Some Medical Conditions Also Increase The Risk Of Developing Kidney Stones Or Renal Calculus:
- Gout causes chronically increased uric acid in blood and urine and results in uric acid stone formation.
- Presence of high amounts of calcium in urine is an inherited condition causing stones in more 50% of cases.
- Hyperparathyroidism, cystinuria, etc. increases the risk of stone formation.
- Medical conditions like diabetes and high blood pressure also increases risk of kidney stones or renal calculus.
- People who have inflammatory bowel disease are at increased risk of developing stones.
- People who have undergone intestinal surgeries are also at increased risk for stones.
- Medications like certain diuretics, antacids which have calcium in them also increase risk of stones.
- Dietary factors such as a high intake of animal proteins, excessive salt intake, excessive sugar, and foods high in oxalate like spinach also increase risk for kidney stones or renal calculus.
How Do They Remove Kidney Stones Without Surgery
Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy is a technique for treating stones in the kidney and ureter that does not require surgery. Instead, high energy shock waves are passed through the body and used to break stones into pieces as small as grains of sand.
Treatment For Kidney Stones
Most kidney stones can be treated without surgery. Ninety per cent of stones pass by themselves within three to six weeks. In this situation, the only treatment required is pain relief. However, pain can be so severe that hospital admission and very strong pain-relieving medication may be needed. Always seek immediate medical attention if you are suffering strong pain.
Small stones in the kidney do not usually cause problems, so there is often no need to remove them. A doctor specialising in the treatment of kidney stones is the best person to advise you on treatment.
If a stone doesnt pass and blocks urine flow or causes bleeding or an infection, then it may need to be removed. New surgical techniques have reduced hospital stay time to as little as 48 hours. Treatments include:
Don’t Miss: Pineapple For Kidney Stones
What Do The Results Mean
Your results will show what your kidney stone is made of. Once your health care provider has these results, he or she can recommend steps and/or medicines that may prevent you from forming more stones. The recommendations will depend on the chemical makeup of your stone.
If you have questions about your results, talk to your health care provider.
Learn more about laboratory tests, reference ranges, and understanding results.
What Does The Treatment Involve
You will be positioned on an operating table. A soft, water-filled cushion may be placed on your abdomen or behind your kidney. The body is positioned so that the stone can be targeted precisely with the shock wave. In an older method, the patient is placed in a tub of lukewarm water. About 1-2 thousand shock waves are needed to crush the stones. The complete treatment takes about 45 to 60 minutes.
Sometimes, doctors insert a tube via the bladder and thread it up to the kidney just prior to SWL. These tubes are used when the ureter is blocked, when there is a risk of infection and in patients with intolerable pain or reduced kidney function.
After the procedure, you will usually stay for about an hour then be allowed to return home if all goes well. You will be asked to drink plenty of liquid, strain your urine through a filter to capture the stone pieces for testing, and you may need to take antibiotics and painkillers. Some studies have reported stones may come out better if certain drugs are used after SWL.
Also Check: Is Watermelon Good For Your Kidneys
What Are The Advantages And Disadvantages Of This Treatment
The main advantage of this treatment is that it treats kidney stones without an incision. As a result, hospital stays and recovery time are reduced.
But, while SWL can work, it doesn’t always work. After SWL, about 5O% of people will be stone free within a month. In others, stone fragments of various sizes remain. Sometimes a repeat procedure is needed.
SWL has the potential to cause kidney injury. Whether or not SWL causes or leads to the development of high blood pressure and diabetes remains controversial. These possibilities are still being studied. You should ask your doctor about risks and benefits of SWL in your situation.
Why Do Doctors Examine The Contents Of The Stone
There are four types of stones. Studying the stone can help understand why you have it and how to reduce the risk of further stones. The most common type of stone contains calcium. Calcium is a normal part of a healthy diet. The kidney usually removes extra calcium that the body doesn’t need. Often people with stones keep too much calcium. This calcium combines with waste products like oxalate to form a stone. The most common combination is called calcium oxalate.
Less common types of stones are: Infection-related stones, containing magnesium and ammonia called struvite stones and stones formed from monosodium urate crystals, called uric acid stones, which might be related to obesity and dietary factors. The rarest type of stone is a cvstine stone that tends to run in families.
