What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Medullary Sponge Kidney
Many people with medullary sponge kidney have no symptoms. The first sign that a person has medullary sponge kidney is usually a UTI or a kidney stone. UTIs and kidney stones share many of the same signs and symptoms:
- burning or painful urination
- fever and chills
People who experience these symptoms should see or call a health care provider as soon as possible.
What You Need To Know
- Adrenal glands, also known as suprarenal glands, are small, triangular-shaped glands located on top of both kidneys.
- Adrenal glands produce hormones that help regulate your metabolism, immune system, blood pressure, response to stress and other essential functions.
- Adrenal glands are composed of two parts the cortex and the medulla which are each responsible for producing different hormones.
- When adrenal glands dont produce enough hormones, this can lead to adrenal insufficiency .
- Adrenal glands may develop nodules that can be benign or malignant, which can potentially produce excessive amounts of certain hormones leading to various health issues.
Development Of Collecting Ducts
Morphologic development of collecting ducts
Figure 1. Renal medulla development in the mouse. Whole mount immunohistochemistry of E13.5 kidney. Ureteric buds and their derivatives are visualized with anti-pancytokeratin antibody . Medulla is not identifiable morphologically at this stage. Longitudinal section through a newborn kidney. Medulla and papilla are identifiable morphologically. UB-derived collecting ducts are visualized with anti-pancytokeratin antibody . Transverse section through P14 kidney stained with hematoxylin and eosin. Long papilla is present at this stage.
Genetic control of collecting duct morphogenesis
Table 1. Gene mutations leading to defects in morphogenesis of renal medulla in mice
| Gene | |
|---|---|
| Thin medulla atrophic papilla hydronephrosis | Reduced UB branching |
| Large initially and small later kidneys | |
| Thin medulla, dilated medullary collecting ducts | Increased apoptosis of papillary collecting duct cells |
| Absent medulla, dilated medullary collecting ducts | Aberrant division of collecting duct cells orthogonal to longitudinal axis of collecting ducts |
| Reduced proliferation of LOH cells, expanded area of apoptotic cells throughout primitive LOH bend | |
| Atrophic papilla hydronephrosis, reduced length of medullary capillaries, impaired organization of vasa recta bundles |
Read Also: How Can Your Kidneys Get Damaged
Nephrotoxicity Induced By Cisplatin
Body weight, kidney coefficient, blood urine nitrogen and serum creatinine of rats in different groups have been reported in our previous study. The results demonstrated that low-dose cisplatin induced slight kidney damage, and medium- or high-dose cisplatin induced significant renal function decline. It should be noted that the initial numbers of rats were 13, 13, 16 and 26 for group C, L, M and H, respectively. Eventually, 2, 3 and 10 rats in group L, M and H died, and the final numbers of animals were 13, 11, 13 and 16 for group C, L, M and H, respectively.
Not only the macroscopic indicators but also microscopic morphology were significantly changed after cisplatin administration. showed the representative pathological examination results of cortex and medulla in different groups. No abnormal changes were observed in control group , and only slight tubular expansion could be observed in medulla in low-dose cisplatin group . But remarkable abnormal histological changes can be observed in both cortical and medullar part in medium-dose cisplatin group and high-dose cisplatin group . The damages manifested tubular necrosis, tubular expansion, renal epithelial casts and interstitial infiltration of inflammatory cells.
Figure 1: Nephrotoxicity was induced by cisplatin.
You May Like: Celery Juice Kidney
Altered Pathways Related To Cisplatin Nephrotoxicity
As can be seen from , several metabolic pathways were affected by cisplatin including amino acid, energy, lipid, pyrimidine and purine metabolism, as well as creatine pathway. Of these metabolic pathways, lipid and amino acid metabolism were the most perturbed ones.
Figure 6: Metabolic pathways interrupted by cisplatin.
