How Is Kidney Cancer Diagnosed
Doctors diagnose kidney cancer by taking a medical history, performing a physical exam, and ordering one or more diagnostic tests.
Your doctor will begin to make a diagnosis by asking you about your symptoms and whether you have any risk factors for kidney cancer. During the physical exam, they will check your blood pressure, feel for lumps in the abdominal area, and look for other signs and symptoms indicative of kidney cancer.
If your doctor suspects you may have kidney cancer, they will order blood work and collect a urine sample for testing. Imaging tests such as a computed tomography scan, magnetic resonance study, and/or ultrasound are an essential part of the workup. In some cases, a biopsy of the kidney may be necessary to confirm diagnosis. In a kidney biopsy, a doctor removes a small piece of tissue from the kidney using a needle. A pathologist then examines the tissue sample under a microscope to check for the presence of cancer cells. If cancer cells are detected, the pathologist will give the cancer a grade. This is a measure of how likely and rapidly the cancer is to spread.
World Kidney Cancer Day 202: Who Is At A High Risk Of Developing Kidney Cancer
Written by Tavishi Dogra | Updated : June 17, 2022 11:33 AM IST
Our kidneys work in tandem with the rest of the body to keep the entire body balanced. Therefore, kidney function is essential in preventing the body from becoming overly stressed. However, kidney diseases, such as kidney cancer, can impair kidney function. Tumours from the tubules that produce urine in the kidney cause kidney cancer or renal cell carcinoma that can spread throughout the body. This happens when healthy cells in one or both kidneys overgrow and lump together . Dr Sanjay Gogoi, HOD and Consultant Urology, HCMCT Manipal Hospital, Dwarka shares an understanding of various forms of kidney cancer, helping in early diagnosis and timely treatment.
Treatment Options For Stage I Renal Cell Cancer
Treatment options for stage I renal cell cancer include the following:
Surgical resection is the accepted, often curative, therapy for patients with stage I renalcell cancer. Resection may be simple or radical. Radical resectionincludes removal of the kidney, adrenal gland, perirenal fat, and Gerota’sfascia, with or without a regional lymph node dissection. Some, but not all,surgeons believe the radical surgery yields superior results.
In patients with bilateral stage Ineoplasms , bilateral partial nephrectomy orunilateral partial nephrectomy with contralateral radical nephrectomy, whentechnically feasible, may be a preferred alternative to bilateral nephrectomywith dialysis or transplantation. Increasing evidence suggests that apartial nephrectomy is curative in selected cases. Apathologist should examine the gross specimen as well as the frozen section from theparenchymal margin of excision.
In patientswho are not candidates for surgery, EBRT or arterialembolization can provide palliation.
You May Like: How Do You Remove Kidney Stones From A Woman
What Are The Various Kinds Of Kidney Cancer
- Different types of kidney cancer can be seen in various age groups. The one which affects the elderly is renal cell carcinoma, also known as RCC, the most common type of kidney cancer. It has subtypes like Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. Some are called papillary renal cell carcinoma. In a nutshell, renal cell carcinoma accounts for the most cases of kidney cancer in older adults.
- In children, we have a type of kidney cancer called Wilms’ Tumor which tumour is also called nephron blastoma. This cancer is seen in children as young as 1-2 years.
- Other rare types of kidney cancer include transitional cell carcinoma of the kidney and upper collecting system, i.e., the pelvis of the kidney and the upper urethra.
In terms of incidence wise, probably RCC will top the list, followed by TCC.
What Causes Kidney Cancer
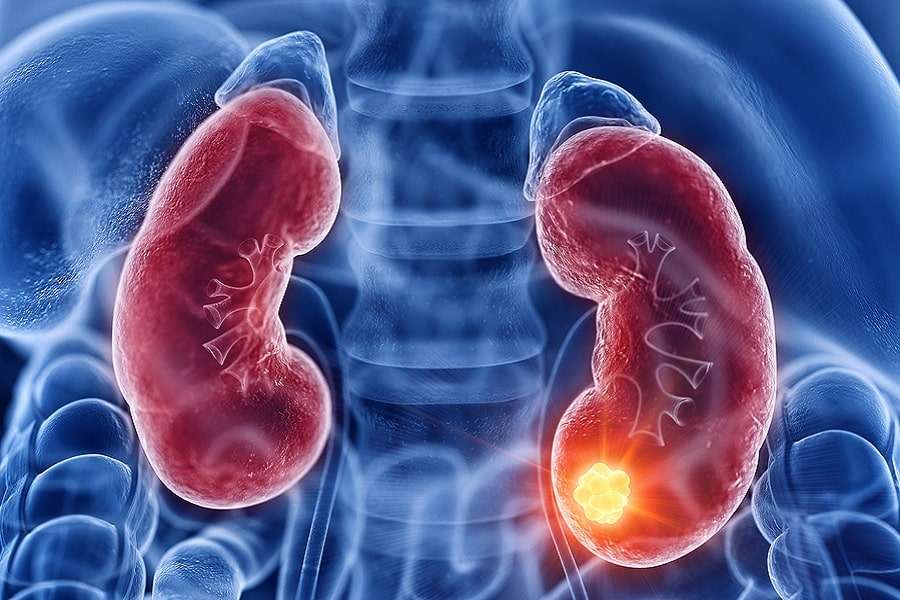
Scientists within the general medical community are working hard to gain a better understanding of the cellular DNA changes that lead to the development of renal cell carcinoma. While the precise causes are still unknown, several risk factors have been identified, including smoking and obesity. Certain inherited genetic syndromes have also been linked to an elevated risk of kidney cancer, including von Hippel-Lindau disease, hereditary papillary renal cell carcinoma, Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome, hereditary renal oncocytoma and hereditary leiomyoma renal cell carcinoma. Screening options are available for high-risk patients.
You May Like: How To Reverse Kidney Problems Naturally
Treatment For Advanced Kidney Cancer
Treatment for advanced kidney cancer may include:
- active surveillance
- immunotherapy
- radiation therapy.
Drugs that reach cancer cells throughout the body are called systemic treatments. Targeted therapy and immunotherapy are the main systemic treatments used to control advanced kidney cancer. Since the development of these more effective systemic treatments, chemotherapy is rarely used for kidney cancer.
Treatment For Kidney Cancer
Treatment for kidney cancer depends on how quickly the cancer is growing.
Treatment is different for early kidney cancer and advanced kidney cancer.
You might feel confused or unsure about your treatment options and decisions. Its okay to ask your treatment team to explain the information to you more than once. Its often okay to take some time to think about your decisions.
If you are a current smoker, your health care team will advise you to stop smoking before you start treatment. To work out a plan for quitting, talk to your doctor or call Quitline
Don’t Miss: Can Kidney Stones Cause Blood In Urine
Signs And Symptoms Of Kidney Cancer
While some people may notice symptoms of kidney cancer, others dont experience any warning signs.
The kidneys are located in the back of the abdomen, and tumors there can grow quite large without any symptoms at all, explains Andrew J. Armstrong, MD, a professor of medicine, surgery, pharmacology, and cancer biology at Duke University School of Medicine in Durham, North Carolina.
- Blood in the urine, which may look red, pink, or cola-colored
- Persistent pain in the back or side
- Unexplained weight loss
- Anemia
Thinking About Taking Part In A Clinical Trial
Clinical trials are carefully controlled research studies that are done to get a closer look at promising new treatments or procedures. Clinical trials are one way to get state-of-the art cancer treatment. In some cases they may be the only way to get access to newer treatments. They are also the best way for doctors to learn better methods to treat cancer. Still, they’re not right for everyone.
If you would like to learn more about clinical trials that might be right for you, start by asking your doctor if your clinic or hospital conducts clinical trials.
Read Also: How To Clean Your Liver And Kidneys
Cancer That Hasn’t Spread
Surgery is the main treatment if your cancer hasn’t spread to other parts of your body. If your cancer is smaller than 3cm and you are older or unwell, your doctor might suggest you have no treatment at first. They will monitor you closely.
Stage 1 and 2 kidney cancers contained in the kidney are often cured with surgery. Stage 3 cancers are called locally advanced cancers. They can sometimes be cured if the surgeon can remove all the cancer.
If you can’t have surgery you might have:
- freezing therapy
- blocking the blood supply to the cancer
Newer Treatments And Clinical Trials
Researchers continue to search for new ways to target and treat kidney cancers.
Currently, we are working on developing new biomarkers that will help oncologists decide which treatment approach will provide the best outcomes for their patients, says Lee.
We are interested in developing novel pathways to attack the cancer. We are doing a lot of working to better understand how the genetics of the kidney cancer and the genetics of the patient impact the response to provide more personalized therapies, and we hope that in the future we will be able to develop more personalized approaches for patients, he adds.
Don’t Miss: Can You Have Kidney Stones For Years
Other Types Of Kidney Cancer
- Transitional cell carcinoma Instead of starting in the kidney itself, these cancers start in the lining of the renal pelvis the area where the ureters, tiny tubes that carry urine to the bladder, meet the kidneys.
- Wilms tumor This type of kidney cancer primarily affects children.
- Renal sarcoma Renal sarcomas begin in the blood vessels or connective tissue of the kidney. They are rare, making up less than 1 percent of all kidney cancers.
Sexuality And Kidney Cancer
Having kidney cancer and treatment can change the way you feel about yourself, other people and sex. These changes can be very upsetting and hard to talk about. Doctors and nurses are very understanding and can give you some support. You can ask for a referral to a doctor or therapist who specialises in body image, sex and relationships.
Read Also: Can Kidney Stones Cause Long Term Damage
There Are Three Ways That Cancer Spreads In The Body
Cancer can spread through tissue, the lymph system, and the blood:
- Tissue. The cancer spreads from where it began by growing into nearby areas.
- Lymph system. The cancer spreads from where it began by getting into the lymph system. The cancer travels through the lymph vessels to other parts of the body.
- Blood. The cancer spreads from where it began by getting into the blood. The cancer travels through the blood vessels to other parts of the body.
Ajcc Stage Groupings And Tnm Definitions
The American Joint Committee on Cancer has designated staging by TNM classification to define renal cell cancer.
| Stage | Illustration |
|---|---|
| T = primary tumor N = regional lymph node M = distant metastasis. | |
| aReprinted with permission from AJCC: Kidney. In: Amin MB, Edge SB, Greene FL, et al., eds.: AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 8th ed. New York, NY: Springer, 2017, pp. 73948. | |
| I | |
| T1a = Tumor 4 cm in greatest dimension, limited to the kidney. | |
| T1b = Tumor > 4 cm but 7 cm in greatest dimension, limited to the kidney. | |
| N0 = No regional lymph node metastasis. | |
| M0 = No distant metastasis. |
| Stage | Illustration |
|---|---|
| T = primary tumor N = regional lymph node M = distant metastasis. | |
| aReprinted with permission from AJCC: Kidney. In: Amin MB, Edge SB, Greene FL, et al., eds.: AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 8th ed. New York, NY: Springer, 2017, pp. 73948. | |
| II | |
| T2a = Tumor > 7 cm but 10 cm in greatest dimension, limited to the kidney. | |
| T2b = Tumor > 10 cm, limited to the kidney. | |
| N0 = No regional lymph node metastasis. | |
| M0 = No distant metastasis. |
References
You May Like: Do Kidney Stones Hurt After They Pass
What Are The Kidney Cancer Stages
Most cancers are grouped by stage, a description of cancer that aids in planning treatment. The stage of a cancer is based on:
- The location and size of the tumor.
- The extent to which your lymph nodes are affected.
- The degree to which the cancer spread, if at all, to other tissue and organs.
Your healthcare provider uses information from various tests, including CT, MRI and biopsy, to determine the stage of cancer.
- Stage I: The tumor is 7 centimeters across or smaller and is only in your kidney. It hasnt spread to lymph nodes or other tissue. .
- Stage II: The tumor is larger than 7 cm across but is still only in your kidney. It hasnt spread to lymph nodes or other tissue.
- Stage III: The tumor has spread to your major blood vessels your renal vein and inferior vena cava or into the tissue surrounding your kidney or to nearby lymph nodes.
- Stage IV: The tumor has spread outside of your kidney to your adrenal gland , or to distant lymph nodes or other organs.
Tumors are also graded, which is a way of rating a tumor based on how abnormal its cells look. Tumor grading can also tell your healthcare provider how fast the tumor is likely to grow. Tumors whose cells dont look like normal cells and divide rapidly are called high-grade tumors. High-grade tumors tend to grow and spread more quickly than low-grade tumors.
Treatment Options For Stage Iii Renal Cell Cancer
Treatment options for stage III renal cell cancer include the following:
Adjuvant systemic therapy
Surgical resection is the standard treatment for patients with clinical stage III renal cell cancer. Several different studies have investigated whether adjuvant systemic therapy improves outcomes. None of these trials have demonstrated any impact on overall survival . However, two agents are associated with longer relapse-free survival.
Adjuvant pembrolizumab
Pembrolizumab is an immune checkpoint inhibitor and a monoclonal antibody targeting the programmed death-1 protein.
Evidence :
Evidence :
Don’t Miss: Is Blueberry Good For Kidney
When Is Chemotherapy Effective In Treating Kidney Cancer
While doctors dont use chemotherapy to treat RCC, it can be effective for some other, less common, types of kidney cancer. These include:
- Transitional cell carcinoma .TCC begins in the cells that line an area called the renal pelvis, which is where the kidneys and ureters meet. TCC cells typically resemble bladder cancer cells.
- Collecting duct carcinoma . CDC is an aggressive type of kidney cancer that starts in the collecting ducts, which collect urine from the kidneys and move it to the ureters. It only causes up to 3 percent of all kidney cancers.
- Renal medullary carcinoma . RMC mainly impacts individuals with sickle cell trait. Its very rare, accounting for less than 0.5 percent of all kidney cancers, but is one of the most aggressive types of kidney cancer.
- Wilms tumors.Wilms tumors, also called nephroblastoma, are a type of kidney cancer that almost always impacts children.
- Malignant rhabdoid tumors . MRTs are a rare type of tumor made up of many large cells. The kidneys are a common area for them to develop. Theyre most common in babies between the ages of 11 to 18 months .
There are some specific situations where doctors may use chemotherapy to treat RCC. This is typically when RCC is advanced and hasnt responded to other types of treatment like immunotherapy or targeted therapy.
- 5-flurouracil
- vinblastine
- vincristine
One example of combination chemotherapy used to treat TCC and potentially other types of kidney cancer includes:
- methotrexate
- doxorubicin
- cisplatin
How Can It Be Treated
- Treatment depends on the age group. This is because there are different tumours in different age groups. For example, the standard treatment method for kidney tumours was the excretion of the whole kidney even today, the same process is used for transitional cell carcinoma. But for other types of tumours like renal cell carcinoma, what has happened in the last two decades is that we have realized the necessity to preserve as much of kidney tissues as possible so kidney failure can be prevented.
- A new treatment has evolved called a partial nephrectomy, whereby only the tumour containing part of the kidney is removed. If possible, the rest of the kidney is preserved. This treatment method is done by open surgical, laparoscopic, or even automated procedures. This is the most effective method. Preservation of kidney function is as known as nephron sparing surgery.
Don’t Miss: How Long To Live With Kidney Disease
Remission And The Chance Of Recurrence
A remission is when cancer cannot be detected in the body and there are no symptoms. This may also be called having no evidence of disease or NED.
A remission may be temporary or permanent. This uncertainty causes many people to worry that the cancer will come back. While many remissions are permanent, it is important to talk with your doctor about the possibility of the cancer returning. Understanding your risk of recurrence and the treatment options may help you feel more prepared if the cancer does return. Learn more about coping with the fear of recurrence.
If the cancer returns after the original treatment, it is called recurrent cancer. It may come back in the same place , nearby , or in another place . If you have had a partial nephrectomy already, a new tumor may form in the same kidney. The recurrent tumor can be removed with another partial nephrectomy or with a radical nephrectomy .
People with recurrent cancer sometimes experience emotions such as disbelief or fear. You are encouraged to talk with your health care team about these feelings and ask about support services to help you cope. Learn more about dealing with cancer recurrence.