 1 out of every 10 cases of ADPKD.
Also Check: Kidney Transplant Tattoos
What Is The Treatment For Adpkd
There is no cure for ADPKD, but a new treatment is available that has been show to slow the progression of ADPKD to kidney failure. For more information, .There may be other ways to treat the symptoms of ADPKD and to make you feel better. Talk to your doctor about the best ways to manage your condition.
Are There Different Types Of Polycystic Kidney Disease
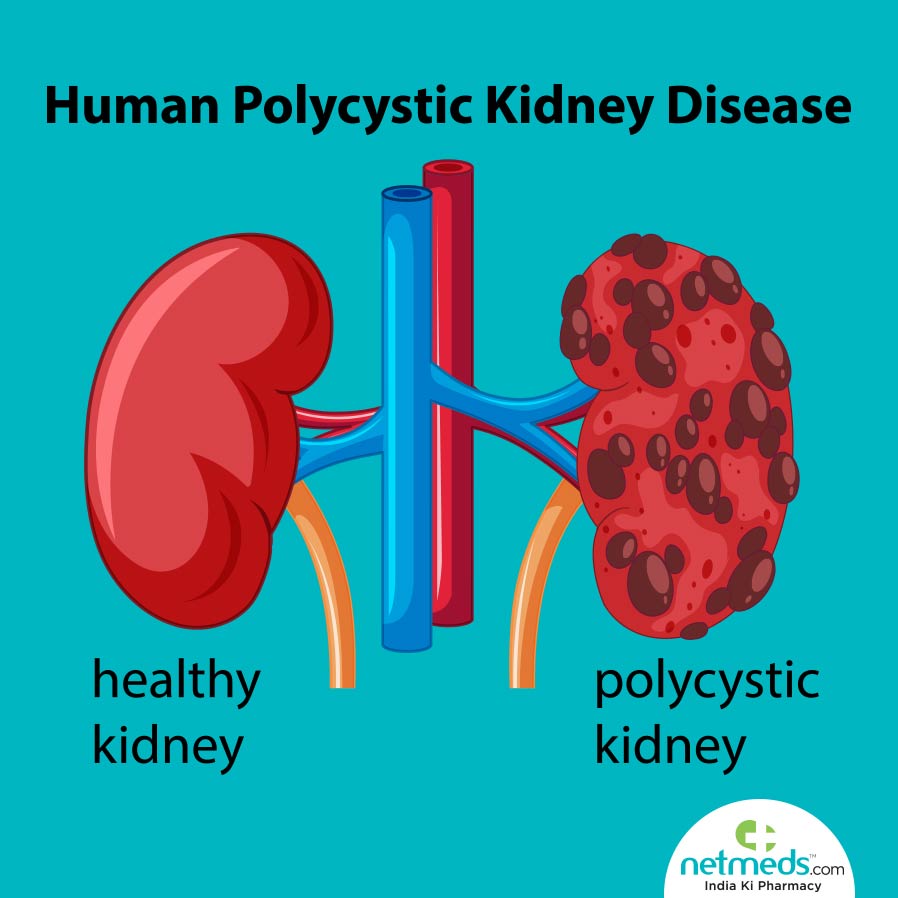
There are two types of polycystic kidney disease:
- Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease : ADPKD is the most common form of PKD. Its usually diagnosed in adulthood, between the ages of 30 and 50. ADPKD is usually diagnosed in adulthood, between the ages of 30 and 50, but it may occur in early childhood or adolescence.
- Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease : ARPKD is a rare form of PKD, also called infantile PKD. It causes abnormal kidney development in the womb or soon after birth.
Also Check: Is Honey Good For Kidney
What Can I Do To Slow Down Pkd
The sooner you know you or your child has PKD, the sooner you can keep the condition from getting worse. Getting tested if you or your child are at risk for PKD can help you take early action.
You also can take steps to help delay or prevent kidney failure. Healthy lifestyle practices such as being active, reducing stress, and quitting smoking can help.
What Is The Treatment For Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease
The treatment for ADPKD is aimed at treating the kidney and non-kidney symptoms. Blood pressure is followed regularly. High blood pressure is treated with medication.
Pain in the area of the kidneys is treated as needed with pain medications, and for chronic pain, with antidepressants. When standard methods to treat kidney pain do not work, then removing the fluid in the kidney cysts may be done.
When kidney function starts to decline, treatment is aimed at slowing down the progression to kidney failure. This involves controlling high blood pressure, restricting protein in the diet, controlling build up of acid and preventing elevated levels of phosphate .
When individuals with ADPKD develop renal failure, they need to have dialysis or a renal transplant. Studies have shown that individuals with ADPKD do better on dialysis than individuals with kidney failure from other causes.
