How Long Does Ckd Take To Progress
The short, and unsatisfying, answer to this question isit depends. It can be difficult to determine which indicators will be accurate across the board because individual studies can only examine a certain number of factors at one time. They also generally look at very specific combinations. Collectively, however, these studies provide small pieces that help fill out the larger picture over time.
Chronic kidney disease progression has been studied extensively, but the majority of studies have focused on the causes of kidney function decline and the likelihood of CKD to progress to end-stage renal disease not necessarily the speed of that progression.
This infographic is by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention .
The goal of accurately, consistently predicting the speed of chronic kidney disease progression remains at the forefront of CKD research. Findings show that the rate is influenced by many factors and can vary widely, particularly in later stages of the disease.
What Is The Life Expectancy Of A Cat With Kidney Disease
I know that this is the biggest question on the minds of any pet parent facing renal failure with their cats.
As much as I wish I could give you an answer, there simply isnt one set in stone.
Life expectancy for cats with kidney disease can be as short as a month or extend out for many years. There are far too many factors for each individual cat to give a direct answer to everyone.
For acute renal failure, life expectancy is heavily influenced by the original cause of the renal failure and any complications since.
If it was due to traumatic injury, and you responded immediately, your cats life expectancy will be greater than if he had received no treatment at all.
At the same time, certain injuries just cant be treated.
Cats suffering chronic renal failure tend to have a higher life expectancy than those suffering from acute renal failure.
This is especially true if the disease is caught early and intervention begins immediately.
Ayurvedic Treatment To Prevent Stage 3 Kidney Disease From Progressing
For those looking for ways to reverse the signs and complications of stage 3 of CKD, ayurvedic treatment with herbs from nature can really help you out. Using ayurvedic medicines, you can easily eliminate the health conditions that cause you CKD. Here is how Chronic Kidney Disease Treatment in Ayurveda can help you from progressing to further stages of CKD:
- Ayurvedic treatment help rejuvenates the cell of the body
- Tends to reduce the risk factors that affect your CKD
- Helps improve high blood pressure
- Improve blood glucose level
- Improves overall well-being
- Enhances the quality of your kidney
Karma Ayurveda has helped thousands of patients suffering from chronic kidney disease in eliminating the root cause of the problem. With our ayurvedic medicines, you can also prevent chronic kidney disease from progressing to harmful stages of renal insufficiency.
If you want to heal your kidney with natural herbs then head to Karma Ayurveda!
Don’t Miss: Lemon Juice Olive Oil Kidney Stone Myth
Symptoms Of Chronic Kidney Disease Stage 3
1. Abnormal Urination
In CKD stage 3, the urine color may change into red, dark yellow, or orange. Also, patients may need to urinate frequently and more frequently at night. It happens because the filters in the kidney got damaged.
Those filters usually filter the blood cells out from the wastes, but blood cells are also mixed with the urine while the filters are damaged. Because of that, the urine color changes into red. Also, the filter damage causes a sense of urination frequently.
2. Fatigue
Fatigue is a symptom of chronic disease such as CKD that affects physical and mental health. While the kidney functions are affected severely, that pushes the patient to need of dialysis. After that, it leads to fatigue, making patients feel exhausted, and leading to increased mortality chances.
3. Pain in the Kidney
Dont relate the normal back pain to kidney pain. Kidney pain can be felt under the rib cage or lower abdomen. It may come in waves with severe pain, or you can feel mild constant pain. Anything other than that wasnt the kidney pain.
4. Muscle Cramps
Muscle cramps may occur if you have CKD because of fatigue and other causes. Imbalances in electrolytes, fluids, nerve damage, and blood flow problems cause muscle cramps in renal disease patients.
5. Bone Disease
If you want to read about how to prevent kidney failure, .
6. High Blood Pressure
Stage 3 Ckd Life Expectancy
 IAMMRFOSTER.COM” alt=”Chronic kidney disease stages gfr > IAMMRFOSTER.COM”>
IAMMRFOSTER.COM” alt=”Chronic kidney disease stages gfr > IAMMRFOSTER.COM”> CKD is associated with an increased risk of developing cardiovascular diseases and in some cases, even death. If CKD exists together with proteinuria, the risks are amplified even further. Renal replacement therapy is usually required. However, the risks of a cardiovascular problem are even greater.
Recommended Reading: Does Red Wine Cause Kidney Stones
Definition And Ascertainment Of Exposure And Outcome Variables
The origin for time-to-event analyses was defined as the date of the first nephrology clinic visit. The interim exposure variable of interest was progression to Stage 4 CKD during the follow-up period defined by two or more consecutive eGFR values < 30 mL/min/1.73 m2 with the date of the second reading taken as date of progression to Stage 4 CKD. In comparison with the number of patients who progressed to Stage 4 , we determined the number of patients with an eGFR decline of 57% or more from baseline on two or more consecutive measurements. An eGFR decline of 57% is equivalent to a doubling of serum creatinine, which is an accepted surrogate outcome in clinical trials.
The primary outcomes of interest included death, first AKI hospitalization and first all-cause hospitalization prior to ESRD. We considered AKI hospitalization to include the first admission with an AKI code as a primary or secondary diagnosis. We ascertained the first all-cause hospitalization over the follow-up period without restriction on the reason for hospitalization or length of stay. ESRD was defined as the need for chronic renal replacement therapy . In a secondary analysis, we partitioned all-cause hospitalization, whether associated with AKI or not, into those with or without a primary or secondary CV diagnostic code , henceforth referred to as CV-related hospitalization and non-CV-related hospitalization, respectively.
Cohort Assembly And Baseline Characteristics
We identified 36,195 eligible adults with index eGFR 30 to 59 ml/min/1.73 m2 between January 1, 2008 and December 31, 2010, with 36% of patients having diabetes mellitus. In the overall cohort, mean age was 73.0 years with 55% being women, 11% black/African American, 12% Asian/Pacific Islander and 10% Hispanic . Overall, 85% had hypertension and three quarters of patients had known dyslipidemia .
During 2 years of follow-up, the median annual change in renal function in the overall cohort was 0.04 ml/min/1.73 m2. A total of 6549 patients experienced fast decline in kidney function over 24 months, with a higher crude risk in those with vs. without diabetes mellitus . Fast progressors were more likely to have prior cardiovascular diseases as well as prior ischemic stroke, transient ischemic attack, peripheral artery disease, proteinuria, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, dementia, dyslipidemia, chronic liver disease, and thyroid disease . Patients who experienced fast progression were also more likely to have higher mean systolic blood pressure than those who were not fast progressors. In addition, fast progressors were more likely to be receiving angiotensin II receptor blockers, loop diuretics, -blockers, calcium channel blockers, alpha blockers, aldosterone receptor antagonists, isosorbide dinitrate/hydralazine, hydralazine, antiarrhythmic therapy, nitrates, digoxin, statin, other lipid lowering therapies, antiplatelet agents, diabetic therapy and erythropoietin .
Fig. 1
You May Like: Fluid Buildup Around Kidney
Stage 3a And Stage 3b
Stage 3 CKD is broken up into two parts based on GFR amounts. As kidney function declines in this phase, waste products begin to build up more quickly and can cause high blood pressure, anemia, diabetes, and bone disease. Symptoms may consist of fatigue, fluid retention, swelling in the arms and legs, shortness of breath, changes in the frequency and color of urination, kidney pain, and problems sleeping due to muscle cramps or restless legs. People with Stage 3 kidney disease should receive treatment from a nephrologist or a doctor who specializes in kidneys, and a dietician, as a better diet may help preserve kidney function. Medications to treat illnesses that may have developed as a result of CKD and regular exercise can be beneficial at this stage.
Simple Steps Can Prevent The Progress Of Chronic Kidney Disease
New York, NY – Early detection and treatment can significantly slow the progression of chronic kidney disease if you already have it. One in nine Americans have CKD and many don’t know it, according to the National Kidney Foundation. If you don’t know you’re at risk for the condition, ask your doctor for the urine and blood tests that can detect it.
Once you know you have chronic kidney disease, follow these steps from the National Kidney Foundation:
If you smoke, quit.
To learn more about chronic kidney disease, contact the National Kidney Foundation at 622-9010 or log on to www.kidney.org
COVID-19 patients can become kidney patients.
You can provide lifesaving support today with a special monthly gift.
Read Also: Does Carbonated Water Cause Kidney Stones
What Tests And Procedures Diagnose Chronic Kidney Disease
Chronic kidney disease usually causes no symptoms in its early stages. Only lab tests can detect any developing problems. Anyone at increased risk for chronic kidney disease should be routinely tested for development of this disease.
- Urine, blood, and imaging tests are used to detect kidney disease, as well as to follow its progress.
- All of these tests have limitations. They are often used together to develop a picture of the nature and extent of the kidney disease.
- In general, this testing can be performed on an outpatient basis.
Urine tests
Urinalysis: Analysis of the urine affords enormous insight into the function of the kidneys. The first step in urinalysis is doing a dipstick test. The dipstick has reagents that check the urine for the presence of various normal and abnormal constituents including protein. Then, the urine is examined under a microscope to look for red and white blood cells, and the presence of casts and crystals .
Only minimal quantities of albumin are present in urine normally. A positive result on a dipstick test for protein is abnormal. More sensitive than a dipstick test for protein is a laboratory estimation of the urine albumin and creatinine in the urine. The ratio of albumin and creatinine in the urine provides a good estimate of albumin excretion per day.
Blood tests
Other tests
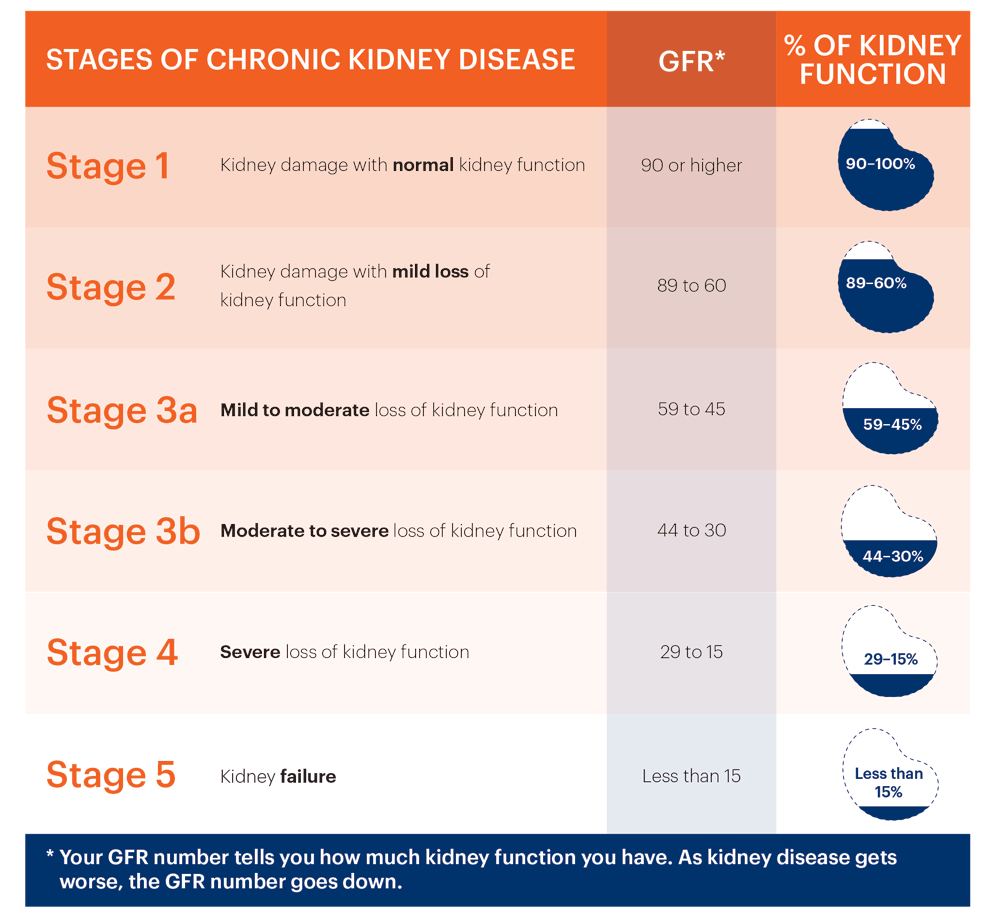
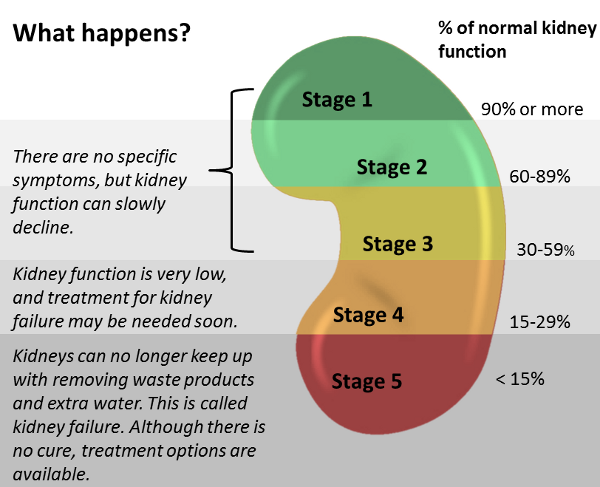
What Are The Stages Of Chronic Kidney Disease
CKD is diagnosed by the eGFR and other factors, and is divided into five stages:
| Stage of Chronic Kidney Disease | eGFR ml/min/1.73 m |
| Stage 1: the eGFR shows normal kidney function but you are already known to have some kidney damage or disease. For example, you may have some protein or blood in your urine, an abnormality of your kidney, kidney inflammation, etc. | 90 or more |
| Stage 2: mildly reduced kidney function AND you are already known to have some kidney damage or disease. People with an eGFR of 60-89 without any known kidney damage or disease are not considered to have chronic kidney disease . | 60 to 89 |
| Stage 3: moderately reduced kidney function. | 45 to 59 |
| Stage 4: severely reduced kidney function. | 15 to 29 |
| Stage 5: very severely reduced kidney function. This is sometimes called end-stage kidney failure or established renal failure. | Less than 15 |
Note: it is normal for your eGFR to change slightly from one measurement to the next. In some cases these changes may actually be large enough to move you from one stage of CKD to another and then back again. However, as long as your eGFR is not getting progressively worse, it is the average value that is most important.
Read Also: Is Watermelon Good For Your Kidneys
Preventing Or Slowing Down The Progression Of Ckd
There are ways to stop CKD becoming any worse or to slow down any progression. You should have checks every now and then by your GP or practice nurse to monitor your kidney function – the eGFR test. They will also give you treatment and advice on how to prevent or slow down the progression of CKD. This usually includes:
- Blood pressure control. The most important treatment to prevent or delay the progression of CKD, whatever the underlying cause, is to keep your blood pressure well controlled. Most people with CKD will require medication to control their blood pressure. Your doctor will give you a target blood pressure level to aim for. This is usually below 130/80 mm Hg, and even lower in some circumstances.
- Review of your medication. Certain medicines can affect the kidneys as a side-effect which can make CKD worse. For example, if you have CKD you should not take anti-inflammatory medicines unless advised to by a doctor. You may also need to adjust the dose of certain medicines that you may take if your CKD gets worse.
- Diet. if you have more advanced CKD then you will need to follow a special diet. See the separate leaflet called Diet in Chronic Kidney Disease.
Treatments For Kidney Failure
The two treatments for kidney failure are kidney transplantation and dialysis. Two different types of dialysis can be done – hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis.
To learn more about each type of treatment, see “Choosing a Treatment for Kidney Failure” in the A-to-Z Guide.
Also Check: Std Kidney Pain
What Are Chronic Kidney Disease Symptoms
You are unlikely to feel unwell or have symptoms with mild-to-moderate CKD – that is, stages 1 to 3. CKD is usually diagnosed by the eGFR test before any symptoms develop.
Symptoms tend to develop when CKD becomes severe or worse. The symptoms at first tend to be vague and nonspecific, such as feeling tired, having less energy than usual and just not feeling well. With more severe CKD, symptoms that may develop include:
- Difficulty thinking clearly.
- A need to pass urine more often than usual.
- Being pale due to anaemia.
- Feeling sick.
If the kidney function declines to stage 4 or 5 then various other problems may develop – for example, anaemia and an imbalance of calcium, phosphate and other chemicals in the bloodstream. These can cause various symptoms, such as tiredness due to anaemia, and bone thinning or fractures due to calcium and phosphate imbalance. End-stage kidney failure is eventually fatal unless treated.
About Chronic Kidney Disease
CKD is a condition in which the kidneys are damaged and cannot filter blood as well as they should. Because of this, excess fluid and waste from blood remain in the body and may cause other health problems, such as heart disease and stroke.
15% of US adults are estimated to have chronic kidney disease, that is about 37 million people.
Some other health consequences of CKD include:
- Anemia or low number of red blood cells
- Increased occurrence of infections
- Low calcium levels, high potassium levels, and high phosphorus levels in the blood
- Loss of appetite or eating less
- Depression or lower quality of life
CKD has varying levels of seriousness. It usually gets worse over time though treatment has been shown to slow progression. If left untreated, CKD can progress to kidney failure and early cardiovascular disease. When the kidneys stop working, dialysis or kidney transplant is needed for survival. Kidney failure treated with dialysis or kidney transplant is called end-stage renal disease . Learn more about ESRD.
Not all patients with kidney disease progress to kidney failure. To help prevent CKD and lower the risk for kidney failure, control risk factors for CKD, get tested yearly, make lifestyle changes, take medicine as needed, and see your health care team regularly.
Read Also: Kidney Medical Term
Manage Or Prevent Heart Disease
People with stage 4 kidney disease have a high risk of having heart disease. In fact, most people with kidney disease do not die of kidney failure – they die of heart disease. Why? Because, in addition to kidney disease, they usually have one or more of the following health risks:
You can help slow – or possibly prevent – heart problems by following your treatment plan. Ask your healthcare professional what you need to do to keep your heart healthy.
How Fast Will Kidney Disease Progress
Kidneys play a central role in eliminating the toxins from the body. Kidneys perform the main task of excreting waste out of the body, making it toxin free and purifying the blood circulating in the body. They also do a major task in secreting certain hormones that help in the metabolism of the nutrients and also control the blood pressure and the blood volume.
When kidney function deteriorates, it results in the accumulation of the toxins in the body causing many health hazards. These hazards include acidosis, problems related to fatty liver, bone diseases, anemia, cholesterol rise etc. How fast will kidney disease progress?
Recommended Reading: Is Cranberry Juice Good For Your Liver And Kidneys