What Are Some Of The Risks Of A Transplant Kidney Biopsy
While the risks of a biopsy are small, complications could occur. Bleeding may occur. About a third of patients have some light red color in the urine for a day or so of little consequence. About 1-3% of patients have bleeding with clots that required a bladder irrigation with a catheter to clear them. If the bleeding is severe enough, a transfusion may be needed. However, this is a very rare occurrence in less than 1% of patients. Very rarely a urine infection may occur, especially in patients with a history of frequent urine infections. Other problems to watch for include fever, pain at the site of the biopsy, dizziness, or not being able to urinate.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 11/05/2019.
References
What Are The Risks Of Kidney Biopsy
Complications are uncommon. In a small number of cases there is some bleeding from the site where the sample has been taken. This is usually minor and soon stops. Occasionally, the bleeding is more severe. Rarely, the bleeding requires a blood transfusion and/or an operation to deal with it. The main reason that you are monitored for several hours after the biopsy is to check for bleeding. There is a small risk that the small wound will become infected after the biopsy.
Three Kinds Of Kidney Disease Does Not Need Renal Biopsy
To make a clear diagnosis, you may be suggested to do renal biopsy. But in fact, three kinds of kidney disease does not need renal biopsy, and eight kinds of kidney patients can not do renal biopsy. In this article, lets have a quick look.
First of all, renal biopsy has some disadvantages.
It is invasive, so you may have some risks, such as bleeding and hematoma. And for some patients, they may have massive hemorrhage to threaten life. Besides, it requires hospitalization. Then can renal biopsy be avoided?
Yes. Under these 3 conditions, the causes can be confirmed without renal biopsy.
1. Nephrotic syndrome caused by malignant tumors. After treating tumor, kidney disease will get into remission.
2. Kidney disease cased by years of diabetes. In early stage, there is microalbuminuria. And it gradually progresses into massive proteinuria.
3. Kidney damage caused by years of high blood pressure.
These 3 kinds of etiology are clear, so the doctor can treat it according to experience. In addition, renal biopsy is not suitable for these 8 types of patients:
1. Patients with obvious bleeding tendency.
2. Patients with congenital solitary kidney.
3. Patients whose has severe renal insufficiency in unilateral kidney.
4, Patients who have hematoma, tumor, cyst, abscess or infection, hydronephrosis.
5. Patients with mentally ill or unable to cooperate with operators.
6. Patients with poor blood pressure control.
7. Patients with thin renal cortex.
Don’t Miss: Does Carbonated Water Cause Kidney Stones
How Is A Kidney Biopsy Done
- The procedure of biopsy is started by laying the patient on the bed in a position that is comfortable and suitable for the biopsy
- Then the patient will get an intravenous placed via which the sedative will be given during the procedure if needed
- Identification of the spot from where the needle is to be inserted in the next step. To execute this, certain procedures such as ultrasound is used.
- After identification, that spot is marked and given local anesthesia.
- Once the needle is inserted through that spot, the movement of the needle to go further at the kidney is again assisted by the ultrasound
- A specialized tool at the front of the needle will collect the sample from the kidneys. Meanwhile, the patient will be asked to stay still and not get overwhelmed by the sound of removal of tissue
- As to avoid the pain of the patient, the doctors will only take a tiny portion of kidney tissue at a time. Therefore, a needle might be inserted more than once to gather enough tissue to be studied under a microscope
As the patients who are required to get a kidney biopsy done do not suffer from the same condition, hence the above procedure is not the only method of performing a kidney biopsy.
For some patients, the method of laparoscopy is used and for some, open kidney biopsy is done.
What Can A Person Expect After A Kidney Biopsy
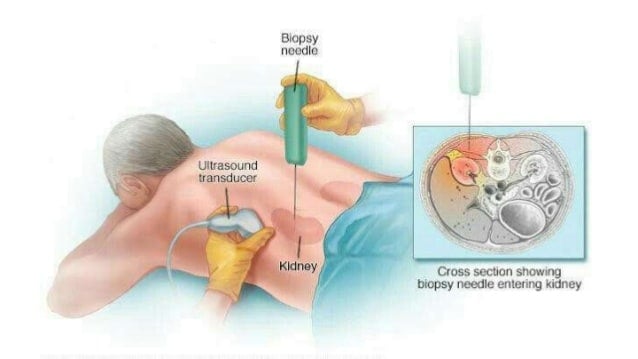
After a kidney biopsy, a person can expect to
- lie on his or her back in the clinic or hospital for a few hours. During this time, the staff will monitor the persons blood pressure, pulse, urine, and blood test results.
- go home the same day, in most cases however, a person will need to rest at home for 12 to 24 hours after the biopsy. Sometimes a person may need to stay overnight at the hospital.
- have some pain or soreness near the point where the needle went through the skin.
- receive written instructions for ensuring a healthy recovery from the procedure. Most people need to wait 2 weeks before resuming strenuous activities, such as heavy lifting or participating in contact sports.
A health care provider most often receives the complete biopsy results from the pathologist in about a week. In urgent cases, a person may receive a preliminary report within 24 hours. The health care provider will review the results with the person during a follow-up visit.
Don’t Miss: What Std Messes With Your Kidneys
Imaging Tests To Look For Kidney Cancer
Imaging tests use x-rays, magnetic fields, sound waves, or radioactive substances to create pictures of the inside of your body. Imaging tests are done for a number of reasons, such as:
- To look at suspicious areas that might be cancer
- To learn how far cancer might have spread
- To help determine if treatment is working
- To look for possible signs of cancer coming back after treatment
Unlike most other cancers, doctors can often diagnose kidney cancer with fair certainty based on imaging tests without doing a biopsy . Some patients, however, may need a biopsy.
How Is The Sample Obtained In A Transplant Kidney Biopsy
There are two ways to obtain the sample during a transplant kidney biopsy. A needle can be used that will go through the skin and into the kidney. The needle then is used to collect the sample. An ultrasound image is used to help guide the needle to the correct spot. This process is called a percutaneous biopsy. The second method would be to take a sample during surgery, this is much less common. Ultrasound guided transplant kidney biopsies are most often done under local anesthesia.
You May Like: Does Red Wine Cause Kidney Stones
How You Have It
Your doctor uses an ultrasound or CT scanner to help them see exactly where the tumour is.
You lie on your front on a couch or bed to have the biopsy. The doctor cleans the skin over the kidney with antiseptic. They inject local anaesthetic into the area to make it numb. This may sting a little at first.
A hollow needle goes through the skin and muscle into the kidney tissue. They take a small sample. You might feel some pressure at this time.
You need to hold your breath for 5 to 10 seconds while the needle is pushed in and out. This is because the kidneys move slightly when you breathe in and out. Your doctor tells you exactly when to hold your breath.
Tell A Healthcare Provider About:
- Any allergies you have.
- All medicines you are taking, including vitamins, herbs, eyedrops, creams, and over-the-counter medicines.
- Any problems you or family members have had with anestheticmedicines.
- Any blood disorders you have.
- Any surgeries you have had.
- Any medical conditions you have.
- Whether you are pregnant or may be pregnant.
Also Check: Is Grape Juice Good For Kidney Stones
How Is A Kidney Biopsy Performed
The procedure typically takes about an hour and includes the following steps:
For people with bleeding problems, the health care provider uses a laparoscopea thin tube with a video camera. This procedure is surgery that requires general anesthesia. The surgeon makes a small incision into the back and inserts the laparoscope to see the kidney. The surgeon can insert tiny tools through the laparoscope to collect tissue samples and can watch after the procedure through the camera to make sure that if there is any bleeding, he or she can stop it.
What Happens During A Kidney Biopsy
During a kidney biopsy, a doctor collects a sample of tissue from your kidney. Most biopsies are done through your back, although people with a transplanted kidney have the biopsy through their lower abdomen .