Also Check: Is Grape Juice Good For Kidney Stones
When To See A Doctor
Since polycystic kidney disease is genetic, knowing your family health history is important. If a close family member is affected by PKD, consider seeking the advice and care of a healthcare professional skilled in kidney diseases, such as a nephrologist, who can ensure proper monitoring and early identification of polycystic kidney disease.
Eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and managing high blood pressure can help people affected by polycystic kidney disease live full lives.
People with PKD should seek immediate medical attention if any of these symptoms are noticed:
- Confusion
- New or worsening swelling of feet, ankles, or legs
- Chest pain or shortness of breath
- Inability to urinate.
Coping And Support For Polycystic Kidney Disease
A diagnosis of PKD may mean changes and considerations for you and your family. You may experience a range of emotions when you receive a PKD diagnosis and as you adjust to living with the condition. Reaching out to a support network of family and friends can be helpful.
You may also wish to reach out to a dietitian, who can recommend dietary steps to help you keep blood pressure low and reduce the work required of the kidneys, which must filter and balance electrolytes and sodium levels.
There are several organizations that provide support and information for those living with PKD:
- The PKD Foundation has chapters all across the country to support those with PKD and their families. Visit their website to find a chapter near you.
- The National Kidney Foundation offers education and support groups to kidney patients and their families.
- American Association of Kidney Patients engages in advocacy to protect the rights of kidney patients in all levels of government and insurance organizations.
You can also talk to your nephrologist or local dialysis clinic to find support groups in your area. You dont have to be on dialysis in order to access these resources.
If you arent ready or dont have the time to attend a support group, each of these organizations have online resources and forums available.
Also Check: Does Red Wine Cause Kidney Stones
What Is The Outlook For People With Polycystic Kidney Disease
For most people, PKD slowly gets worse over time. It is estimated that 50 percent of people with PKD will experience kidney failure by age 60. This number increases to 60 percent by age 70. Because the kidneys are such important organs, their failure may start to affect other organs, such as the liver.
Proper medical care can help you manage PKD symptoms for years. If you dont have other medical problems, you may be a good candidate for a kidney transplant.
Also, you may consider speaking with a genetic counselor if you have a family history of PKD and are planning to have children.
Genetic Abnormality In Polycystic Kidney Disease
including autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease, as well as rare ocular genetic disorders. For more information, please visit www.eloxxpharma.com. This press release contains forward.
ADPKD is due to mutations in either PKD1 gene encoding polycystin-1 or PKD2 encoding polycystin 2 .
Genetic factors: Certain genetic factors can cause kidney disease early in like. Polycystic kidney disease is a disorder in which several cysts arise in the kidneys. As the cysts grow, the kidney.
Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease : Genetic testing for ADPKD is considered medically necessary for adults with multiple cysts on appropriate imaging studies in persons who are at high risk for rapid progression to end-stage renal disease as determined by their treating nephrologist.
?Note: This page may contain content that is offensive or inappropriate for some readers. disease a definite pathological process having a characteristic set of signs and symptoms. It may affect the whole body or any of its parts, and its etiology, pathology, and prognosis may be known or unknown. For specific diseases, see under the.
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease , a genetic disorder, causes fluid-filled cysts to develop on the kidneys.
DefinitionPolycystic kidney disease is a kidney disorder passed down through families. In this disease, many cysts form in the kidneys.
As practitioners, we deal with genetic disease every.
Polycystic Kidney Disease is a genetic condition.
Recommended Reading: Does Red Wine Cause Kidney Stones
Genetic Counselling For Polycystic Kidney Disease
If you or a family member have been diagnosed with PKD, or if PKD runs in your family, it can be helpful to speak to a genetic counsellor. Genetic counsellors are health professionals qualified in both counselling and genetics. As well as providing emotional support, they can help you to understand PKD and what causes it, how it is inherited, and what a diagnosis means for your health, lifestyle, and plans for the future. Genetic counsellors are trained provide information and support that is sensitive to your family circumstances, culture and beliefs.
If PKD runs in your family, a genetic counsellor can explain what genetic testing options are available to you and other family members. You may choose to visit a genetic counsellor if you are planning a family, to find out your risk of passing that condition on to your child, or to arrange for prenatal tests.
is connected with a wide range of support groups throughout Victoria and Australia and can connect you with other individuals and families affected by MCKD.
How Is Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Diagnosed
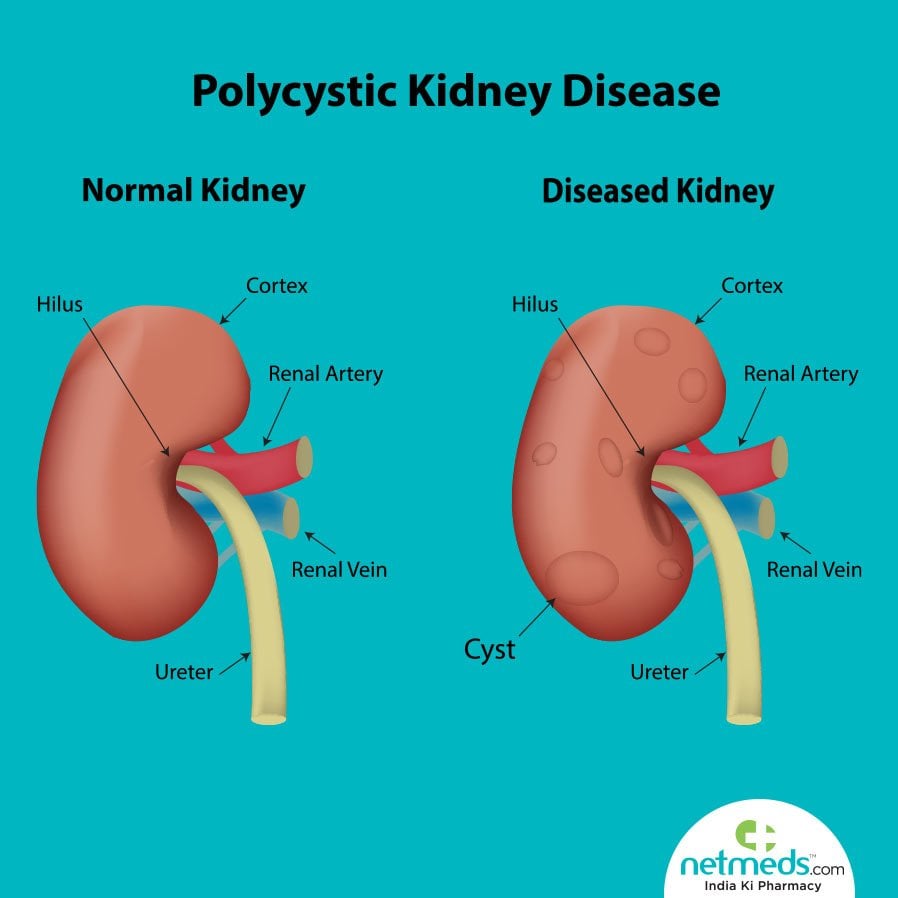
ADPKD can be diagnosed using ultrasound, CT scan or MRI studies of the kidneys. The diagnostic criteria for individuals who have a 50 percent risk of developing ADPKD include:
-
At least two unilateral or bilateral cysts in individuals who are younger than age 30.
-
At least two cysts in each kidney in individuals who are between 30 and 59 years.
-
At least four cysts in each kidney in individuals who are 60 years old or older.
There are two genes known to be associated with ADKPD. PKD1 is found in approximately 85 percent of individuals who have ADPKD. PKD2 is found in about 15 percent of individuals who have ADPKD.
A genetic test can detect mutations in the PKD1 and PKD2 genes, the genes that, when altered, cause autosomal dominant PKD. Although this test can detect the presence of the autosomal dominant PKD mutations before cysts develop, its usefulness is limited by two factors it cannot predict the onset or ultimate severity of the disease and no absolute cure is available to prevent the onset of the disease. On the other hand, a young person who knows of a PKD gene mutation may be able to forestall the disease through diet and blood pressure control.
Genetic testing for PDK1 and PDK2 is also available for prenatal diagnosis and preimplantation genetic diagnosis. However this testing is not usually requested for ADPKD because it is usually an adult-onset condition.
Don’t Miss: Is Seltzer Water Bad For Your Kidneys
Kidney Failure And Transplant Options
One of the most serious complications of PKD is kidney failure. This is when the kidneys are no longer able to:
- filter waste products
- maintain fluid balance
- maintain blood pressure
When this occurs, your doctor will discuss options with you that may include a kidney transplant or dialysis treatments to act as artificial kidneys.
If your doctor does place you on a kidney transplant list, there are several factors that determine your placement. These include your overall health, expected survival, and time you have been on dialysis.
Its also possible that a friend or relative could donate a kidney to you. Because people can live with only one kidney with relatively few complications, this can be an option for families who have a willing donor.
The decision to undergo a kidney transplant or donate a kidney to a person with kidney disease can be a difficult one. Speaking to your nephrologist can help you weigh your options. You can also ask what medications and treatments can help you live as well as possible in the meantime.
According to the University of Iowa, the average kidney transplant will allow kidney function from 10 to 12 years.