Also Check: Is Celery Juice Good For Kidneys
Recombination And Genetic Linkage
The diploid nature of chromosomes allows for genes on different chromosomes to or be separated from their homologous pair during sexual reproduction wherein haploid gametes are formed. In this way new combinations of genes can occur in the offspring of a mating pair. Genes on the same chromosome would theoretically never recombine. However, they do, via the cellular process of . During crossover, chromosomes exchange stretches of DNA, effectively shuffling the gene alleles between the chromosomes. This process of chromosomal crossover generally occurs during , a series of cell divisions that creates haploid cells. , particularly in microbial , appears to serve the adaptive function of repair of DNA damages.
The first cytological demonstration of crossing over was performed by Harriet Creighton and in 1931. Their research and experiments on corn provided cytological evidence for the genetic theory that linked genes on paired chromosomes do in fact exchange places from one homolog to the other.
Genes generally their functional effect through the production of , which are complex molecules responsible for most functions in the cell. Proteins are made up of one or more polypeptide chains, each of which is composed of a sequence of , and the DNA sequence of a gene is used to produce a specific . This process begins with the production of an molecule with a sequence matching the gene’s DNA sequence, a process called .
Calcium Phosphate Stone Formers
From Systemic diseases
Primary hyperparathyroidism and renal tubular acidosis raise average urine alkalinity and foster calcium phosphate kidney stones. Many uncommon genetic diseases do the same.
Idiopathic
Idiopathic calcium phosphate stone formers share a common set of traits. Perhaps because urine contains far more phosphate than oxalate, they form more frequent and larger stones than idiopathic calcium oxalate stone formers. Often the stones originate as crystal plugs at the terminal ends of the kidney tubules.;More crystals deposit over the end of the plug open to the urine, to make the final stone. Crystal plugs damage the cells that line the tubules and cause local scarring.;
Also Check: Is Pomegranate Juice Good For Your Kidneys
How Are Kidney Stones Treated
Once diagnosed, your healthcare provider will first determine if you even need treatment. Some smaller kidney stones may leave your system when you urinate. This can be very painful. If your provider decides that you do need treatment, your options include medications and surgery.
Medications. Medications may be prescribed to:
- Your healthcare provider may recommend that you take an over-the-counter medication like ibuprofen or, if youre in the emergency room, an IV narcotic.
- Manage nausea/vomiting.
- Relax your ureter so that the stones pass. Commonly prescribed medicines include tamsulosin and nifedipine .
You should ask your healthcare provider before you take ibuprofen. This drug can increase the risk of kidney failure if taken while youre having an acute attack of kidney stones especially in those who have a history of kidney disease and associated illnesses such as diabetes, hypertension and obesity.
Surgery. There are four types of surgeries used to treat kidney stones. The first three are minimally invasive, meaning that the surgeon enters your body through a natural opening , or makes a small incision.
Kidney Stone Diet: Foods To Eat And Avoid
Overview
Kidney stones in the urinary tract are formed in several ways. Calcium can combine with chemicals, such as oxalate or phosphorous, in the urine. This can happen if these substances become so concentrated that they solidify. Kidney stones can also be caused by a buildup of uric acid. Uric acid buildup is caused by the metabolism of protein. Your urinary tract wasnt designed to expel solid matter, so its no surprise that kidney stones are very painful to pass. Luckily, they can usually be avoided through diet.
If youre trying to avoid kidney stones, what you eat and drink is as important as what you shouldnt eat and drink. Here are some important rules of thumb to keep in mind.
Read Also: Celery Juice And Kidney Disease
What Happens If I Get A Cystine Stone
The goal of treatment is to help keep stones from forming by reducing the amount of cystine in your urine. With less cystine in your urine, stones are less likely to form. It is important to work with your healthcare provider to reach this goal. ;Kidney stones can cause a lot of pain.; You may need to take pain relievers while you wait for the stone to pass out of your body.;
If a stone is very large and painful, or if it blocks the flow of urine, you may need surgery to remove it.; There are a few different types of surgeries to help get rid of the stones. These include:
- Percutaneous nephrostolithotomy : a procedure that involves passing a special instrument through your skin and into your kidney to take out the stones or break them apart.
- Ureteroscopy: a tiny instrument is passed into the bladder, and then up the ureter , to remove the stone.
- Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy :;a procedure that uses shock waves to break up large stones into smaller pieces. However, this procedure does not work as well for cystine stones compared to other types of kidney stones.
Let Kidney Stones Pass
Stones typically take several weeks to a few months to pass, depending on the number of stones and their size. Over-the-counter pain medications, like ibuprofen , acetaminophen , or naproxen , can help you endure the discomfort until the stones pass. Your doctor also may prescribe an alpha blocker, which relaxes the muscles in your ureter and helps pass stones quicker and with less pain.
If the pain becomes too severe, or if they are too large to pass, they can be surgically removed with a procedure called a ureteroscopy. Here, a small endoscope is passed into the bladder and up the ureter while you are under general anesthesia. A laser breaks up the stones, and then the fragments are removed.
Read Also: Is Grape Juice Good For Kidneys
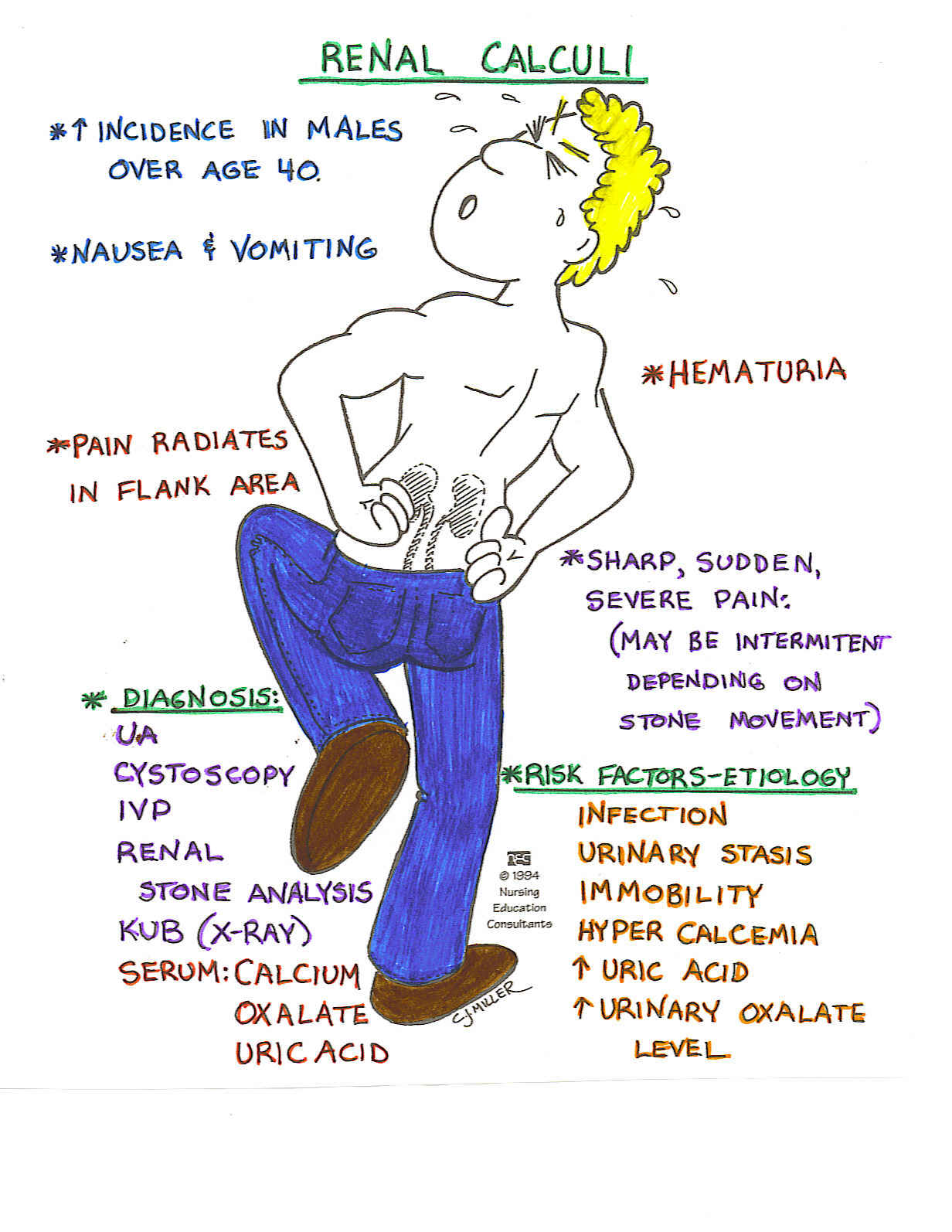
What Are Kidney Stones Or Renal Calculus
Kidney stones or renal calculus;are hard crystalline mineral materials formed in kidneys or urinary tract from minerals in urine. These stones are named on the basis of their locations; for example if it is in the kidney it is called nephrolithiasis and likewise if in ureter, ureterolithiasis etc. It is also classified by their chemical compositions like calcium-containing etc. Majority of people with kidney stones are males in the range of 30 and 40 years whereas they tend to occur at a later age in females. Kidney stones or renal calculus are formed when there is decrease in urine volume and/or excess presence of stone-forming substances in urine. People having medical conditions such as gout and those taking certain medications or supplements are at risk for developing kidney stones. Kidney stone or renal calculus;formation is also related to dietary and hereditary factors.
Where Do Kidney Stones Come From
Kidney stones form develop when certain substances, such as calcium, oxalate, and uric acid, become concentrated enough to form crystals in your kidneys. The crystals grow larger into “stones.” About 80% to 85% of kidney stones are made of calcium. The rest are uric acid stones, which form in people with low urine pH levels.
After stones form in the kidneys, they can dislodge and pass down the ureter, blocking the flow of urine. The result is periods of severe pain, including flank pain , sometimes with blood in the urine, nausea, and vomiting. As the stones pass down the ureter toward the bladder, they may cause frequent urination, bladder pressure, or pain in the groin.
“If you experience any of these symptoms, see your primary care physician,” says Dr. Eisner. “He or she will likely perform a urinalysis and a renal ultrasound, abdominal x-ray, or CT scan to confirm kidney stones are the source of your pain and determine their size and number.”
Also Check: Is Pineapple Good For Kidney Stones
Why You Get Stones
Part of preventing stones is finding out why you get them. Your health care provider will perform tests to find out what is causing this. After finding out why you get stones, your health care provider will give you tips to help stop them from coming back.
Some of the tests he or she may do are listed below.
Medical and Dietary History
Your health care provider will ask questions about your personal and family medical history. He or she may ask if:
- Have you had more than one stone before?
- Has anyone in your family had stones?
- Do you have a medical condition that may increase your chance of having stones, like frequent diarrhea, gout or diabetes?
Knowing your eating habits is also helpful. You may be eating foods that are known to raise the risk of stones. You may also be eating too few foods that protect against stones or not drinking enough fluids.
Understanding your medical, family and dietary history helps your health care provider find out how likely you are to form more stones.
Blood and Urine Tests
Imaging Tests
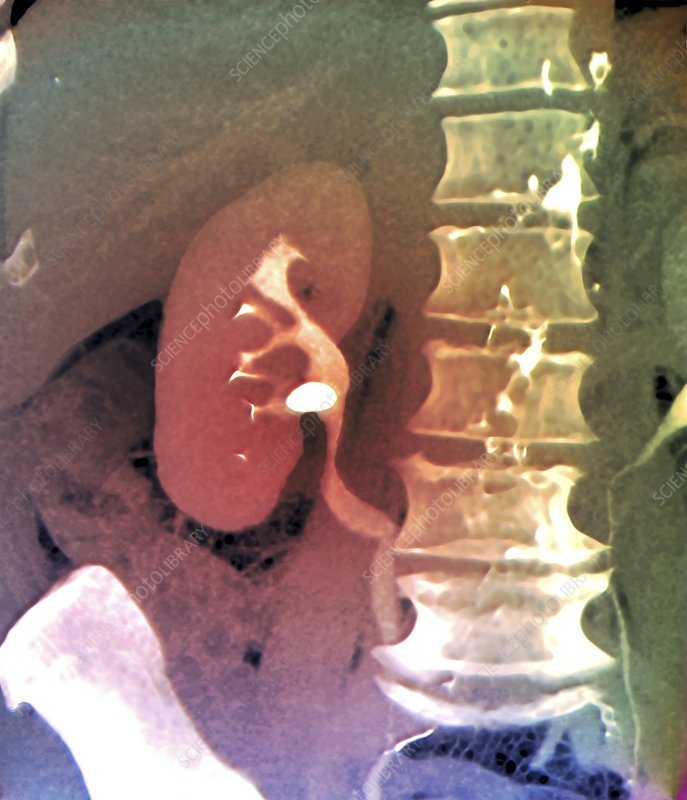
When a health care provider sees you for the first time and you have had stones before, he or she may want to see recent X-rays or order a new X-ray. They will do this to see if there are any stones in your urinary tract. Imaging tests may be repeated over time to check for stone growth. You may also need this test if you are having pain, hematuria or recurrent infections.
Stone Analysis
Difference Between Kidney Stone And Kidney Calculus
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video.
Recommended Reading: Is Celery Juice Good For Kidneys
Signs And Symptoms Of Kidney Stones Or Renal Calculus
kidney stones or renal calculus may cause severe pain whereas in some instances do not produce symptoms at all. If the stone is small in size and does not obstruct urine flow, it usually causes no pain. However, if it increases in size and passes into the ureter causing obstruction, it can result in acute and crippling pain. As the stones migrate from the kidney into the ureter towards the bladder, it causes mild to severe pain in the back. This pain moves with the stone around to the side of the abdomen as well as groin. Some patients may also have blood in their urine . Sometimes the blood is not visible to the naked eye and is visible under a microscope. After the stone has passed in urine, it leads to a drastic reduction in the pain. Sometimes patients may also experience dull back or flank pain though it is not that common. Some patients who have large stones sand with discomfort, i.e. they will pass gritty material in their urine usually with blood.
What Are Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy And Percutaneous Nephrolithotripsy
These procedures are treatments for kidney stones that are used in patients with large or irregularly shaped kidney stones, people with infections, stones that have not been broken up enough by SWL or those who are not candidates for another common stone treatment, ureteroscopy. Stones that are bigger than 2 cm require this procedure.
Both procedures involve entering the kidney through a small incision in the back. Once the surgeon gets to the kidney, a nephroscope and other small instruments are threaded in through the hole. lf the stone is removed through the tube, it is called nephrolithotomy. lf the stone is broken up and then removed, it is called nephrolithotripsy. The surgeon can see the stone, use high frequency sound waves to break up the stone, and “vacuum” up the dust using a suction machine.
This is what the words mean:
- Percutaneous means through the skin
- Nephrolithotomy is a combination of the word roots nephro- , litho- and -tomy
- Nephrolithotripsy is a combination of the word roots nephro- , litho , and -tripsy
Also Check: Is Grape Juice Good For Kidney Disease
When Is It Ordered
Kidney stone analysis is ordered when you have passed a kidney stone and it has been filtered out of the urine or when a stone has been removed from your urinary tract.
Sometimes, your healthcare practitioner may;suspect that you have a kidney stone and will search for a stone either in voided urine or within your body using imaging tests when you have signs and symptoms such as:
- Severe pain in the side of the back that may move to the groin
- Abdominal pain
- Uric acid
- Struvite stones associated with a bacterial infection
These four types make up about 95% to 99% of kidney stones, with calcium oxalate stones being the most common.
Less common stones include:
- Cystinestones associated with an inherited excess of cystine excretion
- Drug-relatedstones that are associated with drugs such as guaifenesin, indinavir, triamterene, atazanavir, and sulfa drugs
However, stone analysis does not give the reason that the stone formed.
You may have an underlying disease or condition that may produce and/or release an excess of a specific chemical into the urine. Not drinking enough fluids and/or having urine with a high or low pH can contribute to your risk of forming stones. Preventing kidney stones from developing again depends upon identifying and addressing the cause of stone formation.
In general, if you have;a: