Kidney And Functions Of Kidneys
The kidney is the most important organ in the human urinary system, and in the blood circulation system, it undertakes the important mission of filtering metabolic waste and excreting it from the body and reabsorbing various nutrients!
Kidneys are located in the upper posterior part of the abdominal cavity, one on each side of the spine, and are influenced by the liver, with the right kidney generally slightly lower than the left by 1-2 cm. In addition to the kidneys, the urinary system also includes the ureter, bladder and urethra, and the main function of the urinary system is excretion.
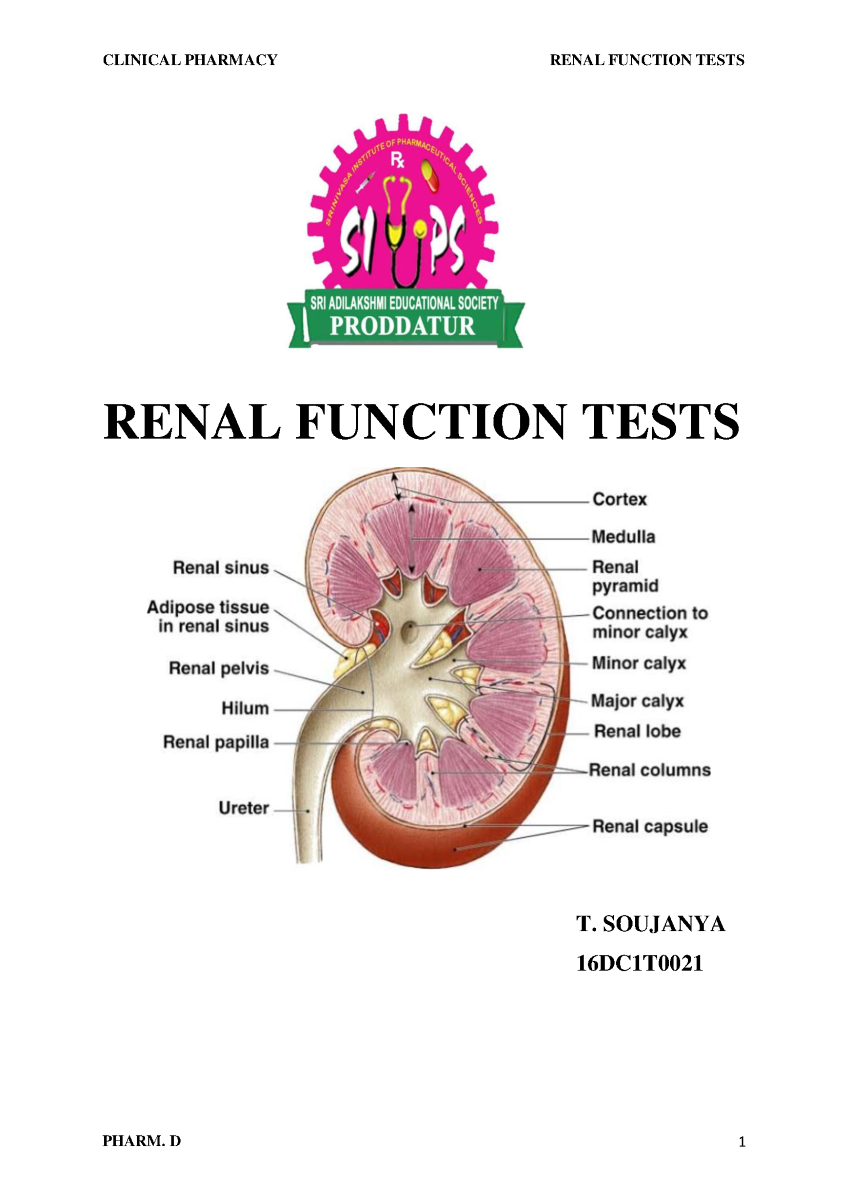
The kidney is shaped like an enlarged version of a fava bean, and each kidney weighs about 100-200 grams, with a soft texture, making it a substantial organ. The kidney cortex is reddish brown, divided into two parts: the outer edge of the kidney is convex, the inner edge is concave, and the middle of the concave surface is the renal hilum. All blood vessels, nerves and lymphatic vessels enter the kidney from this, and the renal pelvis exits the kidney.
Therefore, the renal unit is the basic unit of the kidney microcirculatory system and plays a decisive role in the normal operation of the kidney functions.
What are the functions of the kidneys?
Which Of The Following Is A Primary Function Of The Kidneys
Why Are the Kidneys So Important? Most people know that a major function of the kidneys is to remove waste products and excess fluid from the body. These waste products and excess fluid are removed through the urine. The production of urine involves highly complex steps of excretion and re-absorption.
Kidney And Urinary System Parts And Their Functions
-
Two kidneys.;This pair of purplish-brown organs;is located below the ribs toward the middle of the back. Their function is to:
-
Remove waste products and drugs from the body
-
Balance the body’s fluids
-
Release hormones to regulate blood pressure
-
Control production of red blood cells
The kidneys remove urea from the blood through tiny filtering units called nephrons. Each nephron consists of a ball formed of small blood capillaries, called a glomerulus, and a small tube called a renal tubule. Urea, together with water and other waste substances, forms the urine as it passes through the nephrons and down the renal tubules of the kidney.
Two sphincter muscles.;These circular muscles;help keep urine from leaking by closing tightly like a rubber band around the opening of the bladder.
Nerves in the bladder.;The nerves alert a person when it is time to urinate, or empty the bladder.
Urethra.;This tube allows urine to pass outside the body. The brain signals the bladder muscles to tighten, which squeezes urine out of the bladder. At the same time, the brain signals the sphincter muscles to relax to let urine exit the bladder through the urethra. When all the signals occur in the correct order, normal urination occurs.
Also Check: Grapes For Kidney Stones
Examination Of The Kidney
The kidneys can be examined by palpation and radiographic methods, as shown in the following table:
| Bimanual palpation | In slim patients, the lower renal poles can be felt. In the supine position, 1 hand pushes onto the anterior abdominal wall. The other hand holds the back and pushes against the abdominal wall. |
| X-ray | The renal pelvis is only visible in patients with radiopaque stones. Otherwise, contrast medium is needed: intravenous pyelography or retrograde pyelography. |
| Urinalysis | This is performed on midstream urine. In the urine strip test, erythrocytes, leukocytes, pH, glucose, protein, nitrite, and ketone may be detected in the urine. |
| Sonography | This is done in the supine position. Findings are standard size, extensions of the renal pelvis, kidney stones, cysts, and tumors. |
| Scintigraphy |
How Does Blood Flow Through My Kidneys
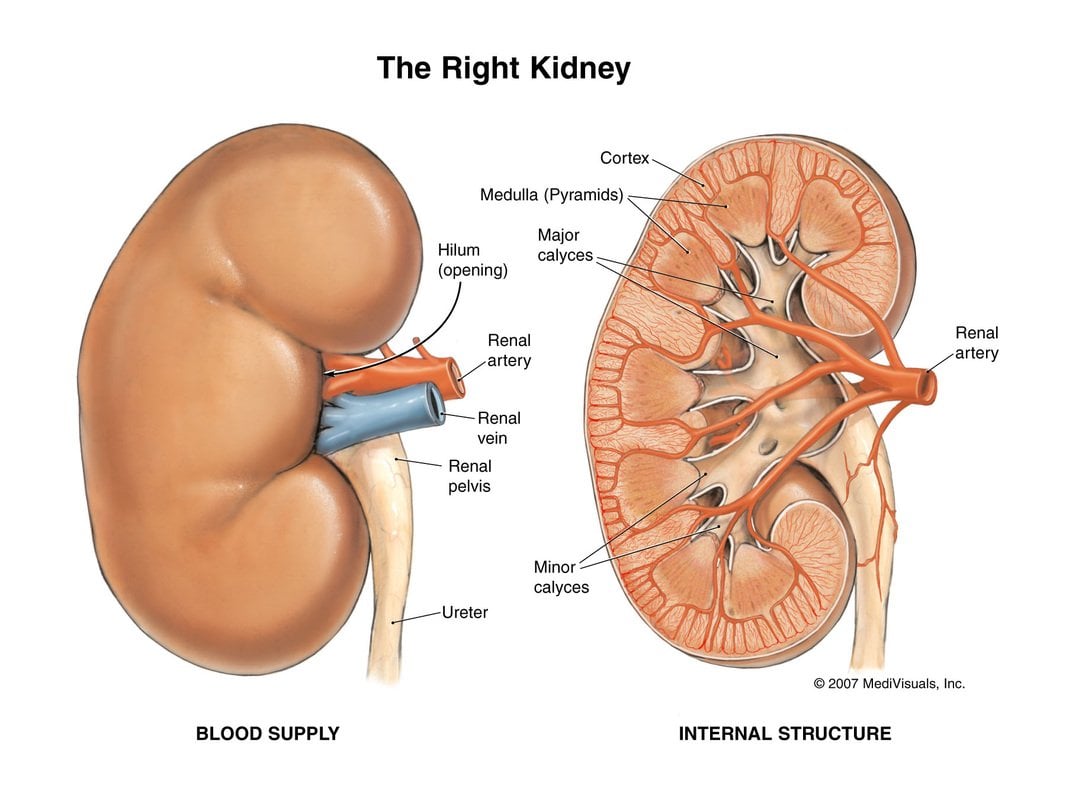
Blood flows into your kidney through the renalartery. This large blood vessel branches into smaller and smaller blood vessels until the blood reaches the nephrons. In the nephron, your blood is filtered by the tiny blood vessels of the glomeruli and then flows out of your kidney through the renal vein.