Your doctor will use one of these methods to take the sample:
- Percutaneous biopsy: In this more common type of kidney biopsy, a doctor numbs the skin located over the kidney and inserts a needle to take a small tissue sample from the kidney. Your doctor may use ultrasound imaging to guide the needle to the best location in the kidney.
- Open biopsy: In an open biopsy, a doctor makes an incision , removes tissue from the kidney, and closes the incision with stitches. Your doctor will give you anesthesia so you do not feel pain during the procedure. This type of biopsy is rare except at the time of kidney transplant.
You May Like: Pomegranate Juice For Kidney Stones
How The Test Will Feel
Numbing medicine is used, so the pain during the procedure is often slight. The numbing medicine may burn or sting when first injected.
After the procedure, the area may feel tender or sore for a few days.
You may see bright, red blood in the urine during the first 24 hours after the test. If the bleeding lasts longer, tell your provider.
How Do I Prepare For The Kidney Biopsy
Please read this information leaflet. Share the information it contains with your partner and family so that they can be of help and support. There may be information they need to know, especially if they are taking care of you following this examination.
Most kidney biopsies are undertaken as a day case procedure. You will need to have some blood tests done beforehand to ensure it is safe to go ahead with the biopsy. These can be done at your doctors surgery, or you may need to attend the hospital. You will need a further blood test on the day of the biopsy.
If you take any blood thinning medicines, these must be stopped before the procedure and your kidney doctor will discuss this with you. On the day of the biopsy take all other medications as normal. It is essential the doctor has a full list of all your medicines, including any not prescribed. If you have not received any advice you should contact the renal department on 675050.
Bring any medication that you take regularly. It is important that your blood pressure is well controlled to be able to go ahead with the biopsy. If your blood pressure is too high on the day the biopsy is planned, the biopsy will be postponed. Some biopsies are done as an inpatient.
Do not drive on the day of the biopsy.
Recommended Reading: Are Grapes Good For Kidney Stones
What Happens After The Kidney Biopsy
Your recovery will vary depending on the type of procedure done and yourhealthcare provider’s practices. You may be taken to the recovery room andwatched closely as the anesthesia wears off. Once your blood pressure,pulse, and breathing are stable and you are alert, you may be taken to ahospital room or discharged to your home.
You will be asked to lie on your back for several hours. A nurse will checkyour urine for signs of bleeding. You may have blood tests to check forinternal bleeding. You may be discharged later the same day or the nextday. If you had a sedative or anesthetic, plan to have someone drive youhome.
The biopsy site may be tender or sore for several days after the biopsy.Take a pain reliever for soreness as advised by your healthcare team. Youmay need to avoid aspirin or certain other pain medicines that may raisethe chance of bleeding. Be sure to take only recommended medicines.
Tell your healthcare team to report any of the following:
-
Blood in your urine after the first 24 hours
-
Inability to urinate
-
Redness, swelling, or bleeding or other drainage from the biopsy site
-
Increased pain around the biopsy site or elsewhere
-
Feeling faint
Your healthcare provider may give you other instructions after theprocedure, depending on your situation.
Your thoughts matter to us. Join our community today.
Before you agree to the test or the procedure make sure you know:
What Are Cystoscopy And Ureteroscopy
Cystoscopy and ureteroscopy are common procedures performed by a urologist to look inside the urinary tract.
Cystoscopy is a procedure that uses a cystoscope to look inside the urethra and bladder. A cystoscope is a long, thin optical instrument with an eyepiece at one end, a rigid or flexible tube in the middle, and a tiny lens and light at the other end of the tube. A urologist fills the bladder with fluid and looks at detailed images of the urethra and bladder linings on a computer monitor.
Ureteroscopy is a procedure that uses a ureteroscope to look inside the ureters and kidneys. Like a cystoscope, a ureteroscope has an eyepiece at one end, a rigid or flexible tube in the middle, and a tiny lens and light at the other end of the tube. However, a ureteroscope is longer and thinner than a cystoscope so the urologist can see detailed images of the lining of the ureters and kidneys.
Recommended Reading: Is Honey Good For Kidney
How To Prepare For A Kidney Biopsy
- Speak with your doctor about your procedure, why youre having it, and what the results could mean. This may help relieve stress and make you feel prepared.
- Arrange for a ride to and from your procedure. You cant drive home after general anesthesia.
- Tell your doctor about any medications youre taking, whether theyve been prescribed to you or you bought them over the counter. Include any vitamins and supplements. Ask which, if any, you should take before or the day of your procedure. Be sure to mention if youre taking blood thinners and ask when to stop them. You may need to stop taking blood thinners up to two weeks before your biopsy.
- Inform your doctor of any allergies to medications or foods.
- Dont eat or drink for at least eight hours before your procedure is scheduled.
- You may take a bath or shower before the biopsy, but dont use lotion, perfume or deodorant. Avoid nail polish as well.
- Leave jewelry at home, including piercings.
- Arrive 90 to 120 minutes before youre scheduled so you have time to fill out the necessary paperwork, undergo needed blood tests and receive IV fluids and sedatives. Your blood and urine will be tested for bleeding issues or high blood potassium that would make it too risky for you to undergo a kidney biopsy.
What Are The Risks Of A Kidney Biopsy
The risks of a kidney biopsy include
- bleedingthe most common complication of a kidney biopsy. Bleeding may come from the kidney or the puncture site. Bleeding from the kidney rarely requires a blood transfusion.
- infectiona rare complication of a kidney biopsy. Health care providers prescribe bacteria-fighting medications called antibiotics to treat infections.
Also Check: What Std Messes With Your Kidneys
Monoclonal Gammopathies And Paraprotein Diseases
Patients with monoclonal gammopathies may require a kidney biopsy to document end organ damage from the offending paraprotein. Although it has been suggested that patients with monoclonal gammopathies and amyloidosis have a higher risk of complications from bleeding diathesis , there is no evidence that this translates to a higher clinical risk with PRBs. One series found a statistically increased risk of bleeding in patients who had renal amyloidosis , but the definition of bleeding was a hemoglobin decrease > 1 g/dl and did not include need for transfusion or intervention. A second series found no difference in overall or major bleeding complications after PRB in patients with systemic amyloidosis versus controls . Another series found no increased risk of PRB complications for patients with monoclonal gammopathies versus controls .
How Do I Prepare For A Cystoscopy Or Ureteroscopy
Your urologist will ask about your medical history to determine whether you need a cystoscopy or ureteroscopy. You may need to give a urine sample to test for a UTI. If you have a UTI, you may need to take antibiotics before either procedure.
Your urologist will also ask about any medicines you are taking, ask if you have any allergies, talk about anesthesia, give instructions for what to do before the procedure, and discuss what to expect afterward. In some cases, you wont need special preparations for a cystoscopy. In other cases, your instructions may include
- when to stop certain medicines, such as blood thinners
- when to stop eating and drinking or, conversely, when to drink plenty of liquids
- when to empty your bladder before the procedure
- whether to arrange for a ride home after the procedure
You May Like: Ginger Tea Dissolves Kidney Stones
What Is A Biopsy
A biopsy is a procedure in which tissue samples are removed from the body by a needle or during surgery, for examination under a microscope to determine if cancer or other abnormal cells are present.
By examining and performing tests on the biopsy sample, pathologists and other experts can determine what kind of cancer is present, whether it is likely to be fast or slow growing, and what genetic abnormalities it may have. This information is important in deciding the best type of treatment. Open surgery is sometimes performed to obtain a biopsy, but in most cases, tissue samples can be obtained without open surgery using interventional radiology techniques.
Some biopsies can be performed in a doctor’s office, while others need to be done in a hospital setting. Most biopsies require use of an anesthetic to numb the area and may require sedation.