Metabolite names appear in blue fonts are differential metabolites identified in the present study. Abbreviations in this figure: TCA, tricarboxylic acid DGs, diacylglycerols LysoPC, lyso-phosphatidylcholine PC, phosphatidylcholine LysoPE, lyso-phosphatidylethanolamines PE, phosphatidylethanolamines PI, phosphoinositol FFAs, free fatty acids BCAAs, branched-chain amino acids GPC, glycerophosphocholine IMP, inosine monophosphate CTP, cytidine triphosphate.
Also Check: Does A Kidney Infection Cause Diarrhea
What Is A Nephron
The nephron in professional medicine is a structural unit of the kidneys.
Nephrons form a collection of organs responsible for the excretory function. Urine on the way through the nephrons is carefully processed and the unnecessary part of the fluid is reabsorbed. Useful substances are sent further. Poisons and other toxic substances are excreted by the urine stream.
Deterioration Of Kidney Function Due To Sickle Cell Disease
Sickle cell disease refers to a group of inherited conditions that affect a persons red blood cells.
A 2016 article notes that red blood cells tend to sickle in the medulla. This is because the medulla contains high levels of acid, salt, glucose, and other substances. It also has low levels of oxygen.
Sickle cell disease can affect the structures and function of the kidney and can lead to many conditions. These conditions can include acute kidney injury, an increased risk of urinary tract infections, chronic kidney disease, and the presence of blood in the urine.
It can also increase the risk of renal medullary carcinoma.
Also Check: What Is The Most Common Type Of Kidney Disease
What Are The Two Types Of Nephrons And How Do They Differ
The nephron is made up of the renal corpuscle and renal tubule.Cortical nephrons are found in the renal cortex, while juxtamedullary nephrons are found in the renal cortex close to the renal medulla. The nephron filters and exchanges water and solutes with two sets of blood vessels and the tissue fluid in the kidneys.
Crossing Vessel Upj Obstruction Vesicoureteral Reflux
Crossing vessel, ureteropelvic junction obstruction, or vesicoureteral reflux can become pathophysiologic if it causes extrinsic or primary intrinsic obstruction leading to hydronephrosis. This can be seen with aberrant crossing vessels in a single system, which leads to UPJ obstruction. Obstruction can also occur from an ectopic ureter, where it is commonly seen inserting inferomedially in an abnormal location and is often associated with the upper pole moiety of a complete duplicated collecting system.
Similarly, a ureterocele in a single system, or sometimes seen in a complete duplicated system, can cause obstruction. From an intrinsic standpoint, UPJO can also be caused by an adynamic/aperistaltic segment of ureter that is due to abnormal embryologic development. Secondary etiologies of obstruction include stones, infections, iatrogenic ureteral damage causing strictures, and other acquired factors that are not due to anatomic variants.
Vesicoureteral reflux is another variation and is caused by an abnormal insertion of the ureter in the bladder in an abnormal position . This insertion site leads to a shorter intramural tunnel length for the ureter to pass through the bladder wall, which leads to inadequate compression of the ureter during bladder filling and contraction and may allow reflux of urine up the ureter. Vesicoureteral reflux can contribute to pyelonephritis and, in extreme situations, irreversible damage to an affected renal unit.
The Nutcracker Syndrome
Don’t Miss: Can Contrast Dye Affect Your Kidneys
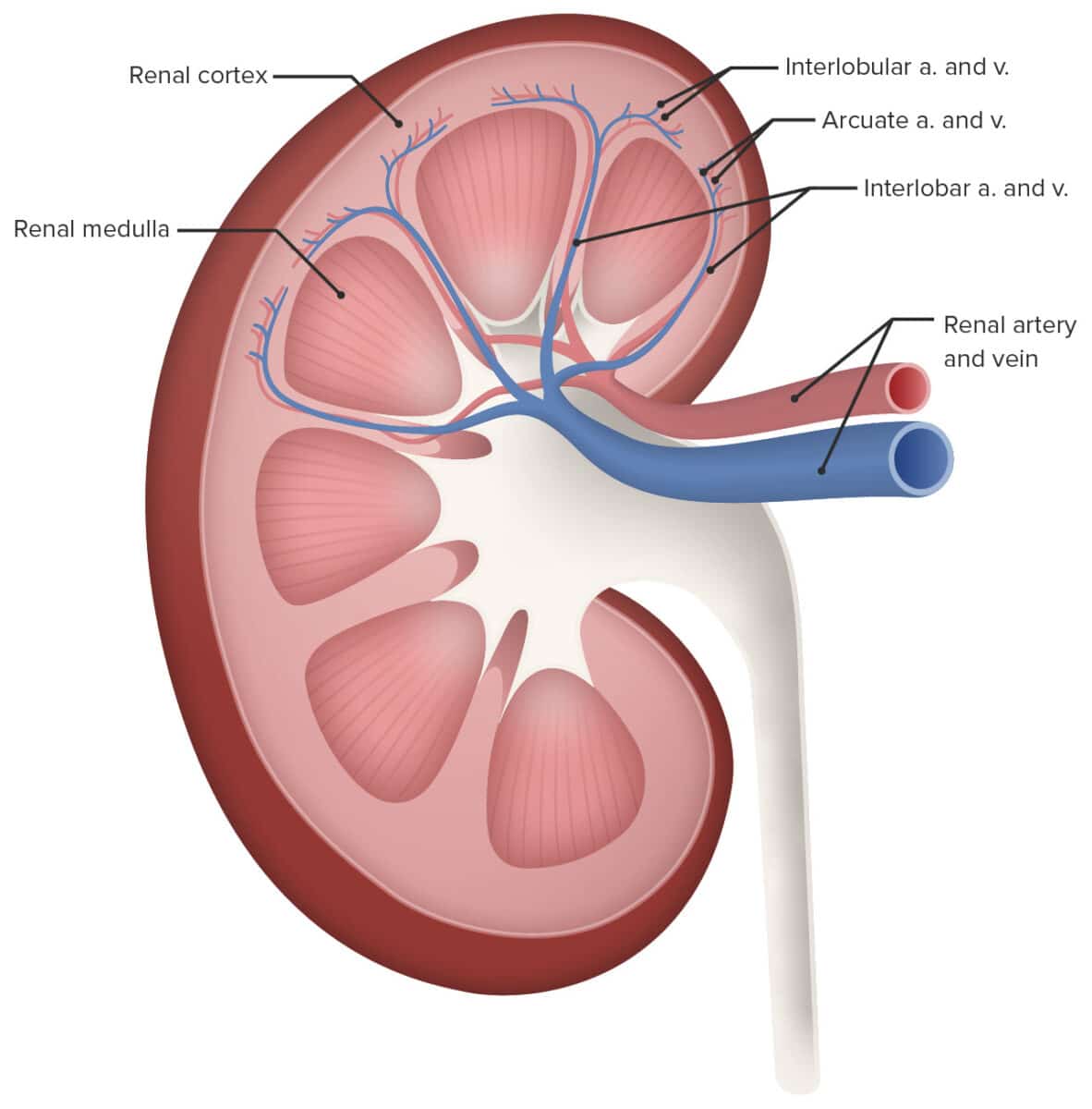
Blood Flows In And Out Of The Kidneys Through Renal Arteries And Veins
Blood enters the kidneys through renal arteries. These arteries branch into tiny capillaries that interact with urinary structures inside the kidneys . Here the blood is filtered. Waste is removed and vital substances are reabsorbed back into the bloodstream. The filtered blood leaves through the renal veins. All the blood in the body moves in and out of the kidneys hundreds of times each daythats about 200 quarts of liquid to be filtered every 24 hours.
What Are The Main Functions Of The Glomerulus And Bowmans Capsule
The capsule aids in the filtering of blood through the glomerulus. Small molecules from the blood are accepted by Bowmans space as long as the kidney filter is working normally if not, cells and large proteins remain in the blood as long as the kidney filter is working normally.
I received my Ph. D. from The Pennsylvania State University. My dissertation research was a study of the effect of experimentally-induced diabetes mellitus on aortic endothelial cell histamine metabolism. After receiving my degree, I took an Instructor position at the University of Louisville School of Medicine, where I team-taught human / mammalian physiology.
You May Like: Does A Blood Test Detect Kidney Problems
Functions Of The Medulla Of The Kidney And Organ As A Whole
Disruptions in the work of this paired organ can lead to many diseases and dysfunctions of other organs and systems. The kidneys perform extremely important functions in the human body. These include:
- elimination of various decay products
- blood pressure control
- direct participation in the process of blood clotting
- metabolism of nutrients
- ridding the body of toxins and toxins.
The excretory function of the kidneys is one of the main ones. She is responsible for cleansing and filtering everything that enters the body.
First, the blood “collects” everything that is useful and necessary, then the kidneys remove all that is unnecessary and unnecessary.
How Can I Strengthen My Adrenal Glands
healthyvitaminsfoodsvitaminshealthy adrenal glandsHow Adrenal Glands Work to Produce Cortisol
You May Like: What Can You Get Kidney Stones From
The Main Causes Of Kidney Disease
Experts identify the following reasons why various diseases of the genitourinary system, in particular, of the kidneys, can occur:
- strong mechanical impact from the outside
- congenital disorders in the work of the kidneys
- poisoning with poisonous substances, toxins
- damage to the body by fungi, parasites or viruses
- circulatory disorders.
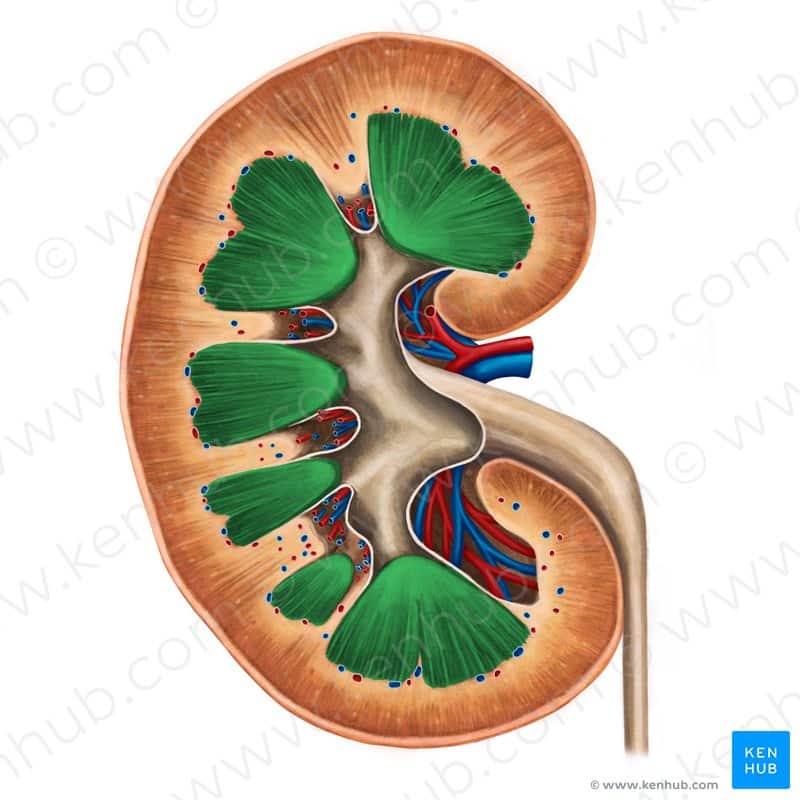
What Are The Papillae
This part of the kidney medulla represents the segments of the collecting tube of the organ. The recesses of these parts are located in a circle on the upper part of the papilla. They form a kind of “lattice” of the papilla. The papillae are surrounded by small renal cups. One such cup can capture 1, 2, sometimes even 3 papillae. A pair of renal cups can join into one large one and form the ureters. They, in turn, are responsible for connecting single cups to the pelvis.
Don’t Miss: How To Reduce Kidney Stone Pain In Tamil
Brief Overview Of Morphology And Function Of Mature Renal Medulla
The medulla of the adult kidney has a modified cone shape with a broad base adjacent to renal cortex and the narrow apex termed papilla. The mature renal medulla consists of the medullary collecting ducts, loops of Henle, vasa recta and the interstitium . The main function of the medulla is to regulate concentration of the urine. The urine flows from the collecting ducts into the renal calyces and pelvis, which undergoes unidirectional peristaltic movements to allow drainage of the urine into the downstream ureter and bladder. In addition, the renal papilla is a niche for adult kidney stem cells which may play a role in repair after ischemic kidney injury.,
What Are Some Common Treatments For The Renal Cortex
Treatments for disorders that affect your kidneys and renal cortex depend on the condition you have. For instance, if you have infections, your provider will prescribe antibiotics.
If you have something that needs to be removed, you may need a procedure or surgery. This could be true if you have a kidney stone, or a cyst or cancer.
You May Like: Why Is Red Meat Bad For Kidneys
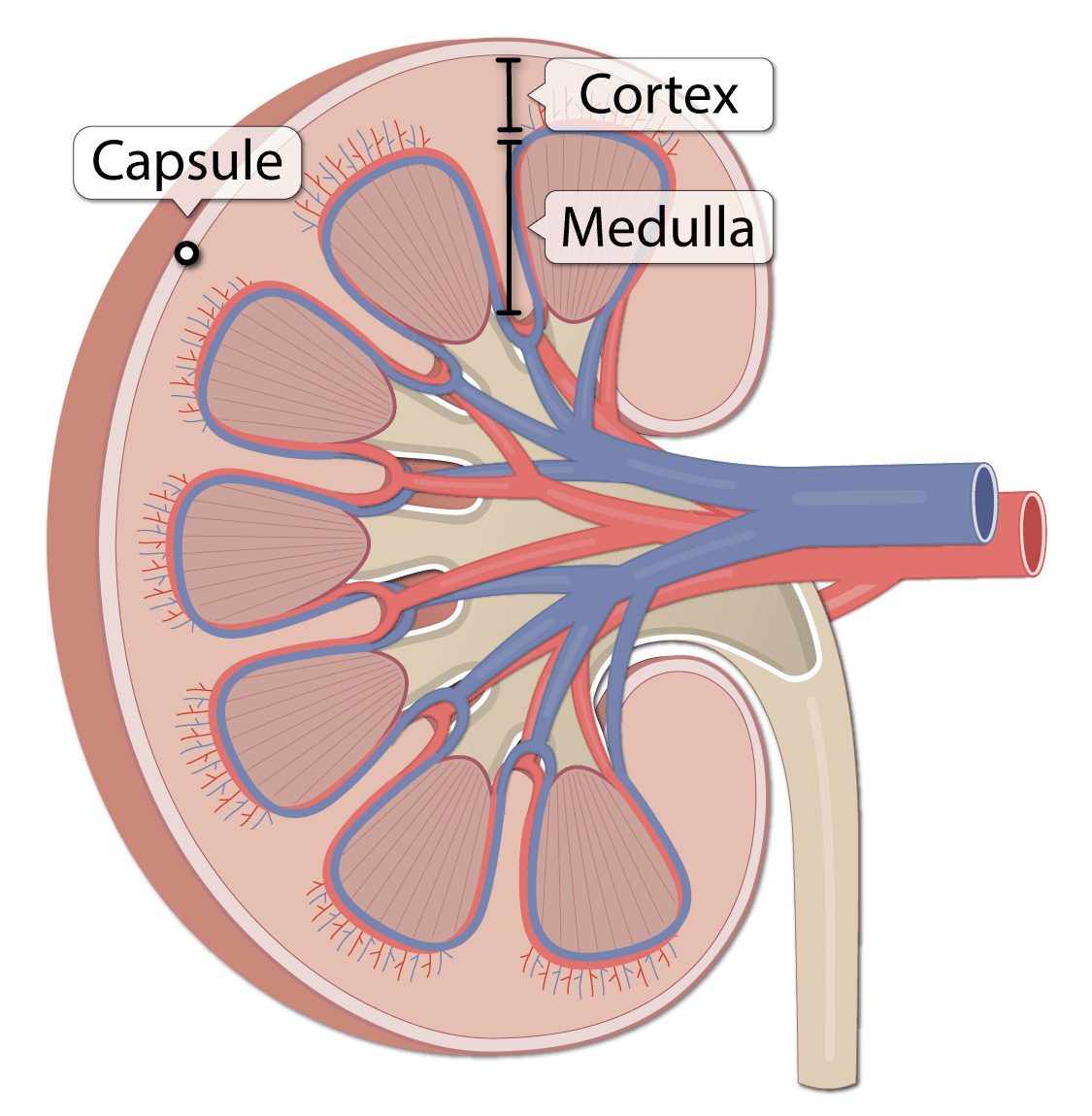
Is Cortex And Medulla The Same
renal medulla: The inner-most region of the kidney, arranged into pyramid-like structures, that consists of the bulk of nephron structure. renal cortex: The outer region of the kidney, between the renal capsule and the renal medulla, that consists of a space that contains blood vessels that connect to the nephrons.
How is the renal cortex different from the renal medulla at the tissue level?
The renal cortex is granular due to the presence of nephronsthe functional unit of the kidney. The medulla consists of multiple pyramidal tissue masses, called the renal pyramids. In between the pyramids are spaces called renal columns through which the blood vessels pass.
Why does the cortex have a different appearance to the medulla?
Cortex and medulla It is darker than its underlying renal medulla because it receives over 90% of the kidney blood supply. The cortex has a grainy appearance, as it mostly contains ovoid and coiled parts of the nephrons .
What is the function of the cortex in the kidney?
Renal Cortex The cortex provides a space for arterioles and venules from the renal artery and vein, as well as the glomerular capillaries, to perfuse the nephrons of the kidney. Erythropotein, a hormone necessary for the synthesis of new red blood cells, is also produced in the renal cortex.
Is The Medulla Deep To The Cortex Of The Kidney
The renal cortex is granular tissue due to the presence of nephronsthe functional unit of the kidneythat are located deeper within the kidney, within the renal pyramids of the medulla.
How can you distinguish between the renal cortex and the renal medulla under the microscope?
The renal medulla, the region internal to the cortex that contains parallel tubules and blood vessels, their shape on your slide depending on how theyre sectioned. The absence of renal corpuscles distinguishes the medulla.
Why does medulla of the kidney have a striped appearance?
The medulla consists of a number of medullary pyramids, named because of their triangular shape. These are striped in appearance because they contain microscopic coiled tubes called nephrons, the functional unit of the kidney .
What separates the cortex from the medulla?
The renal columns are connective tissue extensions that radiate downward from the cortex through the medulla to separate the most characteristic features of the medulla, the renal pyramids and renal papillae.
Recommended Reading: How Does Hypertension Affect The Kidneys
What Color Is Urine When Your Kidneys Are Failing
When kidneys are failing, the increased concentration and accumulation of substances in urine lead to a darker color which may be brown, red or purple. The color change is due to abnormal protein or sugar, high levels of red and white blood cells, and high numbers of tube-shaped particles called cellular casts.
Metabolic Cumulative Fold Change Demonstrated Accumulative Sensitivity Difference
Heat-map, OPLS-DA score plot and parameter Q2 were constructed or calculated based on all differential metabolites. To investigate if there were still differences in case of common metabolites in the two parts, MCFC was calculated based on 39 common metabolites . As can be seen from , MCFC of group L, M and H in medulla were all significantly higher than that in cortex. Thus, the degree of accumulative metabolic change of medulla was higher than cortex, indicating that metabolites in medulla were more sensitive to cisplatin exposure than cortex.
Don’t Miss: Is Coffee Bad For Your Kidneys
How The Kidneys Work
Blood is filtered at high pressure to remove glucose, water, salts and urea.
All the glucose, and some water and salts, are reabsorbed back into the blood. Note that urea is not reabsorbed.
Dr Alice Roberts dissects a pigs kidney and explains the structure and function of the kidney and urinary system
Renal Nerve Anatomy/autonomic Innervation
The kidney receives autonomic supply via both the sympathetic and parasympathetic portions of the nervous system. The preganglionic sympathetic nervous innervation to the kidneys arises from the spinal cord at the level of T8-L1. They synapse onto the celiac and aorticorenal ganglia and follow the plexus of nerves that run with the arteries. Activation of the sympathetic system causes vasoconstriction of the renal vessels. Parasympathetic innervation arises from the 10th cranial nerve , the vagus nerve, and causes vasodilation when stimulated.
You May Like: Is Mio Bad For Your Kidneys
Read Also: How To Restore Kidney Function
What Are The Common Conditions And Disorders That Affect The Renal Cortex
Many different disorders can affect the kidneys, including:
- Chronic kidney disease:Chronic kidney disease may lessen your kidney function. Diabetes or high blood pressure usually causes CKD.
- Kidney cancer: Renal cell carcinoma is the most common type of kidney cancer.
- Kidney failure : Kidney failure may be acute or chronic . End-stage renal disease is a complete loss of kidney function. It requires dialysis .
- Kidney infection : A kidney infection can occur if bacteria enter your kidneys by traveling up your ureters. These infections cause sudden symptoms. Healthcare providers treat them with antibiotics.
- Kidney stones:Kidney stones cause crystals to form in your urine and may block urine flow. Sometimes these stones pass on their own. In other cases, healthcare providers can offer treatment to break them up or remove them.
- Kidney cysts: Fluid-filled sacs called kidney cysts grow on your kidneys. These cysts can cause kidney damage. Healthcare providers can remove them if medically indicated.
- Polycystic kidney disease: Polycystic kidney disease , a genetic condition, causes cysts to form on the kidneys. PKD may lead to high blood pressure and kidney failure. People with PKD need regular medical monitoring.
There are so many other disorders that can affect or be related to your kidneys, and many of them are serious. Some of these conditions include:
Imaging Techniques For The Kidney
KUB is the proper terminology for a radiograph of the abdomen when used to view the urinary tract. The outline of kidneys can usually be seen. Ureters usually are not visible. The most common pathological findings are urinary tract stones. See the image below.
The imaging technique of choice for evaluation of the urinary tract and adrenal glands is CT scanning. It allows evaluation of the relative density of structures. CT scanning without contrast can be used for detection of renal or ureteral stones. See the image below.
The advantages of ultrasonography include that it is readily available, does not require contrast, and avoids radiation exposure. The renal medulla is hypoechoic compared with the renal cortex. The renal cortex is isoechoic or slightly hypoechoic compared with the liver. Ultrasonography is able to identify simple or mildly complicated cysts and is able to differentiate these lesions from a solid mass. It is excellent for detecting hydronephrosis. See the image below.
Radionuclide Renal Scintigraphy
Renal radionuclide imaging is an integral part of nuclear medicine and provides substantial information on the actual renal function.
The following radionuclides are used for dynamic imaging:
- Tc-99m-diethylene triamine pentaacetic acid
For static imaging, Tc-99m-dimercaptosuccinic acid is used.
A diuretic challenge can also be administered.
You May Like: How Do You Get Chronic Kidney Disease