Your blood circulates through your kidneys many times a day. In a single day, your kidneys filter about 150 quarts of blood. Most of the water and other substances that filter through your glomeruli are returned to your blood by the tubules. Only 1 to 2 quarts become urine.
Also Check: What Are The Three Main Regions Of The Kidney?
Aging Changes In The Kidneys And Bladder
The kidneys filter the blood and help remove wastes and extra fluid from the body. The kidneys also help control the body’s chemical balance.
The kidneys are part of the urinary system, which includes the ureters, bladder, and urethra.
Muscle changes and changes in the reproductive system can affect bladder control.
AGING CHANGES AND THEIR EFFECTS ON THE KIDNEYS AND BLADDER
As you age, your kidneys and bladder change. This can affect their function.
Changes in the kidneys that occur with age:
- Amount of kidney tissue decreases and kidney function diminishes.
- Number of filtering units decreases. Nephrons filter waste material from the blood.
- Blood vessels supplying the kidneys can become hardened. This causes the kidneys to filter blood more slowly.
Changes in the bladder:
- The bladder wall changes. The elastic tissue becomes stiffer and the bladder becomes less stretchy. The bladder cannot hold as much urine as before.
- The bladder muscles weaken.
- The urethra can become partially or totally blocked. In women, this can be due to weakened muscles that cause the bladder or vagina to fall out of position . In men, the urethra can become blocked by an enlarged prostate gland.
In a healthy aging person, kidney function declines very slowly. Illness, medicines, and other conditions can significantly degrade kidney function.
COMMON PROBLEMS
Aging increases the risk of kidney and bladder problems such as:
Regulation Of Blood Pressureremoval Of Urearegulation Of Acidity Of Fluidssecretion Of Antibiotics
Which of the following forms the filtration barrier? They are located just underneath your diaphragm and another important function that the kidneys have is maintaining the blood’s water concentration. A) regulation of body fluid concentration. Maintaining volume, ph, and composition of body fluids within normal ranges b. Find the answer to this question here. Controls sodium balance, chloride balance follows sodium, potassium balance, control of h2o. The kidneys accomplish this by conserving or excreting. remove metabolic waste products from the blood and excrete them in the urine which of the following is least likely to be filtered into bowman’s capsule in a normal healthy person? Erythropoietin is a hormone produced by juxtaglomerular cells in response to decreased rbc count. So the question here basically asked which of the functions are missing so a year says that it experienced metabolic place i e. The kidneys remove harmful substances from the body. A) the kidneys regulate the plasma volume. The main function of the kidney is to eliminate excess bodily fluid, salts and byproducts of hypotension is a stimulus for the kidneys to increase the retention of fluid and thus increase blood alternatively, the anterior to posterior orientation follows the same pattern:
Don’t Miss: Is Celery Juice Good For Kidneys
Where Are My Kidneys
The kidneys are small bean-shaped organs approximately 6 cm wide and 12 cm long and consist of two main layers an inner layer called the medulla and an outer layer called the cortex. Most people have two kidneys that are situated at the back of the abdomen on either side of the spine.
Graphic showing a section through the right kidney with the main structures labelled.
The Nephron: Functional Unit Of The Kidney
The nephron is the functional unit of the kidney. It consists of the renal corpuscles as well as the tubules and forms an ingenious filter system .
Image: Blood flow in the nephron by Phil Schatz. License: CC BY 4.0
In each kidney, there are approximately 11.5 million renal corpuscles. A corpuscle is composed of the following components:
- The glomerulus is a tuft of capillaries, woven together by anastomoses. They are supplied with fresh blood by the incoming vas afferens. The blood leaves the glomerulus by the vas efferens.
- The Bowmans capsule surrounds the glomerulus and consists of 2 layers. The parietal layer, formed by a single-layer epithelium lying on a basal lamina, is located on the outside. The visceral layer, formed by the so-called podocytes, is located on the inside. These are specialized cells with many processes lining the capillaries of the glomerulus. Both layers are connected at the vessel pole.
- The mesangium consists of mesangium cells connected with gap junctions. They occupy the space between the capillaries in the nephron. These cells are responsible for the formation of the extracellular matrix and the components of the glomerular basement membrane. They also have a phagocytic function and can contract when necessary to stabilize the capillary walls.
You May Like: Is Celery Juice Good For Kidneys
The Kidneys Relation To The Peritoneum
Image: Normal kidney size and its influencing factors by ncing factors. License: CC BY 2.0
The kidneys, the adrenal glands, and the ureters are retroperitoneal organs. This means that they are located behind the peritoneum.
The capsula fibrosa is a capsule of firm connective tissue surrounding the kidney. Another capsule of fat encloses the kidney and the associated adrenal gland. The fascia renalis is;another capsule of connective tissue.
The Loop Of Henle Distal Convoluted Tubule And Ph
The next section of the tubule is the loop of Henle, which consists of a descending and an ascending limb. Water is reabsorbed in the descending part and some urea secreted, and then in the ascending part, the sodium and chloride ions are actively transported out of the filtrate.
From the loop of Henle, the filtrate moves to the distal convoluted tubule of the nephron. In this region, both sodium ions and chloride ions are reabsorbed. At the same time, some calcium ions can be reabsorbed; the amount of calcium that is reclaimed depends on levels of parathyroid hormones.
This is the region of the nephron which is involved in regulating pH.; Protons can be secreted and bicarbonates reabsorbed, or vice versa, depending on how the pH needs to be adjusted. This substance then passes to the last region of the nephron, the collecting duct.
You May Like: Pineapple For Kidney Stones
Positional Relations To Other Organs
In relation to other organs:
- The adrenal glands are located cranially to the upper kidney poles.
- The subcostalis, Nervus iliohypogastricus, and Nervus ilioinguinalis run dorsally.
Note: Because of the kidneys proximity to these nerves, pain originating from the kidney may spread to the groin.
The right hepatic lobe, pars descendens duodeni, and the right colonic flexure run ventrally to the right kidney. The root of the transverse mesocolon and the splenic flexure are situated anterior to the left kidney, stomach, spleen, and pancreas.
What Do The Kidneys Do
The kidneys have a number of roles in the body;
- The kidneys ensure that the make-up and volume of the fluids in the body is correct.;
- They help control the chemical balance of the blood and regulate the body’s level of;sodium,;potassium;and calcium.;
- The kidneys remove waste products and excess water from the body and so help to regulate blood pressure.
- They activate;vitamin D, which helps to maintain strong bones.
- They produce;erythropoietin, a hormone that is vital for the production of red blood cells.
The kidneys ensure that the make-up and volume of the fluids in the body is correct.;They help control the chemical balance of the blood and regulate the body’s level of sodium, potassium and calcium.;The kidneys remove waste products and excess water from the body and so help to regulate blood pressure. They activate vitamin D, which helps to maintain strong bones, and produce erythropoietin, a hormone that is vital for the production of red blood cells.
You May Like: Is Watermelon Good For Your Kidneys
What Are The Symptoms Of Kidney Failure
In early stages of kidney disease, many people experience few or no symptoms. Its important to note that chronic kidney disease can still cause damage even though you feel fine.
Chronic kidney disease and kidney failure can cause different symptoms for different people. If your kidneys arent working properly, you may notice one or more of the following signs:
- Fatigue
- Poor appetite or metallic taste of food
Location Of The Kidneys
The kidneys are located in the retroperitoneum beneath the diaphragm on each side of the spinal column . They are embedded in a groove, the renal fossa, which consists of the Musculus psoas major and the Musculus quadratus lumborum. The left kidney lies between the level of the 11th rib and the 3rd lumbar vertebra.
Due to the size of the liver, the right kidney lies in a slightly lower position, beginning at the level of the 12th rib and extending to the lower edge of the 3rd lumbar vertebra. Physiologically, the kidneys have moving flexibility of about 34 cm, depending on the posture of the body and the movement of the diaphragm during breathing, because the kidneys are not firmly attached to the back of the abdominal wall.
Image: Kidneys by Phil Schatz. License: CC BY 4.0
Read Also: Is Grape Juice Good For Kidney Stones
Malformations Of The Kidney: Renal Agenesis And Horseshoe Kidney
Renal agenesis refers to the congenital absence of 1 or both kidneys. The absence of 1 kidney may be compensated for by the remaining kidney. Bilateral agenesis, however, is always fatal.
A horseshoe kidney is a frequently occurring abnormality of the kidney. The kidneys are fused together at their lower poles to form the shape of a horseshoe. This malformation is usually asymptomatic.
Function Of The Kidney
The entire blood volume of the body is flushed through the kidneys several times each day. This is how the kidneys can control and regulate, among other things, the blood pressure, the water-and-electrolyte balance, the elimination of metabolic end products and toxic substances, and the acid-base balance.
The kidneys are important in maintaining the internal environment:
- Removing excess water, salt, and waste products
- Maintaining the correct levels of nutrients and chemicals
- Maintaining the acid-base balance
- Maintaining blood pressure
Recommended Reading: Is Grape Juice Good For Kidney Stones
How Is Kidney Failure Treated
Kidney failure treatment is determined by the cause and extent of the problem. Treating your chronic medical condition can delay the progression of kidney disease. If your kidneys start losing their function gradually, your doctor may use one or more methods to track your health. By watching you closely, your doctor can help you maintain your kidneys function as long as possible.
Your doctor may gauge your kidney function with:
- Routine blood tests
- Blood pressure checks
- Medication
Because the kidneys serve such an important purpose, people in kidney failure need treatment to keep them alive. The main treatments for kidney failure are:
- Dialysis: This treatment helps the body filter the blood .
- In hemodialysis, a machine regularly cleans your blood for you. People often receive this kidney failure treatment at a hospital or dialysis clinic, 3 or 4 days each week.
- Peritoneal dialysis cleans the blood in a slightly different way using a dialysis solution and a catheter. Sometimes, people can do their treatment at home.
Shape And Areas Of The Kidneys
The kidneys are bean-shaped and red-brown. Each kidney has a thickness of 4 cm, a width of 57 cm, and a length of approximately 11 cm . Each kidney weighs about 120200 g.
The cranial and caudal edges are called the upper and lower poles . The front surface of the kidney is called the facies anterior, and the back surface, the facies posterior. The kidneys lateral edge has a convex shape. The margo medialis is concave. The renal hilum with the kidney vessels is located on this medial edge. The renal vein lies ventrally to the renal artery, which is, in turn, anterior to the ureter . The renal hilum leads to the renal sinus and the renal pelvis.
Image: Internal anatomy by Phil Schatz. License: CC BY 4.0
Don’t Miss: Is Grape Juice Good For Kidney Stones
Kidney Stones Or Urolithiasis
Image: Kidney stone by Melensdad. License: CC BY 2.5
Kidney stones develop when there is an oversaturation of 1 substance in the urine. Depending on the urinary pH, the substance settles and forms stones.
There are many reasons for high concentrations of kidney stones in the urine. Too little fluid intake, high fluid loss, the state of being nutrition-rich in sodium chloride and calcium, immobilization during a long time, hormonal changes, gout, and many other things may be responsible for the formation of kidney stones.
Inorganic and organic stones are separate categories of kidney stones.
Inorganic stones:
- Stones can be made of calcium oxalate , calcium phosphate , or magnesium-ammonium-phosphate .
These stones are visible on radiographs without the application of a contrast medium.
Organic stones:
- These include uric acid residues and cystine stones .
These stones cannot be seen without the application of a contrast medium.
Symptoms occur when the urine flow is obstructed or the stone gets stuck in a narrow part. Common symptoms include pain in the flanks spreading to the lower abdomen and the back. They can even lead to colic, nausea, and vomiting, and sometimes to blood in the urine. As a result of kidney stones, complications may occur, leading to urinary obstruction and infection.
Small kidney stones often travel through the ureters and bladder by themselves. However, if passage of the stones is not possible, the following measures can be taken: